membrane potentials and excitability
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
cell plasma membrane
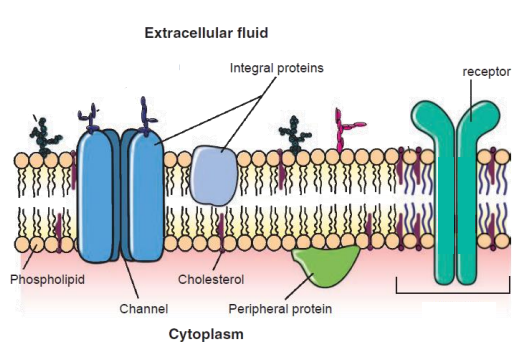
all cells are surrounded by a fluid, lipid-protein bi-layer called the cell membrane
functions: provides cellular structure, fluidity of membrane/cell, physical barrier that prevents free passage of substances
semi permeable membrane
passive transport
seeks to establish equilibrium between intracellular and extracellular compartments
solute will flow from high concentration → low concentration
positively charged particles will flow into negatively charged compartments (opposite charges attract)
simple free diffusion - O2, CO2 lipid soluble molecules freely diffuse across membrane
protein mediated (facilitated) diffusion - channels in membrane allow specific ions to flow through = ion channels
active transport
consumes energy (ATP) to transport molecules against their concentration gradients
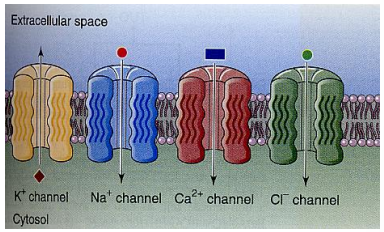
leak channel (ion channel)
they are always open
each channel is selective for specific ions
differences in the number and type of leak channels in the membrane determines the plasma membrane’s selective permeability
at rest the typical plasma membrane has higher permeability for K+ than for Na+ or Cl+
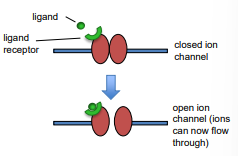
gated channels (ion channel)
ligand dated ion channels
ligand receptor embedded in the channel
ligand binding to receptor induces conformational change to open or close the channel
voltage gated ion channels
voltage sensor in the ion channel protein
changes in membrane potential induce a conformational change to open or close the channel
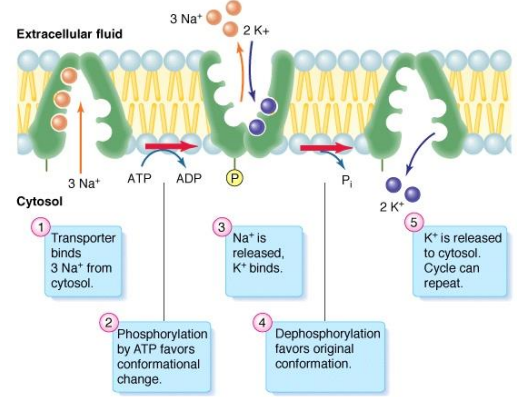
active transport: Na+ -K+ ATPase
maintains Na+ and K+ gradients across plasma membrane
uses energy (ATP)
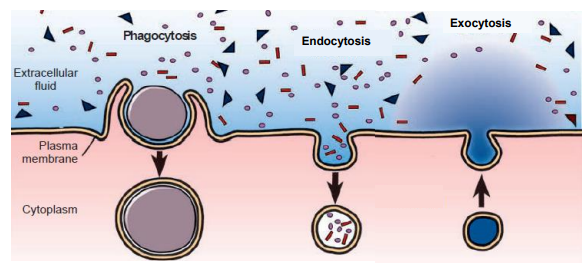
vesicular transport
endocytosis (including phagocytosis)
exocytosis
resting membrane potential (RMP)
difference in electrical charge across the plasma membrane in the cell at rest
approx. -70mV (-60 to -100 mV)
inside the membrane is more negative than the outside
used to transport substance across the membrane - ions will move across membrane is they are given the chance
equilibrium potential
charge gradient + concentration gradient = electrochemical gradient
at equilibrium, the charge gradient balances the concentration gradient, and there is no net flow of ions across the membrane
for each ion at a given concentration gradient, the charge gradient that leads to equilibrium potential. calculated using the Nernst equation
Nernst equation
electrical potential (E) of an ion is calculated using this - it is base on concentrations outside and inside the cell
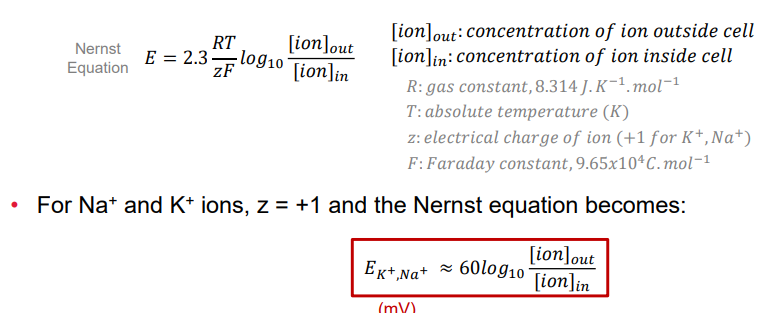
RMP implications for ion flux
if ion channels open in response to specific stimuli, the ions will move towards their equilibrium potential. the membrane potential (MP) will change as a result
given RMP= -70mV and E k+ = -90 mV, if we open K+ channels in the membrane3, an efflux of K+ ions will occur
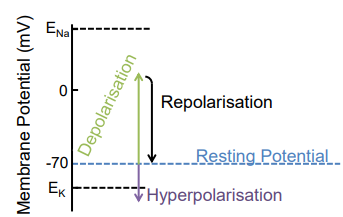
changes in membrane potential
excitable cells (neurons, cardiac cells) actively induce changes in their membrane potential
depolarisation influx of positively charged ions, known as excitatory post synaptic potential (ePSP)
hyperpolarisation: efflux of positively charged ions and an influx of negatively charged ions, known as inhibitory post synaptic potential (iPSP)
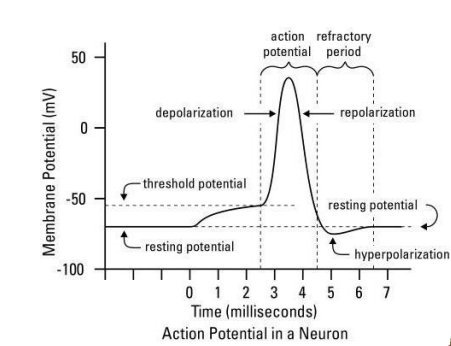
action potentials
if depolarisation at a certain point reaches a threshold voltage of -55mV (action potential threshold), an action potential in generated
brief, rapid, large (100mV) change in membrane potential during which potential reverses
serves as long distance signals (propagates along axon and from neuron to neuron)
involves voltage gates Na+ and K+ channels
action potential text
depolarisation pushes membrane potential across the action potential threshold (-55mV)
reduced voltage open voltage gated sodium channels in that portion of the plasma membrane
at the peak of the AP, voltage gated potassium channels open and sodium channels close
voltage gated potassium channels then close leaving plasma membrane hyperpolarized. resting membrane potential and concentration gradients are restored
refractory period
period when a further stimulus will not trigger another action potential
refractory period lasts 1-2ms. neurons can still transmit up to 500-1000 impulse per second
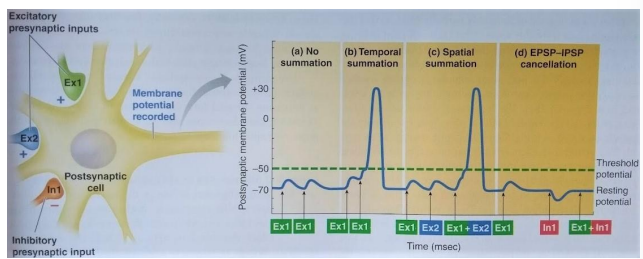
summation
postsynaptic response is the combined effect of thousands of synaptic events (iPSPs and EPSPs) from many neurons
neuron is brought to action potential threshold at the axon hillock via summation - temporal summation, spatial summation
prpagation
APs reproduce along the axon from the axon hillock to the synaptic terminals
depolarisation is one portion of the membrane opens more voltage gated sodium channels in the adjacent portion of the membrane
depolarisation travels along the cell
myelin
functions as an electrical insulator
high density of voltage gates sodium and potassium channels at gaps between myelin (nodes of ravenier)
saltatory conduction (action potential jumps from one node to next) = faster propagation
myelination increases the conduction velocity of action potentials