Marine Biology & Global Change Part One
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Marine Bio Exam 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Incoming solar energy is balanced by
reflected and reradiated energy
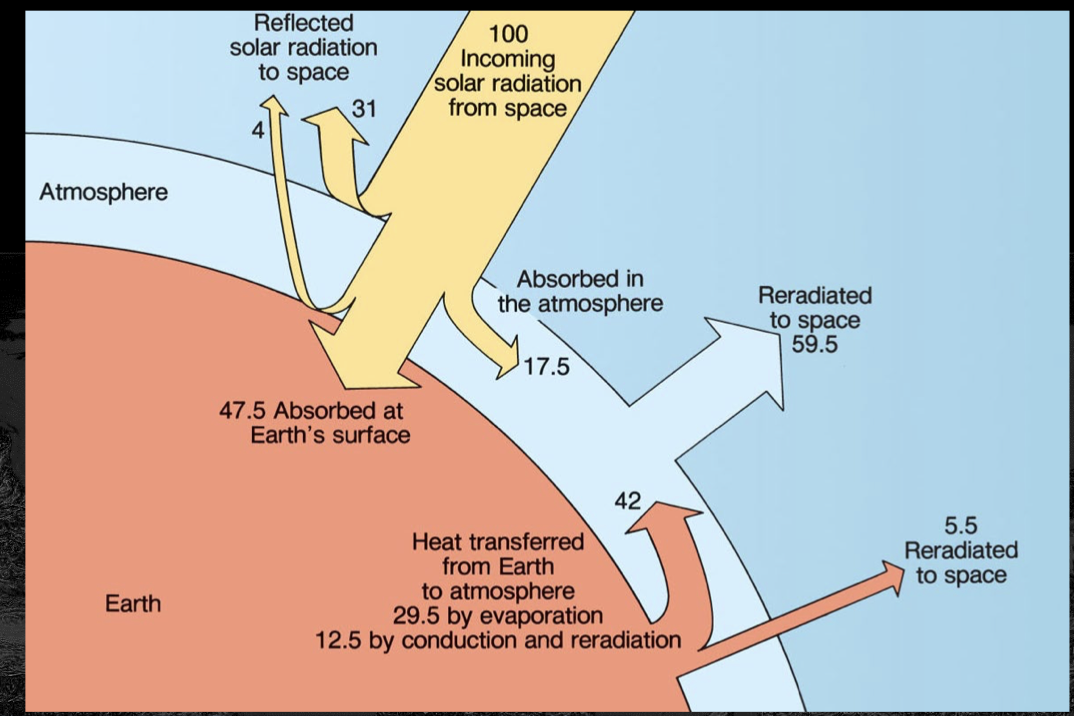
The atmosphere’s loss of heat is balanced by
heat transferred from Earth to the atmosphere by evaporation, conduction, and re-radiation
The hottest year on record
2024 hottest year been in an increase in temp since 2014 breaking records each yr pretty much
Historic trends
Reconstructed temperature
from tree rings, ice cores, coral cores
General negative trend until start of 1900’s
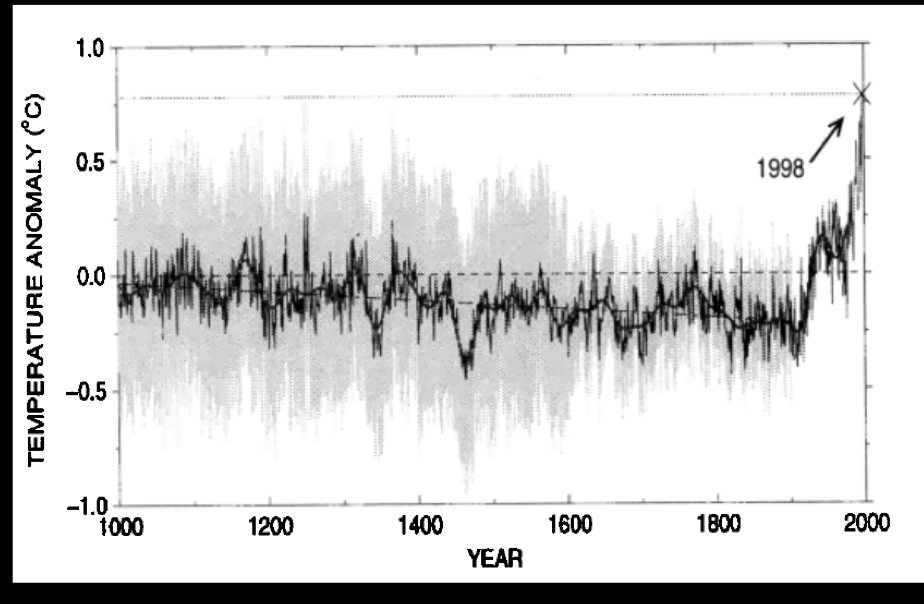
Every decade since 1960 has been
hotter than the previous one
Global Ocean Heat Content
energy absorbed and stored by the oceans
ocean heat content for 2022 for the upper 2,000 meters was
record high, surpassing the previous record set in 2021.
The regions of the North Pacific, North Atlantic, the Mediterranean, and southern oceans also had their highest
OHC since the 1950s.
Why does more than 90% of the heat accumulates in the ocean
because of its large heat capacity
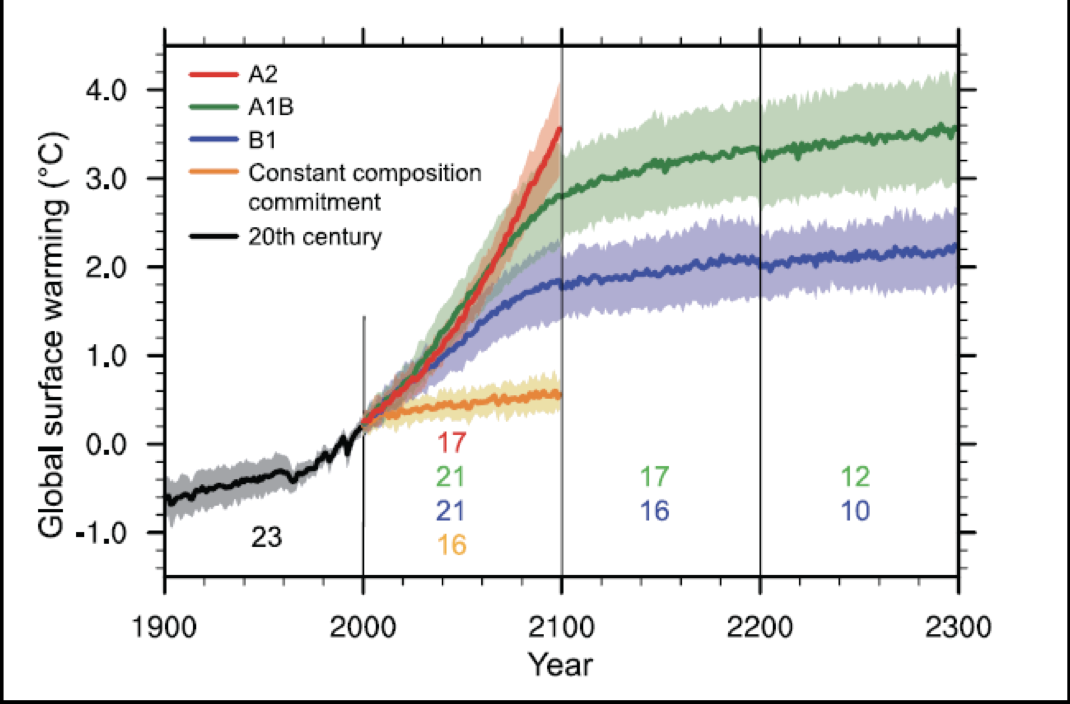
Future trends
Models show an average warming of 1.8°, 2.8°, and 3.4°C for the low (Bl), medium (AIB), and high (A2) scenarios
On average, expect 3°C rise in SST by 2100
Marine heat waves
defined as any time the ocean temperature is above the 90th percentile for a specific length of time.
can last for weeks, months or years
Marine heat waves are ___ and __ over the past century
Marine heat waves are more frequent and last longer over the past century.
Biological impacts
Corals
Bleaching
Fish
Physiology
Life history
Population & Community
• Range shifts
• Population declines
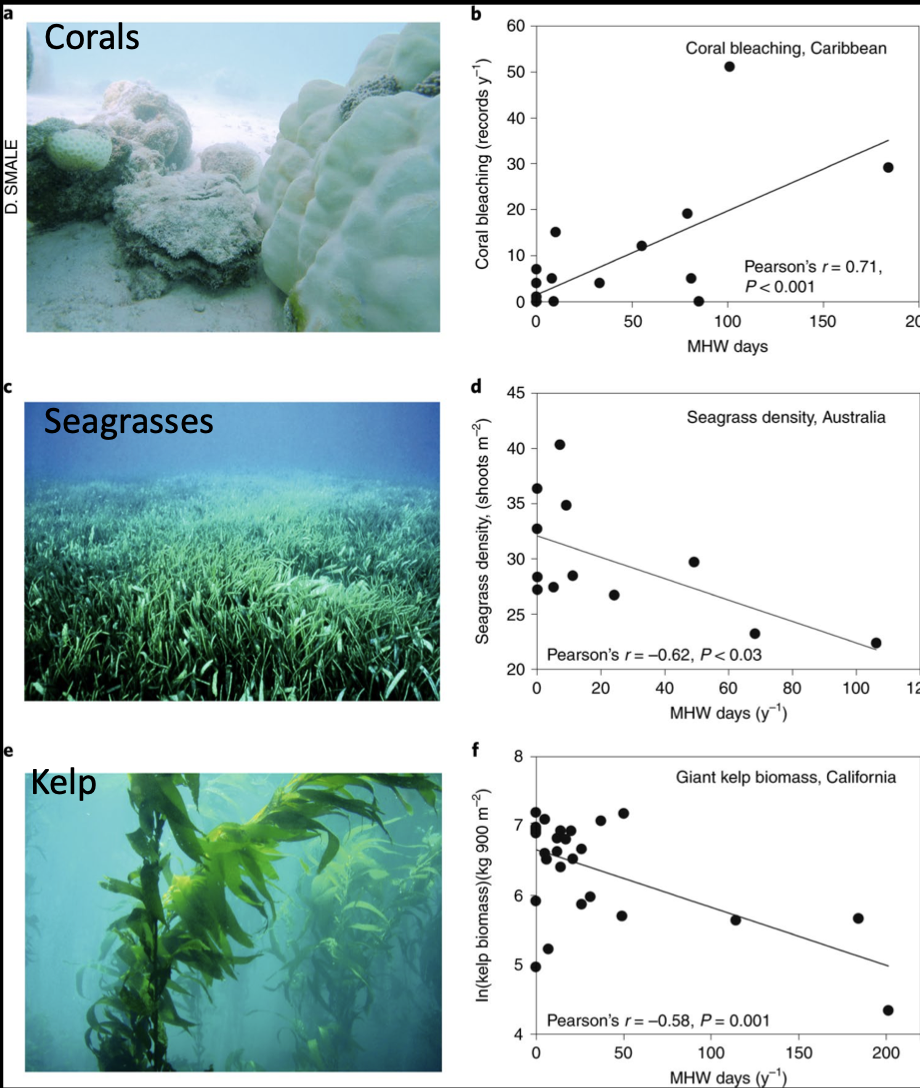
Coral bleaching
is the breakdown of symbiosis between coral and zooxanthellae
Coral polyps form obligate symbiotic relationship with
dinoflagellates of the genus Symbiodinium(zooxanthellae)
Heat stress due to rising SSTs can cause
mass bleaching events
decline in coral abundance
declines in the abundance of coral dwelling fishes an implication of bleaching
Implications of bleaching
Proportionally greater losses of specialists than generalists
Habitat specialists are thought to be more prone to extinction than generalists
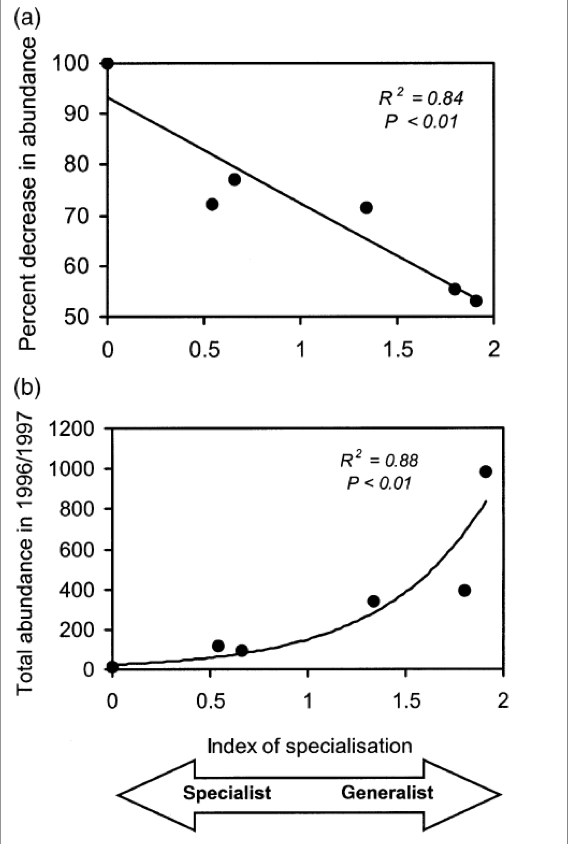
Implications of marine heat waves on species
pos relationships with coral bleaching
neg relationship with seagrass density
neg relationship with kelp biomass
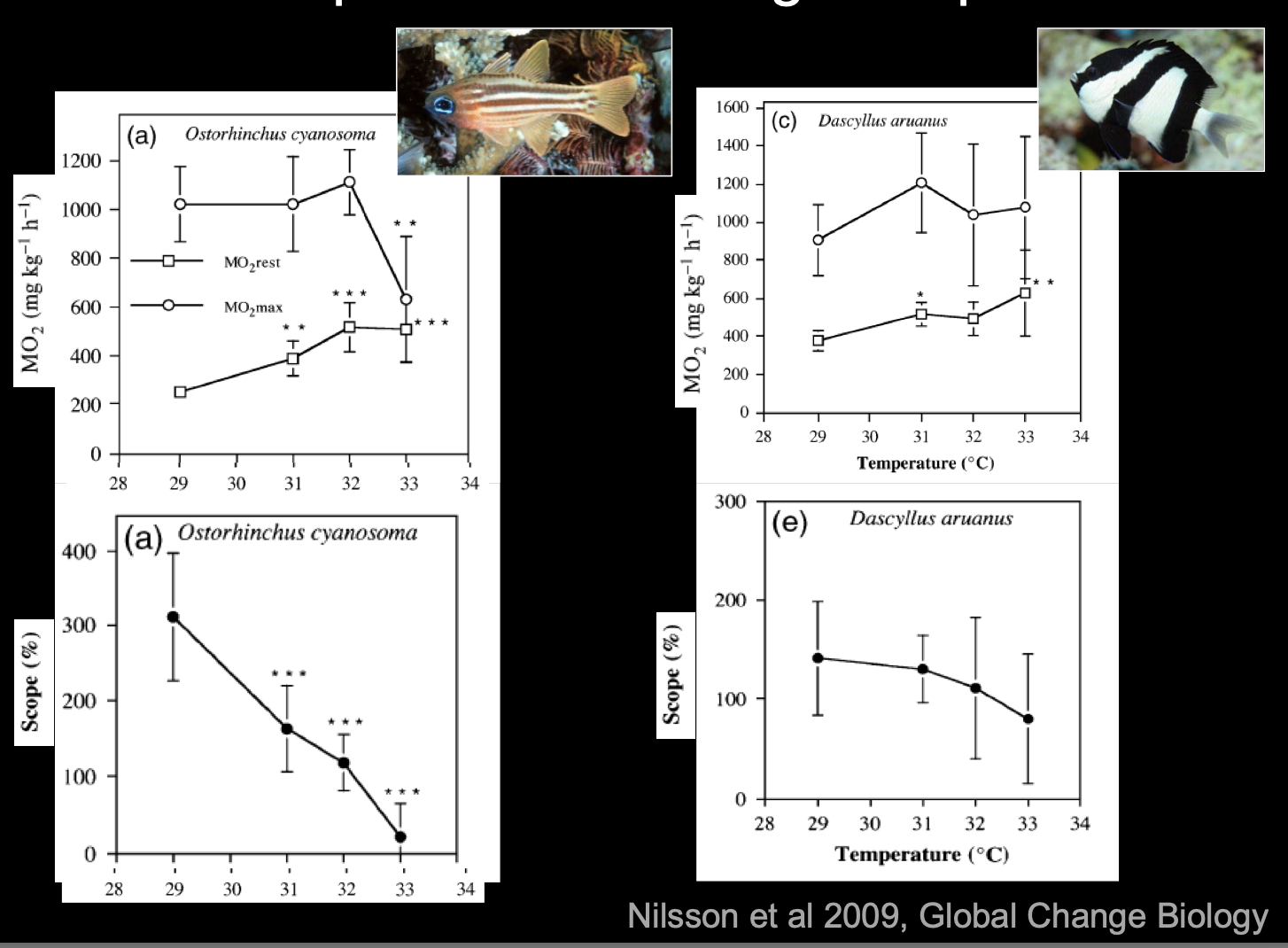
Fish physiology
Elevated temp increases
basal metabolic rate
Fish physiology
aerobic scope
difference between basal and maximal metabolic rates (B)
Impact on fish physiology
Defines amount of aerobic energy that can be allocated to higher level activities
– Growth, reproduction, etc.
• Reduced aerobic scope in higher temperatures
How to measure aerobic scope in fishes
Measure oxygen uptake at rest
(MO2rest)
and when swimming against current(MO2max)
Abiotic factors can be modified
– “Normal” 29 °C
– Projected: 31 °, 32 °, 33 °C
Respirometry apparatus
Oxygen uptake is a proxy for metabolic rate
What does aerobic scope do at high temps?
declines
Impacts on fish: life history
Reduction in aerobic scope
affects higher level functions
Growth and reproductive rates decline beyond aerobic optimum
Tropical species more susceptible due to narrower thermal range
Does growth decline at high temps?
Yes
Independent effects of food and temperature
Increased food does not ameliorate effects of high temperature at 31C
Reproductive failure at high temperatures are a result of
Food and temperature influence multiple proxies of reproductive success
Breeding pairs experience reproductive failure at high temperatures & low rations
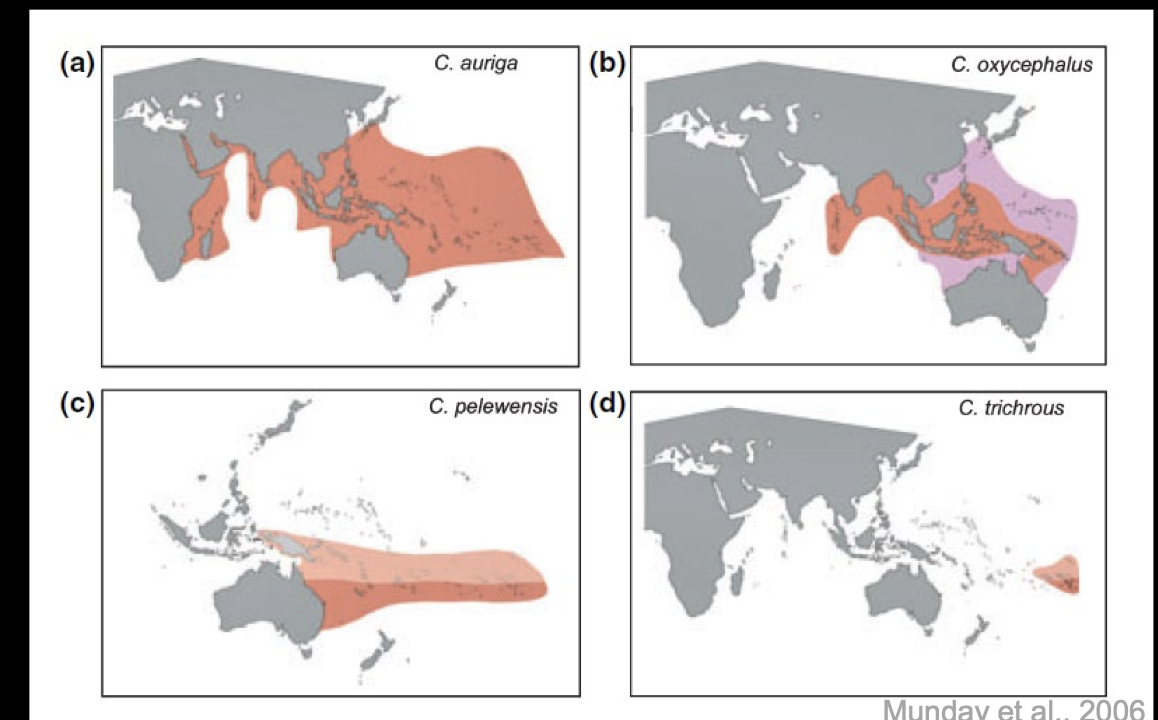
Where are potential range shifts for coral reefs
(a) For species already living in the entire extent of coral reef development (a), range shifts are not expected (nowhere to escape – probably go extinct)
(c) For species living at equator, not at lat extent of coral, range shifts are expected towards the higher lat (b) For species living in mid latitude regions, reaching latitudinal extent of coral range, range contraction towards higher latitude expected.
(d) For species living in restricted ranges along the latitudinal extent of the coral range, range contraction poleward and range reduction expected, resulting in low population sizes – high risk of extinction.
Is the ocean experiencing more rapid seasonal shifts in climate than land
Yes fall is delayed in ocean relative to land and spring is advanced
causing range shift