alcohols, ethers, and thiols
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
how to determine if carbon is reduced or oxidized
if the oxidation state decr. it is reduced
if the oxidation state incr it is oxidized
what reagents and starting material for disubstituted molecules
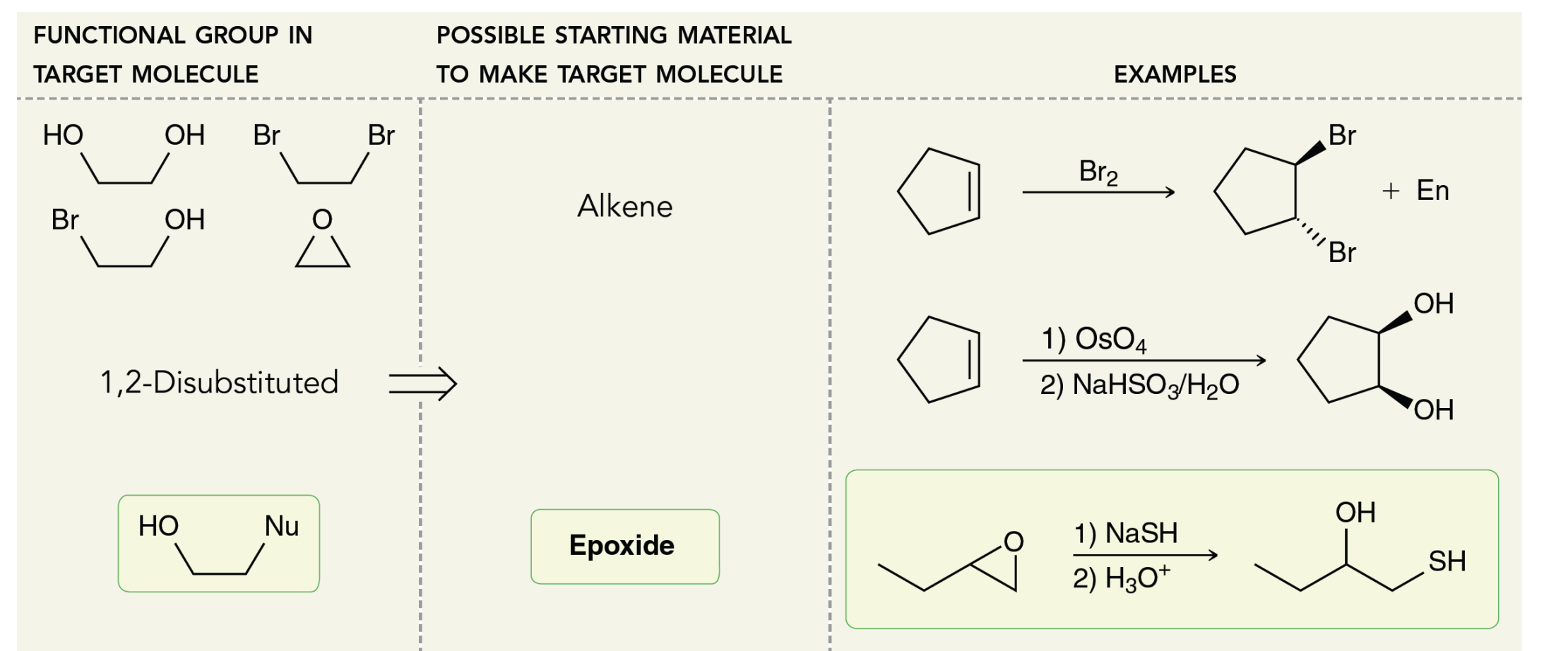
FOR OH AND NUC ALWAYS USE EPOXIDE
what rxn with NaBH4 and a proton source (etoh, meoh, h2o)
or
LAH (LiAlH4) with acid or water
reduction of an aldehyde or ketone to an alcohol
the BH4 acts as a nucleophile and attacks the elec. carbon to form an alkoxide (move double bond up to make neg. O) intermediate, which is then protonated to yield the corresponding alcohol.
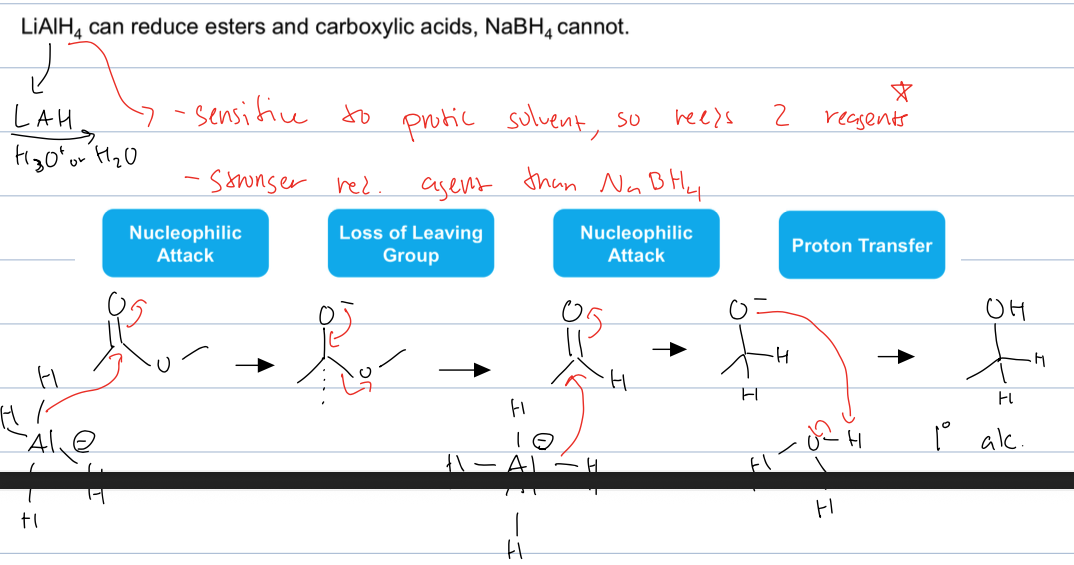
what is rxn with carbox acids and esters only with LAH and acid or water
Reduction of esters or carboxylic acids to alcohols by converting carbonyl groups to alcohols.
where the H attacks the elec. carbon and creates an alkoxide group, then there is Loss of LG to form an aldehyde. Then the process is repeated to form another alkoxide and then the O is protonated to form an alcohol
LAH is sensitive to protic solvent so needs 2 reagents and it is a stronger reducing agent so can reduce carboxilic acids and esters
what is the rxn with MG and Et2O
the preparation of a halogen to a grignard
what are the 4 ways to use a grignard to create an alcohol
reacting with a ketone to form a tertiary alcohol
reacting with an aldehyde to form a secondark alcohol
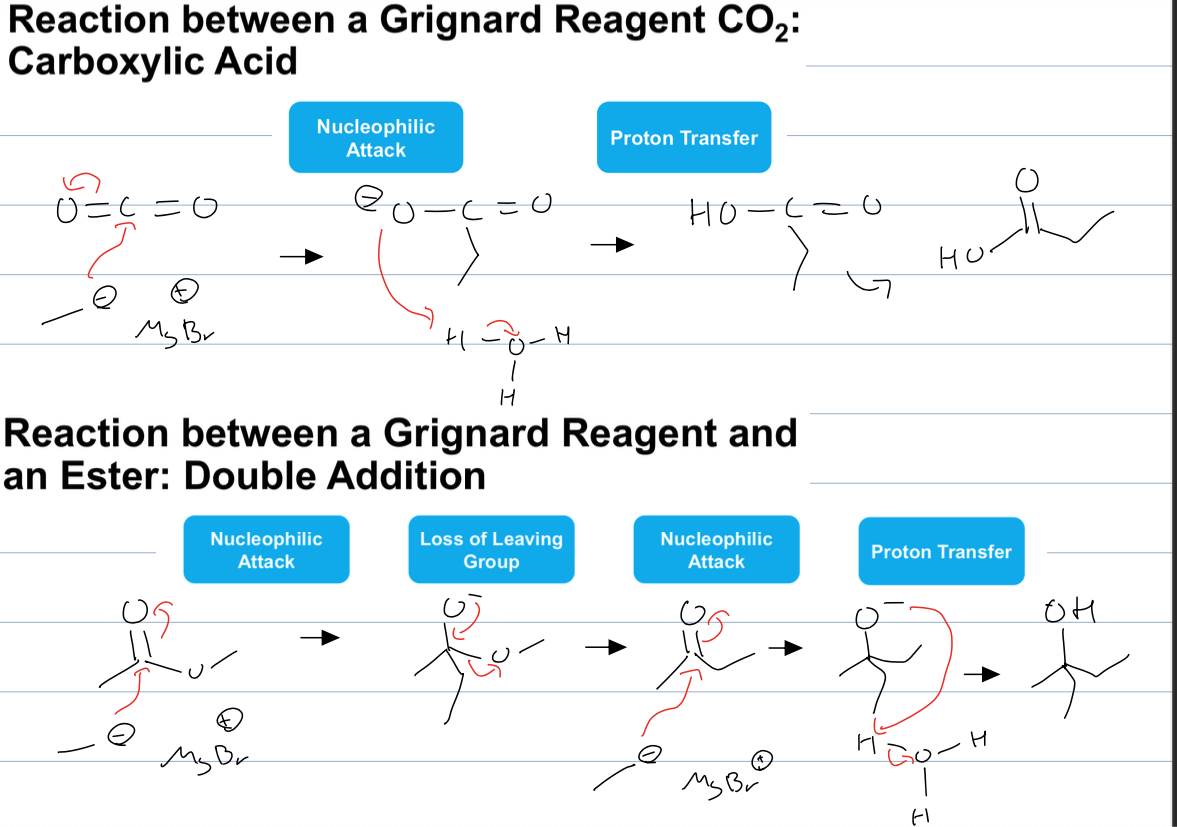
reacting with CO2 to form carboxylic acid
and reacting with an ester to have a double addition and create a tertiary alcohol
what is the rxn with hv (radiation) and Br2
radical bromination where you create an alkyl bromide from an alkane
adds Br at the most sub carbon and anti
can also add at the allylic position of a molecule
what is the allylic position
on the C next to a double bond
this is more favorable because it is the more stable intermediate
why do we need to protect alcohols
to prevent them from reacting in undesired ways during chemical reactions, as they can be sensitive to acidic or basic conditions.
what is the rxn for TMSCL and ET3N and TBAF
protecting alcohols where the alcohol is deprotonated and replaced with TMS
where the O attacks the Si and kicks out the CL and then the ET3N deprotonates the O leaving OTMS as a protecting group.
then TBAF deprotests and reprotonates the O
what are the 2 previous ways to prepate an alcohol
substitutoin via SN1 or Sn2
or addition with BH3 THF anti mark addition of alkenes, or oxymmercuration demurcuration with mark addition and H3O + mark addition
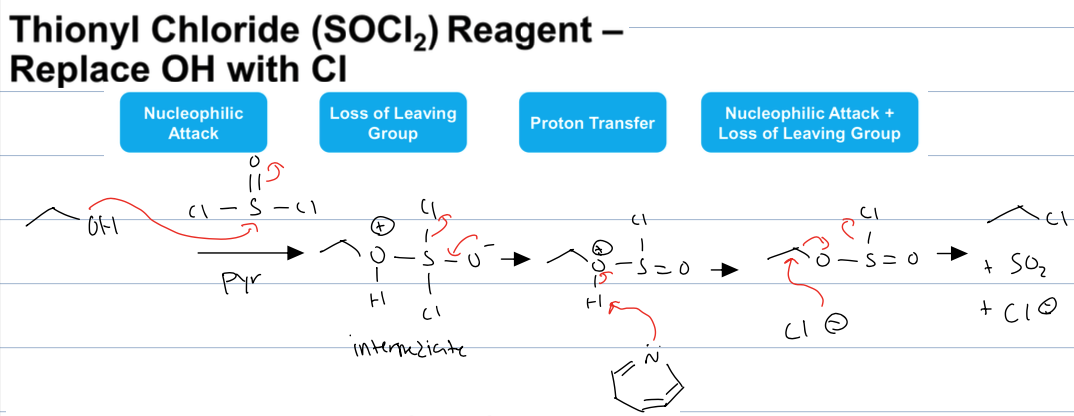
what is the rxn with SOCl2. and Pyr
substitution of OH with CL
where the O attacks the S and creates a chlorosulfite intermediate, which then causes loss of LG to form chloride ion and then the O is deprotonated by the pyridine and then the chloride ion attacks elec C to then cause loss of leaving group to form SO2 another chloride ion and an alkyl chloride
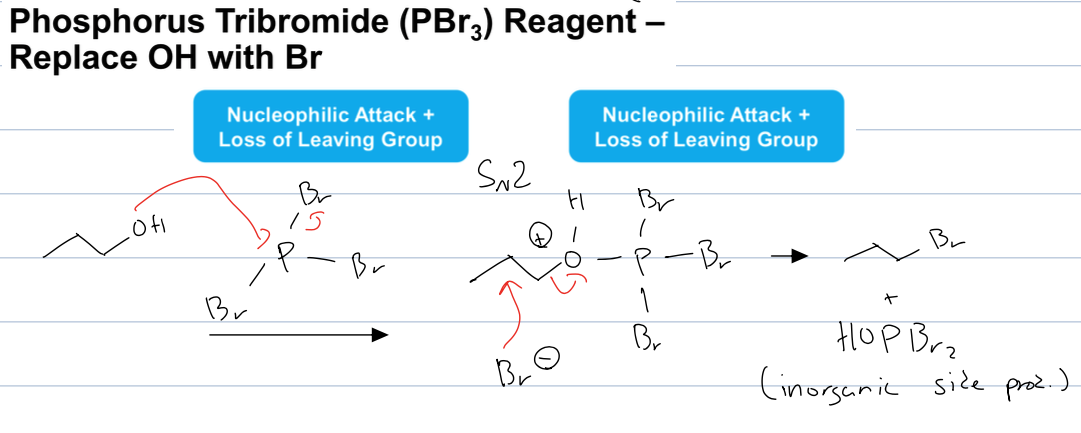
what is the rxn with PBr3
it replaces OH. with BR
where the O attacks the P and causes loss fo LG to from a bromide ion and an intermediate which subsequently leads to the formation of an alkyl bromide through SN2 substitution from the bromide ion and loss of leaving group to form an alkyl bromide and an inorganic side product
inversion of config bc SN2
what is oxidation rxn with secondary alcohol with H2CrO4 or (Na2CrO7, H2So4, H2O) or PCC in CH2Cl2
with chromic acid it oxidezes the alcohol to form a ketone
with PCC it creates a ketone too
what rxn with primary alcohol with H2CrO4 or (Na2CrO7, H2So4, H2O) or PCC in CH2Cl2
with chromic acid it creates a carboxylic acid and with PCC it creates an aldehyde
best way to eliminate alcohols
to toscilate and then use a strong base
what rxn with NaH and an alcohol and an alkyl halide or anything with a halide to form an ether
williamson ether synthesis
where the strong base deprotonates the alcohol to from alkoxide ion which then perfomes SN2 or SN1 with the halide to from an ether
remeber SN1 or SN2 bc os sterochem
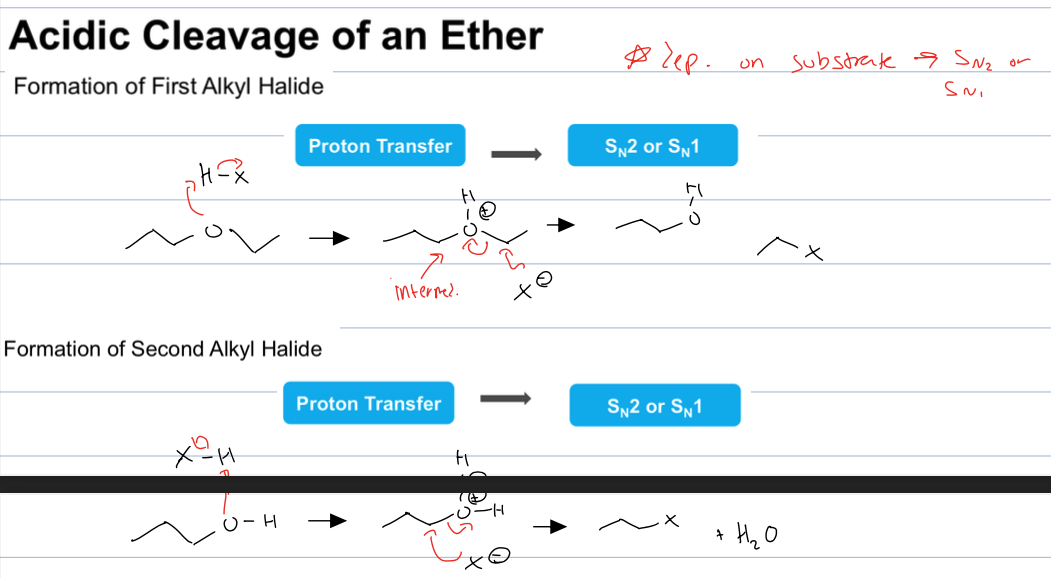
what is rxn when you have an ether and a acid halide
acidic cleavage of an ether
where the O becomes protonated (intermediate) and then there is either SN1 or Sn2 where the halide ion attacks elec. carbon to form an alcohol and an alkyl halide.
rxn can occur twice following the same method but starting with alchol to from another alkyl halide and water
again important to recognize SN1 or SN2
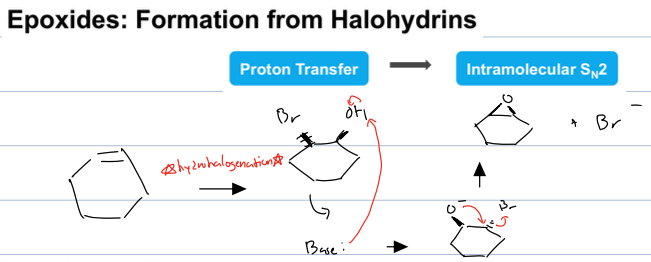
what rxn from an alkene with MCPBA or Br2, H2O and a strong base
epoxide formation from an alkene
for the second rxn it is hhydrohalogenation rxn and then the base deprotonates the Oh and then the negative O goes through an intermolecular SN2 to from an epoxide and a bromide ion
what is rxn with epoxide and strong nucleophile (basic cond.) and what is regio and sterochem
epoxide opening
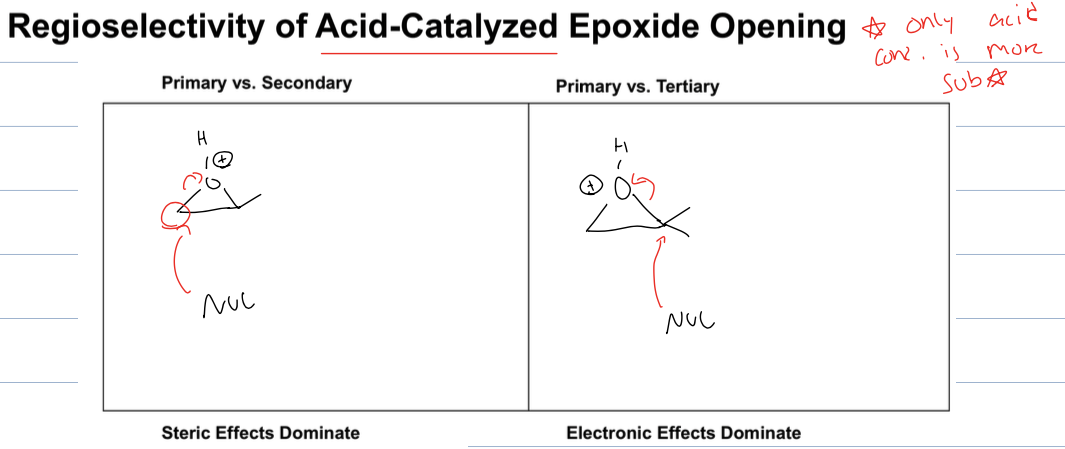
where the strong nuc attacks the less sub side of the epoxide to open it up and create an alkoxide ion and then it is protonated with LAH or water
inversion of config where nuc attacks
what is rxn with epoxide and mild acid (acid cond.)
epoxide ring opening
where the acid protonates first and then the nucleophile attacks the more substituted carbon of the epoxide, leading to the formation of an alcohol.
attacks more sub side because forms carbocation intermediate
inversion of conifg where nuc attacks
it attacks more sub when there is tertiary vs primary side
but attacks the less sub when there is primary vs secondary side
what rxn to crete thiol
SN2 with an alkyl halide and NaSH
what rxn to create disulfides
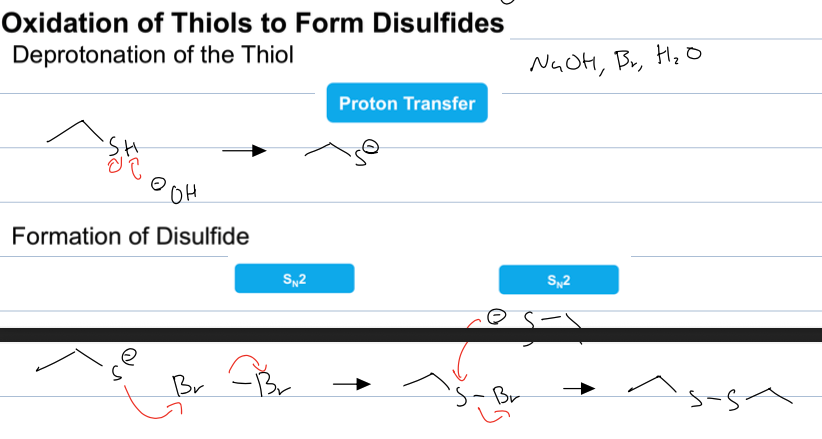
2 thiols and NaOH, and BR to from disulfide
the hydroxide de protonates the thiol creating a sulfide ion and then the sulfide attacks the Br2 creating an SN2 rxn and then the other sulfide ion attacks and S to create disulfide
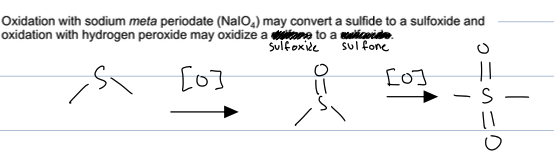
how to crate sulfone from a sulfide
the sulfide reacts with NAIO4 to create a sulfoxide and then reacts with 2 eq of H2O2 to create sulfone