Clinical Manifestations of HIV and AIDS
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
typical course of HIV infection
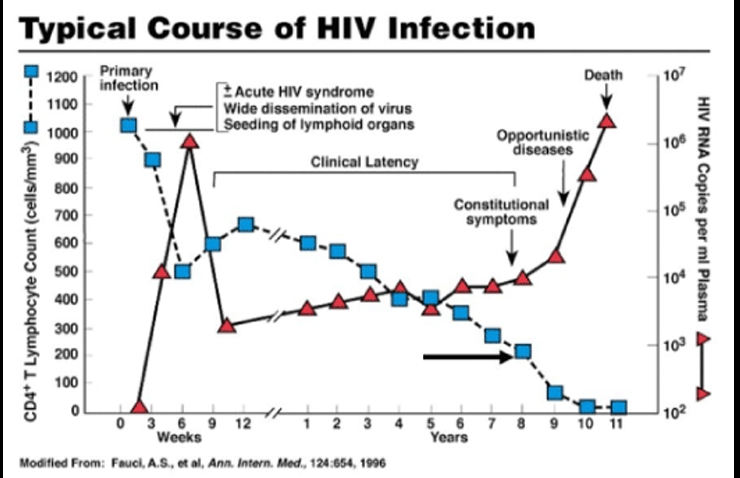
clinical characteristics of acute retroviral syndrome

clinical notes
-have a high degree of suspicion for ARS if risk factors for recent HIV acquisition
-do not be fooled by negative HIV Ab/Ag or HIV Ab testing if high clinical suspicion for ARS
-diagnostic confirmation: HIV-1 RNA (either qualitative or quantitative) viral load
prophylaxis against opportunistic infections in persons with human immunodeficiency virus infection
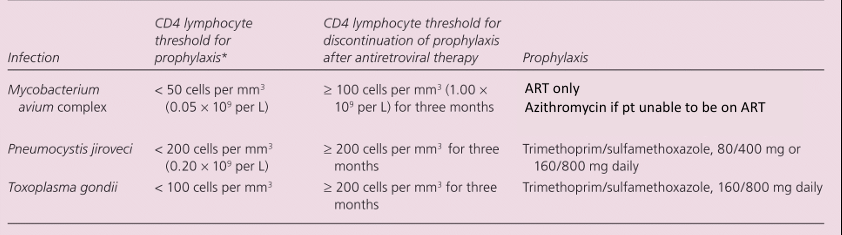
mucosal candidiasis
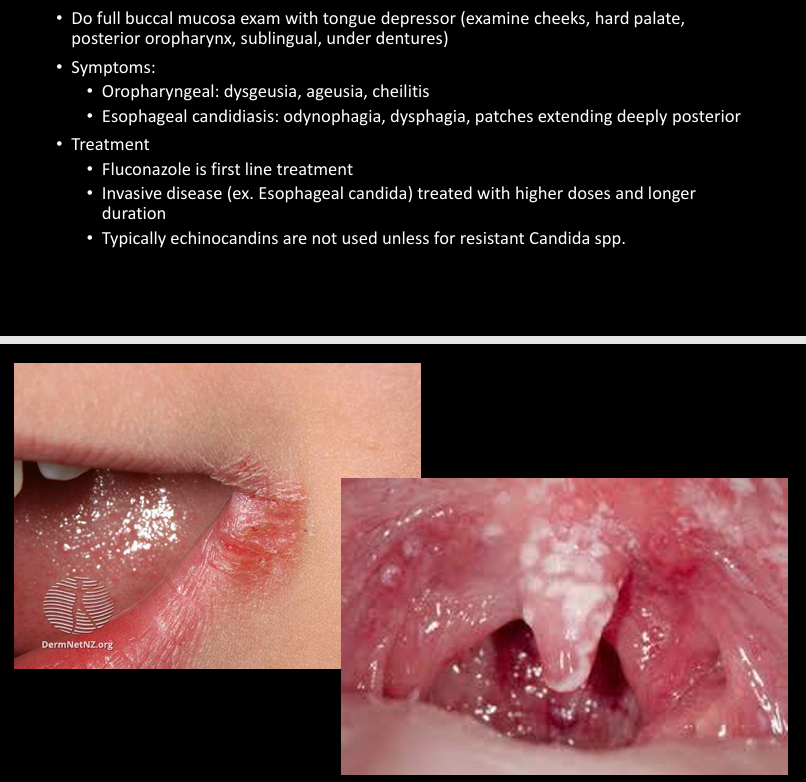
PCP

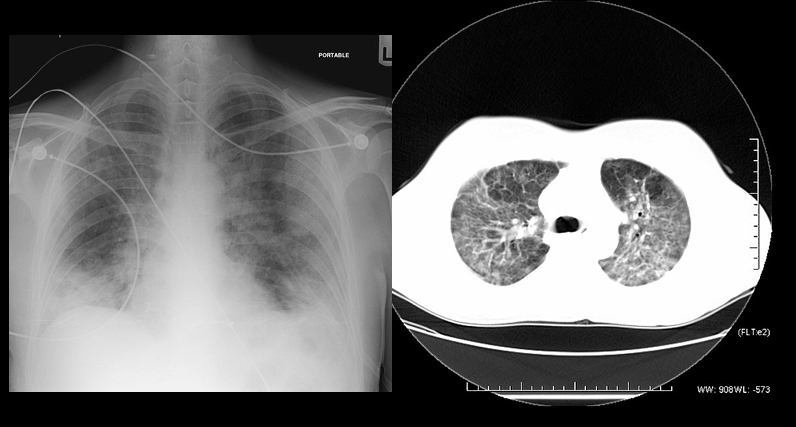
PCP
PCP treatment

when to stop secondary prophylaxis

toxoplasmosis
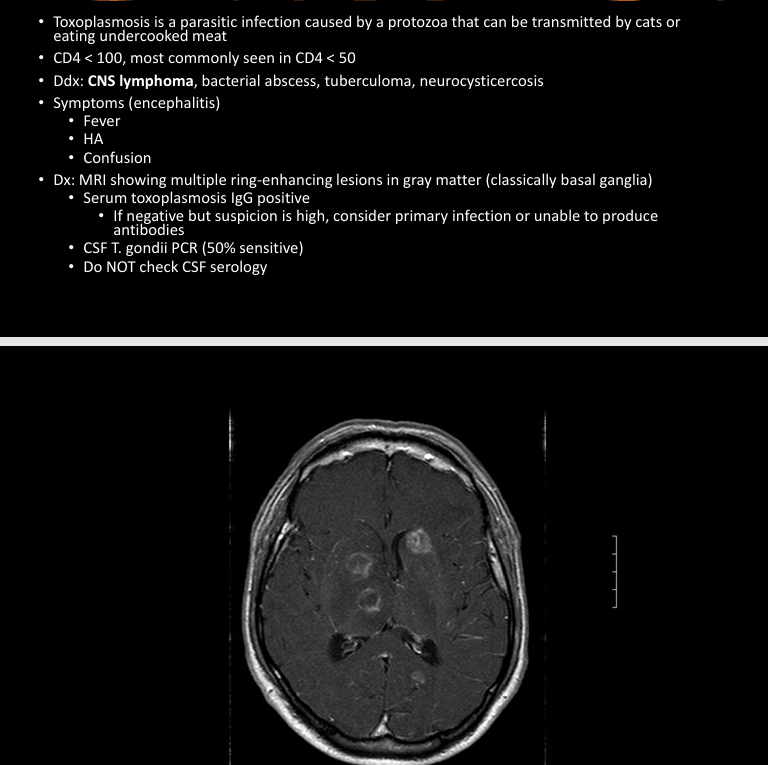
toxoplasmosis treatment

progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)

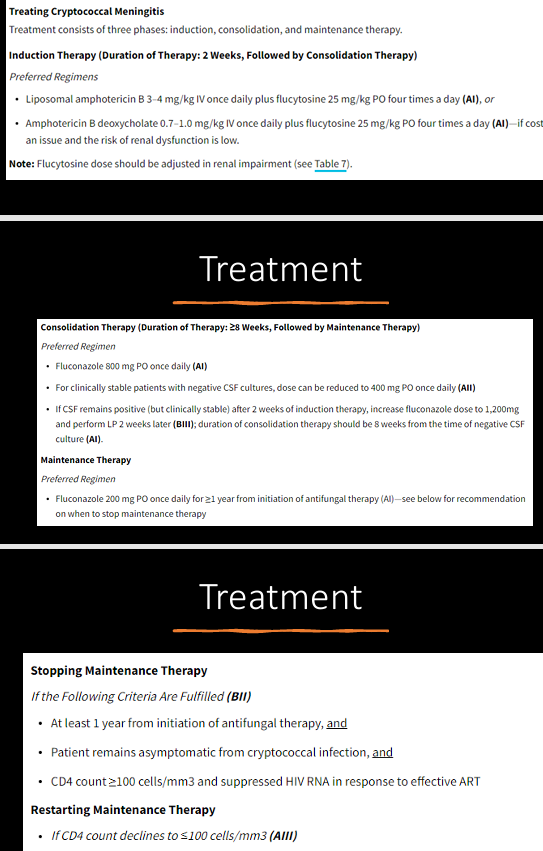
Cryptococcosis

Cryptococcosis diagnosis

Cryptococcosis treatment
non-tuberculous mycobacteria

disseminated MAC

CMV disease

CMV retinitis

CMV GI disease

CMV treatment

Kaposi’s sarcoma
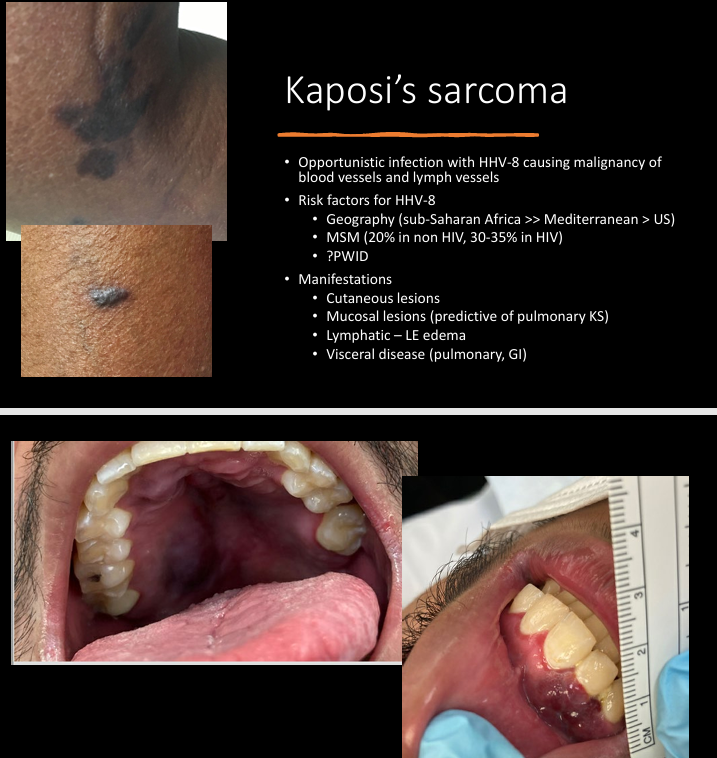
HHV-8 related disease
-primary effusion lymphoma: serositis and effusions (pleural, peritoneal, pericardial)
-multicentric castleman’s disease: nonspecific general symptoms of fever, night sweats, weight loss, generalized lymphadenopathy
Kaposi’s sarcoma treatment
-cutaneous disease: ART only
-visceral disease, disseminated cutaneous disease: doxorubicin + ART; avoid steroids
when to start ART in OIs

IRIS
