exam (II)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 6:57 PM on 12/9/24
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
1
New cards
avogadro’s number
6\.02 x 10^23
2
New cards
molar mass
quantity in grans that = atomic mass of an element
3
New cards
chemical change
occurs when a substance is converted into 1 or more new substances that have different formulas and properties
4
New cards
signs of a reaction
bubbles, change in color, smell, temperature
5
New cards
delta sign (△)
heat is used to start the equation
6
New cards
balanced chemical equation
no atoms are lost or gained; number of atom are equal on both sides
7
New cards
combination reactions
2 or more elements form one product; A+B = AB
8
New cards
decomposition reaction
one substance splits into 2 or more simpler substances; AB = A+B
9
New cards
simple replacement reaction
one element takes the place of a different element in another reacting compound; AB+C = AC + B
10
New cards
double replacement reaction
positive ions in the reactant compounds switch places; AB +CD = AD + BC
11
New cards
combustion reaction
carbon-containing compound burns an oxygen gas to form carbon dioxide and water
12
New cards
incomplete combustion
when oxygen supply is limited, incomplete combustion occur
13
New cards
carbon monoxide
colorless, odorless, poisonous gas
14
New cards
oxidation-reduction reaction
provides us with energy from food; provides electrical energy in batteries
15
New cards
oxidation
involves loss of electron; + oxygen; - hydrogen
16
New cards
reduction
involves gain of electron; - oxygen; + hydrogen
17
New cards
OIL
Oxidation Is Loss of electron
18
New cards
RIG
Reduction Is Gain of electrons
19
New cards
law of conservation of mass
matter cannot be created or destroyed; no change in total mass occurs
20
New cards
mole-mole factors
a ratio of the moles for any two substances in an equation
21
New cards
3 conditions for a reaction to occur
collision: reactant must collide
orientation: reactant must align properly to break and form bonds
energy: collision must provide the energy of activation
orientation: reactant must align properly to break and form bonds
energy: collision must provide the energy of activation
22
New cards
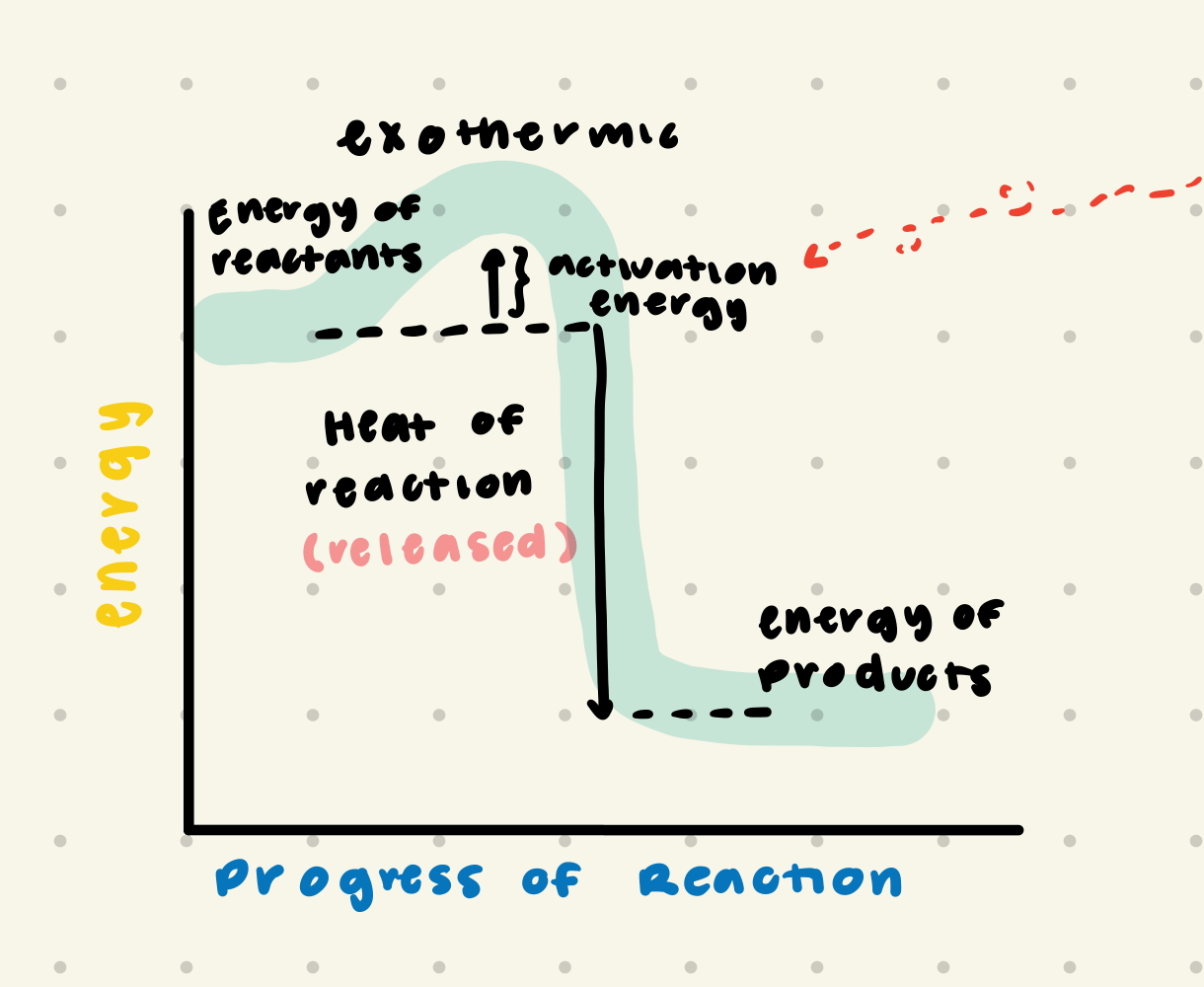
exothermic reaction
heat is released; energy of product is less then the energy of the reactant
23
New cards
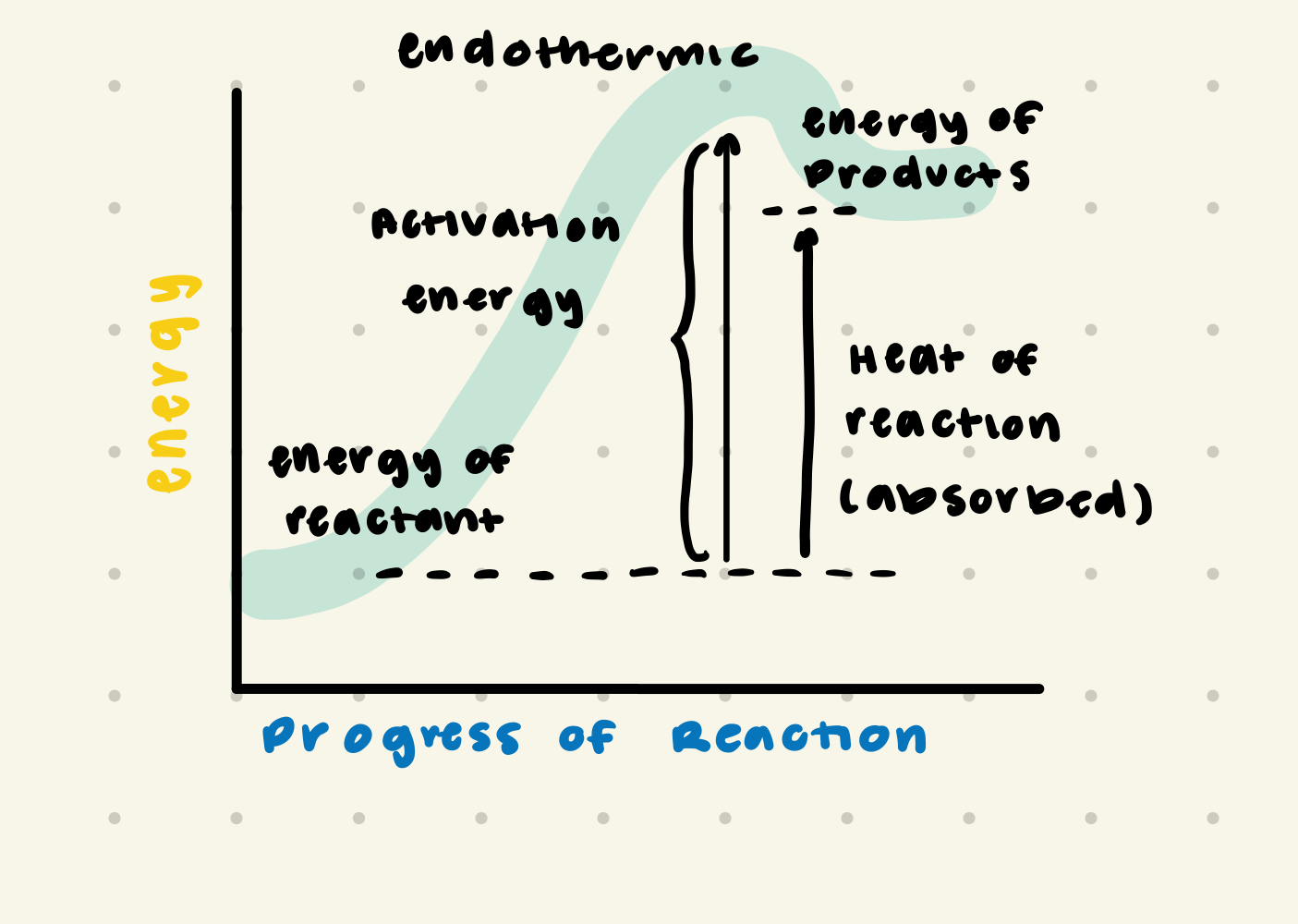
endothermic
heat is absorbed; the energy of the products is greater than the energy of reactants
24
New cards
reaction rate
speed at which reactants is used up; speed at which products forms; increase in temp = reacting molecules move faster; increase speed with concentration of reactants
25
New cards
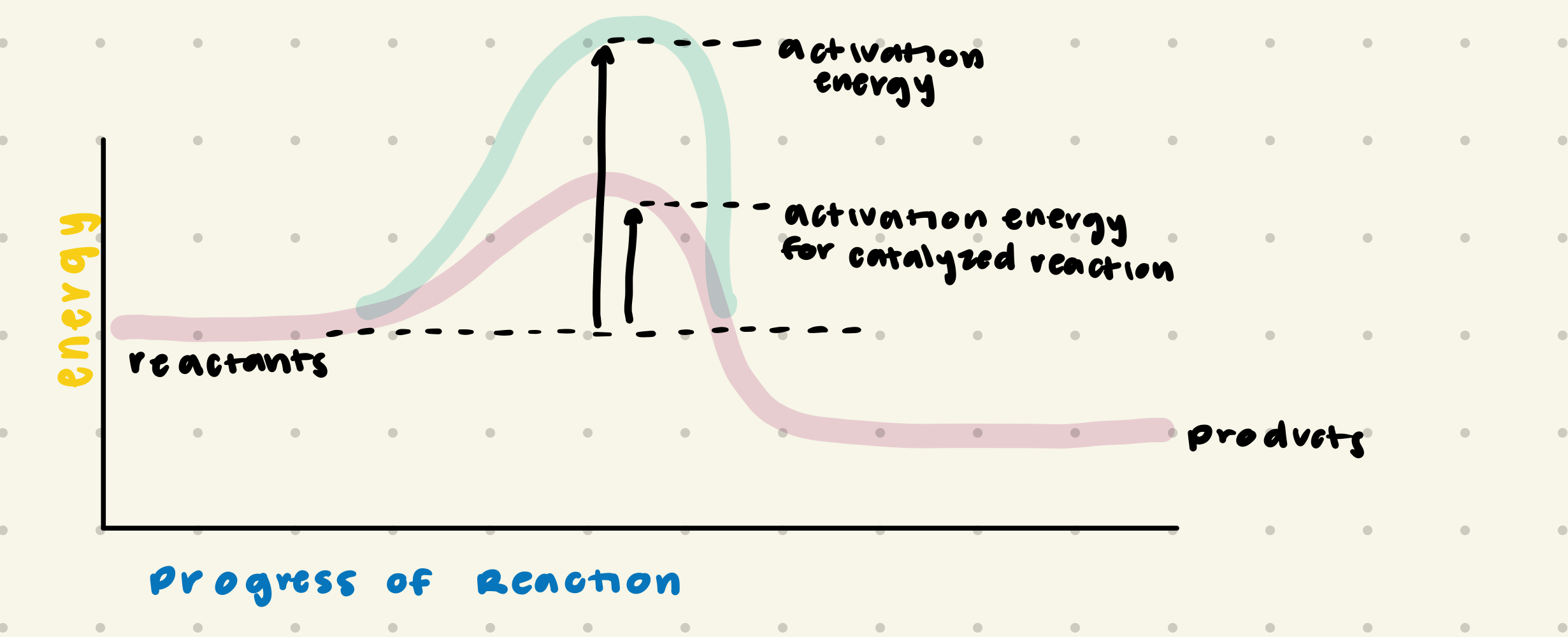
catalyst
increase rate of reaction; lower the energy activation; not used during the reaction
26
New cards
factors that increases reaction rate
1. temp - increase collision, increase collision w/ energy of activation
2. increase reactant concentration - more collision
3. adding catalyst - decrease energy of activation
27
New cards
kinetic molecular theory
a gas consists of small particles that:
move rapidly in a straight line
have no attraction/repulsive forces
very far apart
very small volumes compared to the volume of the container they occupy
kinetic energy that increase with an increase in temp
move rapidly in a straight line
have no attraction/repulsive forces
very far apart
very small volumes compared to the volume of the container they occupy
kinetic energy that increase with an increase in temp
28
New cards
pressure (p)
forces exerted by a gas against the walls of the containers; atm, mmHg, Torr, Pa
29
New cards
volume (v)
space occupied by a gas; L, mL
30
New cards
temperature (T)
determining factor of the kinetic energy of the gas particles; degree celsius, kelvin
31
New cards
amount (n)
quantity of gas present in a container: g, n
32
New cards
volume (def.)
increase with an increase in the temperature at a constant pressure
33
New cards
temperature (def.)
relates to the average kinetic energy of the molecules and is measured in kelvin temp. scale
34
New cards
pressure
the measure of the gas particle collisions with the sides of a container and is measured in units of mmHg, Torr, atm, Pa, kPa, PSI
35
New cards
atmospheric pressure
gas particles in the air exert pressure on us; decreases as altitude decreases, 1 atm at sea level; changes with the weather and altitude
36
New cards
barometer
measured the pressure exerted by the gases in the atmosphere; indicates atmospheric pressure as the height to millimeters of the mercury columns; 1 atm = 760mm high in barometer tube
37
New cards
units for atmosphere
atm; 1 atm
38
New cards
units of millimeters of Hg
mmHg; 1 atm = 760 mmHg
39
New cards
units for Torr
torr; 1 atm = 760 Torr
40
New cards
units for inches of Hg
inHg, 29.9 Hg
41
New cards
units for pounds per square inch
psi
42
New cards
units for pascal
Pa; 1 atm = 101,325 Pa
43
New cards
units for kilopascal
kPa; 1 atm = 101.325 kPa
44
New cards
boyle’s law
volume decrease, pressure increases; p1 v1 = p2 v2
pressure of a gas is inversely related to its volume when T is constant
pressure of a gas is inversely related to its volume when T is constant
45
New cards
kinetic energy theory
motion (kinetic energy) of the gas particles will also increase
increase in temp. = gas particle movement increases
amt. and pressure of the gas help constant, the volume of the container will increase
increase in temp. = gas particle movement increases
amt. and pressure of the gas help constant, the volume of the container will increase
46
New cards
charles’s law
kelvin temp. of gas is directly related to the volume; v1/t1 = v2/t2; gas increase = volume increase
47
New cards
gay-lussac’s law
kelvin temp. of gas doubled and the volume amt. of gas does not change, pressure also doubles; p1/t1 = p2/t2; k doubles = p doubles
48
New cards
combines gas law
pressure, volume, temp relationship for gas; p1v1/p2 = p2v2/p2
49
New cards
avogardo’s law
volume of gas is directly related to the number of moles of gas; v1/n1 = v2/n2
50
New cards
standard temperature and pressure (STP)
volume of gas can be compared @ STP, when they have same temp and pressure
51
New cards
standard temperature
0 degree celsius or 273K
52
New cards
standard pressure
1 atm (760 mmHg)
53
New cards
molar mass
a mole of gas occupies a volume of 22.4L
54
New cards
partial pressure
pressure that each gas in a mixture would exert if it were by itself in the container
55
New cards
dalton’s law of partial pressures
pressure depends on a total number of gas particles, not on types of particles
56
New cards
the ideal gas law
PV=nRT
57
New cards
“R”
0\.0821 L(atm)/mol(K)
58
New cards
partial pressure
Pa= XaPt
59
New cards
Xa
mol fraction of n; mole A / total mole
60
New cards
solutions
a homogeneous mixture of 2 or more substances;
2 components: solvent and solute
2 components: solvent and solute
61
New cards
solutes
present in a smaller amount;
maybe liquid, gases, or solids;
mix w/ solvent;
spread evenly throughout the solutions
maybe liquid, gases, or solids;
mix w/ solvent;
spread evenly throughout the solutions
62
New cards
water (solvent)
universal solvent;
polar
polar
63
New cards
solutions formation
both solute and solvent are polar or both non polar; not polar-nonpolar
64
New cards
strong electrolytes
dissociates 100% in water, producing positive and negative ions
65
New cards
weak electrolytes
dissociates only slightly in water; forms a solution with a few ions and mostly ions from undissociated molecules
66
New cards
nonelectrolytes
dissolves as molecules in water; does not produce ions in water, do not conduct an electrical current
67
New cards
solubility
the maximum amount of solute that dissolves in a specific amount of solvent; expressed as grams of solute in 100 grams of solvent, usually water
68
New cards
unsaturated solutions
contain LESS THAN the max amount of solute; CAN DISSOLVE more solute
69
New cards
saturated solutions
contain MAX AMT of solute that can dissolve; may HAVE UNDISSOLVED SOLUTE at bottom of container
70
New cards
effects of temperature on solubility
depends on temp.
most solids increase as temp. increases
gasses decreases as temp. increases
most solids increase as temp. increases
gasses decreases as temp. increases
71
New cards
concentration of solutions
amount of solute/ amount of solutions
72
New cards
units of concentration
mass percent (m/m)
volume percent (v/v)
mass/volume (m/v)
molarity (moles solute/liters solutions)
volume percent (v/v)
mass/volume (m/v)
molarity (moles solute/liters solutions)
73
New cards
mass percent
g of solute / g of solute + g of solvent x 100
\
g of solute / 100 g of solution
\
g of solute / 100 g of solution
74
New cards
volume percent
mL of solute / mL of solution x 100
\
mL of solute / 100 mL of solution
\
mL of solute / 100 mL of solution
75
New cards
mass/ volume percent
g of solute/ mL of solution x 100
\
g of solute / 100 mL of solution
\
g of solute / 100 mL of solution
76
New cards
molarity
the moles of solute per volume (L) of solution;
moles of solute / liter of solution
moles of solute / liter of solution
77
New cards
dilution
water is added; volume of solution increases; concentration decreases; mass of solute in the solution remains the same
78
New cards
solute concentration
in the intial and diluted solutions moles of solute is the same
79
New cards
for (%) concentration
C1 V1 = C2 V2
80
New cards
for molarity
M1 V1 = M2 V2
81
New cards
molarity in chemical reactions
molarity x mole / 1 L x volume (L) = moles
\
moles x 1 L /moles = volume (L)
\
moles x 1 L /moles = volume (L)
82
New cards
solutions
transparent, do not separate, contain particles, ions, or molecules that cannot be filtered and pass through semipermeable membrances
83
New cards
colloids
medium-sized particles, cannot be filtered, can be separated by semipermeable membranes
84
New cards
suspensions
heterogeneous, non-uniform mixtures; very large particles that settle out of solution; can be filtered, must be stirred to stay suspended
85
New cards
osmosis
water (solvent) flows from a lower to a higher solute concentration; level of the solution with the higher solute concentration rises; concentration of the two solution become equal with time
86
New cards
osmotic pressure
equal to the pressure that would prevent the flow of additional water into the more concentrated solutions; greater than the number of dissolved particles in the solution increases
87
New cards
osmotic pressure II
hydrostatic pressure required to prevent the net flow of water through a semi-permeable membrane solutions
\
IIV = nRT
\
IIV = nRT
88
New cards
“M”
total particle molarity or osmolarity
89
New cards
isotonic solution
exerts the same osmotic pressure as body fluids such as red blood cells (RBCs)
90
New cards
hypotonic solution
has a lower solute concentration; water flows into cells by osmosis
91
New cards
hypertonic solution
higher solute concentration; means water flows out of cell by osmosis
92
New cards
hemolysis
increase in fluid causes the cells to swell and burst increase
93
New cards
crenations
RBCs shrink in size
94
New cards
dialysis
solvent and small particles pass through an artificial membrane; large particles are retained inside; waste particles such as urea from blood are removed using hemodialysis
95
New cards
acids
molecular substances that produce ions
96
New cards
acids (arrehenius)
produces hydrogen ions when they dissolve
electrolytes
sour taste
turns blue litmus paper RED
corrodes same metals
electrolytes
sour taste
turns blue litmus paper RED
corrodes same metals
97
New cards
naming acid
“-ate to -ic acid” or “-ite to -our acid”
98
New cards
2 categories that bases falls into
1. ionic compounds containing hydroxide ions in water
2. molecular compounds that react with water to produce hydroxide ions
99
New cards
bases (arrehenius)
produces hydroxide ions (OH-) in water
taste bitter or chalky
also electrolytes
feels soapy and slippery (dissolves layers of skin and cause to slip past)
turn litmus paper BLUE
taste bitter or chalky
also electrolytes
feels soapy and slippery (dissolves layers of skin and cause to slip past)
turn litmus paper BLUE
100
New cards
naming bases
\+ hydroxide