BIOH 201: Lab 05 - Skeletal System Notes
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Bone Markings
various ridges, grooves, depressions, and other distinctive features found on the surfaces of bones
Types of Bone Markings
Projections for muscle attachment
Depressions for muscle attachment
Projections to form joints
Passages for nerves and blood vessels.
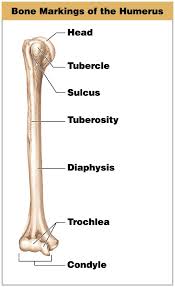
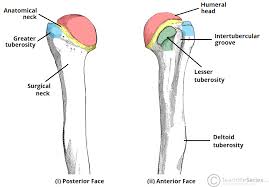
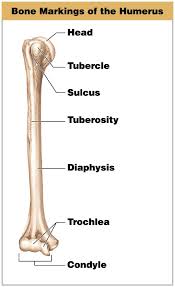
Tuberosity
A rounded, raised area on a bone providing leverage and support for muscles.
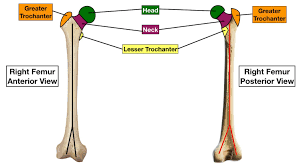
Trochanter
A large, rough process found specifically on the femur, serving as a major attachment point for hip and thigh muscles.
Tubercle
A small rounded surface on a bone, often found on the humerus that facilitates muscle attachment.
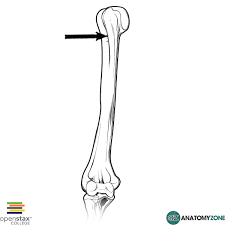
Process
A general term for any raised area or projection on the surface of bones, which may serve various functions.
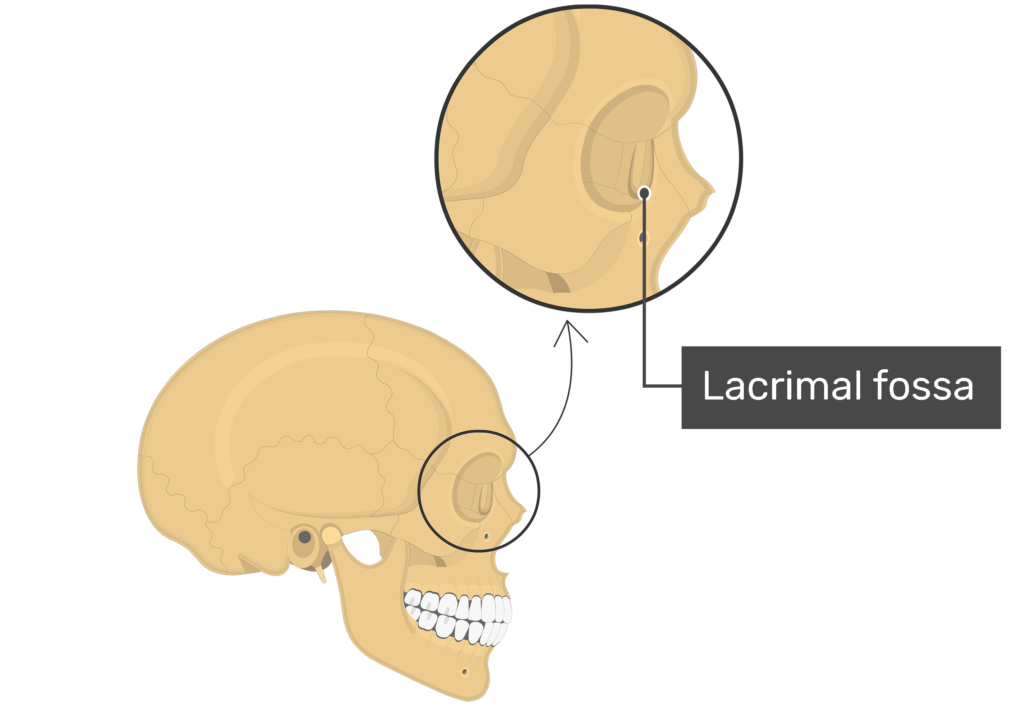
Fossa
A shallow depression or hollow area on a bone surface,
Sulcus
A groove or furrow on the bone surface that serves as a pathway for nerves, blood vessels, or tendons.
Head
A rounded end of a bone that joins with another bone to form a joint, like the head of the femur in the hip joint.
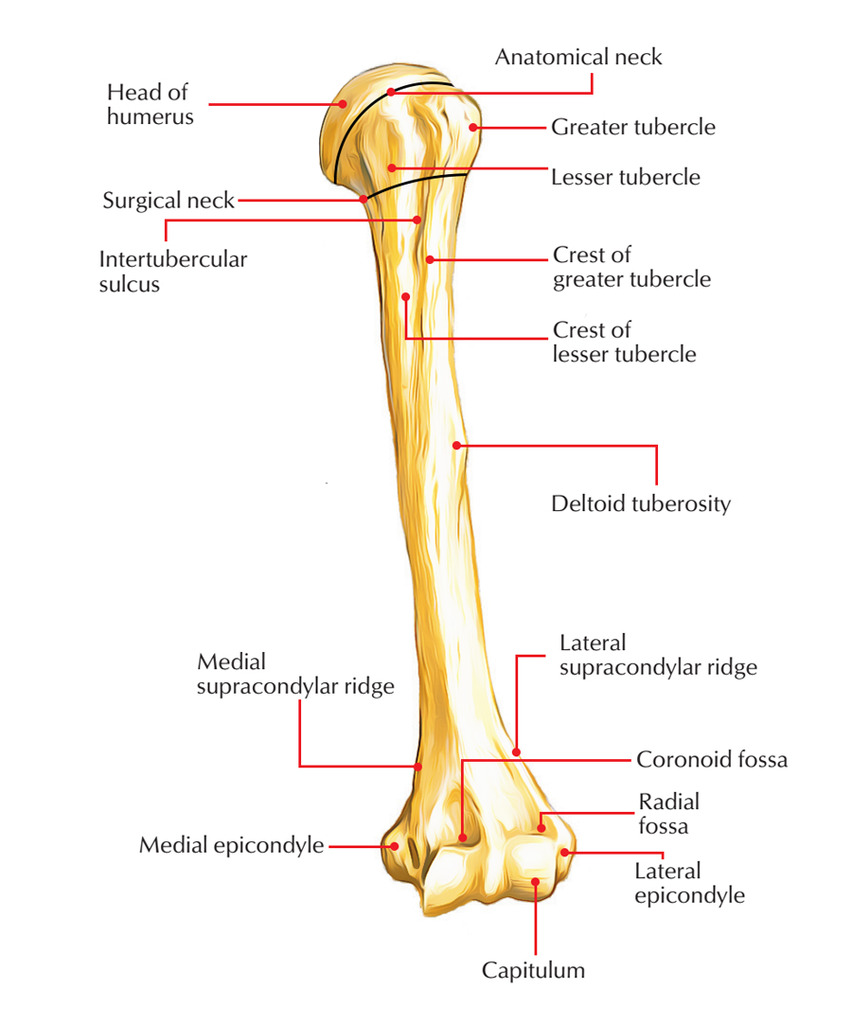
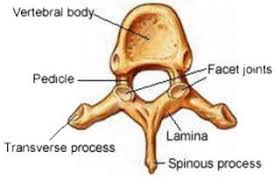
Facet
A flat surface on a bone allowing smooth articulation with another bone, common in vertebrae.
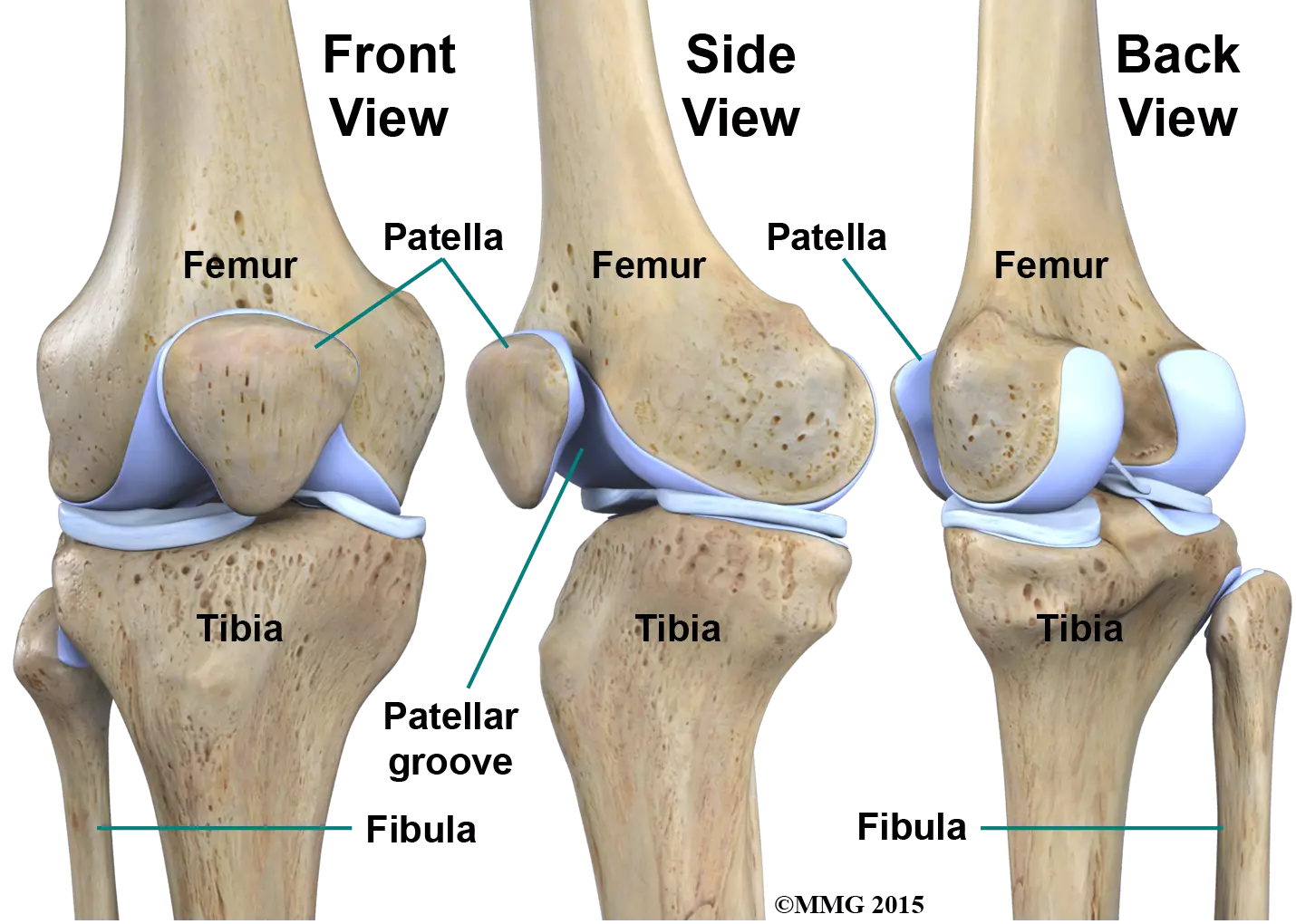
Condyle
A rounded projection at the end of a bone that connects with another bone to form a joint.
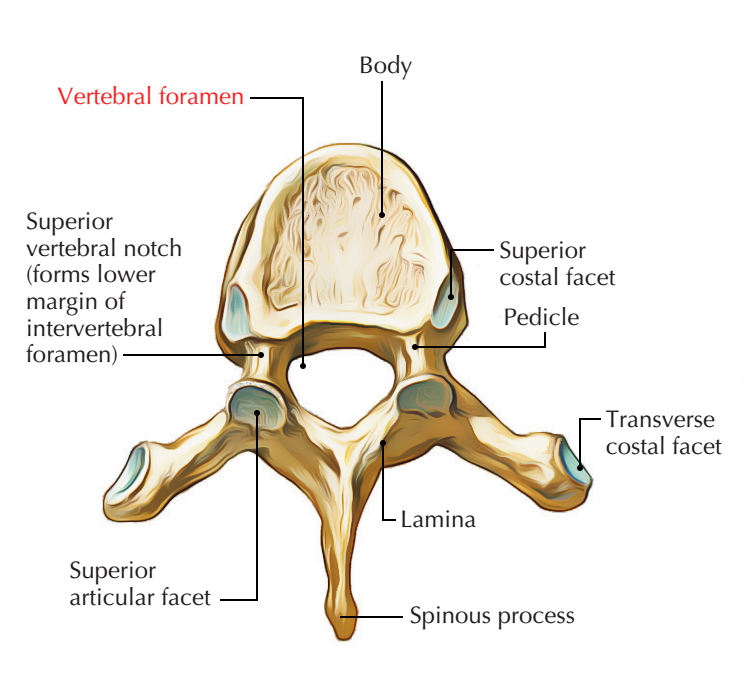
Foramen
Round holes in the bone that allow the passage of nerves, blood vessels, and other structures.
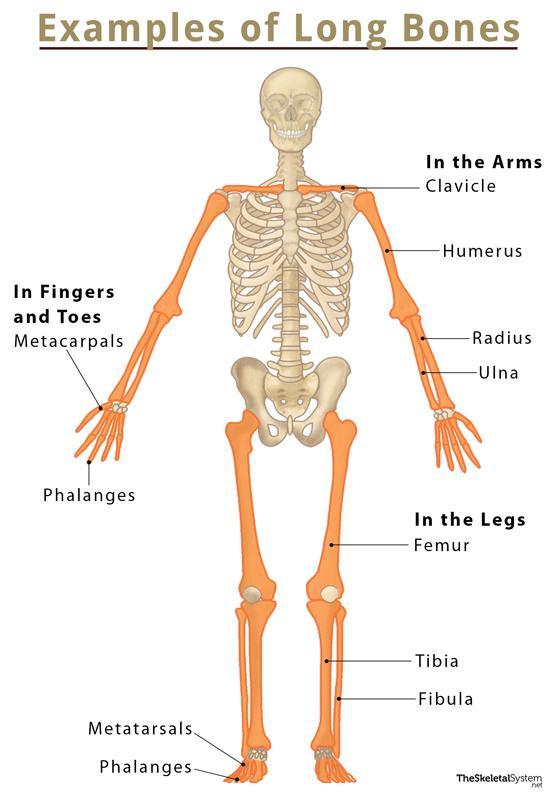
Long Bones
Support body weight and facilitate movement
long bones
humerus
ulna and radius
femur
tibia and fibula
metacarpals and metatarsals
phalanges
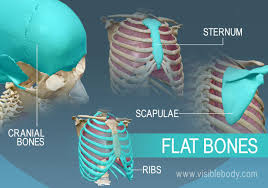
Flat Bones
Provide protection to internal organs such as brain, heart, and lungs
flat bones
cranial bones
scapulae
sternum
ribs
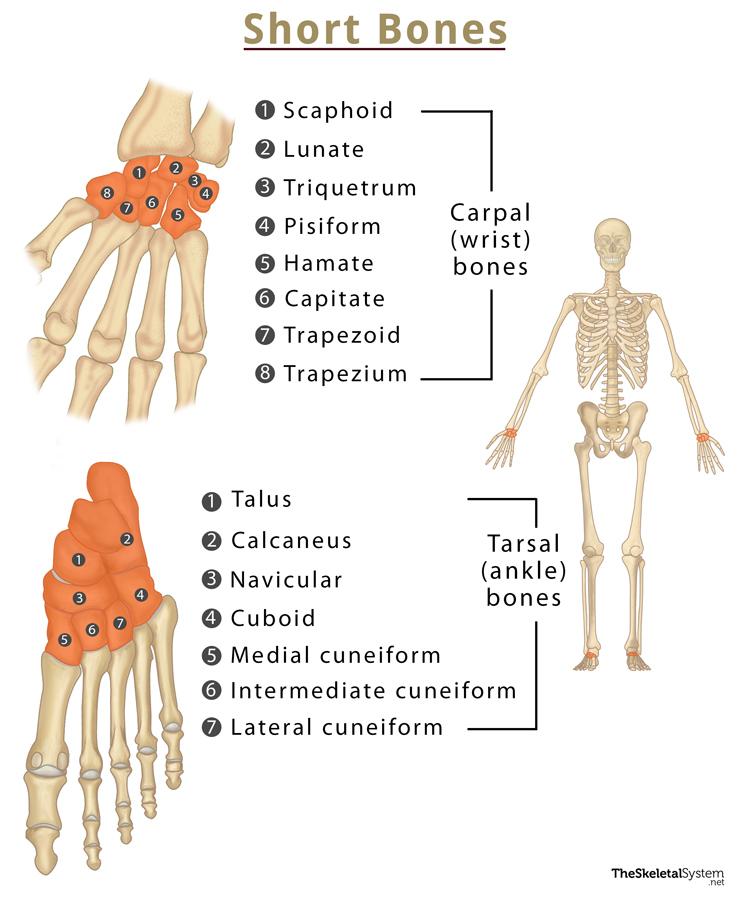
Short Bones
cube-shaped, components of the wrist and ankle joint
short bones
carpals
tarsals
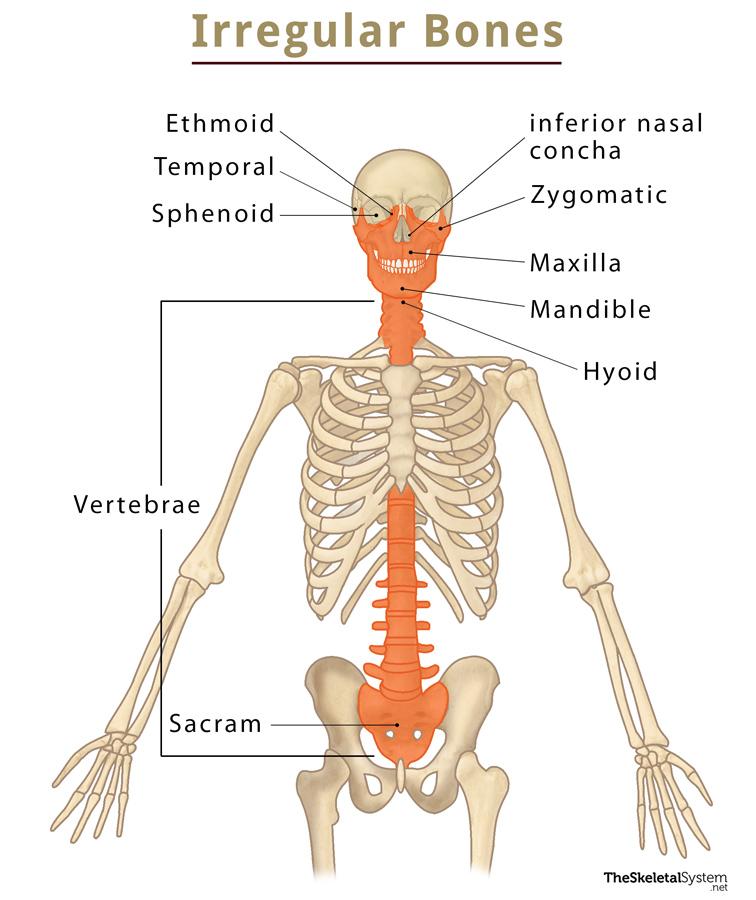
Irregular Bones
bones varying in shape and structure
irregular bones
vertebrae
sacrum
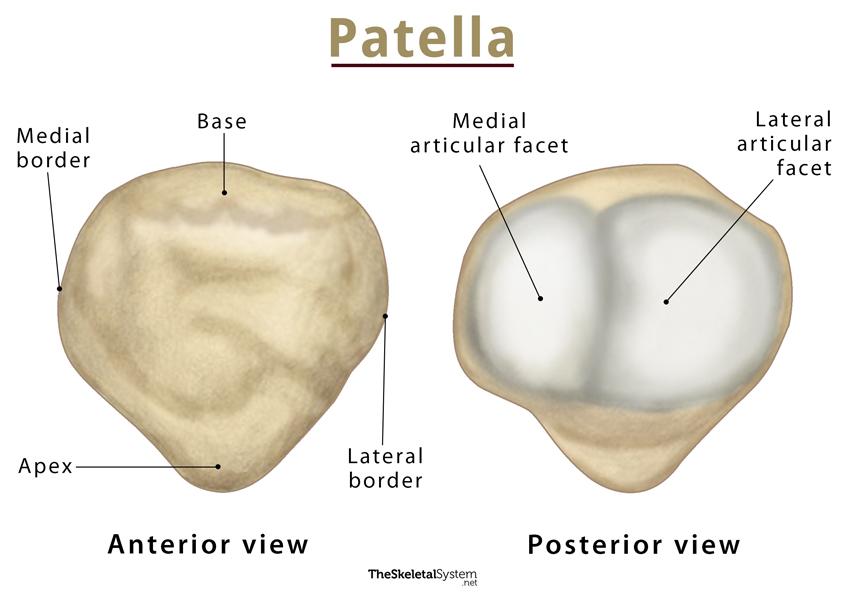
Sesamoid Bones
reinforce and protect tendons from stress and wear.
sesamoid bones
patella
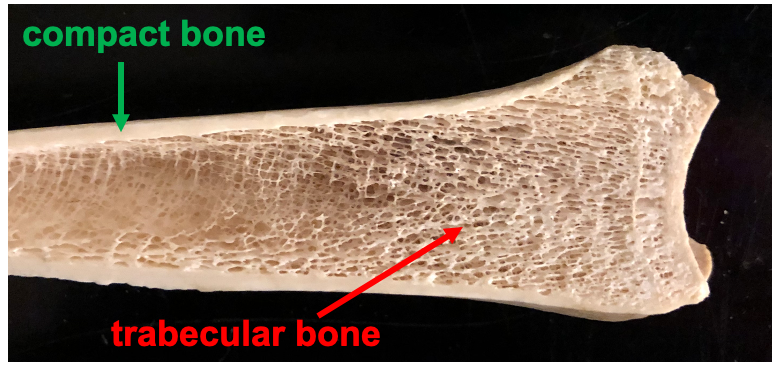
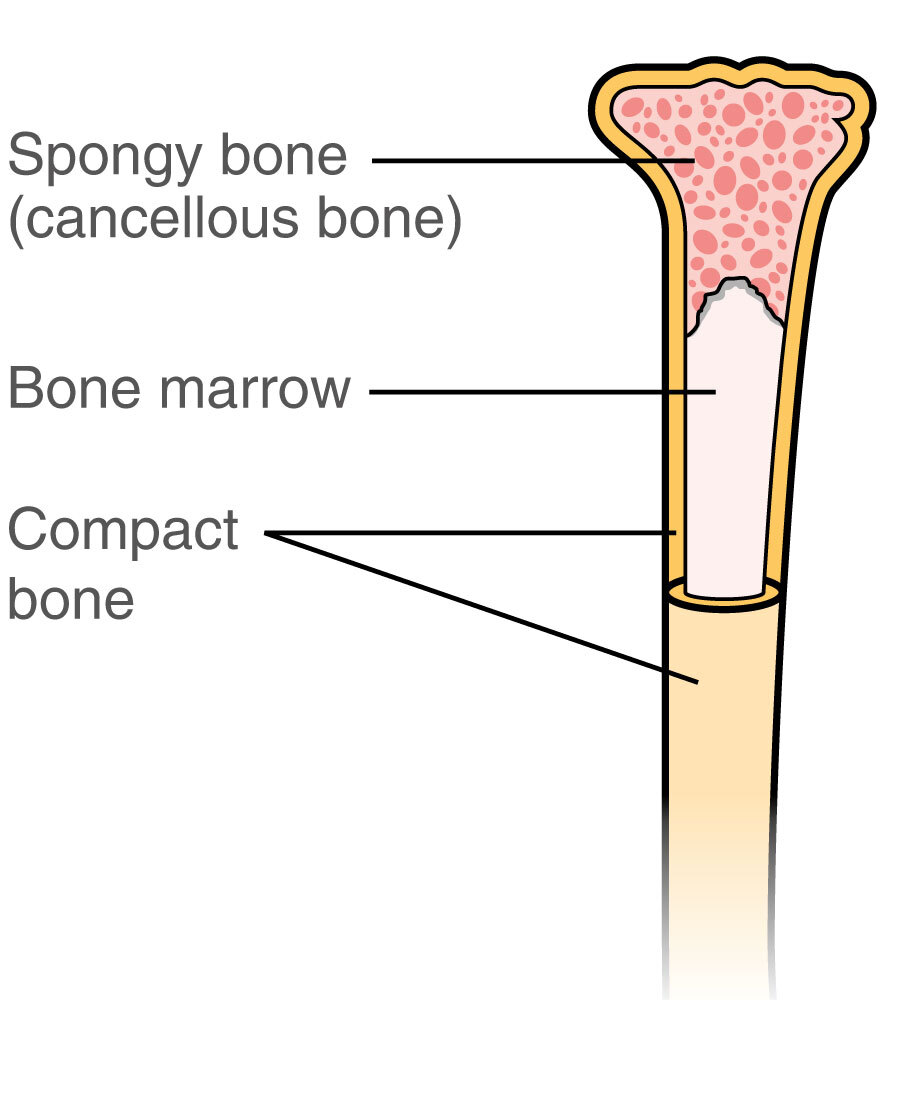
Compact Bone
dense bone tissue found on the exterior of the bone, covered in articular cartilage
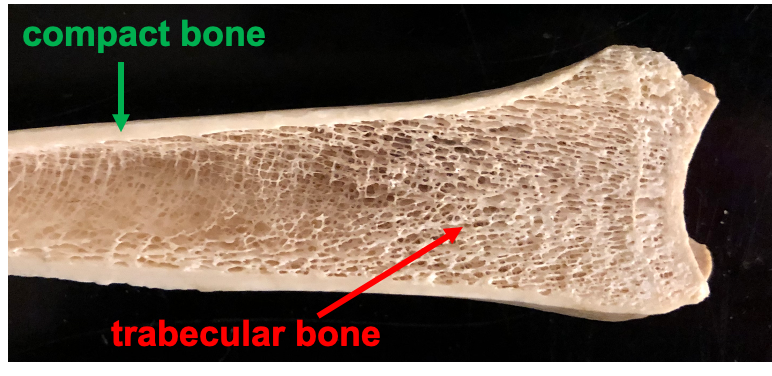
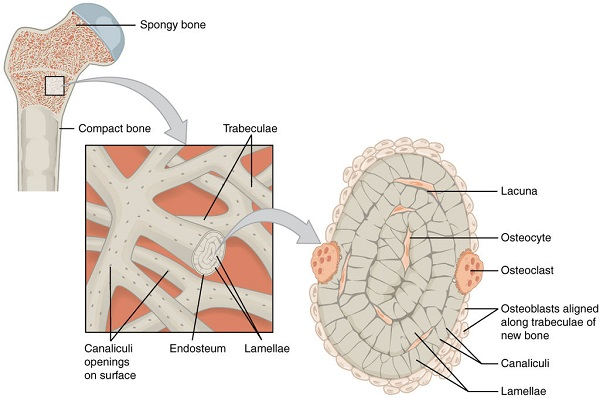
Spongy Bone
found in the interior of the bone and consists of slender fibers and lamellae that join to form a reticular structure, the ends of femurs are mostly spongy bone
Medullary Cavity
cylindrical cavity found in the interior of the long bones of the limbs filled with marrow and surround by compact bone
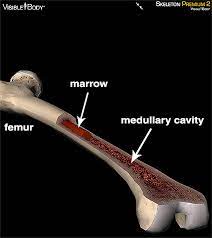
Bone Marrow
fills the medullary cavity and spaces inside spongy bone
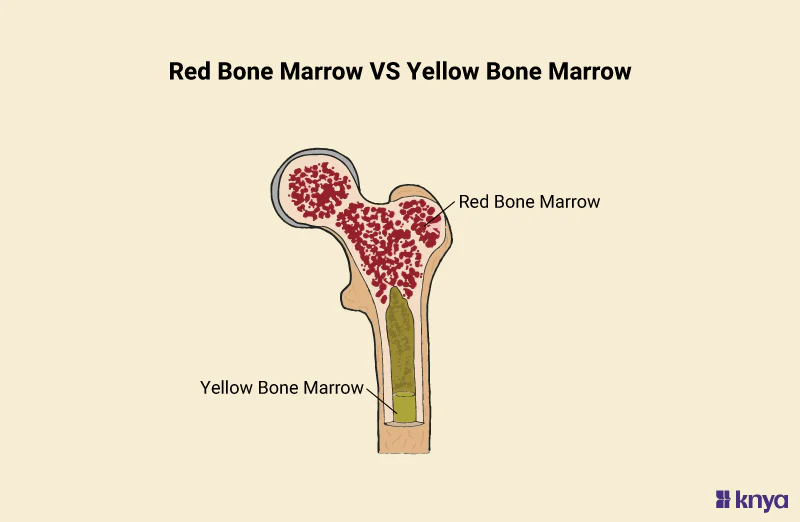
yellow marrow
mostly fat
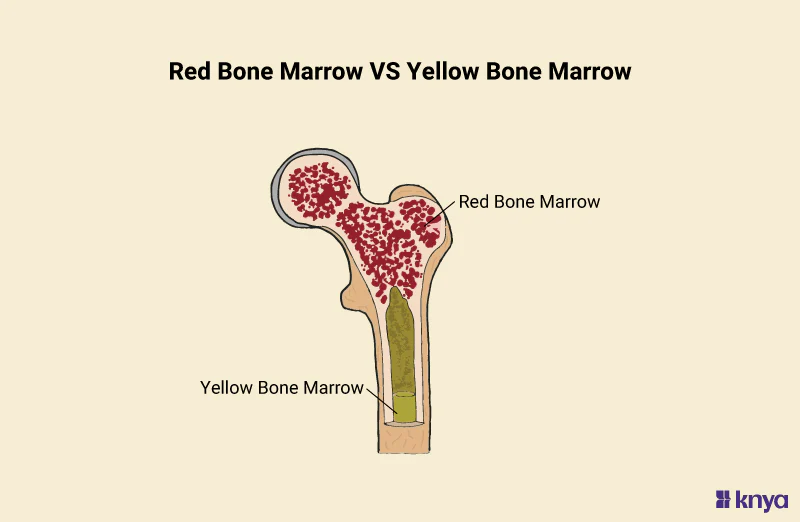
red marrow
hematopoietic tissue, site of blood cell production
Osteoclasts
secretes enzymes that dissolves and break down old or damaged bone cells
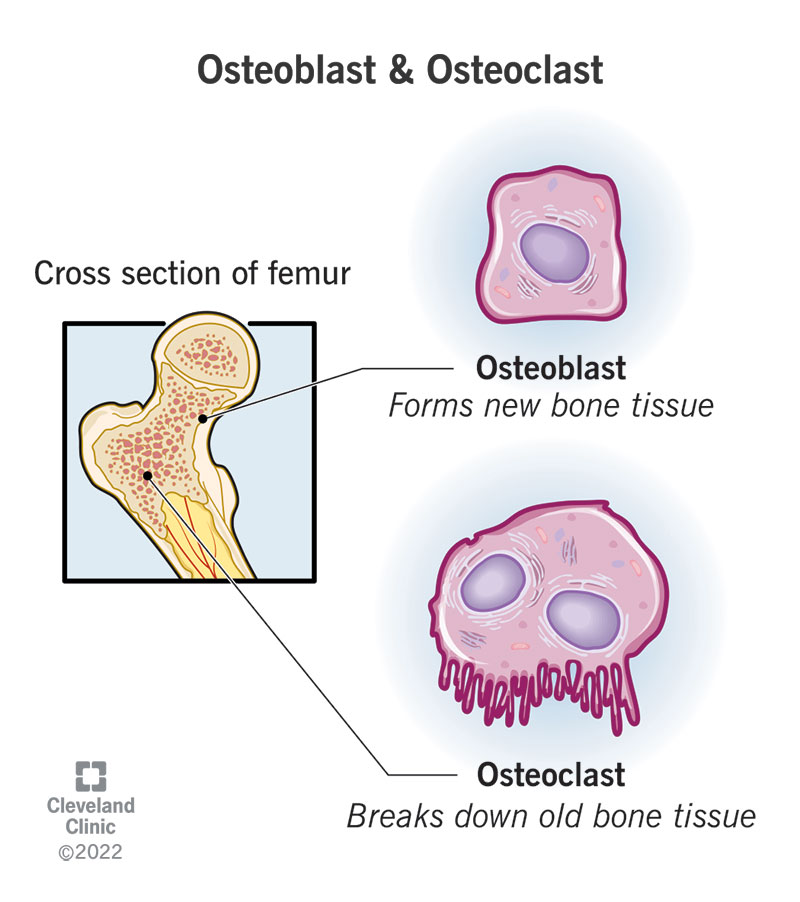
Osteoblasts
cells that form new bones and grow and heal existing bones
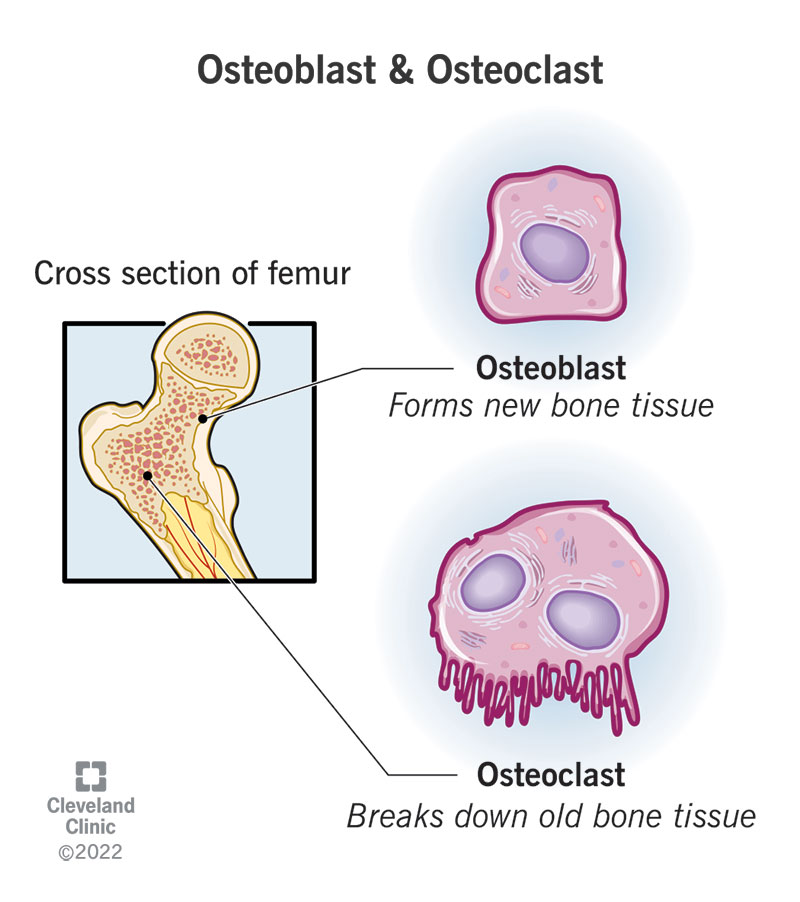
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that maintain bone structure and communicate with other bone cells.
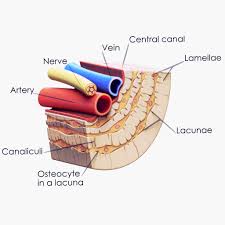
Lamellae
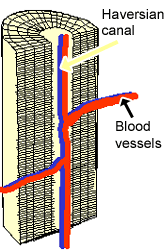
thin layers of bone matrix in compact bone tissues, arranged in concentric circles around the central Haversian canals, providing support and strength
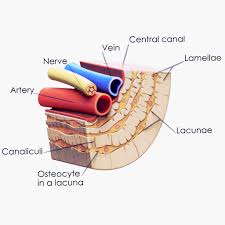
Canaliculi
Tiny channels connecting lacuna
Trabeculae
lattice like network of spongy bone tissue
Flexion/Extension
flexion is bending the joint, extension is straightening a joint
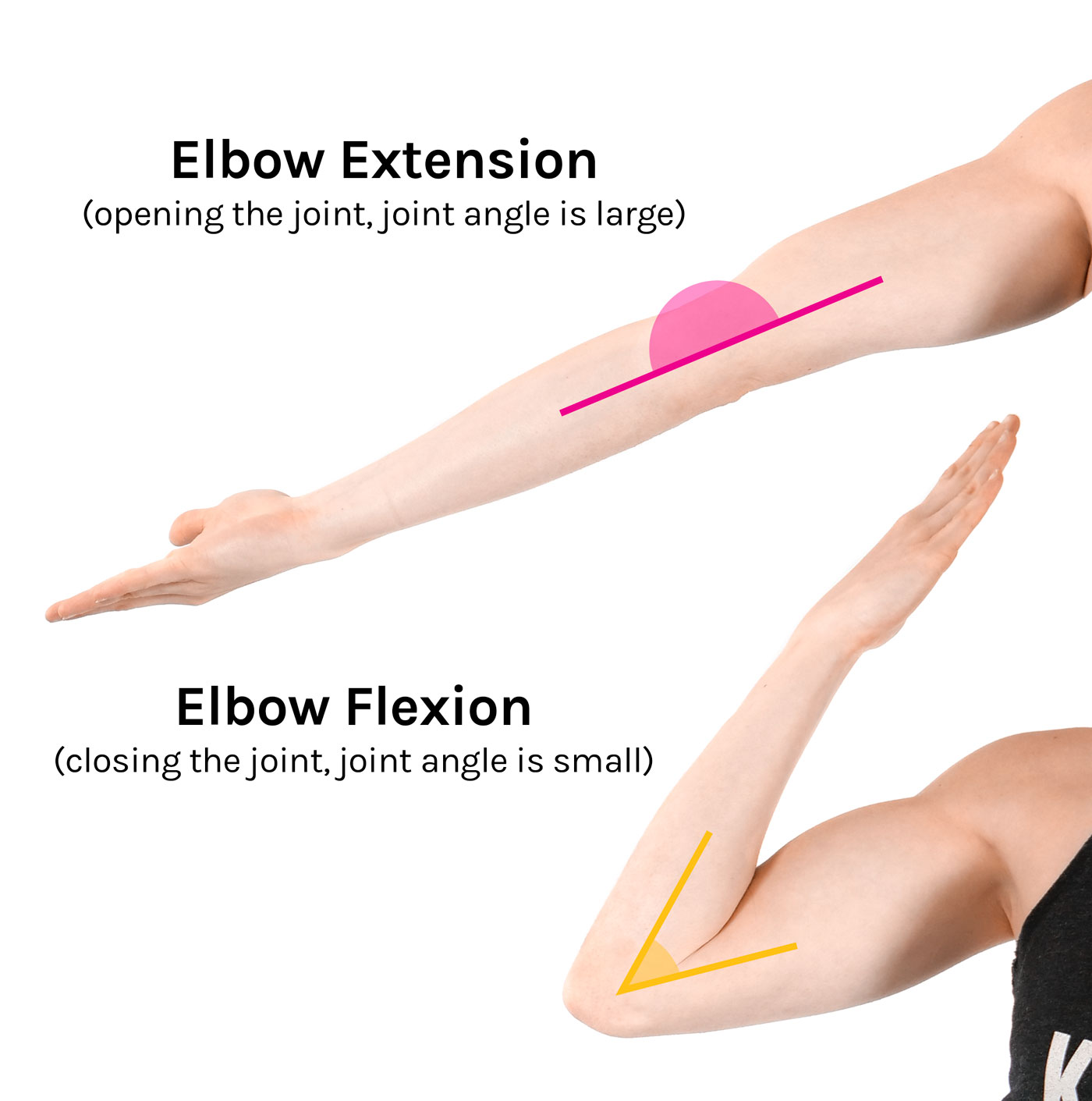
flexion- extension
elbow
tibiofemoral (knee)
phalangeal joints
glenohumeral (shoulder)
coxal (hip)
radoiocarpal (wrists)
altanto- occipital (head)
Abduction/Adduction
abduction is away from the midline, while adduction is movement towards the midline

abduction-adduction
glenohumeral (shoulder)
coxal (hip)
metacarpophalangeal (knuckles 2-5)
carpometacarpal of thumb metatarsophalangeal (toes)
Rotation
circular movement of an object around a central line
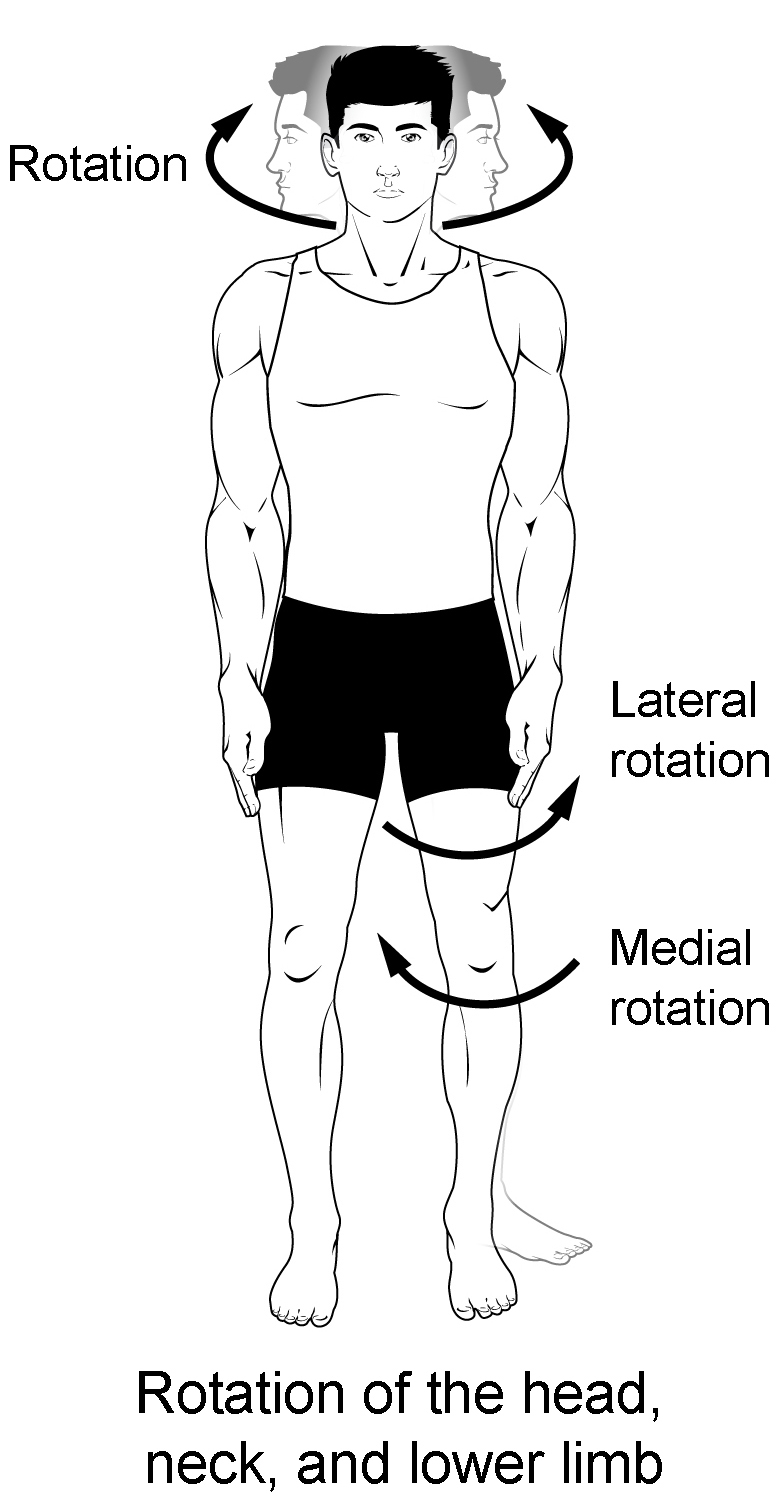
rotation
atlantoaxial (head)
glenohumeral (shoulder)
coxal (hip)
Circumduction
a circular movement at a joint that combines flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction, allowing the limb to make a circular motion. cir
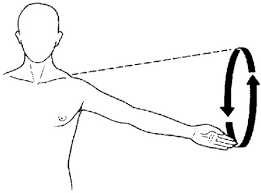
circumduction
metacarpophalangeal (knuckles 2-5)
carpometacarpal of thumb
glenohumeral (shoulder)
coxal (hip)
Pronation/Supination
supination is turning the palm upwards while pronation is turning the palm downwards
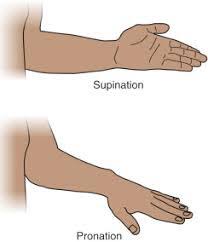
pronation- supination
radioulnar
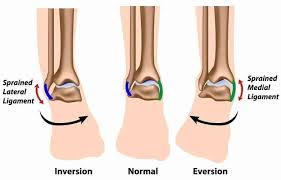
Inversion/Eversion
Movement inversion tilts the ankle inwards, eversion tilts the ankle outward away from the midline
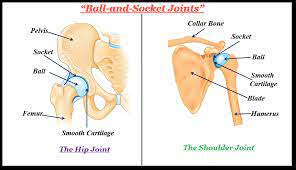
Ball and Socket Joint
hip joint
shoulder joint (glenohumeral)
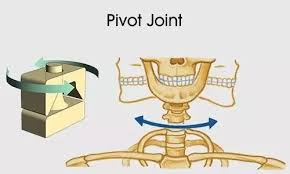
Pivot Joint
between the axis and atlas vertebrae
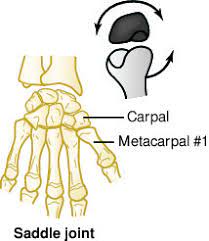
Saddle Joint
between the first metacarpal (of thumb) and the trapezium (carpal of thumb)
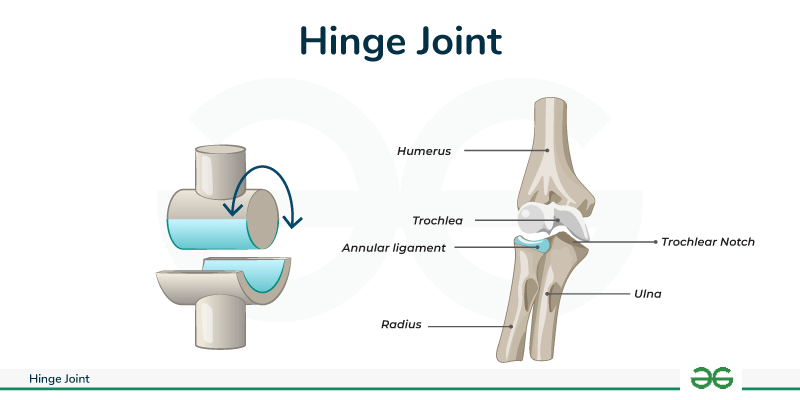
Hinge Joint
Allows for flexion and extension; a classic example is the elbow joint.
hinge joint
elbow joint (humeroulnar)
finger joints
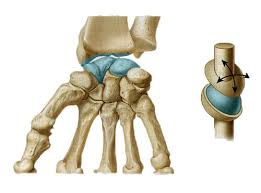
Condylar Joint
between radius and carpal
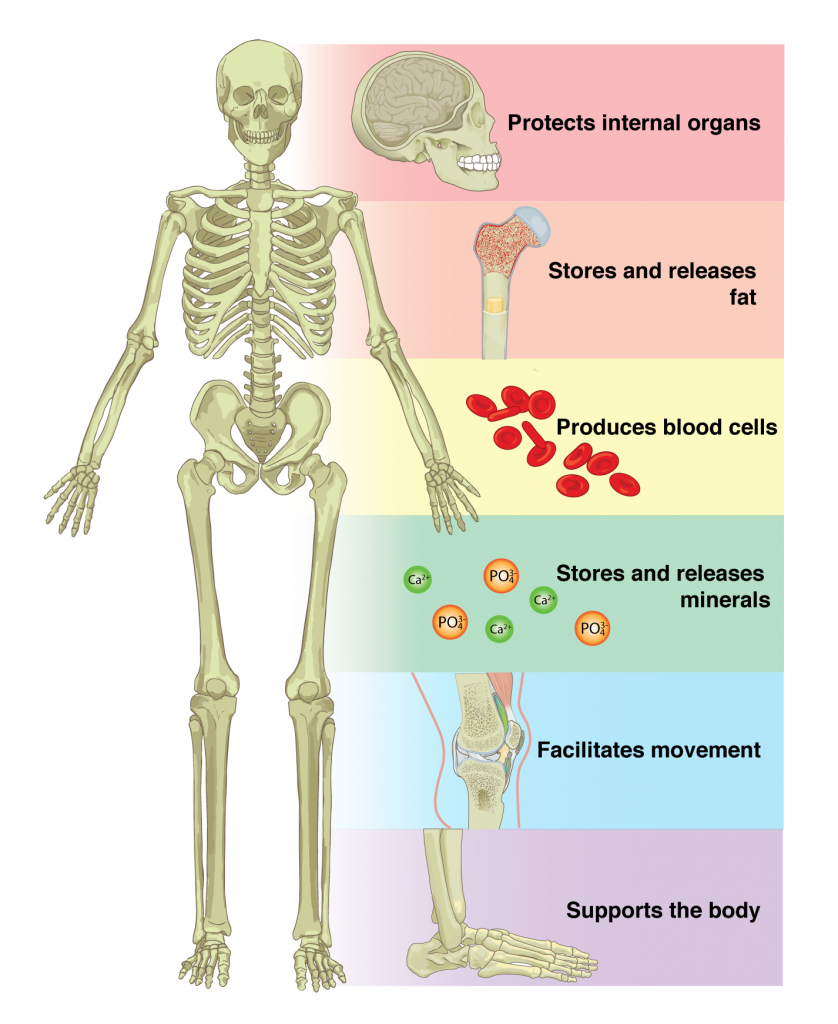
functions of the skeletal system
movement (appendicular)
blood cell production
protecting internal vital organs ( axial skeleton)
store calcium and phosphorous
muscle attachment
osteon
structural unit of compact bone central canal
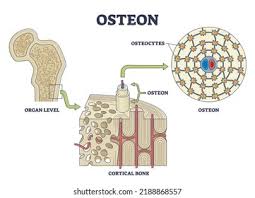
central canal
canal to allow passage of blood vessels