L4 - Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Define endocrinology
Study of endocrine glands and hormones
Define hormone
Mediator molecule release to regulate cell function in body
Name as many endocrine organs as can think of
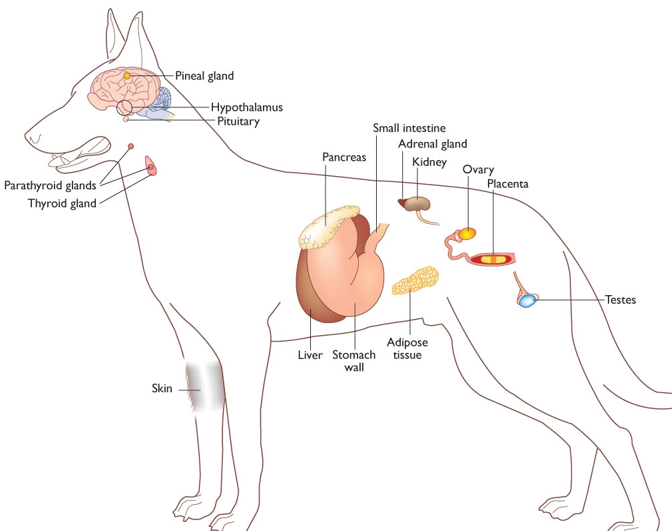
Where is hypothalamus located?
Diencephalon in brain, most ventrally
What are hypothalamus functions?
Homeostasis
Meeting point of NS and endocrine
Operate ANS
Activate endocrine system
Secrete hormones regulate anterior pituitary gland/adenohypophsis
Produce hormones release via posterior pituitary gland/neurophysis
Milk letdown
Sexual behaviour
Development
What releasing hormones form hypothalamus and function?
Thyrotropin releasing hormone (TRH)
Corticotropic releasing hormone (CRH) - stimulate adrenal gland
Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
Growth hormone releasing hormone (GRH) - stimulate growth hormone release
Prolactin releasing hormone (PRLH)
Melanocyte stimulating releasing hormone (MSRH) - stimulate skin cells produce melanin
Somatostatin - regulate inhibition of hormones
How does hypothalamus communicate to anterior pituitary glnad?
Hypothalamic-pituitary portal system
What is posterior pituitary gland formed of and release?
Neurosecretory neurons - like hypothalamus extension
Release Vasopressin/ADH and oxytocin
What is posterior pituitary also called?
Neurohypophysis
What is anterior pituitary also called?
Adenohypophysis
Hypothalamus release ADH. What does posterior pituitary release, what is target organ and function?
Release ADH
Target Kidney tubules
Maintain water balance
Hypothalamus release ocytocin. What does posterior pituitary release, what is target organ and function?
Release oxytocin
Target mammary gland for milk let-down
Target uterus for uterine muscle contraction during parturition
How is anterior pituitary controlled?
Hypothalamic releasing hormones via hypothalmic-pituitary portal vessel
What are parts of anterior pituitary gland?
Pars distalis - most hormone production
Pars tuberalis
Pars intermedia
Hypothalamus release TRH. What does posterior pituitary release, what is target organ and function?
Release prolactin, target mammary gland for milk production
Release TSH, target thyroid gland to regulate metabolism and calcium deposit
Hypothalamus release CRH. What does posterior pituitary release, what is target organ and function?
Release ACTH, target adrenal cortex for glucocorticoid synthesis
Hypothalamus release GnRH. What does posterior pituitary release, what is target organ and function?
Release LH + FSH
Target testes for spermatogenesis and testosterone synthesis
Target ovaries for follicular development + ovulation
Hypothalamus release GHRH. What does posterior pituitary release, what is target organ and function?
Release GH(STH) for somatic growth and metabolism regulation
Effect entire body, no specific targetWhat is
What is pathway to stimulate hormone release from glands?
NS relay info to hypothalamus which release releasing hormones act on pituitary for synthesis/release hormones into blood
Negative feedback loop maintain levels
What is pineal gland/epiphysis and function?
Amll gland in diencephalon in mst vertebrates
Secrete melatonin base on light changes
Also secrete serotonin and peptides
What is pineal gland innervation?
Cranial cervical ganglion
What is size of dog adrenal gland?
2.5 × 1 × 0.5cm
What is function of adrenal cortex zona glomerulosa and how is it regulated?
Secretes aldosterone (mineralcorticoid) to regulate electrolytes (Na+ and Cl- reabsoption and K+ secretion at kidney)
Regulates blood pressure
Regulated by RAAS and extracelluar K+ concentration
What is function of adrenal cortex zona reticularis?
Secrete steroid and sex hormones, precursor for oestrogen in small quantities
What is function of adrenal cortex zona fasciculata and how is it regulated?
Release glucocorticoids (stress hormones)
Form ‘flight-or-fight’ response
Regulated by ACTH form HPA axis
What is the action of glucocortioids on liver?
Promote glycogen storage
Gluconeogenesis
Antagonise insulin
What is the action of glucocortioids on muscle?
Catabolism/proteolysis
What is the action of glucocortioids on fat/adipose tissue?
Mobilisation + redistribution
Lipolysis
What is the action of glucocortioids on brain?
Thirst + hunger
What is the action of glucocortioids on bone?
Reduce Ca2+ levels cause bone weakening
What is the action of glucocortioids on immune system?
Suppress immune response (anti-inflammatory and destroy lymphocytes)
Release neutrophils from marginated pool (in capillary and arterioles)
What is the action of glucocortioids on kidney?
Inhibit ADH cause polyuria and PUPD
Increase GFR
What is pathway of glucocorticoid release?
Stress stimulate hypothalamus paraventricular nuclei cause CRH release
CRH stimulate anterior pituitary gland corticotrophin cells to secrete ACTH
ACTH stimulate adrenal cortex to release glucocorticoids/cortisol
Glucocorticoids create negative feedback loop to decrease production
What are effects of catecholamines (adrenaline/norepinephrine and adrenaline/epinephrine)?
Increase HR, CO, blood glucose and bloodflow
Arterial vasodialation heart + skeletal muscle
Pupil dialtion
What are 2 stress pathways?
Hypothalamus → Spinal cord → Adrenal medulla → Adrenaline + noradrenaline
Hypothalamus → Anterior pituitary gland → adrenal cortex → Cortisol + aldosterone