America in World War I STEM ECHS
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
MIlitarism
A policy of glorifying military power and keeping a standing army always prepared for war

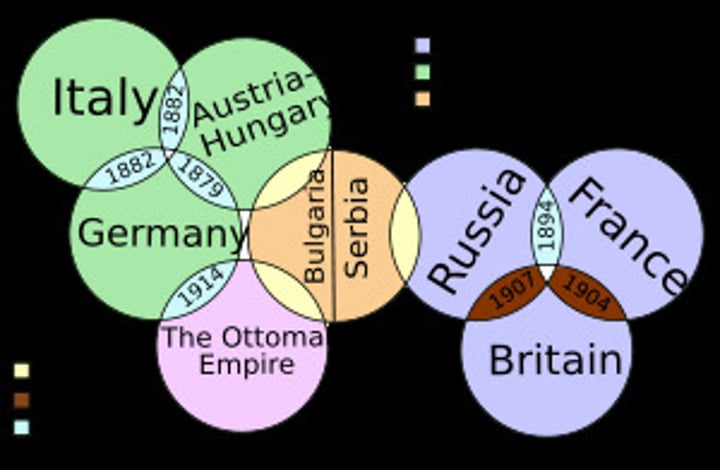
Alliances
agreements between nations to aid and protect one another
Imperialism
A policy of extending a country's power and influence through diplomacy or military force.

Nationalism
A strong feeling of pride in and devotion to one's country

Archduke Franz Ferdinand
Heir to the Austria-Hungarian throne, was assassinated in Sarajevo, started World War I.
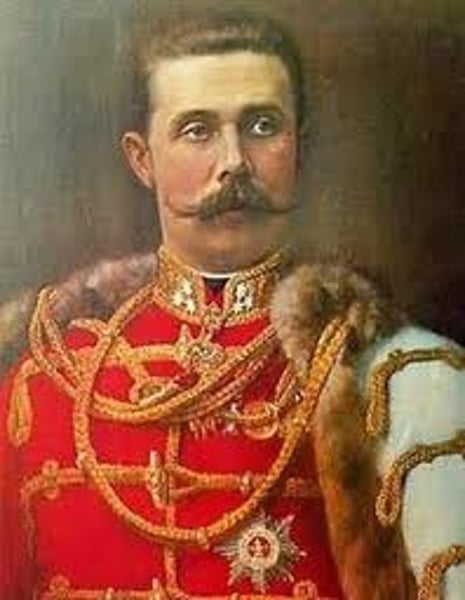

Gavrilo Princip
The assassin of Archduke Francis Ferdinand of Austria, a member of the Black Hand

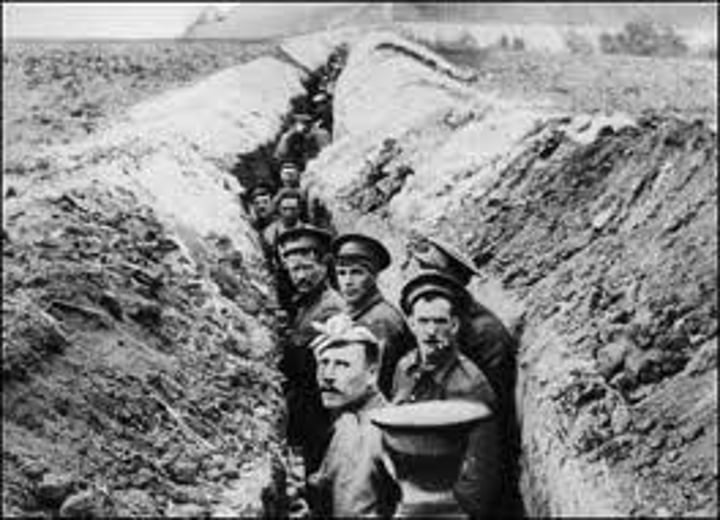
Trench Warfare
A form of warfare in which opposing armies fight each other from trenches dug in the battlefield.

Propaganda
Ideas spread to influence public opinion for or against a cause.

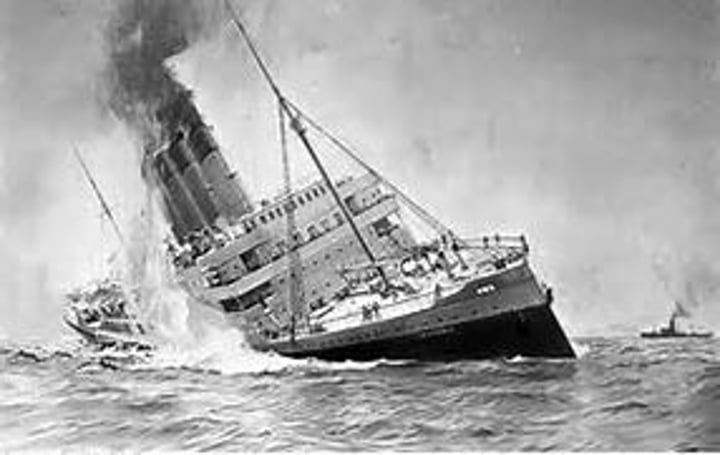
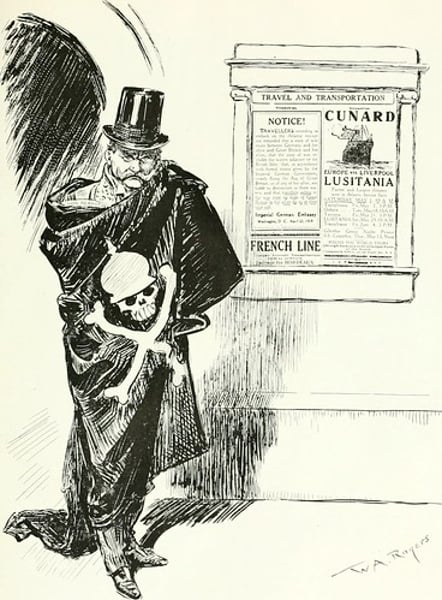
Lusitania
A British passenger ship that was sunk by a German U-Boat on May 7, 1915. 128 Americans died. The sinking greatly turned American opinion against the Germans, helping the move towards entering the war.

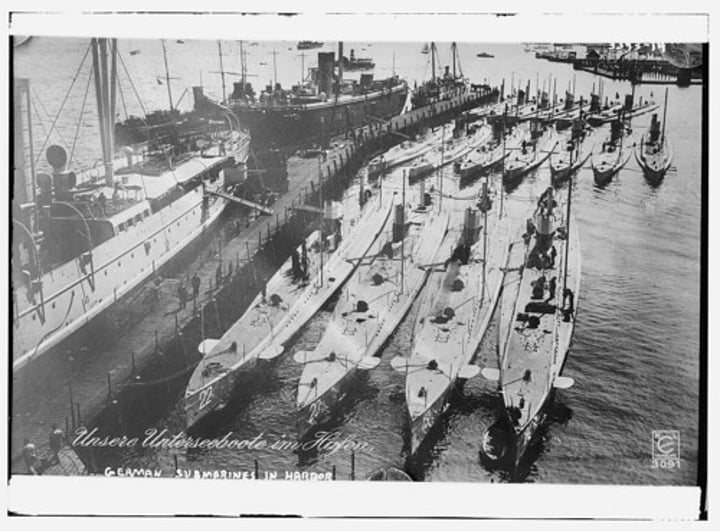
Freedom of the seas
the right of merchant ships to travel freely in international waters

Sussex pledge
A promise Germany made to America, after Wilson threatened to sever ties, to stop sinking their ships without warning.

Espionage & Sedition Acts
two laws, enacted in 1917 and 1918, that imposed harsh penalties on anyone interfering with or speaking against U.S. participation in WWI

Schenck v. U.s.
A United States Supreme Court decision concerning the question of whether the defendant possessed a First Amendment right to free speech against the draft during World War I. Ultimately, the case served as the founding of the "clear and present danger" rule.

war industries board
Government agency established to coordinate the purchase of war supplies during World War I.

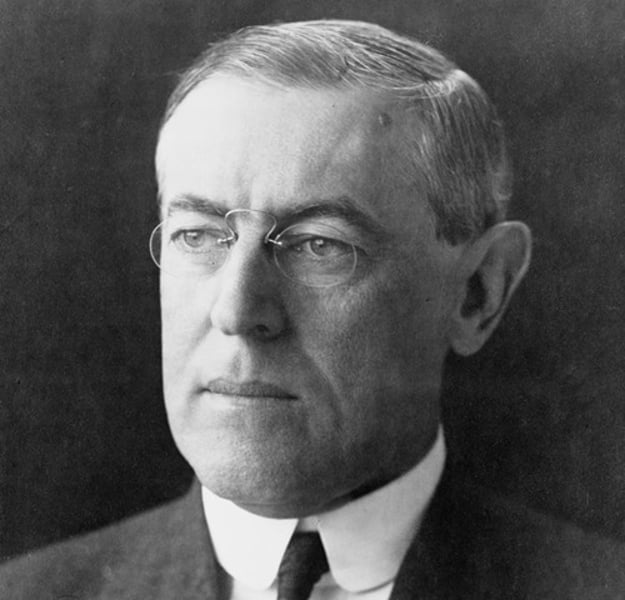
Woodrow wilson
28th president of the United States, known for World War I leadership, created Federal Reserve, Federal Trade Commission, Clayton Antitrust Act, progressive income tax, lower tariffs, women's suffrage (reluctantly), Treaty of Versailles, sought 14 points post-war plan, League of Nations (but failed to win U.S. ratification), won Nobel Peace Prize

Selective service act
This 1917 law provided for the registration of all American men between the ages of 21 and 30 for a military draft. By the end of WWI, 24.2 had registered; 2.8 had been inducted into the army. Age limit was later changed to 18 to 45.

Armistice
An agreement to stop fighting

Reparations
As part of the Treaty of Versailles, Germany was ordered to pay fines to the Allies to repay the costs of the war. Opposed by the U.S., it quickly lead to a severe depression in Germany.

War Guilt clause
A provision in the Treaty of Versailles by which Germany acknowledged that it alone was responsible for WWI

Zimmerman Note/telegram
1917 - Germany sent this to Mexico instructing an ambassador to convince Mexico to go to war with the U.S. It was intercepted and caused the U.S. to mobilized against Germany, which had proven it was hostile
Fourteen points
A series of proposals in which U.S. president Woodrow Wilson outlined a plan for achieving a lasting peace after World War I.

League of nations
A world organization established in 1920 to promote international cooperation and peace. It was first proposed in 1918 by President Woodrow Wilson, although the United States never joined the League. Essentially powerless, it was officially dissolved in 1946.

Treaty of Versailles
(WW) 1918, , Created by the leaders victorious allies Nations: France, Britain, US, and signed by Germany to help stop WWI. The treaty 1)stripped Germany of all Army, Navy, Airforce. 2) Germany had to rapair war damages(33 billion) 3) Germany had to acknowledge guilt for causing WWI 4) Germany could not manefacture any weapons.

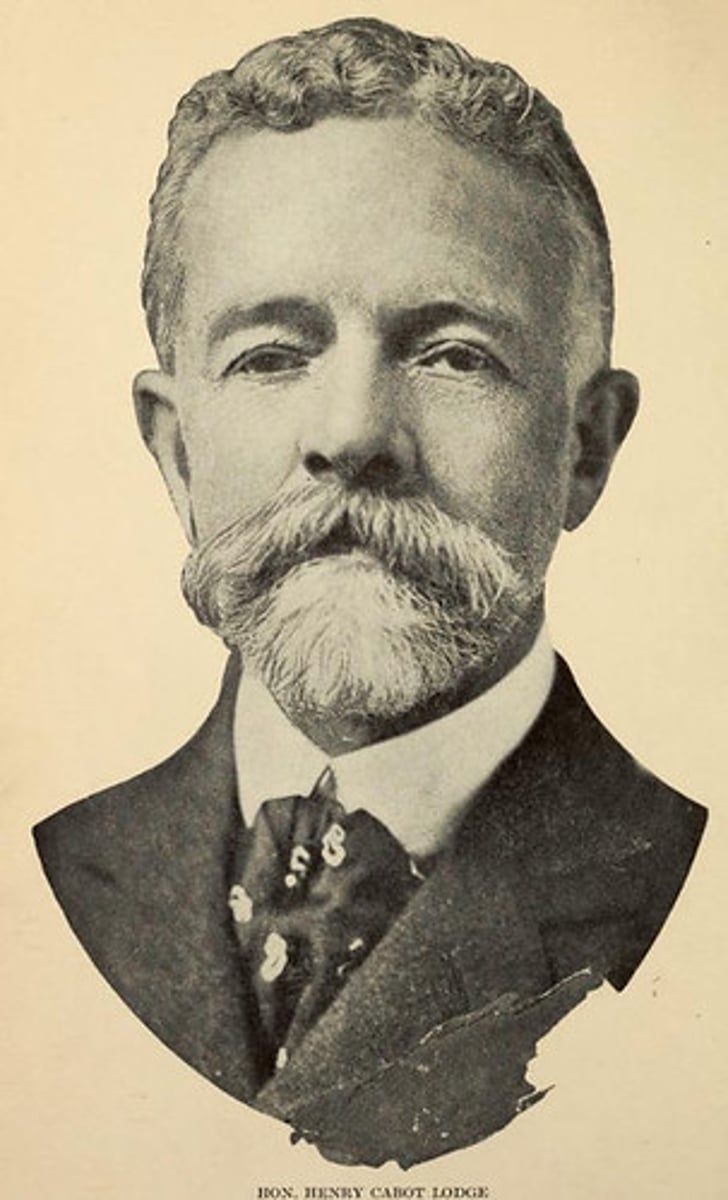
Henry Cabot Lodge
Henry Cabot Lodge was a Republican who disagreed with the Versailles Treaty, and who was the chairman of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee. He mostly disagreed with the section that called for the League to protect a member who was being threatened.

Alvin York
killed 25 machine-gunners and captured 132 German soldiers when his soldiers took cover; won Congressional Medal of Freedom

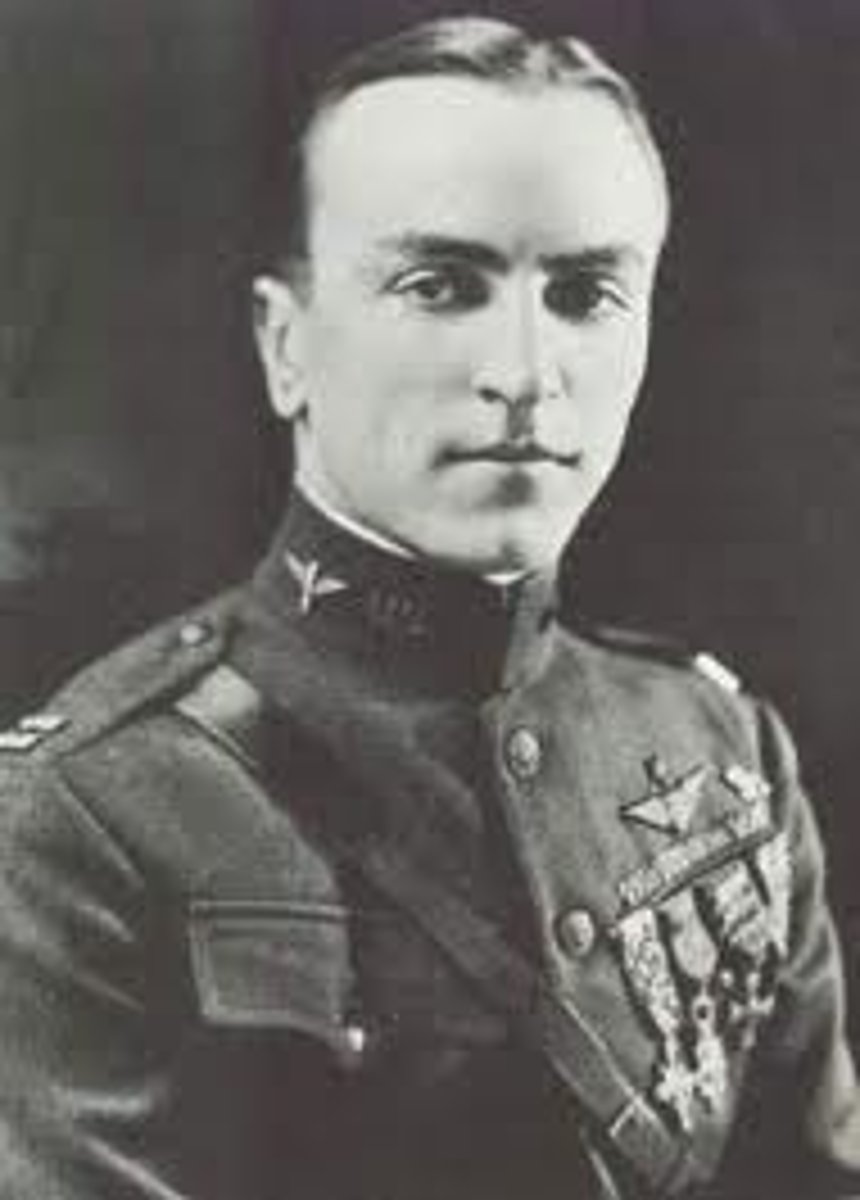
Eddie rickenbacker
Famous "ace" pilot who downed 26 enemy fighters in WWI

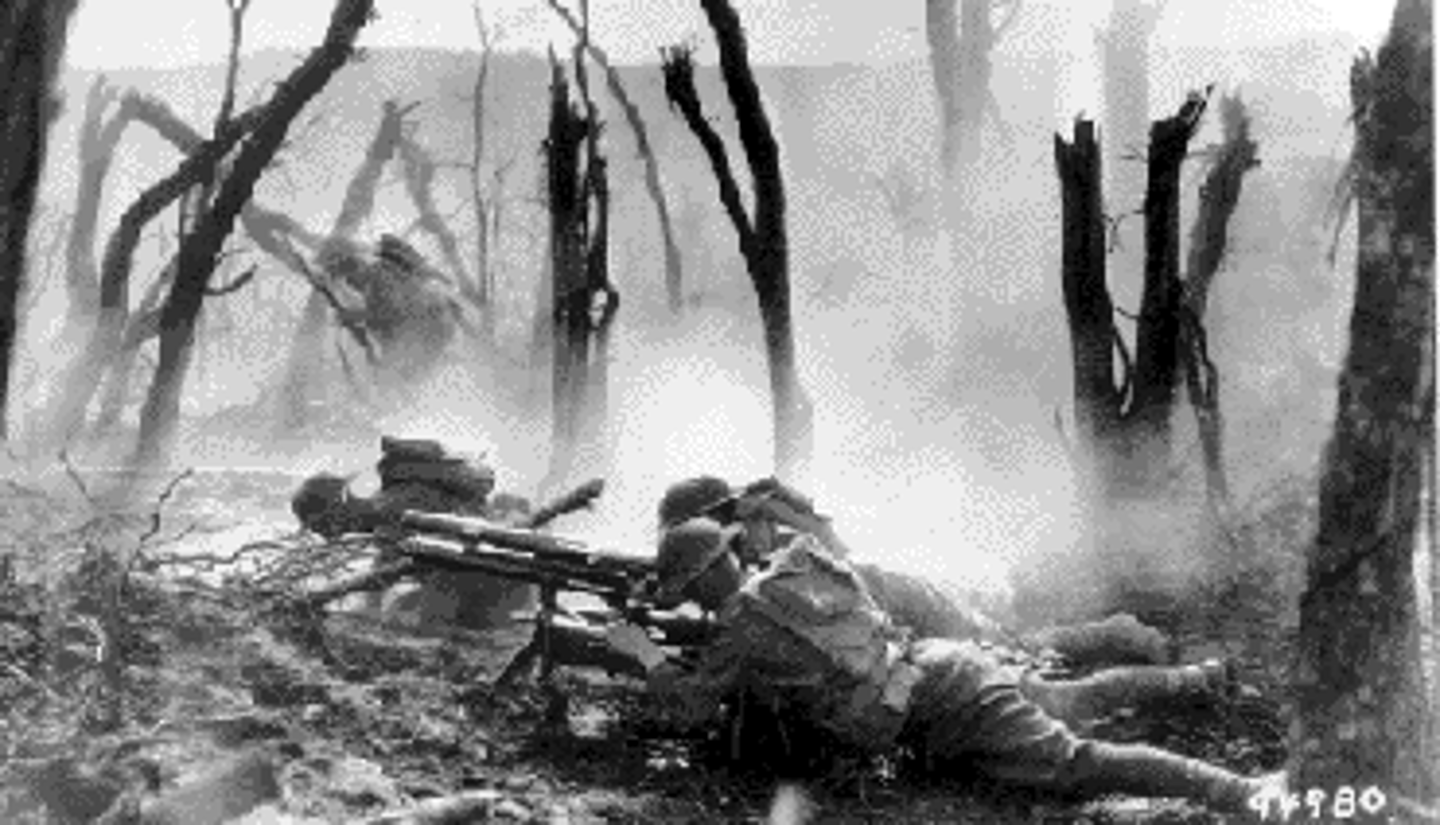
battle of argonne forest
The largest battle in U.S. history involving over 1 million soldiers, they would be successful in breaking through the German defenses. It was part of the 100 days offensive that would lead to the end of World War I. The U.S. soldiers were led in battle by John J. Pershing.

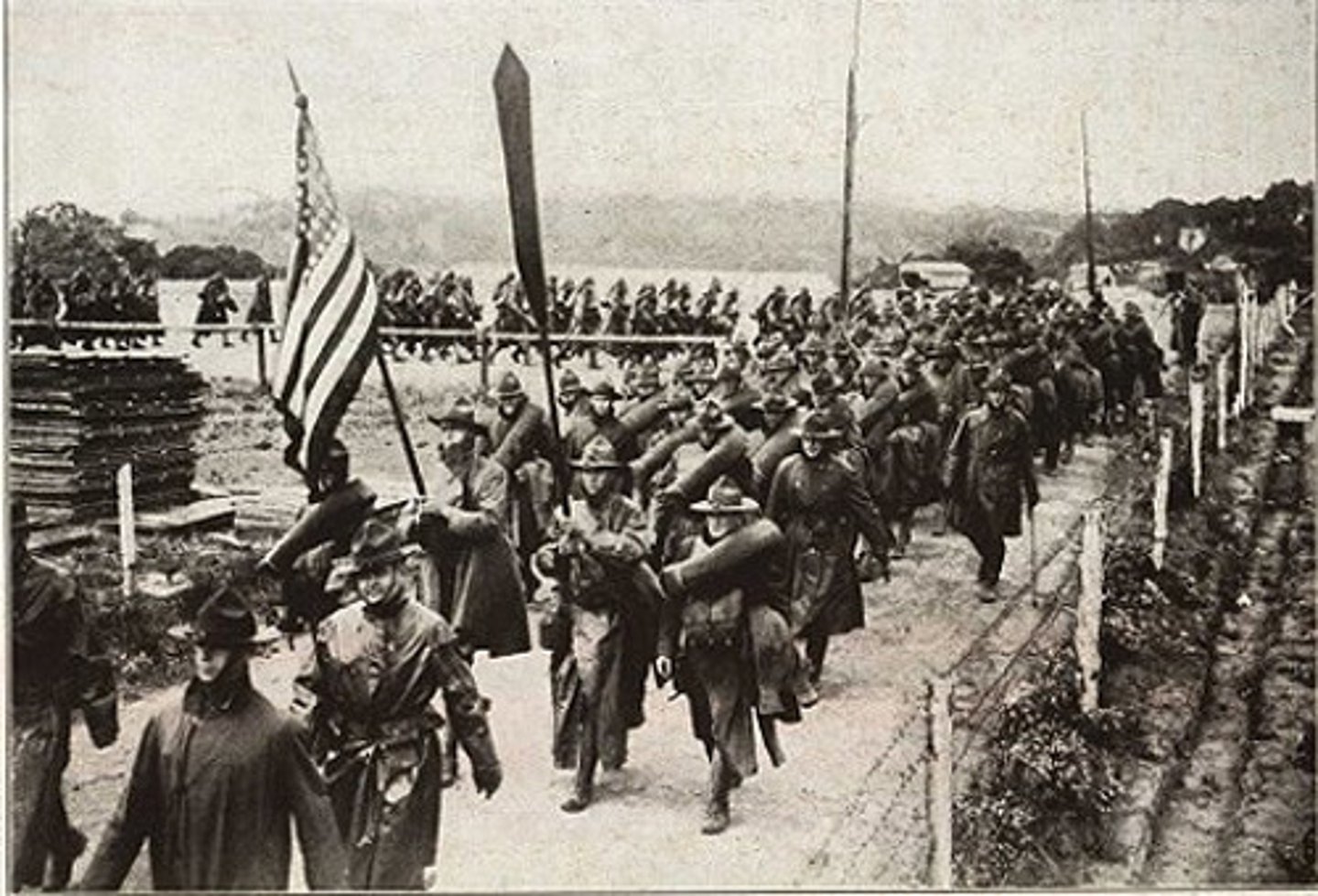
American expeditionary force
About 2 million Americans went to France as members of this under General John J. Pershing. Included the regular army, the National Guard, and the new larger force of volunteers and draftees and they served as individuals

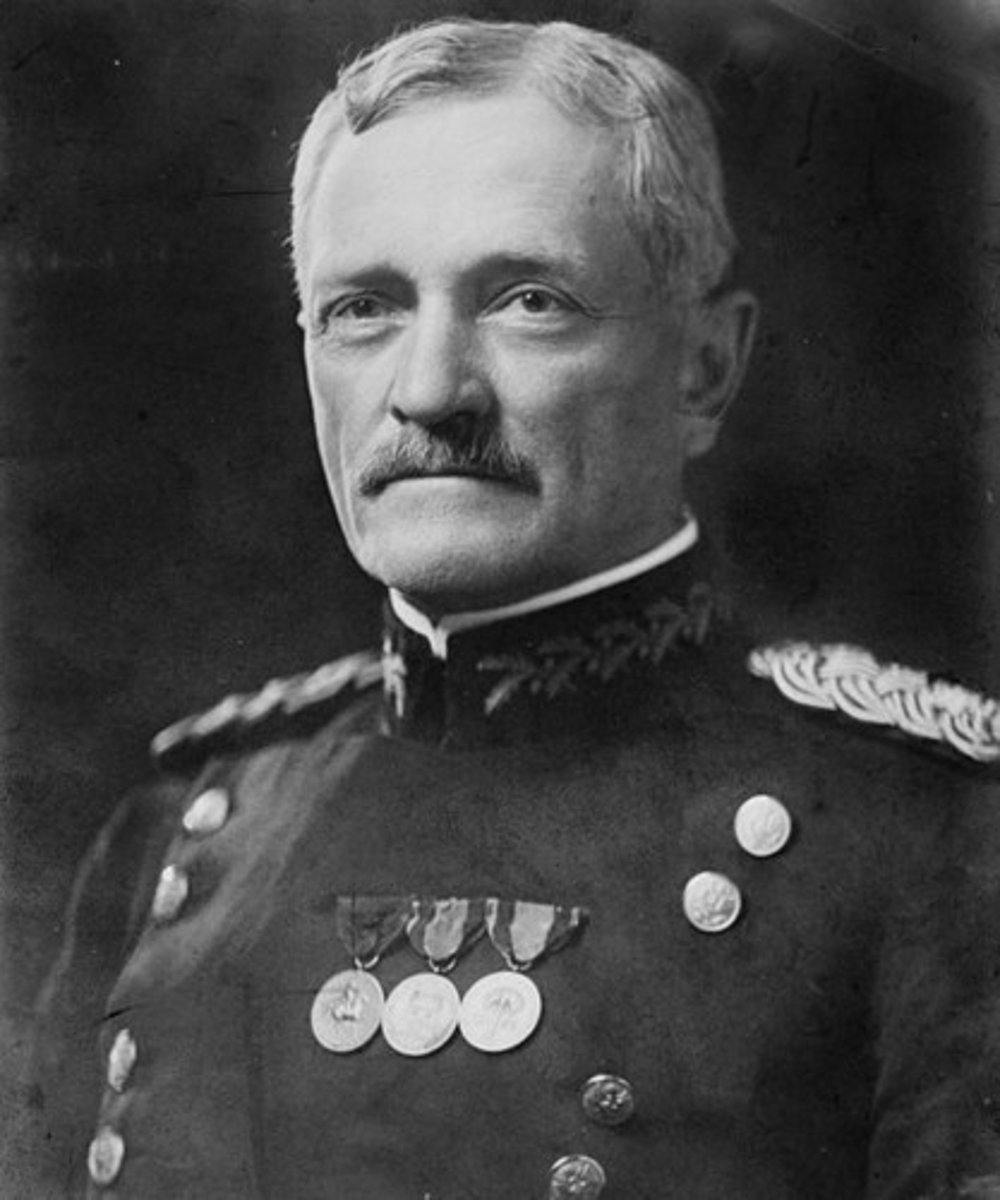
John J. Pershing
this American general led a punitive force into Mexico in pursuit of Pancho Villa after Villa's attack on Columbus, NM in 1916. During WWI, he also led the American Expeditionary Forces.

Isolationism
A national policy of avoiding involvement in world affairs
