Muscle Physiology
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What are the functions of muscle tissue?
produce body movements
stabilise body positions
storing and moving substances within the body
generating heat
what neurons stimulate skeletal muscles to contract?
somatic motor neurons
In somatic motor neurons where do the axons extend from?
brain or spinal cord
What structure brings oxygen and nutrients and removes heat and waste products to muscles?
capillaries
what are four properties of muscle tissue that helps it to function and aids homeostasis?
Excitability
Contractibility
Extensibility
Elasticity
What is meant by excitability?
Ability of muscles fibres to generate electrical impulses called action potential influencing muscle contraction
What is meant by contractibility?
Ability for a muscle to contract when stimulated by a nerve
What is meant by extensibility?
Ability of muscle tissue to stretch without damage
What is meant by elasticity?
Ability of muscle tissue to return to its original length and shape after contraction or extension
What does skeletal muscle contain?
connective tissue, blood vessels and nerves
How many layers of connective tissue are there?
3 layers
What are the 3 layers of connective tissue?
epimysium
perimysium
endomysium
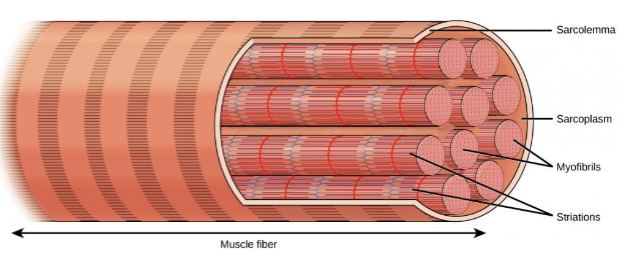
What are the components of skeletal muscle fibre?
sarcolemma
myofibrils
sarcoplasm
sarcoplasmic retinaculum
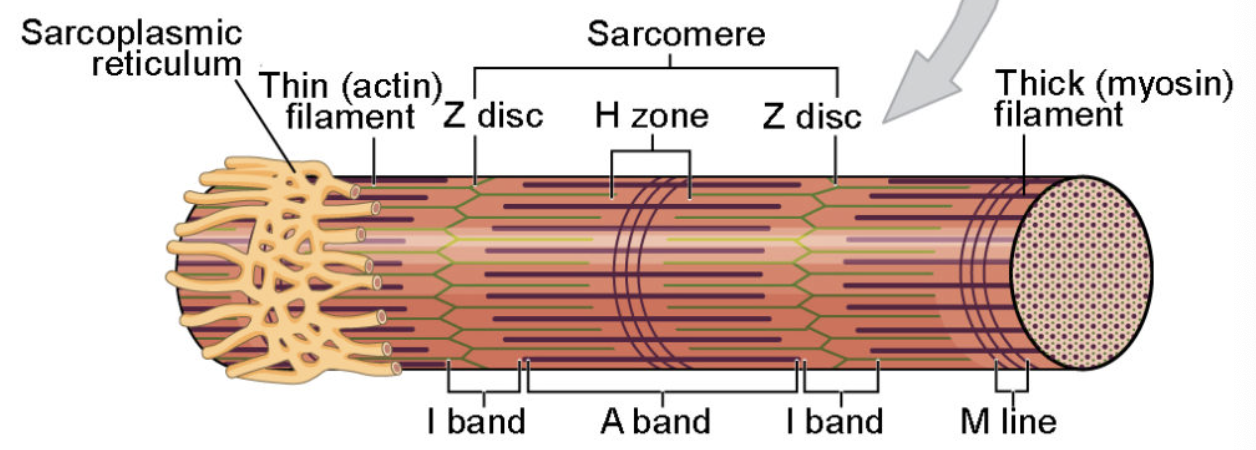
What are sarcomeres made up of?
thick filaments and thin filaments
what structure makes up thick filaments?
mysoin
what structures make up thin filaments?
actin and tropomyosin
Myofibril anatomy?
what are the types of proteins involved in muscle contraction called?
contractile proteins
regulatory proteins
what do contractile proteins do?
generate force during muscle contraction
what are types of contractile proteins?
myosin
actin
what do regulatory proteins do?
help switch muscle contraction processes on and off
what are types of regulatory proteins?
tropomyosin
troponin
What is the muscle contraction mechanism called?
sliding filament mechanism
Describe sliding filament mechanism?
muscles contract when myosin filaments pull actin filaments
Describe the process of muscle contraction
Action potential arrives at neuromuscular junction
causes calcium to be released from sarcoplasmic reticulum
Calcium binds to troponin which causes it to change shape
causes troponin and tropomyosin to change position on actin filaments
Myosin binding sites are exposed on actin molecules
Myosin heads bind to actin filaments, forming cross-bridges
Formation allows myosin heads to change shape and pull the actin filaments towards centre of the sarcomere, myosin releases ADP and Pi
ATP attaches to myosin head causing it to detach from actin
ATPase enzyme hydrolyses ATP into ADP and Pi allowing myosin heads to return to original position
myosin heads attach further along the actin filament and the process repeats
When does muscle contraction stop?
when muscles run out of ATP