USLO 5.1 Identify the steps in DNA replication
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
DNA replication
the biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original molecule;
DNA
"carrier molecule" of all hereditary information; made up of the nucleotide monomers adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T); the genetic material passed from parent to offspring; the molecule that directs and regulates the construction of proteins via genes
DNA Polymerase
Enzyme that makes DNA from a DNA template; it reads the DNA strand and adds complementary nucleotides to the growing DNA strand
Semiconservative Replication
Each original DNA strand is a template from which a new complimentary strand is generated. Each new strand is actually made of one "old" original strand and one "new" strand. [so that the old original strand is partly or semi-conserved in the new strands]
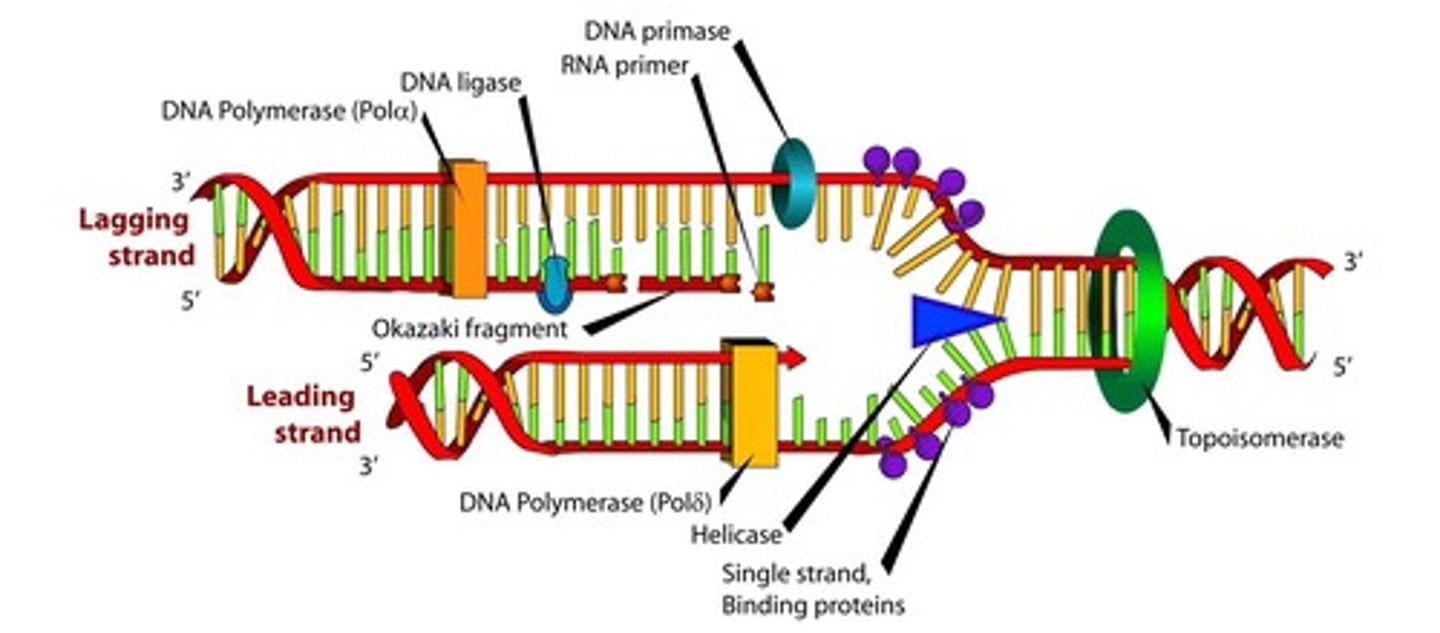
Helicase
Separates DNA strands by breaking the hydrogen bonds between nitrogenase bases/complementary base pairs; the "unzipper" of DNA for replication; allows stabilizing proteins and other enzymes to gain access to the DNA
Nucleotides
Monomer building blocks of DNA - Adenine (A), Guanine (G), Thymine (T), and Cytosine (C)
Gyrase (DNA gyrase)
Enzyme used to relax the supercoiled genome in preparation for DNA replication; relieves the strain on the DNA strand
The Central Dogma of Life
the "central way of thinking about" how genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein; the process that is followed by all cells to generate protein
RNA
Made up of the nucleotide monomers adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and uracil (U); generated through the process of transcription in which DNA is used as a template to create it
Gene
Composed of DNA and transcribed into mRNA and finally into a functional protein
Protein
Created through the process of translation, where the mRNA molecule is read within ribosomes and amino acids are placed in accordance with the mRNA sequence
Where DNA is located in eukaryotic cells
within the nucleus
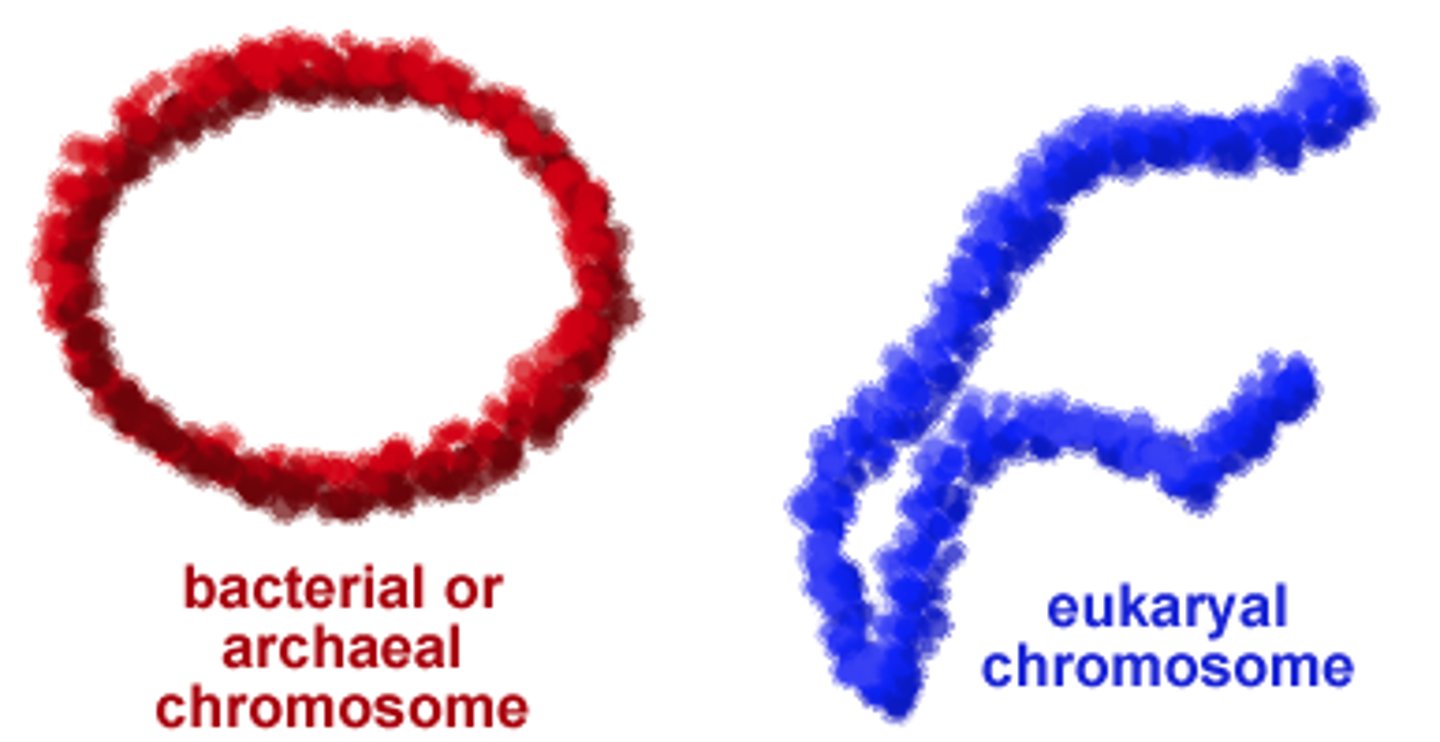
How DNA is organized in eukaryotes
in multiple linear chromosomes
Where DNA is located in prokaryotes
not contained within a nucleus [with the nucleoid region of the cytoplasm]
How DNA is organized in prokaryotes
in a single circular chromosome
Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic chromosome structure illustration
What base does the T base bind to?
A
What base does the A base bind to in DNA?
T
What base does the A base bind to in RNA?
U
What base does the C base bind to?
G
What base does the G base bind to?
C
Ligase
enzyme that glues the DNA fragment strands together, especially the fragments made during lagging strand synthesis
Leading strand synthesis
continuous (in one piece)
Lagging strand synthesis
in pieces or fragments (discontinuous)
Semi-conservative replication illustration

DNA replication illustration