Section 3: Environmental Chemistry
0.0(0)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Last updated 7:32 PM on 3/26/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Bioaccumulation
the increasing concentration of the material in an organism over time.
2
New cards
Phytoremediation
clean up of the environment using plants.
3
New cards
Leachate
liquid that dissolves and carries substances as it passes through soil.
4
New cards
Anaerobic
processes or environments that do not require or contain oxygen.
5
New cards
Biomagnification
the increase in concentration of a chemical or element as it moves up the food chain.
6
New cards
Dilution
mixing of a substance with air or water (which reduces its concentration)
7
New cards
Aerobic
processes or environments that require or contain oxygen.
8
New cards
Permeable
fluids can flow through.
9
New cards
Dispersion
scattering of a substance away from its source.
10
New cards
Factors affecting air transport
* Pollutant’s properties
* Wind speed
* Direction of prevailing winds
* Precipitation
* Wind speed
* Direction of prevailing winds
* Precipitation
11
New cards
Photolysis
breakdown of compounds by sunlight.
12
New cards
Deposition
the laying down of sediment carried by wind, flowing water, the sea or ice
13
New cards
Crude Oil
(petroleum) a mixture of many chemicals. This includes Paraffin Wax, Asphalt & Methane.
14
New cards
WHMIS (Workplace Hazardous Materials Information System)
a system of easy- to- see warning symbols on hazardous materials.
15
New cards
MSDS (Material Safety Data Sheets)
detailed information sheet about a potentially hazardous product.
16
New cards
Waste Collection Sites
where waste is collected in such a manner that does not allow harmful chemicals from entering the environment.
17
New cards
Transport of Consumer goods
when goods are transported to retailers through where the product is first bought
18
New cards
Transport
1. __release__ of the chemical at the source
1. __dispersion__ of the chemical in the atmosphere
2. __deposition__ of the chemical in soil or water
19
New cards
Transport in Groundwater
Movement of underground water between soil grains
20
New cards
Factors Affecting Groundwater Transport
* Number of pores in the soil
* Connection of the pores
* Connection of the pores
21
New cards
Substances that contaminate groundwater
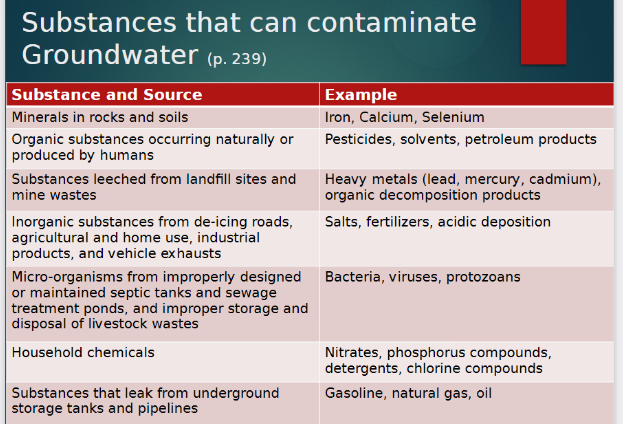
22
New cards
Transport in Surface Water
The movement of water above ground to different water bodies
23
New cards
Transport in Soil
* evaporation
* absorption by plants
* runoff
* soaking into soil dissolving
* absorption by plants
* runoff
* soaking into soil dissolving
24
New cards
Dispersion
scattering of a substance away from its source
25
New cards
Deposition
change of state from a gas to a solid
26
New cards
Water table
top of the groundwater zone
27
New cards
Permeable
fluids can flow through
28
New cards
Biodegradation
breakdown of materials by organisms like earthworms, bacteria, and fungi (through hydrolysis)
29
New cards
Factors affecting biodegradation
* Temperature (bacteria like it warm)
* Soil moisture (should be moist)
* pH (preferably between 5-8)
* oxygen supply (more O2 for aerobic bacteria)
* nutrient availability (cut grass has more nutrients than paper but both decompose)
* Soil moisture (should be moist)
* pH (preferably between 5-8)
* oxygen supply (more O2 for aerobic bacteria)
* nutrient availability (cut grass has more nutrients than paper but both decompose)
30
New cards
Impact of oil spills on the environment
they get evaporated or dispersed into water. This can make water unsafe for aquatic organisms to live in & unsafe for any other organisms to ingest.
31
New cards
Impact of oil spills on people
they leak into water sources & kill off the organisms we need for food sources, like fishing & hunting
32
New cards
New oil spill clean-up procedures
new & improved government regulations have been established to deal with future spills
33
New cards
Transport of Consumer goods
when goods are transported to retailers through where the product is first bought
34
New cards
Disposal of Hazardous Chemicals
when chemicals cant normally be disposed of, they must be disposed of in an orderly manner
35
New cards
Waste Collection Sites
where waste is collected in such a manner that doesnt allow harmful chemicals from entering the environment
36
New cards
Hydrocarbons
emissions that contaminate soil by clogging up soil pores
37
New cards
Concentration of pollutants can be changed using
* Dispersion
* Dilution
* Biodegradation
* Phytoremediation
* Photolysis
* Dilution
* Biodegradation
* Phytoremediation
* Photolysis