Institutions Ch 7 (Done)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
Mortgages
__________ are loans to individuals or businesses to purchase homes, land, or other real property
Many mortgages are securitized
Securitization occurs when securities are packaged and sold as assets backing a publicly traded or privately held debt instrument
Mortgages differ from bonds and stocks
Mortgages are backed by a specific piece of real property
Primary mortgages have no set size or denomination
Primary mortgages generally involve a single investor
Comparatively little information exists on mortgage borrowers
Four basic types of mortgages are issued by financial institutions:
Home mortgages are used to purchase one- to four-family dwellings (called “single-family mortgages”)
$12.55 trillion outstanding in 2021
Multifamily dwelling mortgages are used to purchase apartment complexes, townhouses, and condominiums
$1.88 trillion outstanding
Commercial mortgages are used to finance the purchase of real estate for business purposes
$3.31 trillion outstanding
Farm mortgages are used to finance the purchase of farms
$0.30 trillion outstanding
collateral
All mortgage loans are backed by a specific piece of property that serves as ____________ to the mortgage loan
down payment
A ______________is a portion of the purchase price of the property a financial institution requires the mortgage borrower to pay up front
Private mortgage insurance (PMI)
____________________________ is generally required when the loan-to-value ratio is more than 80% (i.e., the borrower makes a down payment of less than 20%)
Federally insured mortgages
Repayment is guaranteed by either the Federal Housing Administration (FHA) or the Veterans Administration (VA)
Conventional mortgages are not federally insured
amortized
A mortgage is ___________ when the fixed principal and interest payments fully pay off the mortgage by its maturity date
Balloon payment mortgages
________________________ require fixed monthly interest payments for a 3- to 5-year period, at which point full payment of the mortgage principal is due
Fixed-rate mortgages
___________________ lock in the borrower’s interest rate
Therefore, required monthly payments are fixed over the life of the mortgage and lenders assume interest rate risk
Adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMs)
________________________________ have interest rates tied to some market interest rate
Required monthly payments can change
Discount points are fees or payments made when a mortgage loan is issued (at closing)
One discount point paid up front is equal to 1 percent of the principal value of the mortgage
Discount points
_________________are fees or payments made when a mortgage loan is issued (at closing)
Mortgage contracts generally require the borrower to pay an assortment of fees to cover the mortgage issuer’s costs of processing the mortgage
E.g., application fee, title search, title insurance, appraisal fee, loan origination fee, closing agent and review fees, etc.
Mortgage refinancing occurs when a mortgage borrower takes out a new mortgage and uses the proceeds obtained to pay off the current mortgage
Mortgages are most often refinanced when a current mortgage has an interest rate that is higher than the current interest rate
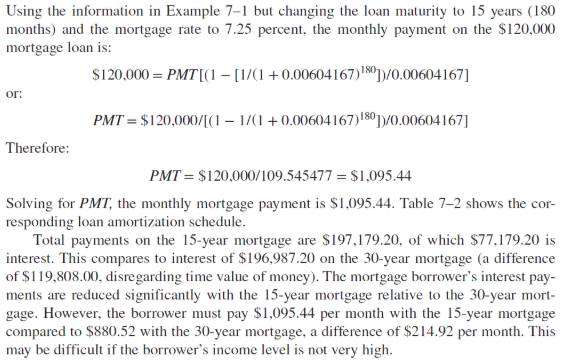
The fixed monthly payment made by a mortgage borrower generally consists partly of repayment of the principal borrowed and partly of the interest on the outstanding (remaining) balance of the mortgage
During the early years of the mortgage, most of the fixed monthly payment represents interest on the outstanding principal and a small amount represents a payoff of the outstanding principal
amortization schedule
An ___________________ shows how the fixed monthly payments are split between principal and interest
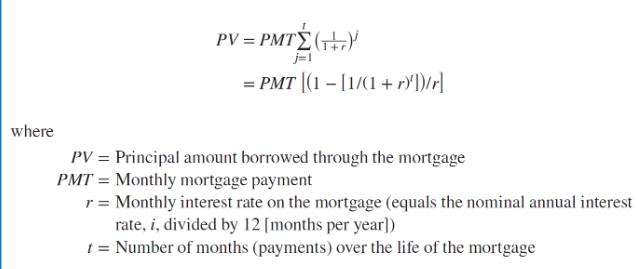
The present value of a mortgage can be written as:
Comparison of Interest Paid
Jumbo mortgages are those that exceed the conventional mortgage conforming limits
Limits are set by the two government-sponsored enterprises, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, and are based on the maximum value of any individual mortgage they will purchase from a mortgage lender ($726,200 in 2023, with some exceptions)
Jumbo mortgages
_________________are those that exceed the conventional mortgage conforming limits
Subprime mortgages are mortgages to borrowers who have weakened credit histories
These borrowers may have weakened credit due to payment delinquencies and possibly more severe problems such as charge-offs, judgments, and bankruptcies
Subprime mortgages
_________________ are mortgages to borrowers who have weakened credit histories
Alt-A mortgages are considered riskier than a prime mortgage and less risky than a subprime mortgage
Interest rates on Alt-A loans are usually between prime and subprime rates
Alt-A mortgages
__________________ are considered riskier than a prime mortgage and less risky than a subprime mortgage
Option ARMs are adjustable rate mortgages that offer the borrower several monthly payment options:
Minimum payment option - Lowest of the four payment options and carries the most risk
Interest-only payment - Monthly payments must increase substantially after the initial interest-only period lapses
30-year fully amortizing payment - Borrower pays both principal and interest on the loan, based on a 30-year term
15-year fully amortizing payment - Based on a 15-year term
Option ARMs
______________ are adjustable rate mortgages that offer the borrower several monthly payment options:
Minimum payment option
Lowest of the four payment options and carries the most risk
Interest-only payment
Monthly payments must increase substantially after the initial interest-only period lapses
30-year fully amortizing payment
Borrower pays both principal and interest on the loan, based on a 30-year term
15-year fully amortizing payment
Based on a 15-year term
Second mortgages are loans secured by a piece of real estate already used to secure a first mortgage
Should a default occur, the second mortgage holder is paid only after the first mortgage is paid off
Second mortgages
_________________ are loans secured by a piece of real estate already used to secure a first mortgage
Home equity loans
__________________ let customers borrow on a line of credit secured with a second mortgage on their homes
Reverse-annuity mortgages (RAMs)
Borrower receives regular monthly payments from a financial institution rather than making them
When the RAM matures (or the borrower dies), the borrower (or the borrower’s estate) sells the property to retire the debt
RAMs are attractive mainly to older homeowners who have accumulated substantial equity in their homes
FIs remove mortgages from their balance sheets through one of two mechanisms:
By pooling recently originated mortgages together and selling them in the secondary market
By securitizing mortgages (i.e., by issuing securities backed by newly originated mortgages)
Advantages of securitization:
FIs can reduce their liquidity risk, interest rate risk, and credit risk
FIs generate fee income, which helps to offset the effects of regulatory constraints
Mortgage market is unique in that the U.S. government is deliberately involved in the development of its secondary markets
In 1938, the government established the Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA, or Fannie Mae) to buy mortgages from depository institutions so they could lend to other mortgage borrowers
To encourage continued expansion in the housing market and to promote competition for FNMA, the U.S. government created the Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA, or Ginnie Mae) and the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (FHLMC, or Freddie Mac)
Mortgage Sales
FIs have sold mortgages and commercial real estate among themselves for over 100 years
A large part of correspondent banking involves small banks making loans that are too big for them to hold on their balance sheets and selling parts of these loans to large banks with whom they have had a long-term deposit and lending correspondent relationship
Large banks often sell parts of their loans (i.e., participations) to smaller banks
correspondent banking
A large part of _____________________involves small banks making loans that are too big for them to hold on their balance sheets and selling parts of these loans to large banks with whom they have had a long-term deposit and lending correspondent relationship
Mortgage sales occur when an FI originates a mortgage and sells it to an outside buyer
May be sold with or without recourse
Securitization of mortgages involves the pooling of a group of mortgages with similar characteristics, the removal of these mortgages from the balance sheet, and the subsequent sale of interests in the mortgage pool to secondary market investors
Mortgage-backed securities allow mortgage issuers to separate the credit risk exposure from the lending process itself
There are three major types of mortgage-backed securities:
Pass-through security
Collateralized mortgage obligation (CMO)
Mortgage-backed bond
Pass-through mortgage securities
__________________________ “pass through” promised payments of principal and interest on pools of mortgages created by FIs to secondary market participants holding interests in the pools
Three agencies are directly involved in the creation of mortgage-backed pass-through securities
Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA; Ginnie Mae)
Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA; Fannie Mae)
Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (FHLMC; Freddie Mac)
government-related issuer standards
Private mortgage issuers, such as banks and thrifts, also purchase mortgage pools, but they do not conform to _______________________
Government National Mortgage Association (GNMA)
Began operations in 1968 when it split off from the Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA)
Government-owned agency with two major functions: sponsoring mortgage-backed securities programs of FIs and providing timing insurance
Federal National Mortgage Association (FNMA)
Originally created in 1938 and, since 1968, FNMA has operated as a private corporation owned by shareholders
Creates mortgage-backed securities (MBSs) by purchasing packages of mortgage loans from banks and thrifts
Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation (FHLMC)
Performs a similar function to that of FNMA except that its major securitization role has historically involved thrifts
Government Sponsorship and Oversight of FNMA and Freddie Mac
FNMA and FHLMC represent a huge presence in the financial system, as they have over 44 percent of the single-family mortgages and mortgage pools in the U.S.
In the early 2000s, these two agencies came under fire for several reasons
The Housing and Economic Recovery Act of 2008 gave the authority for the government’s takeover of the GSEs
The takeover of Fannie and Freddie, and specifically the commitment to meet all of the firms’ obligations to debt holders, exposes the U.S. government to a potentially large financial risk
To date, Treasury has provided $119.8 billion to Fannie Mae and $71.6 billion to Freddie Mac to keep them solvent
FHFA told the two GSEs in October 2019 to prepare for transition out of government control
Collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOs) are mortgage-backed bonds with multiple bond holder classes, or tranches
Each bond holder class has a different guaranteed coupon
Mortgage prepayments retire only one tranche at a time, so all other trances are sequentially prepayment protected
Collateralized mortgage obligations (CMOs)
______________________________________ are mortgage-backed bonds with multiple bond holder classes, or tranches
Mortgage-backed bonds (MBBs)
MBBs are bonds collateralized by a pool of assets, also called asset-backed bonds
The relationship for MBBs is one of collateralization rather than securitization; the cash flows on the mortgages backing the bond are not necessarily directly connected to interest and principal payments on the MBB
International investors participate in U.S. mortgage and mortgage-backed securities markets
The value of mortgages held by foreign banks has decreased by 67.2 percent (from $51.6 billion in 1992 to $16.9 billion in 2014), before rebounding to $91.1 billion in 2021
This compares to primary mortgages issued and held by domestic entities of $18.06 trillion in 2021
After the United States, Europe is the world’s second-largest and most developed securitization market
Germany is one of the countries that moved toward making widespread use of securitization in its mortgage markets
Synthetic securitizations are a far more common form of mortgage financing in countries outside the U.S.
Refers to structured transactions in which banks use credit derivatives to transfer the credit risk of a specified pool of assets to third parties, such as insurance companies, other banks, and unregulated entities
Can replicate the economic risk transfer characteristics of a traditional securitization without removing the portfolio of assets from the originating bank’s balance sheet
Reasons to prefer synthetic securitization might include the complexity and prohibitive cost of a traditional securitization transaction as well as its potentially unfavorable tax implications