IMED1001 - Lymphatic System (Week 9)
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Immune vs Lymphatic System
- Immune System: Collection of all proteins, cells, tissues, organs, widely distributed throughout the body, that function to protect the body
- Lymphatic System: Transport system for cells of the immune system and antigens (foreign substances/cells) to move around the body. Tissues where cells of the immune system hang out
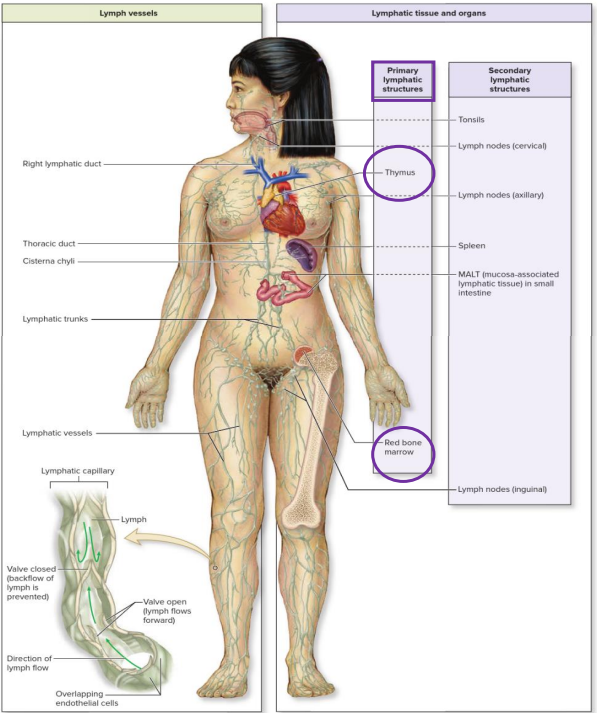
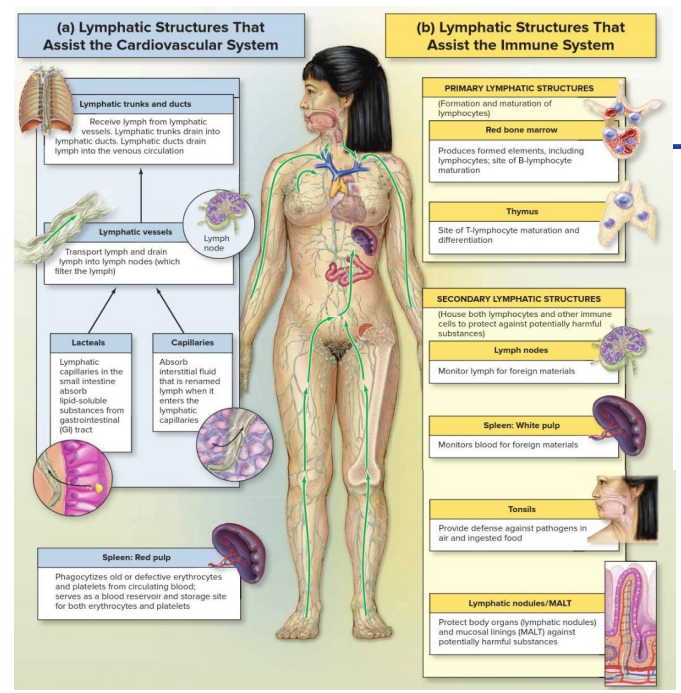
Lymphatic Anatomy
- lymph: fluid
- lymphatic capillaries
- lymphatic vessels
- lymph nodes
- lymphatic nodules
- lymphatic trunks and ducts
- tonsils
- spleen
- thymus
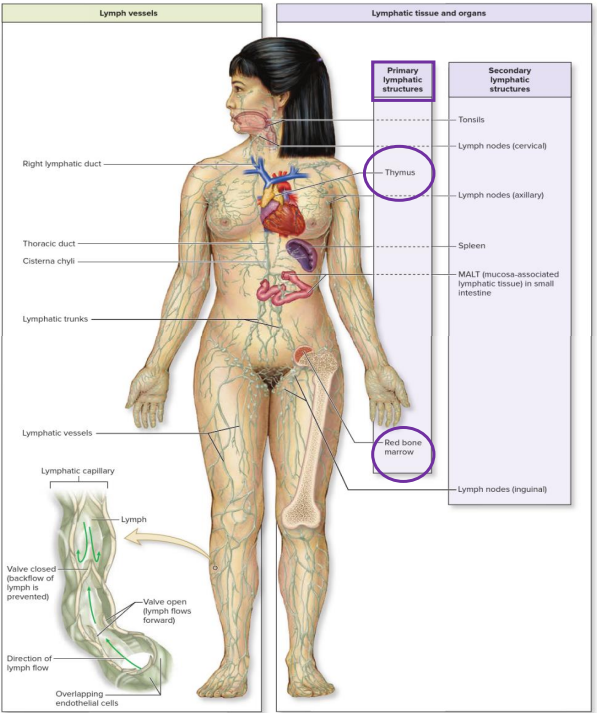
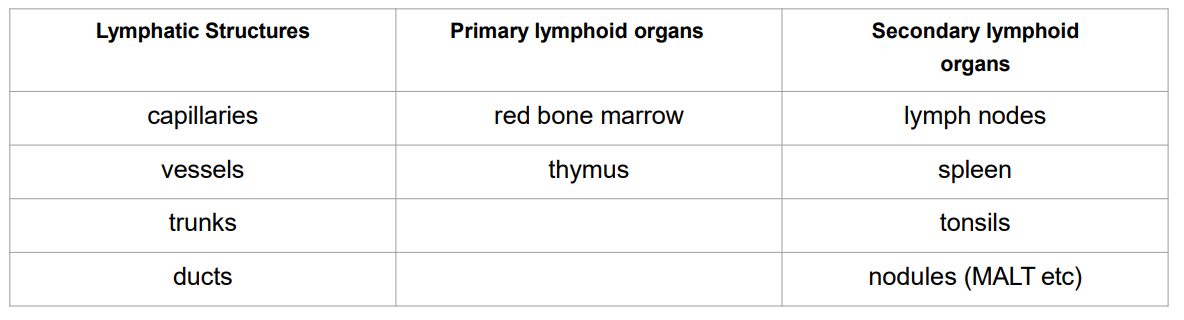
Overview of Lymphatic System
- Primary lymphoid organs function is: lymphocyte generation
- secondary lymphoid organs function is: lymphocytes exposed to antigen and activated for effector function
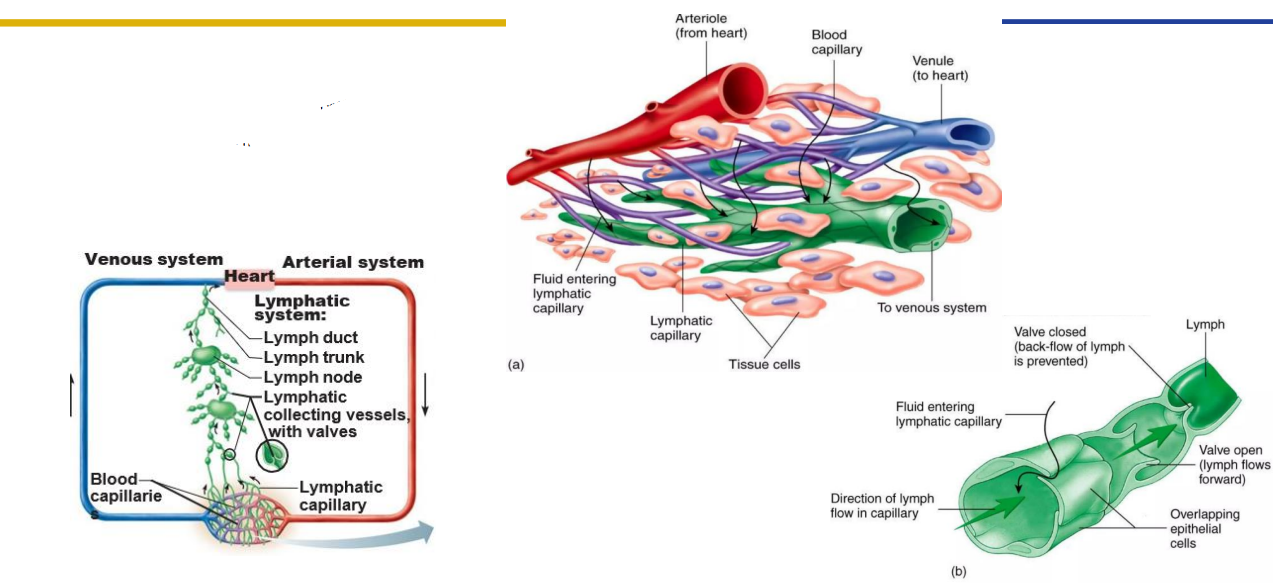
Lymph Capillaries
- Lymph is water plus solutes from two sources: Plasma (ions, nutrients, gases, some proteins) and Cells (hormones, enzymes, waste products)
- we dont take formed elements into the lymph, these stay in the blood
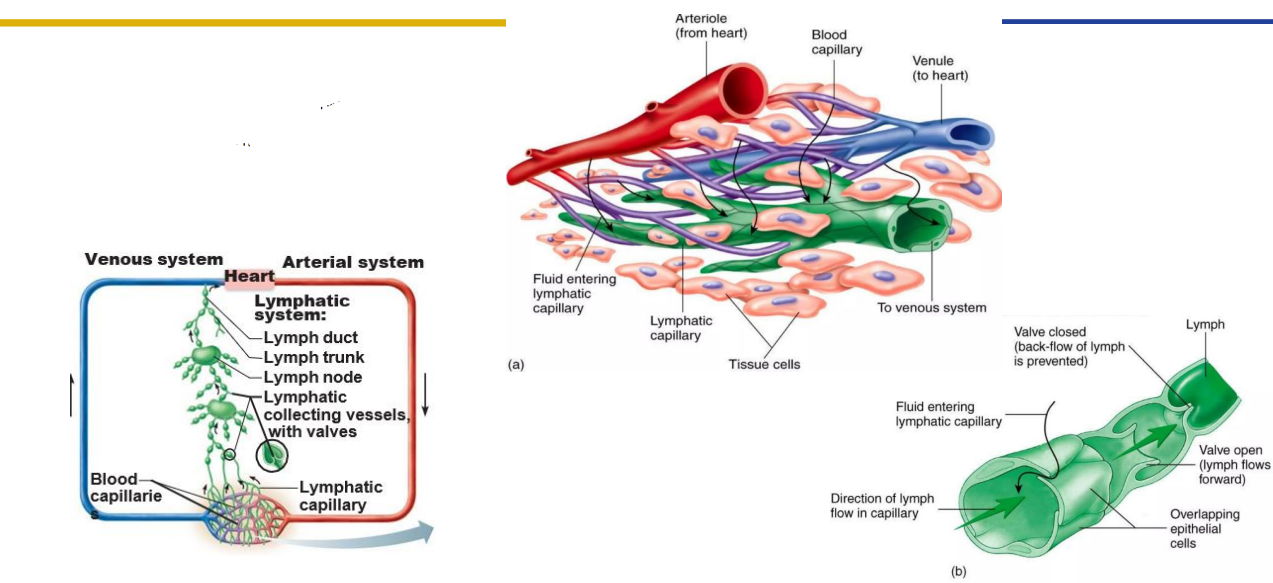
Lymph Capillaries Path of Fluid
- form lymph fluid can carry away from tissues
- More permeable then blood capillaries (take up cell debris, pathogens and cancer cells)
- Epithelium overlap to function as a series of one-way valves
- Found in all parts of the body except nervous system, bone and avascular tissues (without blood vessels - cornea, epidermis)
- Lacteals: specialised lymph capillaries present in intestinal mucosa -> absorb digested fat (as chylomicrons) and deliver fatty lymph (chyle) to the blood
Lymph Drainage
- One-way system, lymph flows toward the heart
- Lymphatic Capillaries: join to form lymphatic vessels
- Lymphatic Vessels: have valves that ensure one-way flow (beaded appearance)
- Lymph nodes: distributed along vessels and filter lymph
- Lymphatic vessels drain to trunks which drain to ducts: drain tissues of body and move lymph into major veins
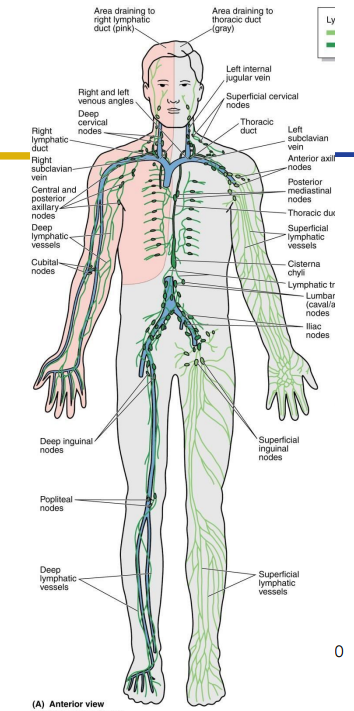
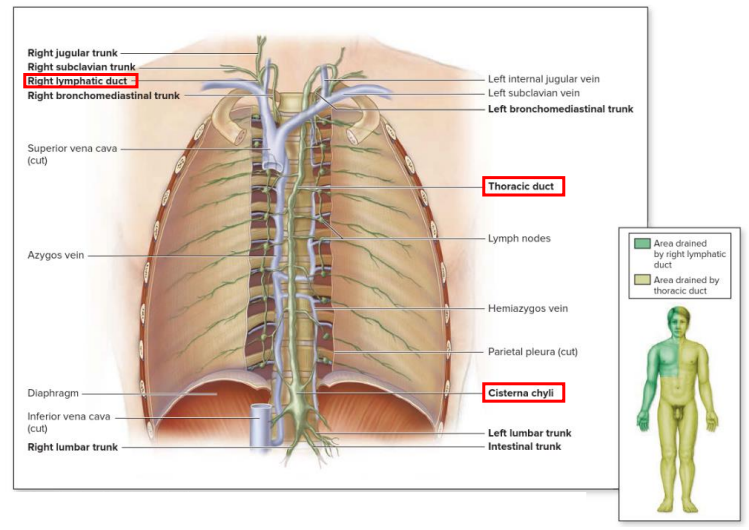
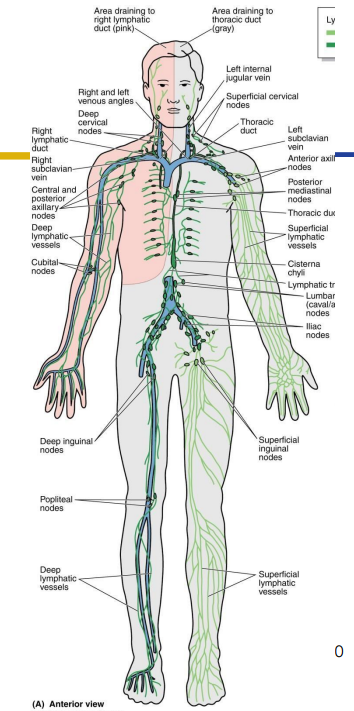
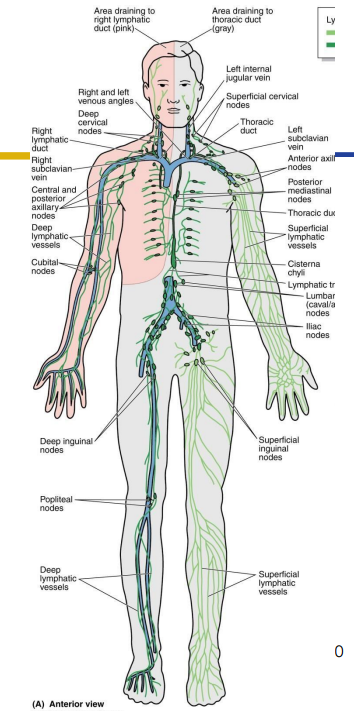
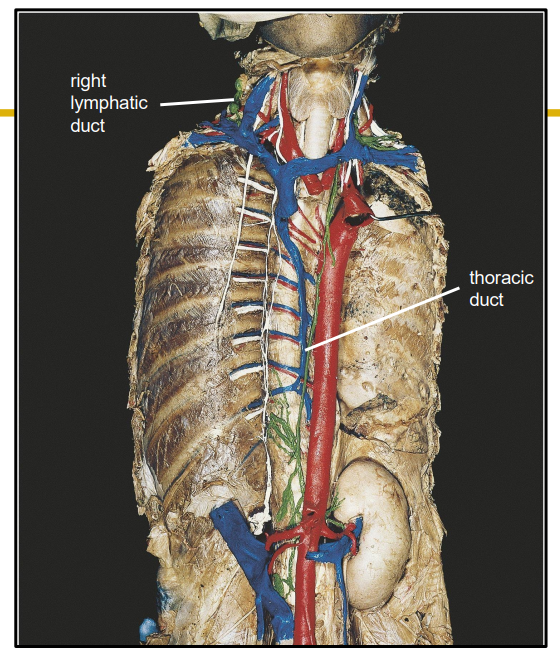
Lymph Drainage Ducts Involved
Lymph delivered into one of two large ducts:
- Right lymphatic duct drains right upper arm and right side of head and thorax
- Thoracic Duct arises as cisterna chyli; drains rest of body.
- Ducts empty into junction of internal jugular and subclavians, which drain to brachiocephalic veins and then to superior vena cava
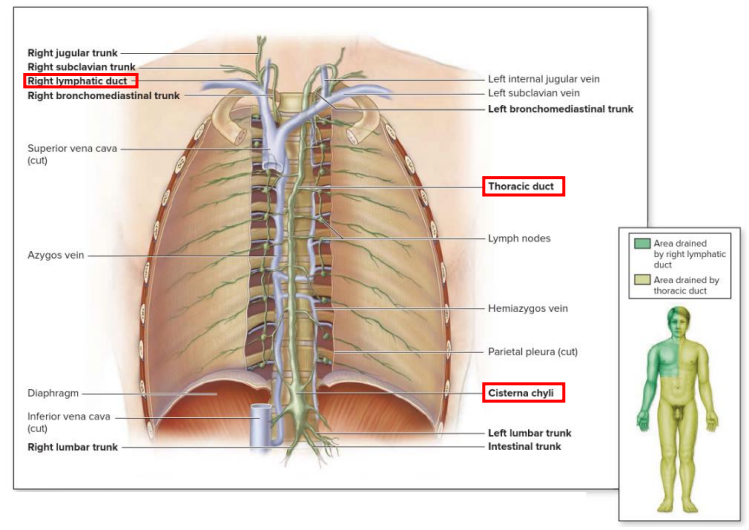
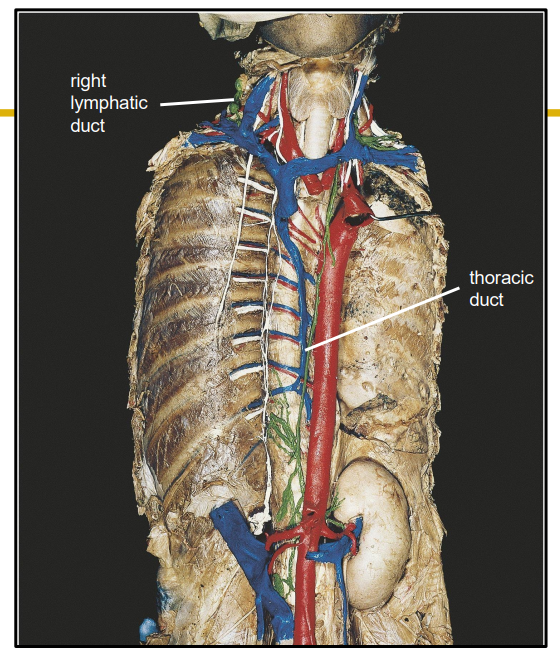
Lymphatic Ducts DIAGRAM
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 12
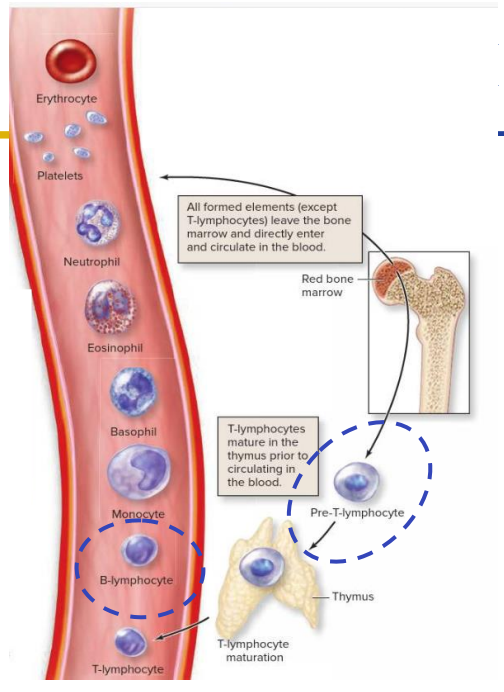
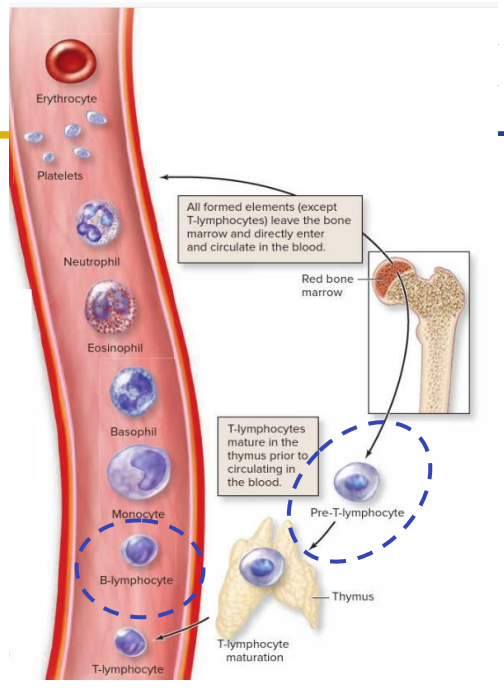
Primary: Red Marrow
- Red bone marrow (located in some spongy bones) produces all the formed elements (cellular blood components) via hemopoiesis
- Synthesise mature B-lymphocytes and immature T-lymphocytes (pre T-lymphocytes).
- Both are types of white blood cells
- Immature T-lymphocytes migrate from the bone marrow to the thymus to complete maturation
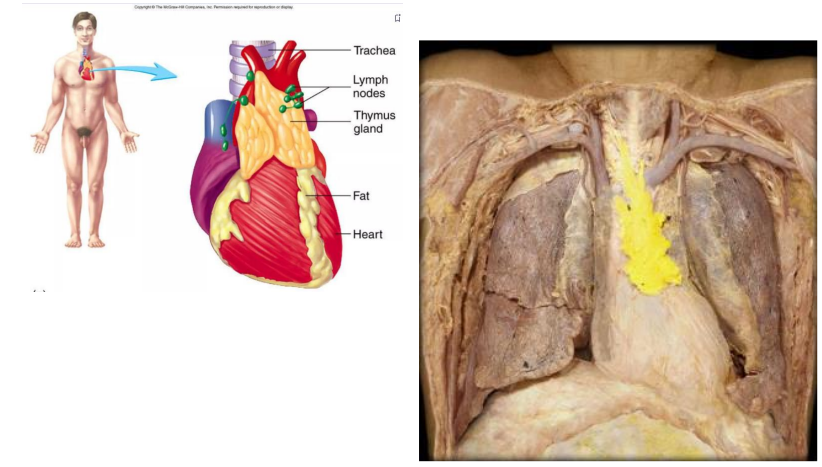
Primary: Thymus
- located in superior mediastinum
- site of maturation of T cells
- Those that remain can react to foreign substances
- Endocrine functions (thymosin)
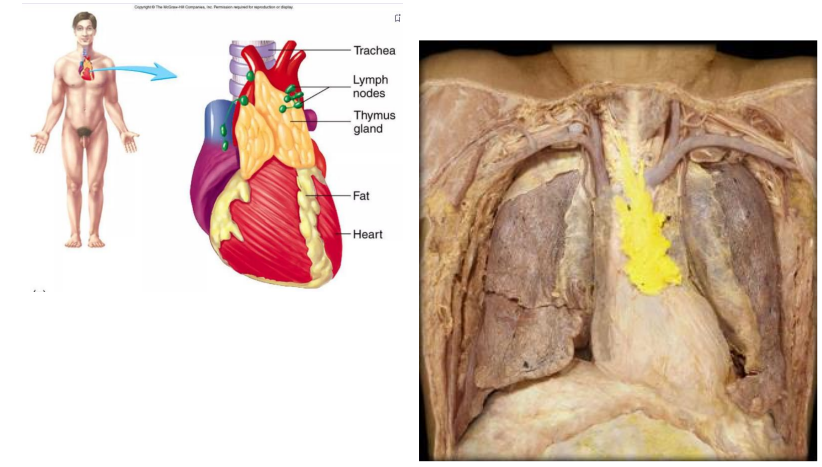
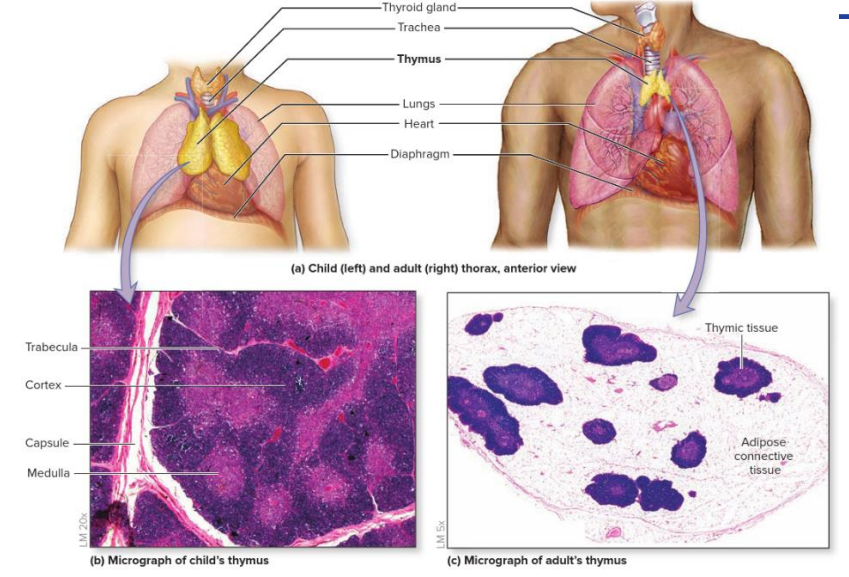
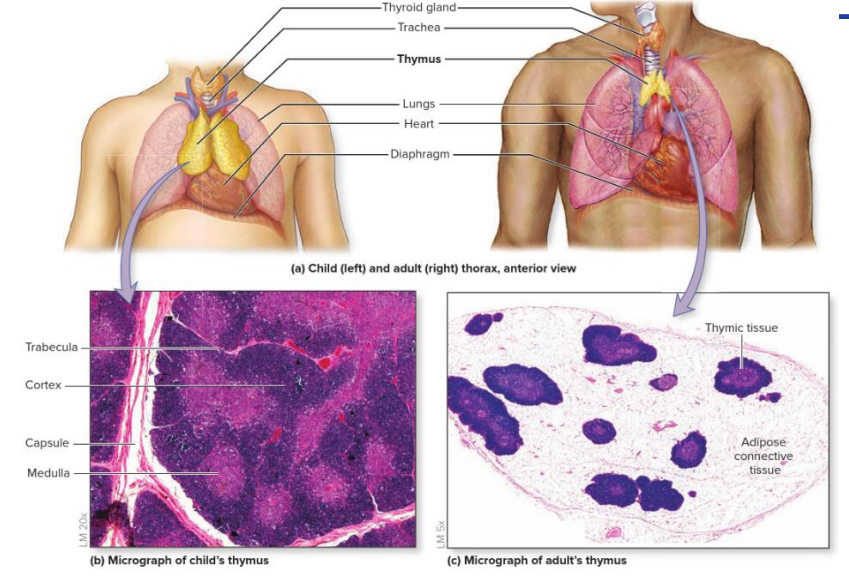
Thymus Specific info
- reaches maximum size around puberty, after which shrinks as cells regress and are replaced with adipose tissue
- Older individuals are therefore at higher risk of infection
- thymus is small in older people,
Secondary Lymphatic Organs
- Lymphatic organs contain lymphatic tissue (lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells)
- Lymphocytes: B and T cells - white blood cells derived from bone marrow
- Fine network of reticular fibres. Produced by reticular cells. Act as filter to trap microorganisms and other particles
- May be encapsulated (in a CT capsule): encapsulated - lymph nodes, spleen, thymus
- non-encapsulated: mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). Found beneath epithelium as first line of attack against invaders.
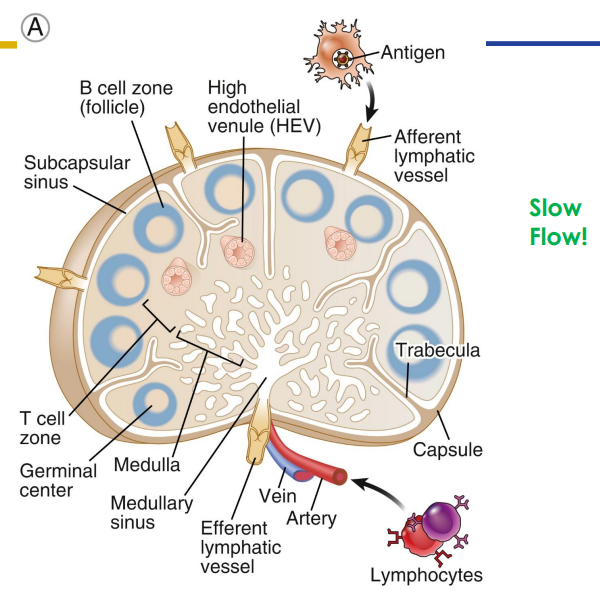
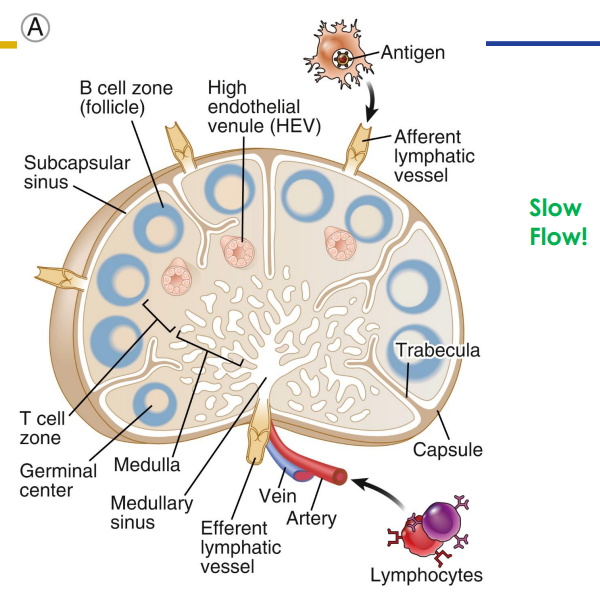
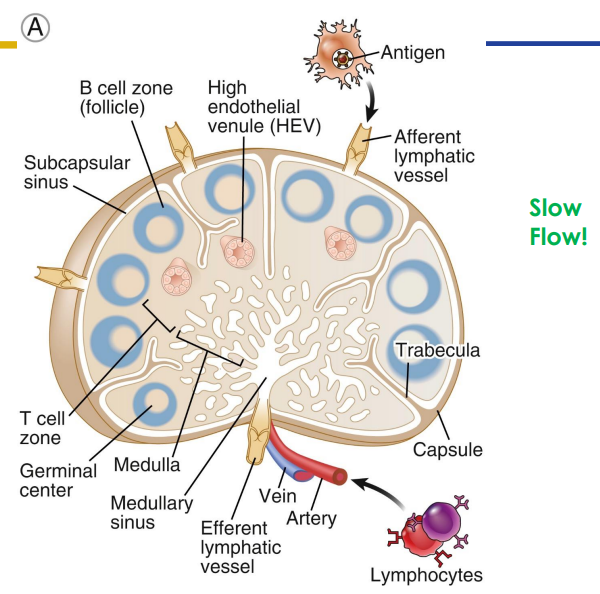
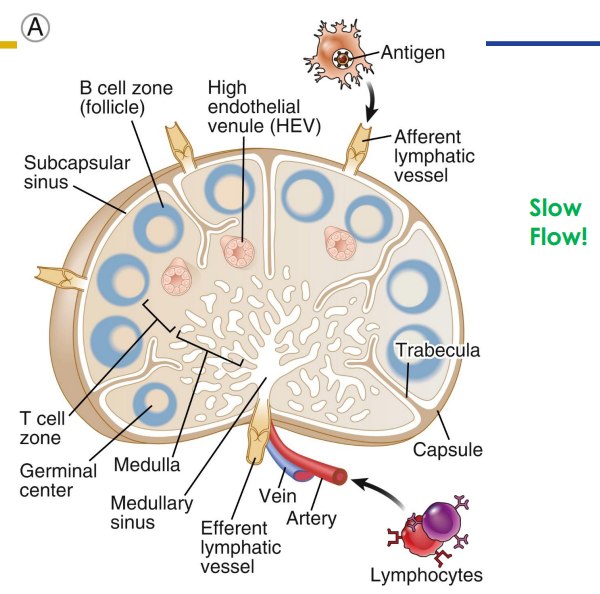
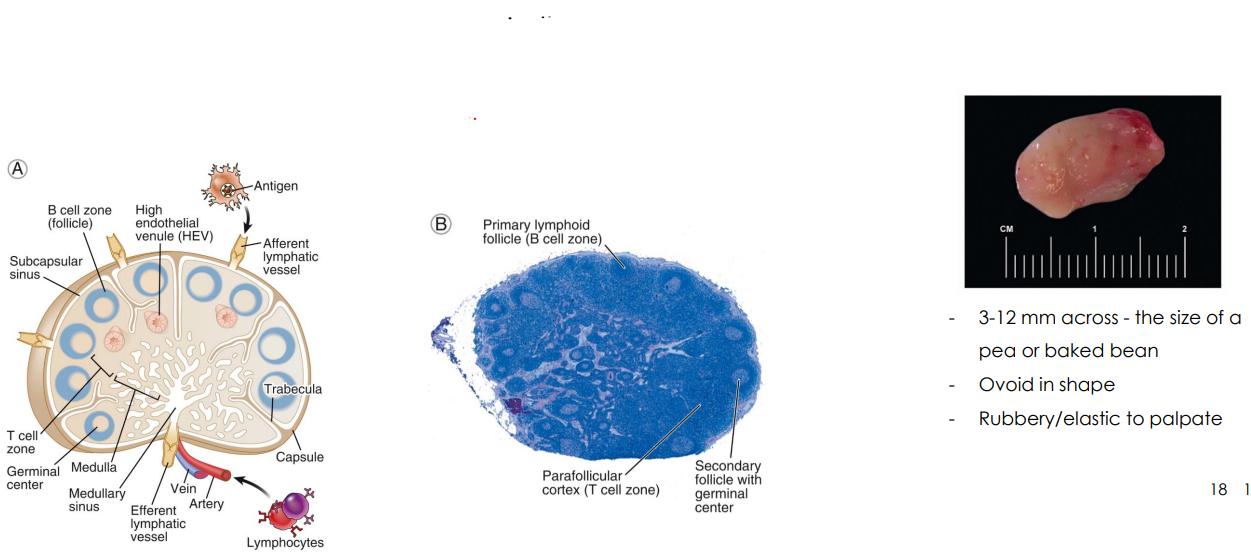
Secondary: Lymph Nodes
- only structures to filter lymph
- substances removed by phagocytosis or stimulate lymphocytes to proliferate
- Cancer cells often migrate to lymph nodes, are trapped there, and proliferate. Can move from lymphatic system to circulatory system spreading cancer through body
- Afferent (more) and efferent (less) vessels
- Organised into cortex and medulla (next slide) with dense connective tissue capsule surrounding
- slow flow (its like a lot of people leaving through a small gap)
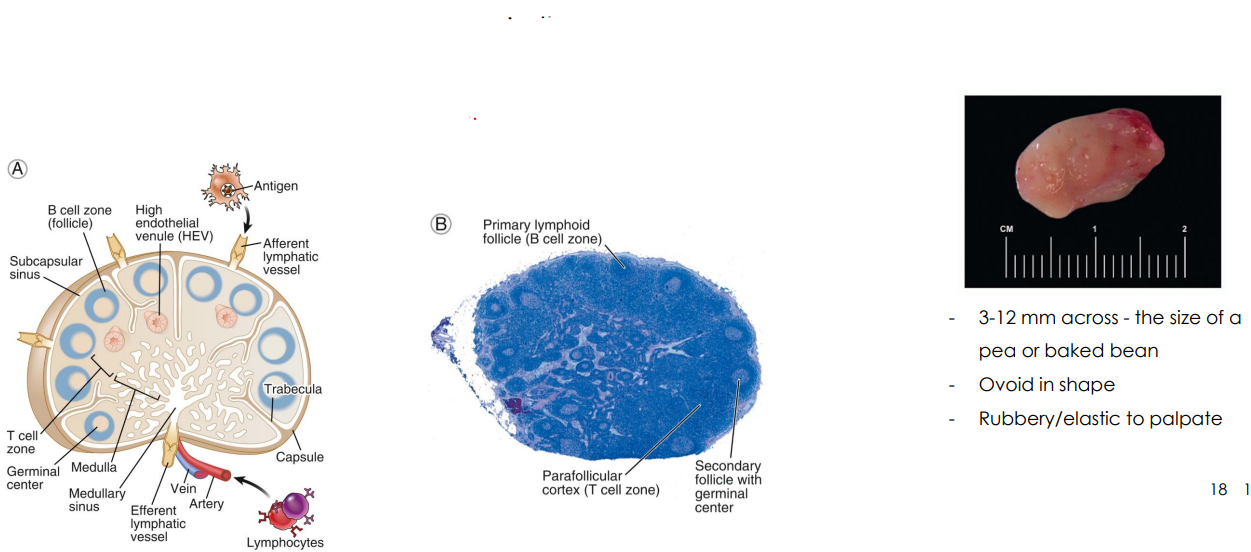
Lymph Node Size etc.
- Two histologically distinct regions
- Cortex: cortex contains follicles with germinal centers
- Medulla: lymph sinuses contain macrophages
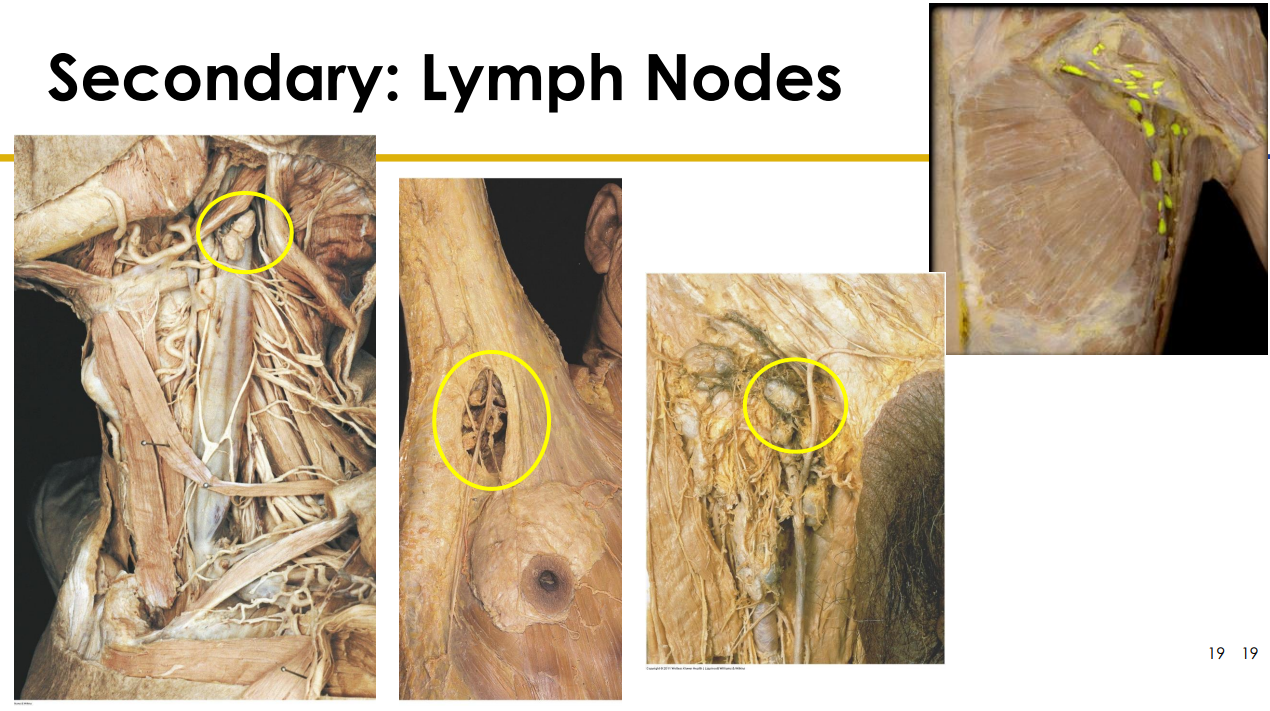
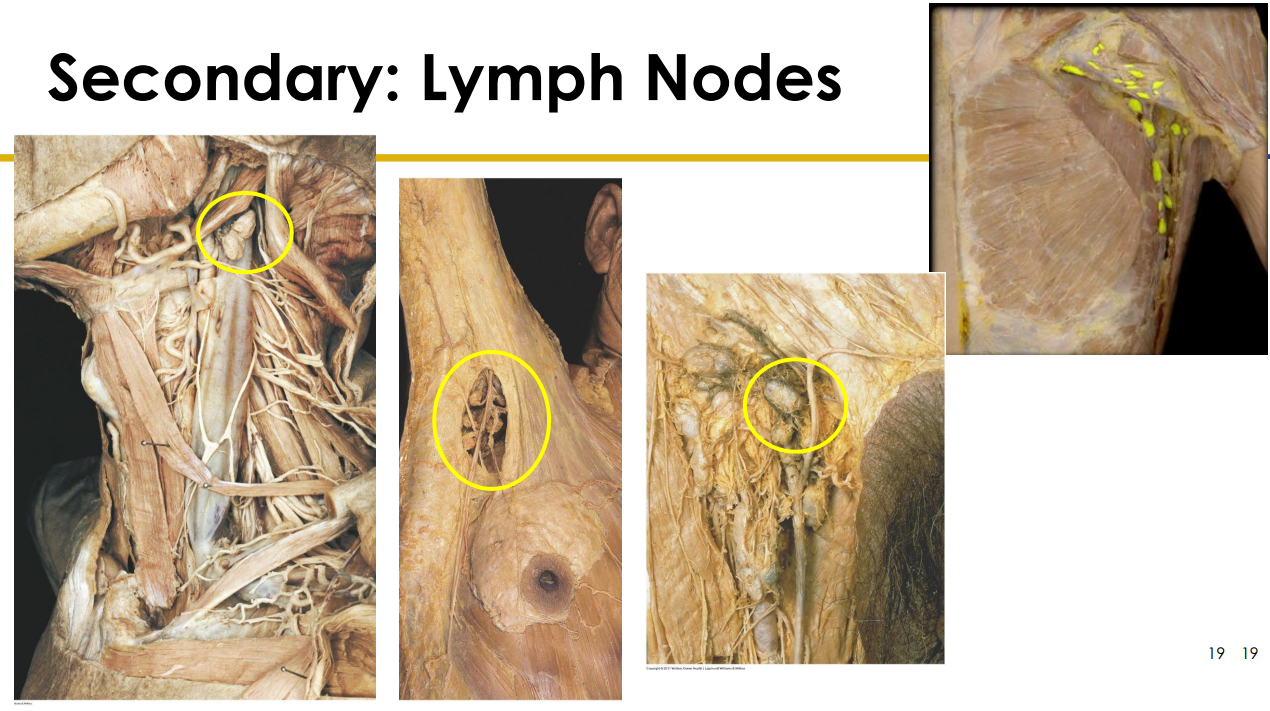
Lymph Node Diagram Cadaveric
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 19
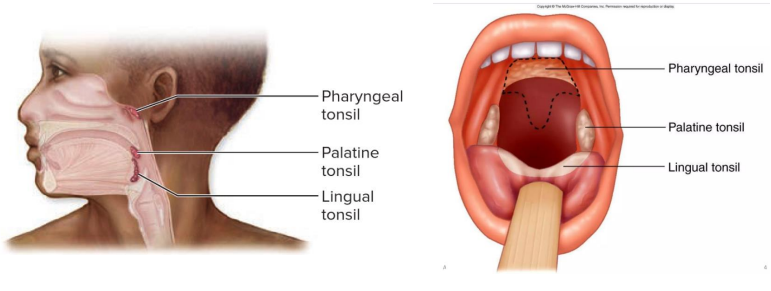
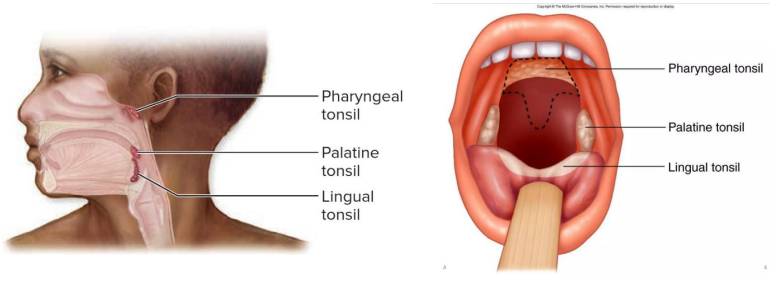
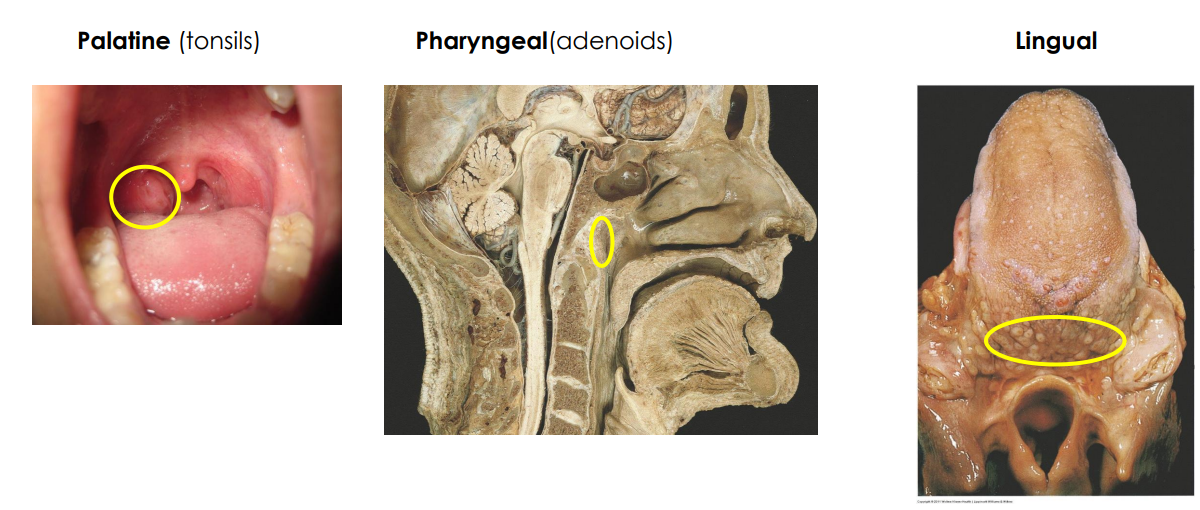
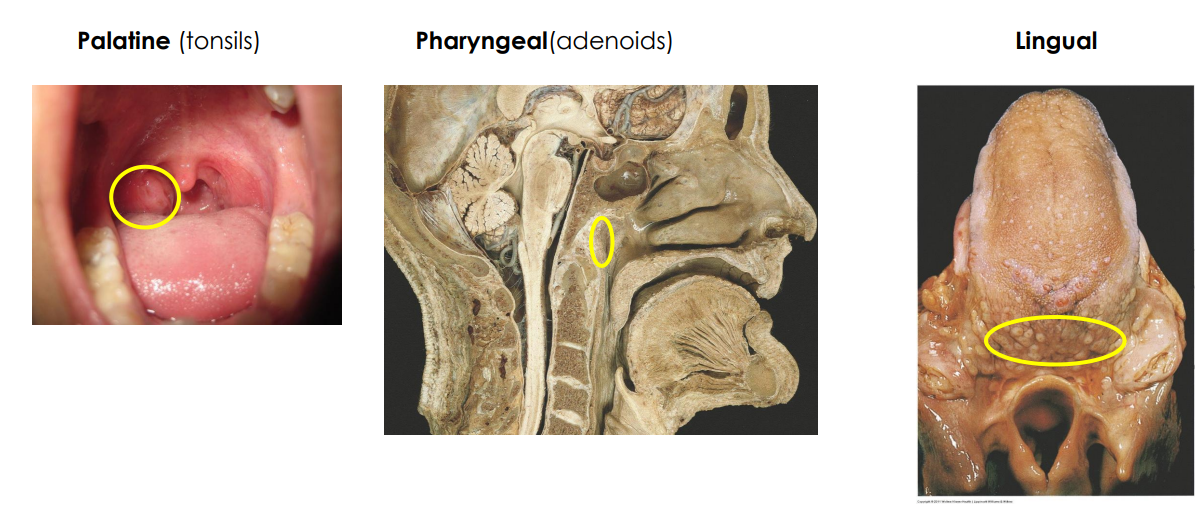
Secondary: Tonsils
- large groups of lymphoid tissue in nasopharynx and oral cavity
- Provide protection against bacteria and other harmful material
- Palatine (tonsils, usually what people refer to when they say tonsils)
- Pharyngeal (adenoids)
- Lingual
Tonsil Parts Diagram
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 21
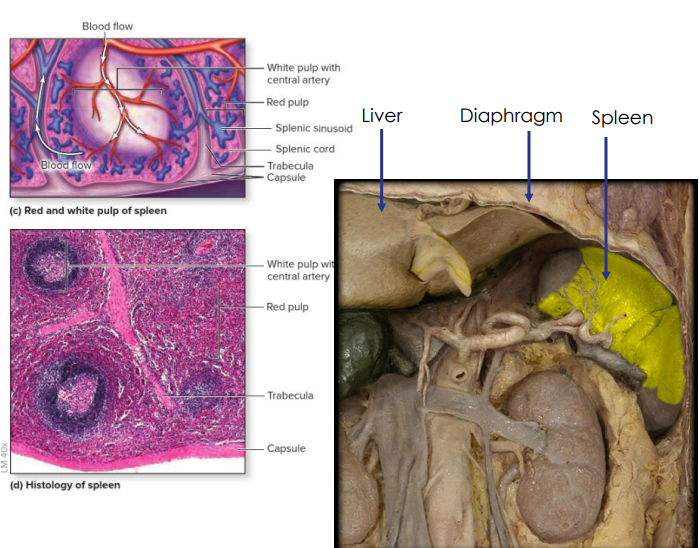
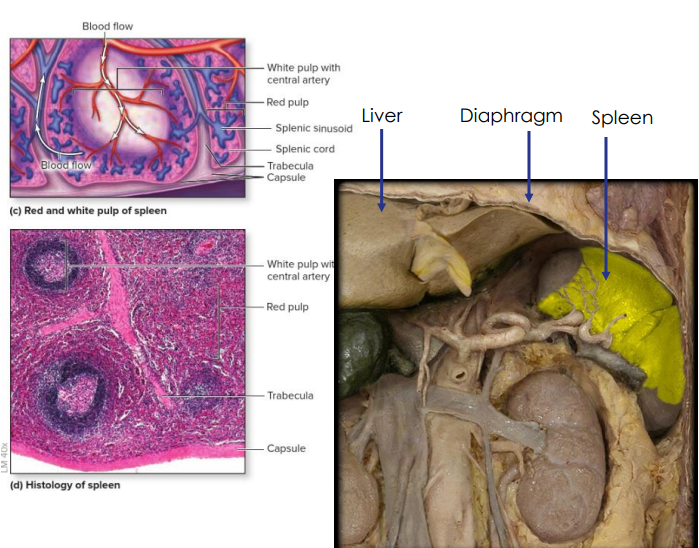
Secondary: Spleen
- located in left hypochondriac region
- Usually not palpable as it lies deep in the rib cage, but may be felt in individuals of slender build
- Distinct areas of white pulp (25%) - lymphatic tissue and red pulp (75%) - fibrous network of macrophages and RBCs.
- Immune response initiated against substance in blood
- monitors blood, detects and responds to foreign antigens, destroys defective red blood cells
- Regulates blood volume
- Limited reserve of RBC
- can be ruptured in traumatic abdominal injuries
- Splenectomy
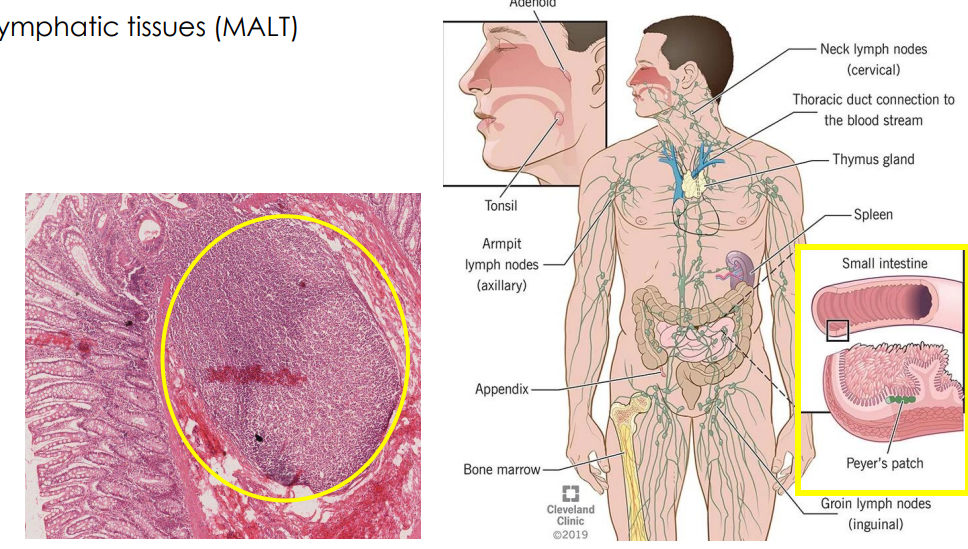
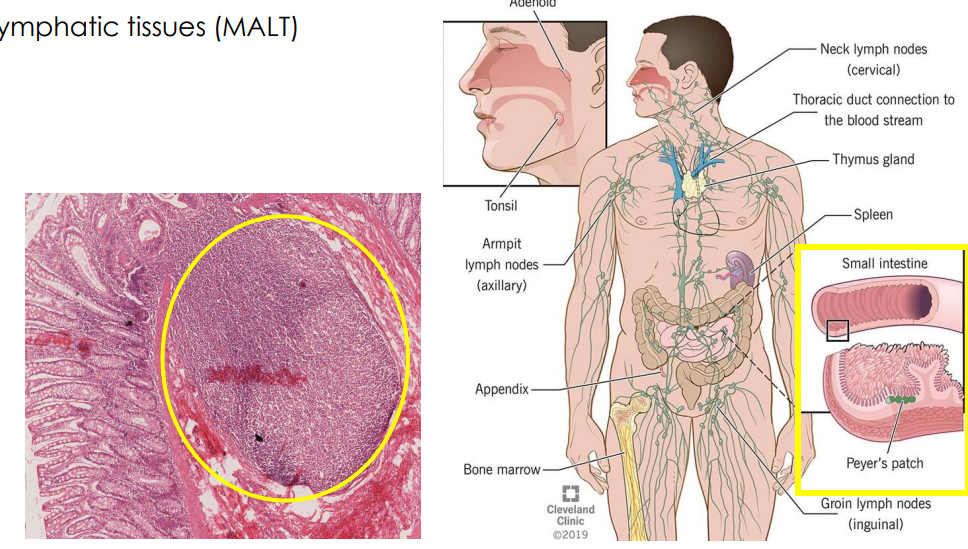
Secondary: MALT
- Mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue (MALT)
- Bronchial-associated lymphoid tissue (BALT) (found in respiratory system)
- Gastrointestinal-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT). e.g Colon GALT
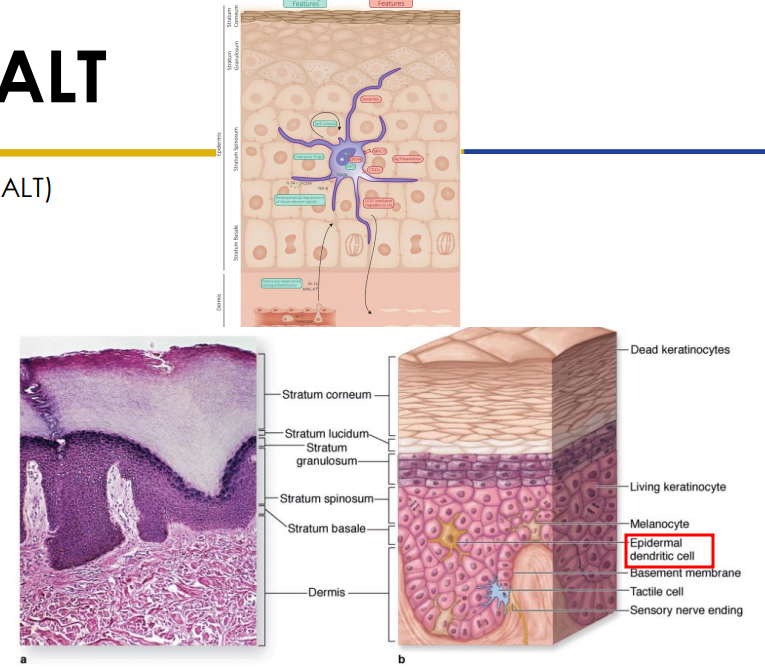
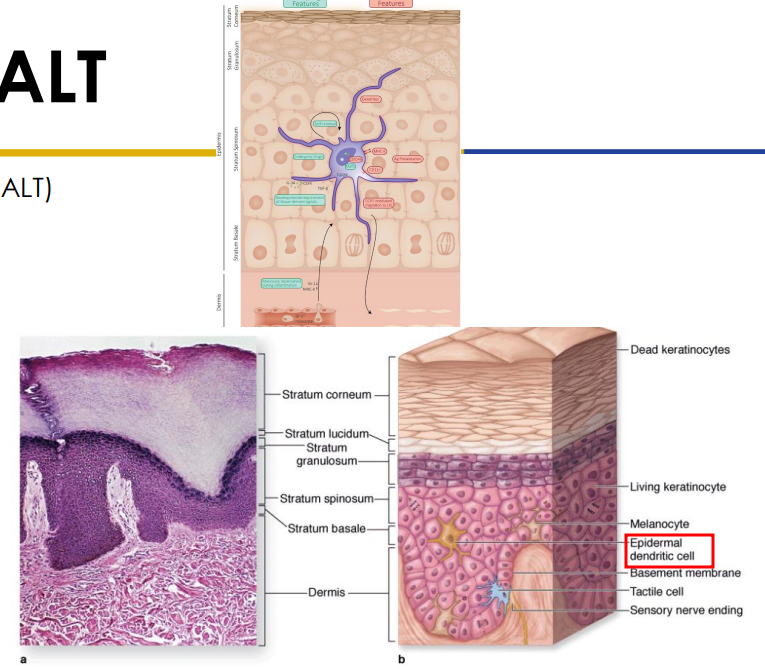
Secondary: SALT
- Skin associated lymphatic tissues (MALT)
- Stratum spinosum houses epidermal dendritic (langerhans) cells (2-8% epidermal cells)
- dendritic antigen presenting cells (APCs)
- T-lymphocytes can also be found in the stratum spinosum. Dendritic cells + T cells: SALT (Skin Associated Lymphoid Tissue)
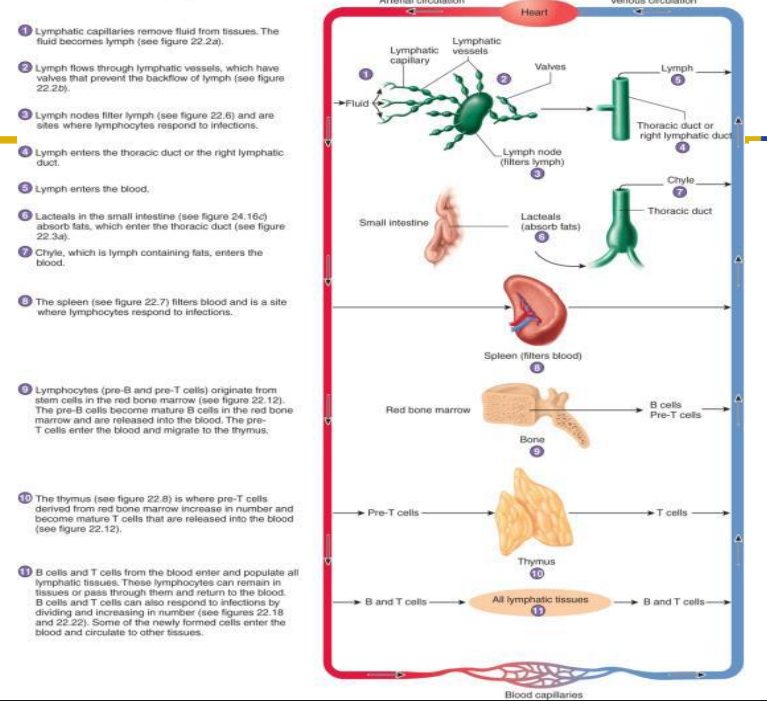
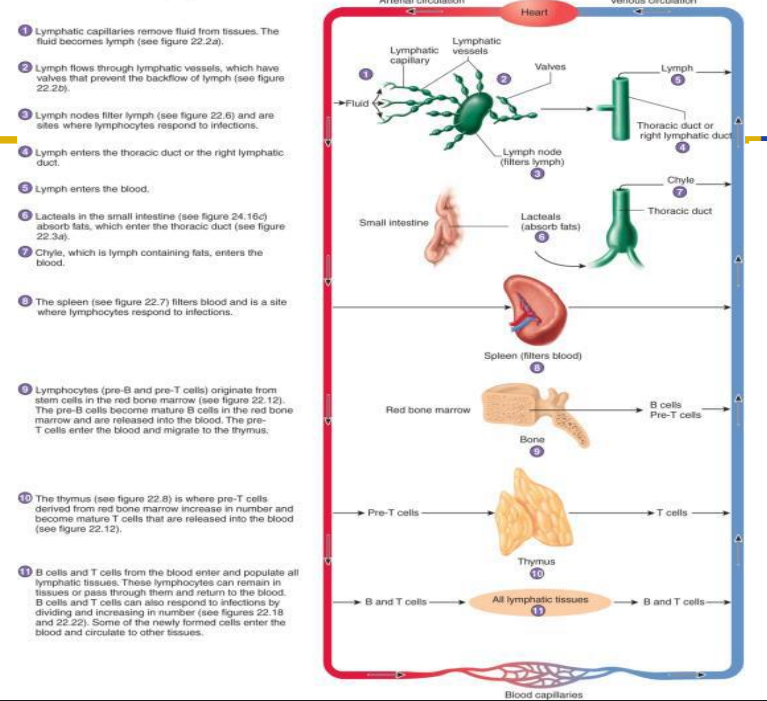
How the Lymphatic System is connected to Cardiovascular System
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 25
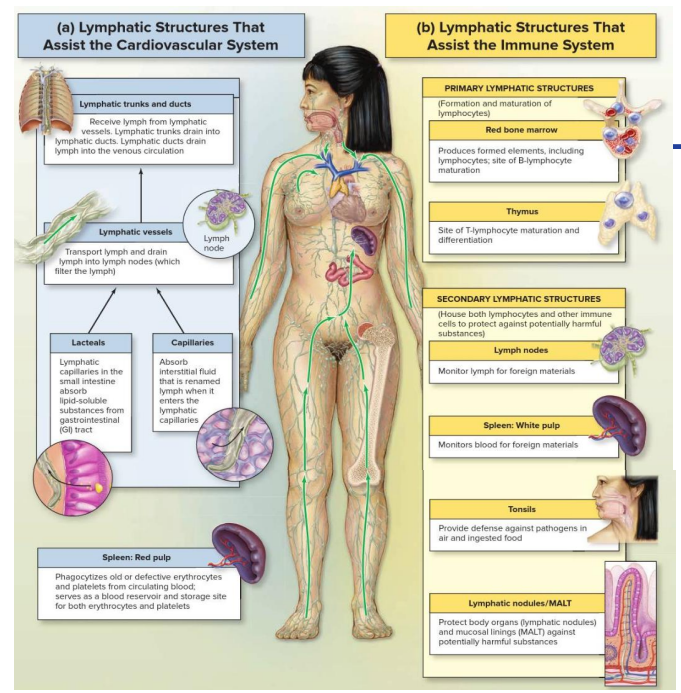
Homeostasis
- Ability to maintain a relatively constant internal environment
- The lymphatic system works with the cardiovascular system and the immune system, to achieve homeostasis
- Helps the immune system by housing and transporting immune cells
- Helps the cardiovascular system by returning interstitial/extra-cellular fluid (ECF) from capillary beds (includes excess fluids and excess proteins) to the venous system.
Lymphatic Disorders** (DONT NEED TO KNOW)
- Tonsillitis: Inflammation of the tonsils - bacterial infection
- Lymphoma: cancer (benign or malignant) of the lymphoid tissue or cells, often begins in the lymph nodes, immune system suppressed
- Hodgkin's Disease: malignancy in lymphoid tissue (malignant B cells)
- Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma: any cancer of lymphoid tissue - except Hodgkin's. Can effect cells, nodes or organs
- Lymphedema: swelling due to accumulation of fluid in interstitial fluids, usually related to blocked lymphatic vessels
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 27

TAKE HOME MESSAGES
DIAGRAM ON SLIDE 28
