Kines 202 Exam 1
1/153
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
154 Terms
what is anatomy?
the study of the structure of the body
what is physiology?
the study of the function of the body
what are the 11 systems of the body?
respiratory, digestive, urinary, reproductive, endocrine, lymphatic/immune, integumentary, skeletal, muscualr, cardiovascular, and nervous
what are the two body cavities?
dorsal (posterior) and ventral (anterior)
what cavities are in the dorsal cavity?
cranial and spinal/vertebral
what cavities are in the ventral cavity?
thoracic and abdominopelvic
proximal
closer to the trunk
distal
farther from the trunk
medial
closer to the midline
lateral
farther from the midline
anterior
front side of the body
superior
towards the head
inferior
towards the feet
cranial
towards the head
cudal
towards the tail
superficial
closer to the surface
deep
farther from the surface
plantar
bottom of the foot
dorsal (foot)
top of the foot
plamar
palm side of the hand
dorsal (hand)
back of the hand
ipsilateral
on the same side of the body
contralateral
on the opposite side of the body
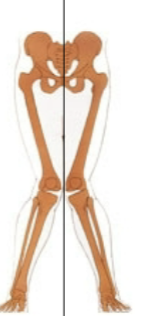
varus
distal segment (foot) deviates toward midline relative to proximal segemnt
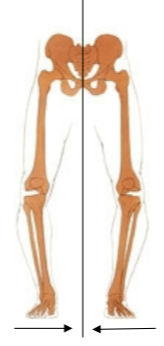
valgus
distal segment (foot) deviates away from the midline relative to proximal segemnt
sagittal plane
divides the body into left and right halves
What is thr axis for the sagittal plane?
mediolateral axis
what are the movements in the sagittal plane?
flexion, extension (hyperextension), dorsiflexion, and plantar flexion
frontal plane
divides the body into front and back halves
what is the axis for frontal plane?
anteroposterior axis
what maovements are in the frontal plane?
abduction/adduction, lateral flexion, elevation/depression, unlar and radial deviation, eversion/inversion
transverse plane
divdes the body into top and bottom halves
what axis is in the transverse plane?
longitudinal axis
what are the movements in the transverse plane?
internal/external rotation, pronation/supination, horizontal abduction/adduction
multi-joint exercises
bench press, bent-over rows, and squats
single joint exercises
knee extensions, bicep curls, lateral raises
what is an example of sagittal plane motion?
running
what is an example of frontal plane motion?
juming jacks
what is an example of transverse plane motion?
pirouette
how many bones are in the human body?
206
how many bones are in the axial skeleton?
80
how many bones are in the appendicular skeleton?
126
% of mineral in bones
30
% of collagen in bones
30
% of water in bones
10
% of void space in bones
30
what is bone composed of?
calcium carbonate, calcium phosphate, collagen, and water
what is found in the void space?
bone marrow
what is bone made of?
cortical and cancellous bone
cortical bone
low porosity, stiff, strong
cancellous bone (trabecular)
high porosity, injury prone, spongier/softer
Wolff’s Law (ON EXAM)
bone reshape themselves based upon stress — bone adapts to those stresses along the lines of stress
example of Wolff’s Law
jumping jacks = vertical line of stress
functions of the skeletal system (ON EXAM)
protection of the heart, lungs, brain, etc
support by maintaining posture
movement by serving as points of attachment for muscles and acting as levers
mineral storage such as calcium and phsphorus
hemopoiesis
What is hemopoiesis
process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow
types of bones in the body (ON EXAM)
long bone
flat bone
short bone
irregular bone
sesamoid bone (floating bone)
bone projections
condyle
epicondyle
crest
head
neck
facet
spine
process
line
tubercle
tuberosity
trochanter
suture
bone depression
fossa
fovea
sulcus
sinus
foramen
meatus
facet
diaphysis
long shaft
epiphysis
most proximal and distal aspects of the long bone (the ends)
metaphysis
small section between the epiphysis and the diaphysis
edosteum
thin membrane lining the medullary cavity
periosteum
tough outer sheath surrounding the bone except where the articular cartilage is
articular (hyaline) cartilage
covering the epiphysisi to provide cushioning and reduce friction
what are the three types of bone cells?
osteoblasts, osteoclasts, and osteocytes
osteoblasts
responsible for building new bone
osteoclasts
responsible for breaking down bone
osteocytes
mature bone cells; maintain metabloism of the bone
fracture
a break in the continuity of bone
avulsion fracture
fracture where a fragment of bone tears away from the main bone mass
stress fracture
microfracture in bone due to overuse
what is periostisis a precusor to?
osteoarthritis
what the difference between rheumatoid arthristis and osteoarthrists (ON EXAM)
RA is an autoimmune disorder while OA is not
ORIF
open reduction with internal fixation
osteoporosis
decrease in bone mineral density
muscle
muscle-tendon fucntional unit
muscle functions as.. (5) (ON EXAM)
energy converters
internal force generators
actuators
pumps
temperature regulators
types of muscles (3)
skeletal
cardiac
smooth
skeletal muscle structure in order (ON EXAM)
whole muscle — fascicle — fiber — myofibril — myofilaments
what are the two types of myofilaments?
actin and myosin
t/f muscles forms into tendon to attach to the bone
true
epimysium
the layer that covers the entire muscle
perimysium
found around each fasicle
endomysium
covers the individual muscle fibers
motor unit
a single motor nueron and all of the muscle fibers that neuron innervates
origin
where a muscle begins (proximal ends)
insertion
where a muscle ends (distal ends)
what are the three types of muscle contractions?
concerntric, eccentric, and isometric
isometric contraction
tension is developed within muscle but there is no appreciable change in the length of the muscle or change in joint angle
concentric contraction
tension developed by muscle against resistant is suffiencent for the muscle to shorten
eccentric contraction
tension developed by muscle agaisnt some resisitance is sufficient for the muscle to lengthen
agonist
prime mover
antagonist
muscle the performs action opposite of what the agonist is
hypertrophy (ON EXAM)
increase in size of muscle via increase in diameter of individual muscle fibers (large body buildier)
atrophy (ON EXAM)
decrease in size of muscle due to systematic under use of tissue (arm shrinking while being in cast)
how many weeks does it take to hypertrophy? how many to atrophy?
6 weeks; 2 weeks
where does a sprain happen?
joints and ligaments
where does strains happen?
any muscle in the body
muscle soreness
mild injury affecting the myofilaments and is associated with change in normal movement
muscle strain
substantial tearing of the muscle fibers and connective tissue