B1: cell structure
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What is a eukaryotic cell?
Contain their genetic material (DNA) enclosed in a nucleus.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
The DNA is not enclosed in a nucleus, but in a circular strand of DNA and maybe plasmids (small rings of DNA) too. Prokaryotic cells are much smaller than eukaryotic cells.
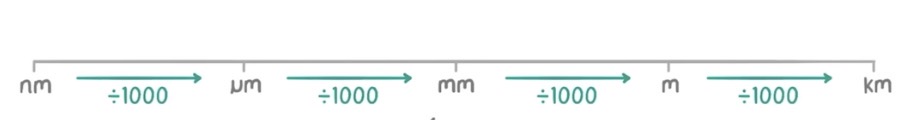
What are the standard units used in cell biology and how to convert between them?
metre, millimetre, micrometre, nanometre
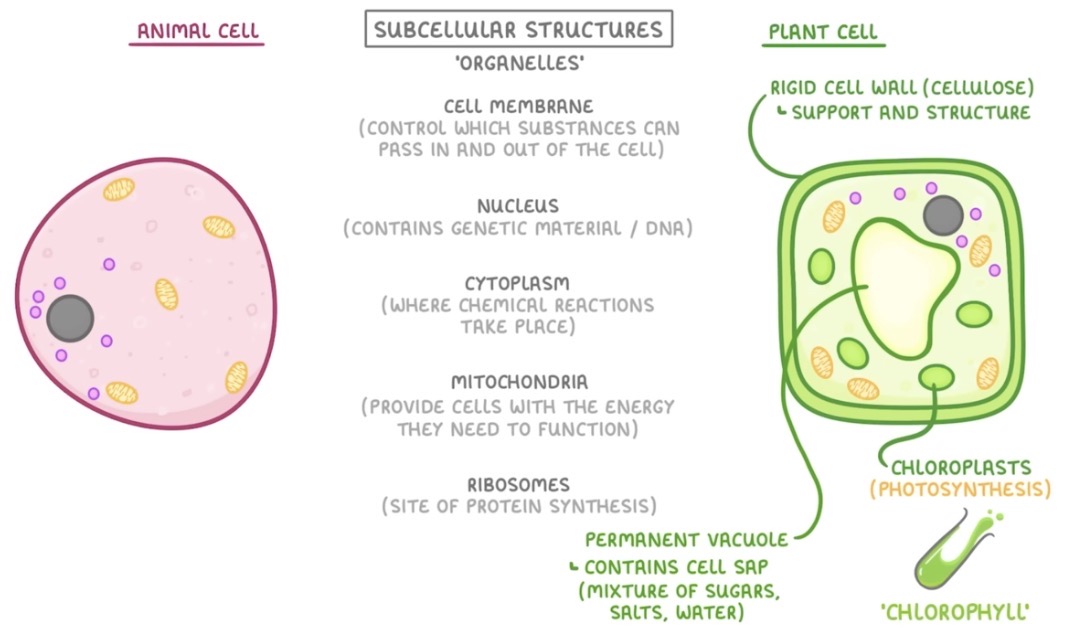
What are the parts of animal and plant cells and their functions?
Label this microscope drawing.
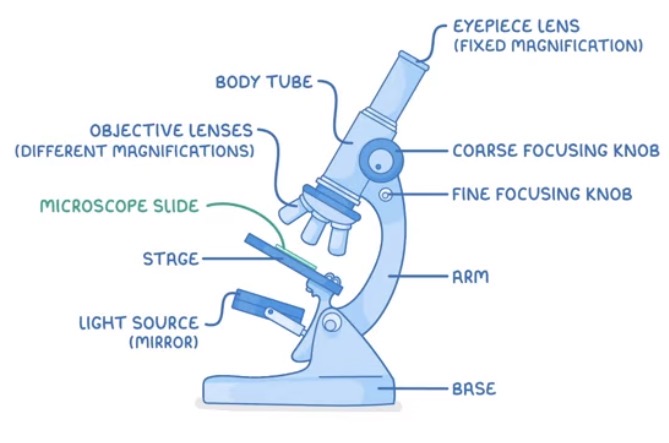
Required Practical: microscopes
Place the prepared slide onto the stage and secure with clips. Start with the stage at the lowest point.
Start with the lowest power objective lens.
Slowly turn the coarse focusing dial to raise stage until you see the specimen.
Swap to fine focus and adjust until specimen is clear.
Move up objective lens and readjust.
Electron vs light microscope
Electron microscope: higher magnification
Electron microscope: higher resolution
Electron microscope: B&W image
Light microscope: colour image
What is the equation for magnification?
Magnification = image size / actual size
What is a specialised cell?
A cell that has differentiated.
Name 3 specialised animal cells with function and adaptations.
Nerve cell - sends electrical impulses around the body
Long axon to carry the impulses across body
Fatty sheath insulates the axon to speed up impulses
Muscle cell - contract to move body
Contain protein fibres which can change their length
Contains lots of mitochondria to provide energy for muscle contraction
Sperm cell - fertilises ovum
Has a long flagellum to swim to the ovum + are streamlined
Contain lots of mitochondria to give energy needed for swimming
Name 3 specialised plant cells with function and adaptations.
Root hair cell - absorbs water + nutrients for plant
Hairs to increase surface area
Thin cell wall to improve absorption
Xylem cell - carries water and minerals from roots to leaves
Thick walls containing lignin for plant support
End walls between cells broken down to form a long tube for easy transport
Phloem cell - carries dissolved sugars up and down the plant
No nucleus and only limited cytoplasm
Each phloem cell has a companion cell with mitochondria to provide energy
What are the key facts about chromosomes?
The nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made up on DNA molecules. Chromosomes carry many genes. In body cells the chromosomes are normally found in 23 pairs.
What is the cell cycle?
Chromosomes + organelles replicate and line up along the cell equator
They are pulled apart and two nuclei reformed
Cytokinesis - cytoplasm and cell membrane divide to form two identical daughter cells
Why is mitosis needed?
Growth
Repair
Replace
Asexual reproduction
What is a stem cell?
An undifferentiated cell.
What are embryonic stem cells and its disadvantages?
Pluripotent: can be grown into any type of human cell
Created from leftover embryos before differentiation
DISADVANTAGES
Risk of immune rejection
Ethical / religious concerns
What are meristems in plants and how could they be used?
Found in roots and buds of the plant
Can differentiate into any type of plant tissue, at any point in the plant’s life
Could be used to clone plants to stop extinction of rare species or produce cloned crops for farmers (for example rare plants with disease resistance can be cloned)
What are adult stem cells and how could they be used?
The stem cells found in bone marrow can differentiate to form cells found in our blood
Multipotent: can only differentiate into cells from the tissue in which they’re found
May be used to treat leukaemia - bone marrow transplant containing stem cells to form blood cells, however risk of transferring viral infections
What is therapeutic cloning and how could it be used?
An embryo is produced with the same genes as the patient
Stem cells from the embryo can be transplanted without being rejected by the patient’s immune system
Then the stem cells can differentiate to replace cells which don’t work properly
Could be useful for diabetes / paralysis
When does differentiation happen in plant and animal cells?
Most animal cells differentiate at an early stage. Many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate throughout their life.
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the movement of particles from a high to low concentration, passively.
What are some substances transported in and out of cells by diffusion?
Oxygen and carbon dioxide in gas exchange
Urea from cells into the blood plasma for excretion by the kidneys
What factors affect diffusion?
Temperature: higher temperature, faster diffusion
Surface area: greater surface area, faster diffusion
Difference in concentration: larger concentration gradient, faster diffusion
What is osmosis?
The diffusion of water from a high to low water concentration through a partially permeable membrane, passively.
Explain osmosis in terms of animal and plant cells.
Cytoplasm has a low concentration of water (dilute). If a cell is placed in water, osmosis will take place and the cell will become swollen (plant cell wall stops bursting - becomes turgid). If a cell is placed in a very concentrated solution, water will move out of the cell and it will shrink (flaccid).
Required Practical: the effects of osmosis plant tissue
Use a cork borer to cut 3 potato cylinders of the same diameter. Use a knife and ruler to trim the cylinders to 3cm each.
Measure the mass of each cylinder using a balance.
Measure 10cm³ of three different salt concentrations into 3 different boiling tubes. Add in the potato cylinders.
Leave overnight. Then, remove the potato cylinders and dry gently with a paper towel.
Measure the new masses with a balance.
Calculate the percentage change in mass. This is (Change in value / original value) x 100.
What is active transport?
The movement of particles from low to high concentration against the concentration gradient and across a partially permeable membrane, requiring energy / ATP.
Give a human and a plant example of where active transport is found
Root hair cells absorb mineral irons from the soil
Glucose from gut to the blood (needed for respiration)
What increases the effectiveness of an exchange surface?
Large surface area
Thin membrane (short diffusion pathway)
Efficient blood supply (in animals)
Being ventilated (in animals, for gas exchange)