3.2: The cell Surface
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Plasma Membrane
Has 2 layers (intracellular and extracellular); will appear as a pair of dark parallel lines viewed with electron microscope; made 98% lipids, 75%phospholipids, 20%cholesterol molecules, and 5%glycolipids.
Function: defines cell boundaries, governs interactions with other cells, controls passage of material in/out of the cell
Phospholipids
75%of membrane; have a hydrophilic phosphate containing head outward and a hydrophobic tails inward
Function: Maintain fluidity by drifting laterally from place to place, spinning on their axes, and flexing their tails, and help regulate what travels in/out of the cell
Cholesterol
20% of membrane; holding phospholipids still and stiffens the membrane in spots. Higher concentration of this will increase membrane fluidity by preventing phospholipids from packing together
Glycolipids
5% of membrane; phospholipids with short carbohydrate chain on the extracellular face; contributes to glycocalyx- a carbohydrate coating on the cell surface with multiple functions (unique to each individual except identical twins)
Membrane Protein
2% of membrane; accounts for 50% of the membranes total weight.
Functions: Receptors, second-messenger systems, enzymes, channels, carriers, cell-identity markers, cell-adhesion molecules
Integral (Transmembrane) Protein
Pass completely though the membrane protruding from both sides; has a hydrophilic region in contact with the cytoplasm/extracellular fluid and a hydrophobic region passing through the lipid; anchored to the cytoskeleton; most are glycoproteins (conjugated with oligosaccharides on the extracellular face of membrane)
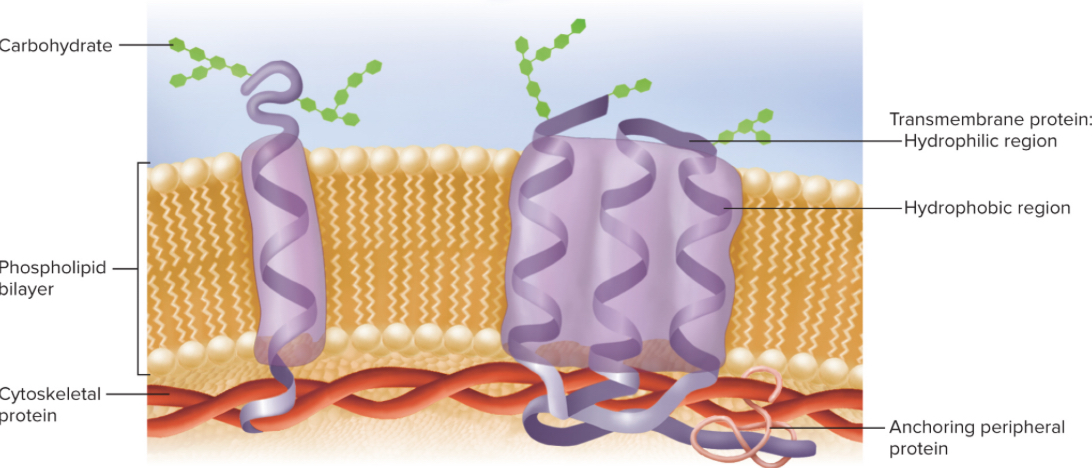
Peripheral Protein
Do not protrude into the phospholipid layer but adhere to either the inner or outer face of the membrane; those on the inner face and anchored to the cytoskeleton
Receptor
Surface proteins that are binding sites for chemicals; specific for one messenger (or signal); function is to receive signals between cells
Enzymes
Carry out final stages of starch and protein digestion in small intestine; helps produce second messenger; breakdown hormones and other signaling molecules whose jobs are done
Cell-Identity Markers
The carbohydrate chains on glycoproteins that differentiate from cells that belong and which are foreign cells in the body
Cell-Adhesion Molecules
Cells adhere to one another and to extracellular material through these certain membrane proteins; most cells need to be linked to the extracellular material to survive
Molecular Motors
Produce movement by changing shape and pulling on other molecules; needs fibrous proteins to occur (actin and myosin), that pull on the integral protein
Function: Moves materials within a cell, enables cells to move around in tissues, and makes cells change shape (surrounds and engulfs particles or divides in 2 separate pieces)
Carriers
A transmembrane proteins; utilizes pumps(carriers that consume ATP/energy) to carry our their functions
Functions: Binds to glucose, electrolytes, or other solutes and transfers them from one side of the plasma membrane to the other
Channel Proteins
A transmembrane protein with passages that allow water and hydrophilic solutes through the membrane; regulates passage with gates, therefore controlling of things such as nerve signals or muscle contractions
Gated Channel Proteins
Channel proteins that control when something can pass, depends on stimuli (ligand regulated-chemicals, voltage regulated- electrical potential/voltage, mechanically regulated- physical stress on a cell)
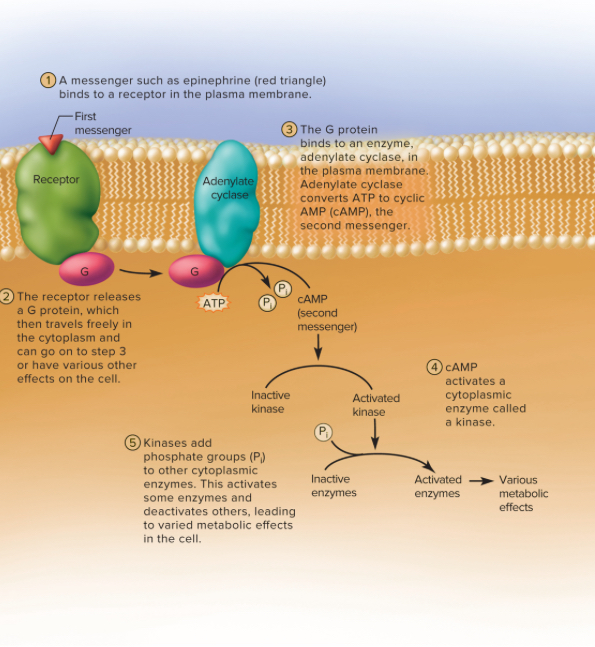
Second-Messenger System
When a first messenger binds to a surface receptor, it triggers a G protein (GTP) to relay the signal to adenylate cyclase (a peripheral membrane protein). Adenylate cyclase then removes 2 ATP from the G protein and converts in to cyclic AMP (cAMP), the second messenger. The cAMP activates cytoplasmic enzymes called kinases which add phosphate groups to other cellular enzymes that activates some enzymes and deactivates others, leading to varying metabolic effects on the cell.
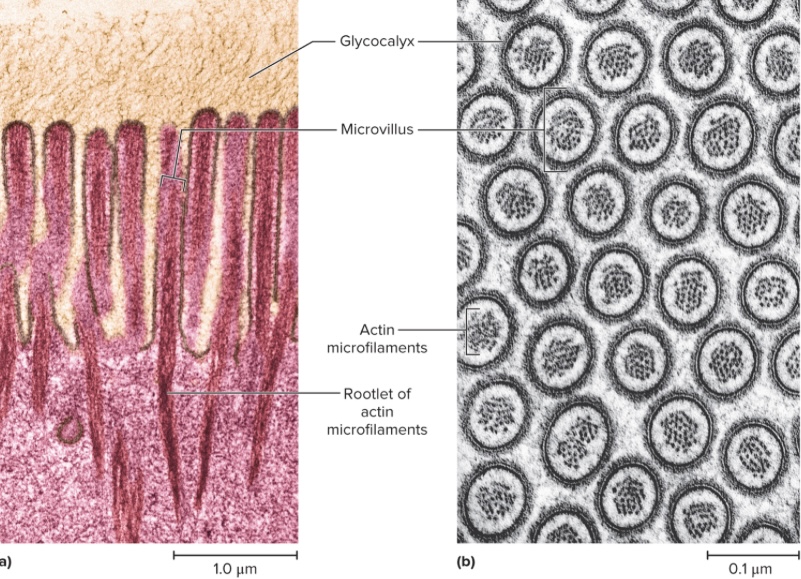
Glycocalyx
Fuzzy coat, external to the plasma membrane, composed of carbohydrate moieties of membrane phospholipids and glycoproteins; unique to everyone except identical twins
Function: protection, cell adhesion, immunity to infection, fertilization, embryonic development, transplant compatibility
Microvilli
Extension of cell surface with general function of absorption; expands cells surface area; 1-2 um in length; very dense and appear as brush border of “fringe”; some have actins- bundle of stiff filaments that are attached to the inside of the plasma membrane at the tip of the microvillus; at the base or terminal mesh, allows milking of nutrients from outside world (Function: absorption (intestines/kidneys) and sensory buds in inner ear)
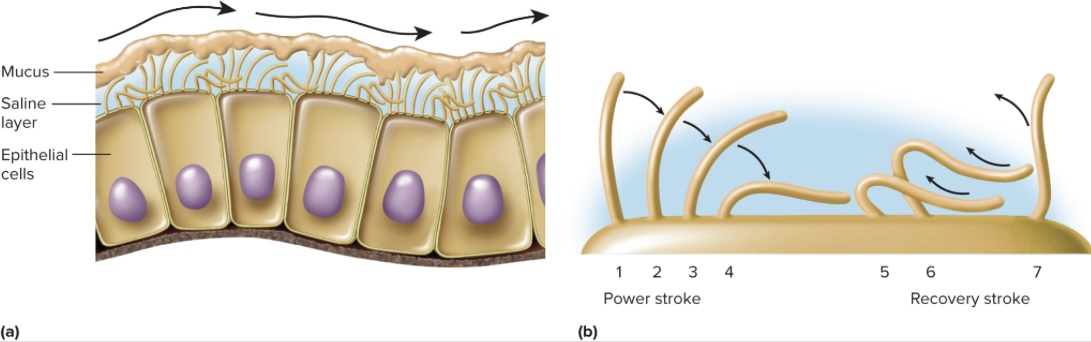
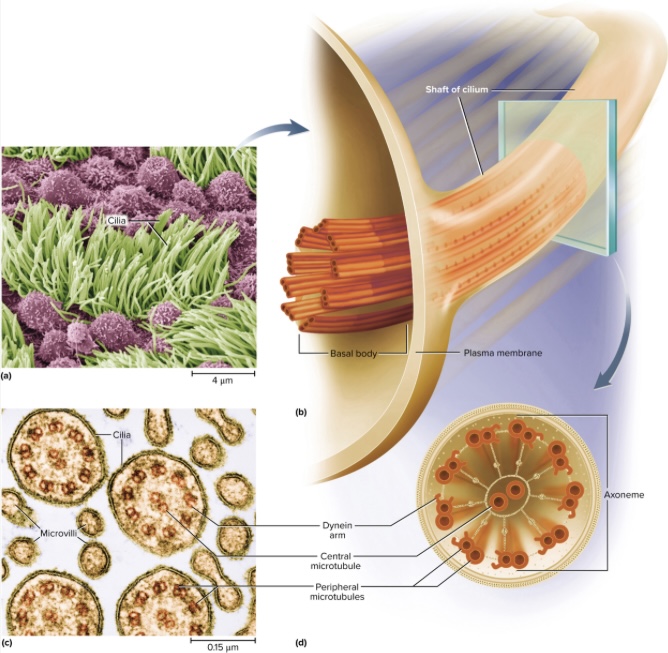
Cilia
Hair-like projections 7-10 um in length; located in saline(so they don’t get stuck), function is unknown but possibly sensory (produced by Cl pump and draws Na+ and H2O)
each cilium bends stiffly forward and produced power stroke that pushes substance along, cilia is then pulled back by recovery stroke that restores it upright, ready to do it again (wave like motion)
Primary/Single/Non-motile Cilia
found on nearly every cell (widespread); “antennas” for monitoring nearby conditions; helps with balance in inner ear/light detection in retina/sensory cells in nose (think 5 senses)
Ciliopathies
Defects in structure or function of cilia
Motile Cilia
Less widespread; found in respiratory tract, uterine tubes, ventricles of brain, ducts of testes; about 50-200 of each cell; beats in waves, sweeping material across a surface in one direction; power stroke followed by recovery stroke
Cilia Structure
Axoneme: 2 central microtubules surrounded by 9 paired structures of microtubules (called basal body once continued into cell); dynein arms “crawl” up adjacent microtubules, bending the cilium (uses energy from ATP)
Flagella
Whip-like structure with axoneme identical to cilium’s; tail of sperm is the only functional flagellum in human; stiffened by course fibers that gives tail more propulsive power
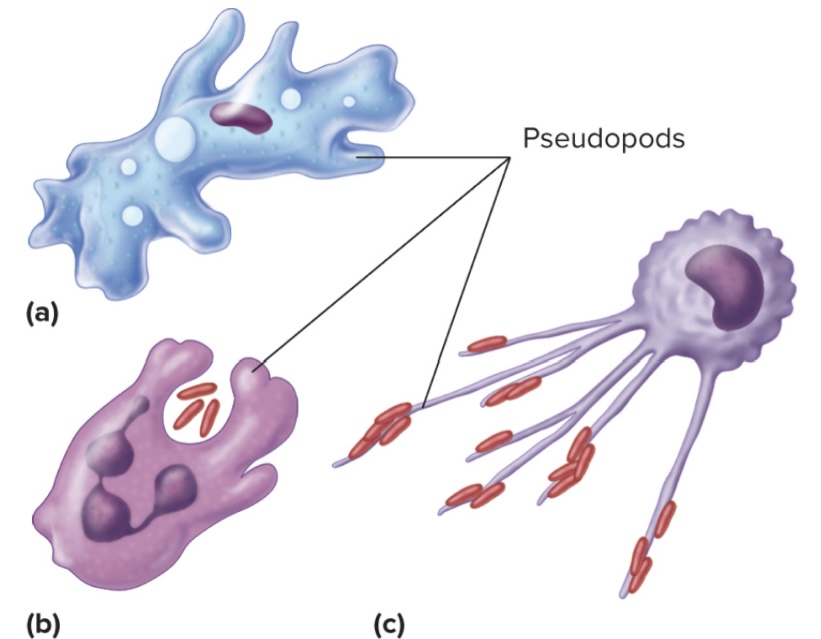
Pseudopods
Continuously changing extensions of a cell, vary in shape and size; can be used to move whole cell and capturing foreign particles