Earth and Space - Science
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
What is the biosphere?
A part of the earth occupied by living organisms. For example city or a farm.
Atmosphere
layers of gases surrounding a planet. eg. Carbon dioxide
Geosphere
Layer of the earth made up of solid rock and other rocky materials.
Hydrosphere
A hydrosphere refers to the total amount of water on a planet.
What is the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle shows how carbon moves between teh different spheres. Such as the atmosphere.
Why is there a carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle describes how carbon is reused in each sphere.
Global warming meaning?
Refers to the increase on the average surface temperature of the earth, caused by greenhouse gases.
How can climate change affect biotic factors?
Distribution diseases
Migration - more because enviroment changes
Extinction - species don’t adapt fast enough
What is combustion? What is the effect?
Refers to the process of burning fossil fuels to produce energy, during this carbon dioxide is released. Increase in population; more people need electricity. This leads to an increase in the release of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
What are the carbon fluxes? And what is a flux?
A flux is the process that enables carbon to move between spheres. Fluxes include, photosynthesis, decomposition, fossilisation (Fossil fuels and limestone), excretion, respiration, combustion.
What is a reservoir? What are some examples?
Places where caron is stored - plants in the ocean, animals on the farm.
What are the different forms of carbon in each sphere?
CO2 - atmosphere, CHO (food) - biosphere, CaCO3 (rocks)- Geosphere, Dissolved organic carbon - hydrosphere
Word equation for respiration?
Glucose + oxygen → Carbon dioxide + water + (energy)
Word equation for photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide + water → Glucose + Oxygen
Word equation for combustion?
Fuel + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + (energy)
What is the difference between a source and a sink?
A source is where the carbon comes from, before undergoing a flux. (Sun) A sink is where the carbon is transferred into. (Plants)
What is fossilisation?
minerals replace the components of bones, turning them to stone. Carbon is stored in the bones.
Difference between weather and climate?
Weather is the short-term condition of the atmosphere in a given location. Climate is the long term, average condition of the atmosphere for a location. Eg. On average the amazon is hot and humid.
Factors affect weather and climate?
Weather - Temp, wind
Climate - Latitude, elevation
What is the greenhouse affect?
a process of long-wave radiation from the cooling earth being absorbed and re-emitted by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere such as water vapour + CO2. This results in the earth maintaining its optimum heat.
How does the greenhouse affect the earth?
Trapping long wave radiation - maintains Earth’s ideal surface temp
What are greenhouse gases? Examples
Gases that trap heat. Eg. CO2, Methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), Water vapour ( H2O(g)),
How do ice core show past climate?
Snowfall layers compacted form ice. The deeper the ice, the older it is. small bubbles of air that contain a sample of the atmosphere – possible to measure the past concentration of atmospheric gases, including major greenhouse gases. (Older ice will have less CO2)
How did glacial retreat show past climate?
When glaciers retreat, they often deposit large mounds of sediments such as small rocks and sand, known as till. Where till is found there must have been glaciers - cold. Coloured red with iron deposits - hot.
high temperature - evaporate, leave behind a layer of salt preserved in the rocks - hot
How did pollen record show past climate?
By analyzing all types pollen from the layers of the rock, scientists can obtain records of changes in vegetation going back millions of years ago.
How did fossil records show past climate?
By analyzing the chemical composition of shells of fossilized marine animals. The oxygen isotopes in shells give an indication of the temperature changes in the ocean over the last millions of years.
How did Sea level show past climate?
Sea levels reflect the state of the climate system. During ice ages - ice sheets/glaciers. Warm interglacial periods - water is in the oceans.
Difference between global warming and climate change?
Global warming refers only to the Earth's rising surface temperature, while climate change includes warming and the “side effects” of warming—like melting glaciers, heavier rainstorms, or more frequent drought
How has CO2 levels been affected since the industrial revolution?
Human activities have raised atmospheric CO2 by 50%. Temp rising. ice cover - rapidly decreasing.
Difference between natural greenhouse affect and enhanced?
The greenhouse effect traps the Sun's energy for the Earth's surface. It is essential for life on Earth. The enhanced greenhouse effect is where extra greenhouse gases in our atmosphere trap too much of the Sun's energy. Caused by human activities and leads to global warming.
Define Enhanced greenhouse affect
Increase in average surface temp, which was the result of an increase GHG concertation due to human activity.
How do human activities affect the carbon cycle and contribute to the enhanced greenhouse effect.?
Increases concertation of GHG
Deforestation - no plants to suck in CO2, more carbon in atmosphere
Agriculture - Methane released by cows, nitrous oxide used in fertilisers (released into air/water)
Fossil fuels - combustion produces CO2
Car exhausts - car heating up produces nitrous oxide
Abiotic effects of climate change?
Temp changes - animals can’t adapt fast enough
Melting ice caps - sea level rising (floods to habitats)
Changes to permafrost - soil cannot hold vegetation
Biotic effects of climate change?
Extinction, habitat loss - vegetation gone
what is biodiversity?
Refers to the number and variety of species and their genetic diversity. This also includes ecosystems.
Draw the natural/enhanced greenhouse effect diagram,
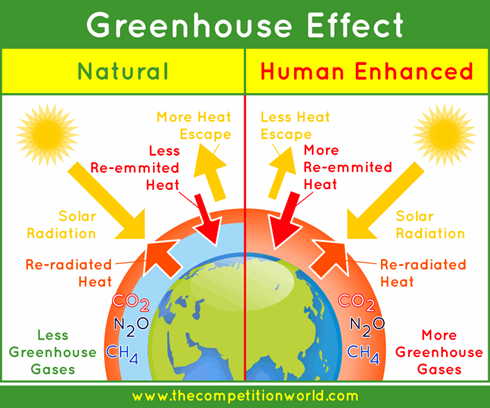
What is decomposition?
The breaking down of animals though bacteria and fungus in the soil.
Reflective surafce?
Albedo