L18b: equine distal limb ultrasonography
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
what is ultrasound considered the diagnostic method of choice for assessing in equine?
tendon injuries
frequency
number of cycles per second of the sound wave
what happens to the wavelength if the frequency of the sound wave is higher?
the wavelength must be shorter
what type of probe do we use to measure the tendons and ligaments of the equine distal limb>
linear probe
what depth does the linear probe penetrate into the tissue?
6cm in depth
what is the correlation between frequency and detail on ultrasound?
high-frequency ultrasound waves pick up more details, but are not able to go far in depth (superficial structures)
what are the properties of sound waves?
reflection
absorption
scattering
attenuation
refraction
what do biological tissues do to sound waves?
cause impedance which influences the velocity of sound through the tissue
what properties of sound waves contribute to artifacts seen on ultrasound?
refraction
scattering
attenuation
sound traveling through a medium is weakened by reflection, refraction, scattering, and absorption of heat by tissies
what does time of the returning echoes inform?
how long it takes for the image to appear in relation to the probe tells you the depth of the tissue
what is the depth of the tissue that is closer to the probe?
this tells you it is a more superficial tissue
what are the modes of ultrasound?
brightness mode (B-mode)
motion mode (M-mode)
doppler modes
B-mode ultrasound system
measures the intensity of the returning echoes, which is expressed in terms of pixel brightness on the unit monitor
what are the particular appearance of tissues based on in B-mode ultrasound?
normal appearance
tissue type
density
echogenicity
the characteristic/ability sound waves and produce of a tissue to reflect echoes
hyperechoic appearance
light grey or white
hypoechoic appearance
Low level of gray echoes
anechoic
appears as black
what structure will be the most hyperechoic on ultrasound?
bone or gas
what structure will be most anechoic on ultrasound?
blood/fluids
which structure is more hyperechoic on ultrasound: connective tissue or fat?
connective tisssue
which structure is more hyperechoic on ultrasound: spleen or liver?
spleen
which structure is more hyperechoic on ultrasound: liver or renal cortex?
liver
hypoechoic to
darker than
hyperechoic to
brighter than
from hypoechoic to hyperechoic put the tissues in order
medulla
cortex
liver
spleen
prostate
what is most echogenic on ultrasound?
bone and gas
what is least echogenic on ultrasound?
fluids
what echotexture is shown?
heterogenous
what echotexture is shown?
homogenous
MCQ: in comparison to the tendons, what is the echogenicity of the liver?
hypoechoic
MCQ: how do gases interact with the ultrasound waves?
strong reflector and strong attenuator
what are the roentgen signs?
number
size
shape
position
appearance / echogenicity
where on the forelimb should the hair be clipped?
from just below the accessory carpal bone to below the fetlock
where on the hindlimb should the hair be clipped?
from the metatarsal region up to the chestnut
what transducer is used to look at the proximal suspensory ligament?
micro-convex
why do we apply gel when doing an ultrasound?
to remove air to prevent potential artifacts
what is the imaging technique for ultrasound of the distal equine limb?
scan from palmar and plantar approaches
use both transverse and longitiudinal planes
what is the typical scanning order for equine distal limb ultrasound?
start proximal and move distal
begin with transverse views, then longitudinal
add oblique views as needed
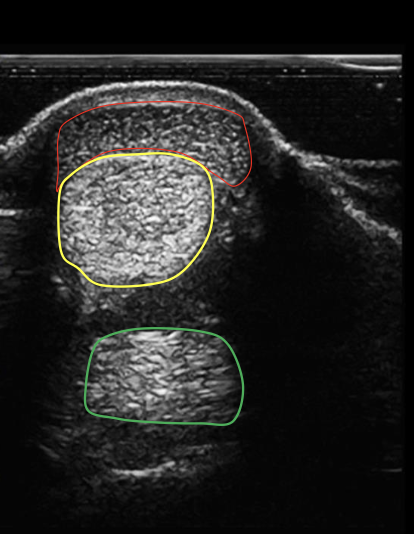
what structure is circled in red?
superficial digital flexor tendon
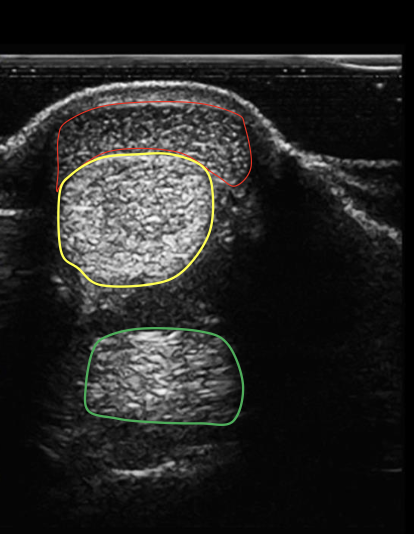
what structure is circled in yellow?
deep digital flexor tendon
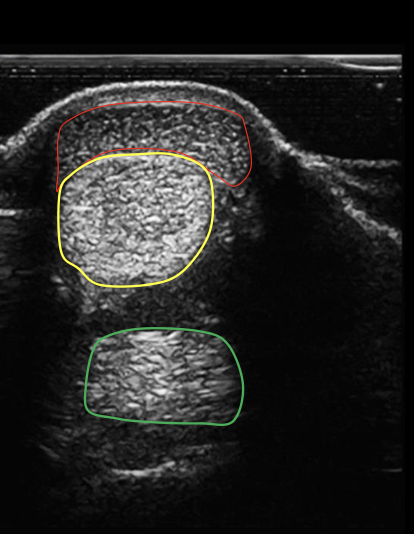
what structure is circled in green?
suspensory ligament
how will tendons appear on a longitudinal scan?
uniform striation
hyperechoic
separated by anechoic spaces
uniform heterogenicity
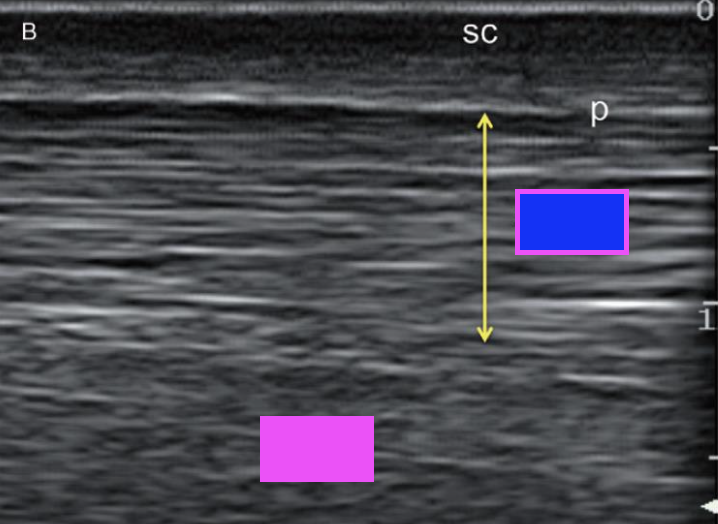
what structure is indicated by the yellow arrows?
superficial digital flexor tendon
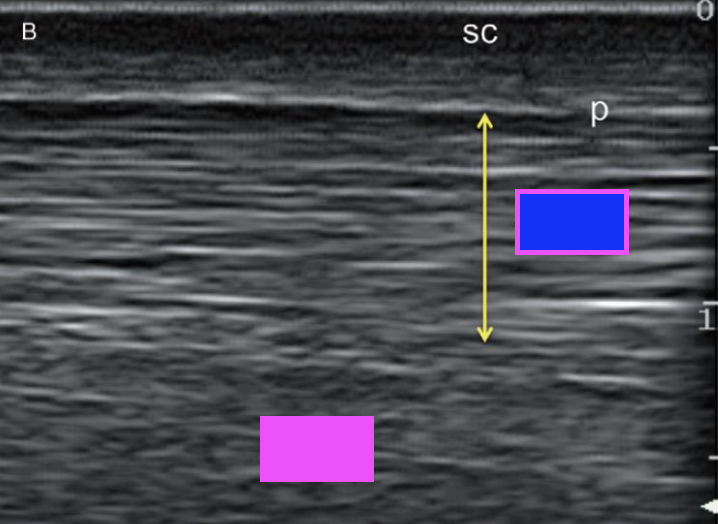
what type of ultrasound scan does this show?
longitudinal scan
how do tendons appear on a transverse scan on ultrasound?
coarse granular dots
hyperechogenic interface
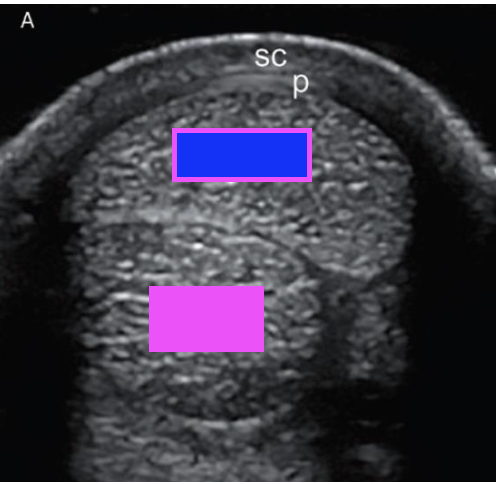
what type of ultrasound scan is shown?
transverse scan
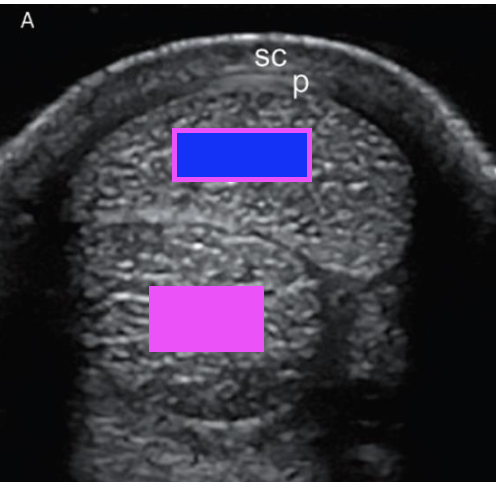
what structure does the pink box indicate?
deep digital flexor tendon
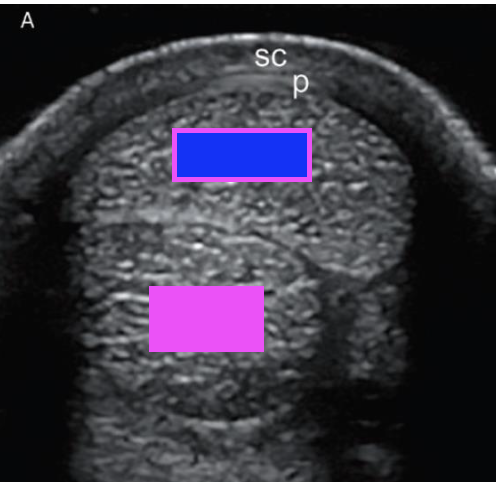
what structure does the blue box indicate?
superficial digital flexor tendon
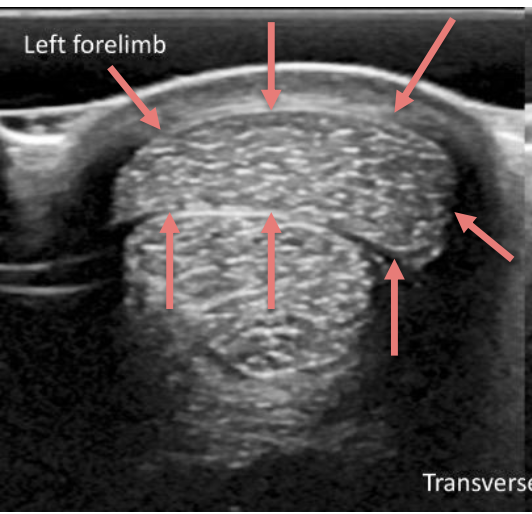
MCQ: This is a transverse scan of the Mid carpal region of an 8- years-old horse. What is the structure annotated by the arrows?
SDFT
MCQ: Transverse scan of the DDFT at the Mid-MC region appears as a/an
oval structure
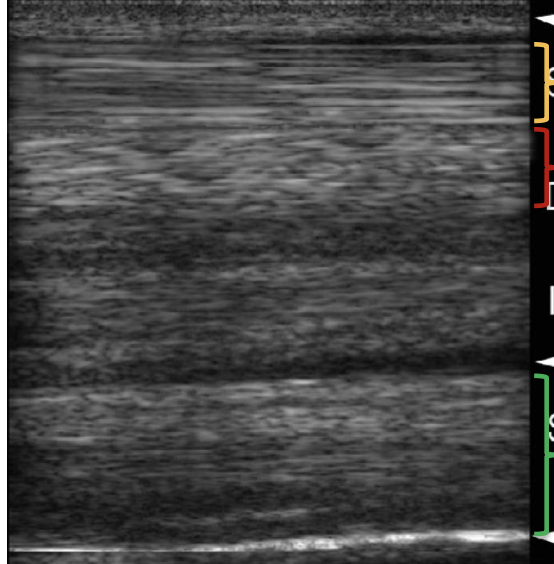
what structure is indicated by the green bracket?
suspensory ligament
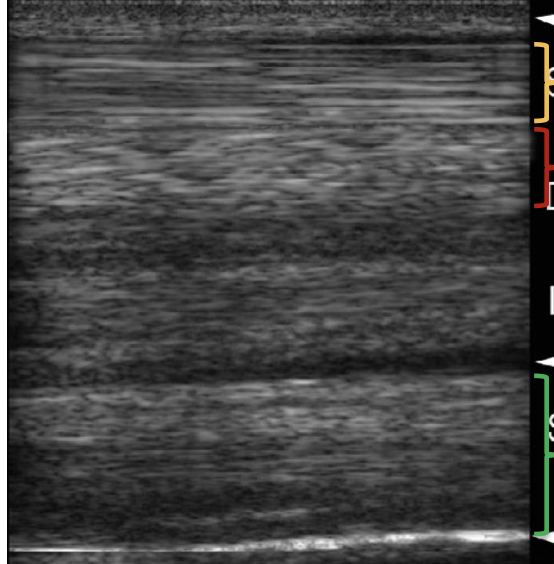
what structure is indicated by the red bracket?
DDFT
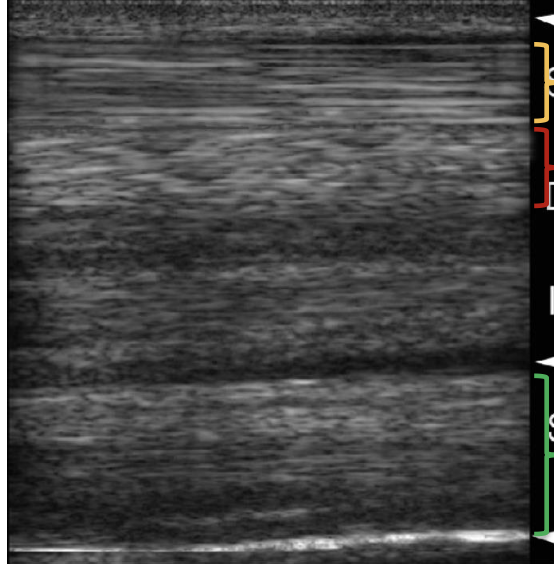
what structure is indicated by the yellow bracket?
SDFT
how may the suspensory ligament in adult and older horses appear on a longitudinal scan?
have a thinner or less marked striation at the origin and proximal body
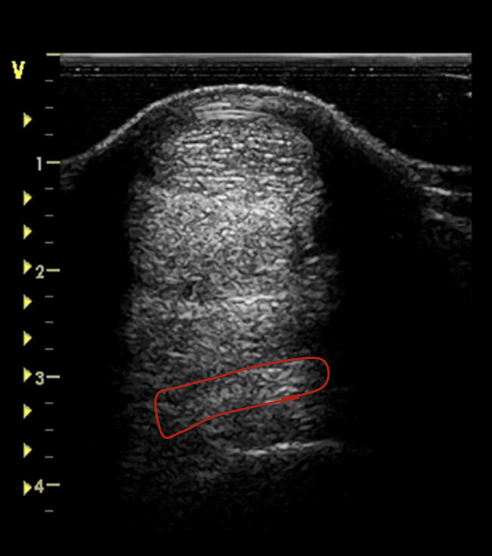
what is the red circling?
suspensory ligament at proximal MC 3
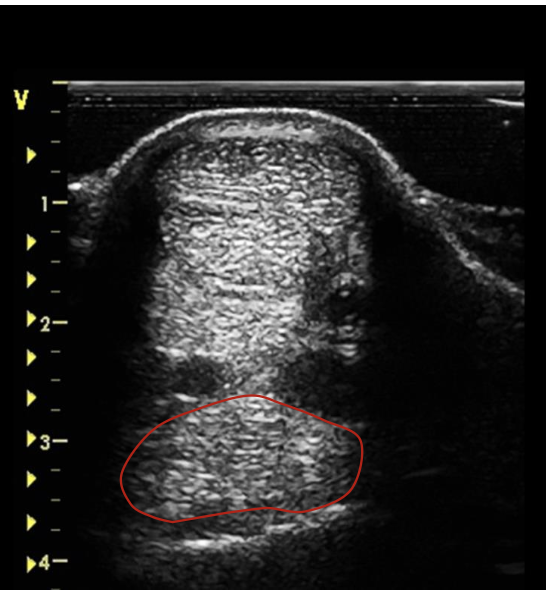
what is the red circling?
suspensory ligament at the mid MC 3
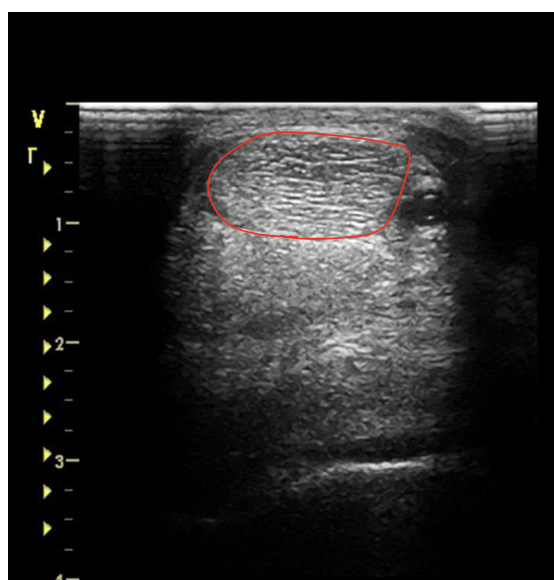
what is the red circling?
SDFT just below the carpal joint
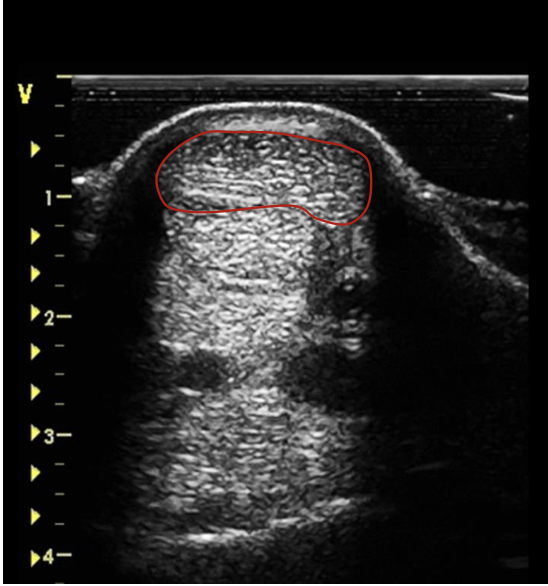
what is the red circling?
SDFT at the mid MC 3
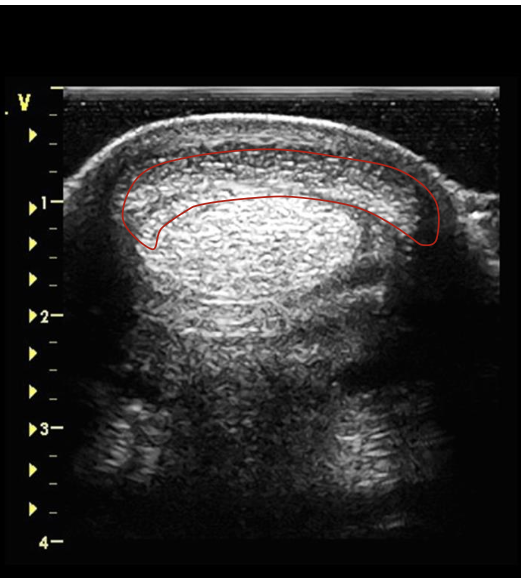
what is the red circling?
SDFT at the distal MC 3
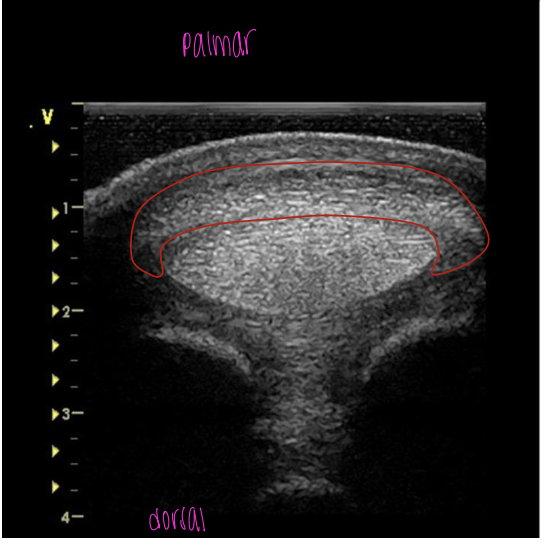
what is the red circling?
SDFT at proximal fetlock joint
where does the DDFT start on a transverse scan?
dorsolateral to the SDFT
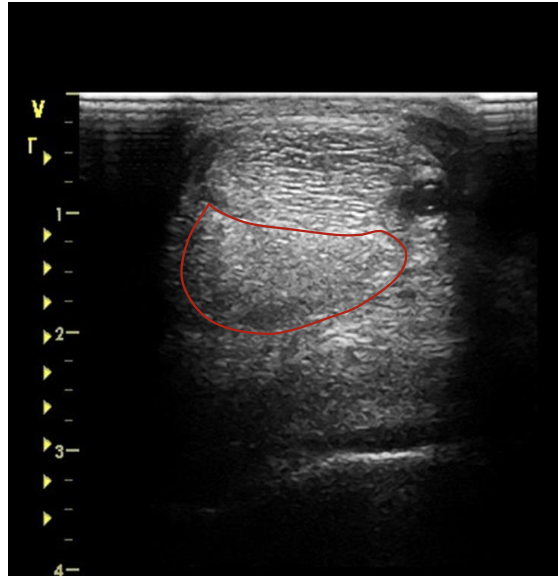
what is the red circling?
DDFT just below the carpal joint
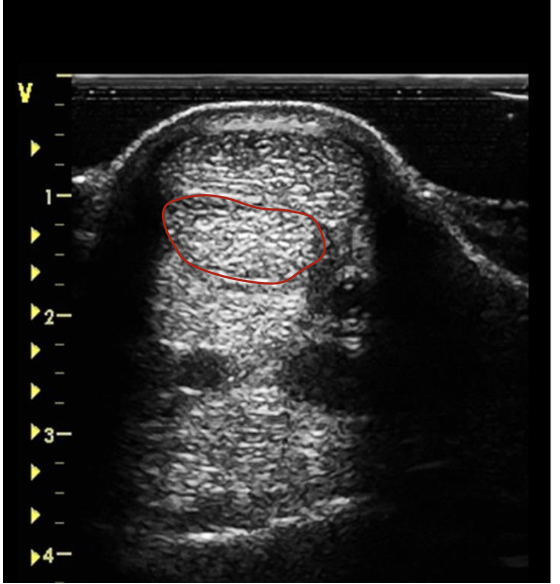
what is the red circling?
DDFT mid MC 3
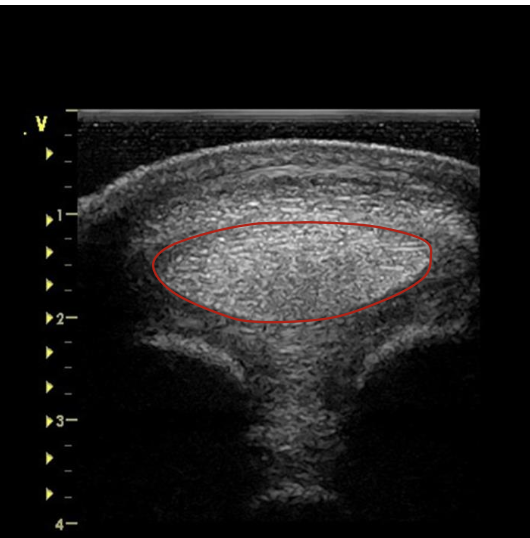
what is the red circling?
DDFT at proximal fetlock joint
what are the portions of the suspensory ligament on a transverse scan?
proximal origin
body
lateral and medial branches
how does the suspensory ligament appear in younger horses?
mottled, hypoechoic appearance
how is the suspensory ligament appearing at every portion?
bilaterally symmetrical at any level
how does the suspensory ligament appear at the origin and body on transverse scan?
rectangular in cross-section
body is coarser, more heterogenous, and less echogenic than tendons
how do the medial and lateral branches of the suspensory ligament appear on transverse scan?
both initially start as oval but then become tear drop as the move distally