CHEM UNIT 3 AOS 2 - Collision theory
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
State collision theory
Particles must collide to have a chance to react
Particles must collide with sufficient energy to break the bonds in the reactants
Particles must collide in the correct position or orientation
Activation energy
The minimum amount of energy required to break the bonds of the reactants and start the reaction
What is reaction rate dependent on?
Activation energy → when the energy of a collision is greater than or equal to the activation energy, a reaction can happen
What are the 4 factors that affect rate of reaction? (SCaT Cat)
Increase surface area (solids)
Increase concentration (aqueous)
Increase temperature (all)
Add a catalyst (all)
Increasing concentration
Increasing conc of a substance increases the number of reactant particles in a given volume
This increases the frequency of collisions and therefore the number of successful collisions in a given time
Increasing pressure
Increasing the pressure of a substance increases the number of reactant particles in a given volume
This increases the frequency of collisions and therefore increases the number of successful collisions in a given time
Increasing surface area of a solid
Only particles on the surface of a solid can participate in the reaction
Increasing surface area increases the number of particles on the surface
This increases the frequency of collisions and therefore the number of successful collisions in a given time
Increasing the temperature
Increasing the temperature increases the average kinetic energy of the reactant particles and thus their average speed
This increases the frequency of collisions and therefore increases the number of successful collisions in a given time
However, more importantly, it also increases the proportion of particles that have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy, increasing the number of successful collisions
What do catalysts do?
Provide an alternative reaction pathway which reduces the overall activation energy
Adding a catalyst
Catalysts provide an alternative pathway by lowering the activation energy of the reaction
This increases the proportion of particles that have sufficient energy to overcome the activation energy, increasing the number of successful collisions
What are the types of catalysts?
Homogenous and heterogenous
What is homogenous
Same physical state as the reactants and products of the reaction
What is heterogenous
Different physical state as the reactants and products of a reaction
What physical state would be most successful for catalysts and why?
Sponge like solid or powdered solids because they have a high surface energy such that the reactants adsorb to the surface which causes the bonds in the reactants to break
Why do chemist prefer heterogenous catalysts?
Easier to separate from the products
Easier to reuse
Able to use at high temps
What is rate of reaction?
The change in concentration of a reactant or product per unit time
Lists methods of measuring rate
Mass of solid formed
Volume of gas formed
Decrease in mass of container due to gas evolving
pH
Temperature
How would I measure how much gas was produced?
Using a gas syringe connected to a conical flask
What does it mean when no more gas is produced in the reaction?
The reaction has come to an end as one reactant has been exhausted (limiting reactant)
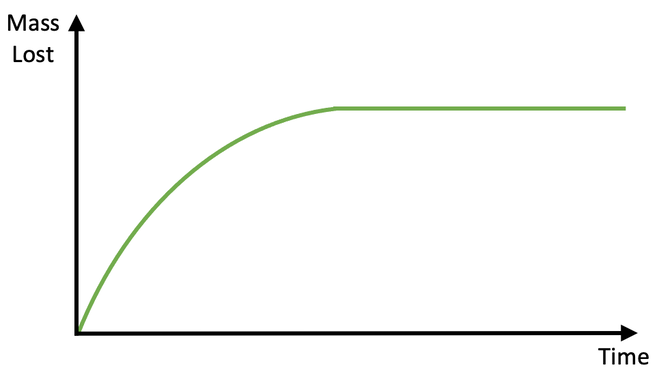
How do I read this graph?
Start of the graph is when the reaction rate is the fastest as the concentration of the reactants is highest
Rate decreases overtime as concentration of reactants decrease
Graph plateaus as reactants are exhausted and the reaction comes to an end
How do I measure reaction rate from the production of a precipitate?
Recording the time taken for the solution to become cloudy
What does a reversible reaction mean?
A reaction can occur in both the forward and reverse directions
Why is it bad that some reactions dont reach completion?
Consequences for industry
Having large amounts of unreacted chemicals is expensive
What is yield?
The extent of the conversion of reactants into products
Define system
The chemical reaction
Define surroundings
Everything outside of the system that can exchange energy and/or matter with the system
Q > K
System shifts to the left to achieve equilibrium → more reactants are formed
Q < K
System shifts to the right to achieve equilibrium → more products are formed
Q = K
System is at equilibrium
What affects the value of K?
Temperature
What is Le Chateliers principle?
If an equilibrium system is subjected to a change, the system will adjust itself to partially oppose the effect of the change
What happens when pressure in increased?
Le Chateliers principle states that the system will adjust itself to partially oppose the change
To oppose the change, pressure must decrease
The position of equilibrium will move in the direction of the fewest gas particles
What happens when pressure is decreased?
Le Chateliers principle states that the system will adjust itself to partially oppose the change
To oppose the change, pressure must increase
The position of equilibrium will move in the direction of the most gas particles
What if there are equal numbers of reactant and product particles?
Change in pressure will not shift the position of equilibrium
What happens if I add an inert gas?
Increases pressure
No effect on position on equilibrium or K
What happens if I dilute my solution with water?
All species will decrease in concentration
To increase concentration, the system will shift in the direction of the most particles
What happens if I add a catalyst?
No change in position of equilibrium or K
What happens when I increase the temperature of an exothermic reaction?
K decreases
What happens when I increase the temperature of an endothermic reaction?
K increases
Value of K (Less than 10^-4)
Negligible reaction occurs - high concentration of reactants and low concentration of products
Value of K (Between 10^-4 and 10^4)
Extent of reaction is significant - Significant concentration of reactants and products
Value of K (Greater than 10^4)
Almost a complete reaction - high concentration of products and low concentration of reactants