Med Surg Week 3 Diagnostic Exams
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
What are the 6 types of diagnostics that we talked about?
Blood work, MRI, CAT scans, cardiac exams, urine & stool, scopes
What tube is a CBC done in?
Use a lavender top.
What is CBC? What is included? What does it tell you?
Complete blood count
Hgb, Hct, WBC, RBC, platelets, MCV (mean corpuscular volume which is the average size of RBC)
Can tell you about general health or diagnose things like anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia or cytosis (high)
Can monitor tx that affect blood cell counts
What color are chemistries?
Light green top
What’s a BMP? What’s included?
Basic metabolic panel
Na, K, Cl, CO2, BUN, Cr, Glucose.
BUN and Cr for assessing kidney function.
What’s CMP? What’s included? Why choose this over BMP?
Complete metabolic panel
Na, K, Cl, BUN, Cr, glucose, CO2 AND..
Liver panels (ALP, ALT, AST), Ca, total protein, albumin, bilirubin (liver)
CMP gives more information. Why not do the whole thing?
Other chemistry tests?
Troponin, BNP (both cardiac related)
What is BNP? What does this lab tell us?
A type of natriuretic peptide. Used to assess HF. If elevated, correlated with HF because more fluid and stretching in the heart causes more BNP to release.
Normal: less than 125 pg/mL
What is troponin? What does this lab tell us?
Troponin is part of muscle. If elevated, means MI. Heart tissue is dying from low blood flow.
Normal: 0 to 0.4
Normally ordered as a series (up to 3 in 24 hrs)
What color are coagulation studies?
Blue top
Some types of coagulation studies?
PT (prothrombin time), aPTT (activated partial thromboplastin time), PT/INR (Prothrombin time/international normalized ratio)
What is PT?
Prothrombin Time
Measures time it takes for body to clot when there’s damage that came from outside the body (extrinsic)
What is aPTT?
activated partial thromboplastin time
Measures time it takes for body to clot when damage comes from inside the body (intrinsic)
Used to assess and monitor heparin therapy (done in hospital or subacute)
What’s PT-INR
Prothrombin time/international normalized ratio
Used to monitor/assess warfarin therapy. See if they are appropriately anticoagulated (not too much and not too little)
What is risk of being too anticoagulated?
Excess bleeding, hemorrhage, internal bleeding
What color top is blood bank tests?
Pink, red, or lavender too
What does blood bank tests tell you?
Blood type (ABO) Important for transfusions
Rh factor (positive or negative, also important for transfusions and pregnancies)
Also scans for other antibodies
Usually send 2 tubes
When do you do blood bank tests?
Done before surgery if you suspect pt will lose a lot of blood. Done when pt needs blood.
How long are blood bank tests valid for?
3 days
What color tops are special blood work tests? Example of special test?
Silver/gray. Lactic Acid
What’s a lactic acid test for?
See if pt in acidosis or sepsis (seen in ED, ICU, Med Surg floors)
What condition does the lactic acid need to be in?
Must be on ICE. Must be processed quickly. If stored at room temperature, the value will appear higher than reality.
How long is lactic acid stable on ice? How fast do you need to get it to the lab to be processed?
Stable for 90 minutes on ice.
Get to lab within 15 min.
What are blood cultures for?
Seeing if the blood is infected with bacteria, fungal, viral.
Take blood from 2 different sites to ensure it’s not just the line that’s infected.
One vial for aerobic, another for anaerobic.
How long can it take for bacteria to appear in the blood culture?
Up to 3 days. Bacteremia can lead to sepsis.
How long can it take for fungi to appear in blood culture?
30 days
What’s MRI? When do you use?
Magnetic resonance imaging
Uses a large magnet and radio waves to make a detailed 3d image
Use when looking at soft tissues and you want more detail that you can’t get with CT.
Good for brain, spinal cord, heart, breasts, tumors,CAD, breast cancer screen
Advantages of MRI?
Better detailed picture inside the body
Easier to see hard-to-see pathologies like cancer (prostate, uterine, liver, metastasized)
Doesn’t use radiation
Non invasive
Contrast really helpful to see vessels
Disadvantages of MRI?
Claustrophobic
Takes longer (stay still for 20-60 min)
NO METAL
Contrast has s/e of n, dizzy, itchy
Nurse considerations for MRI
Allergies to contrast
Anxiolytics if claustrophibic
Kidney function assessment (because of contrast)
Provide education
Hydration (with use of contrast to flush it out of body and kidneys)
What’s a CT Scan?
Computed Tomography Scan. Uses X-rays to take snapshots and then forms an image by stitching them together.
Can use with or without contrast
When to use CT scan?
Assessing muscle, bone, vascular disorders
What are the specialized CT?
CTPA (pulmonary arteries). Can use this to help remove PE.
CTCA (coronary arteries)
Can visualize the blocks/thrombus. Especially with contrast
Advantages of CT?
Shorter compared to MRI
Gives general picture (tissues, organs, skeletal structures)
Disadvantages of CT
Uses X-ray radiation
May not get a clear/detailed picture
Nursing Considerations for CT
Provide Education
May need anxiolytic for claustrophobic pt
Check for allergies bc contrast
Assess kidney function bc contrast
Hydration bc of contrast
ECG/EKG
Electrocardiogram
What does ECG do?
Measure electrical activity of heart
Diagnose MI, HF, dysrhythmias
Can monitor heart continuously if needed
12 leads means 12 patches. Gives 12 different views of the heart.
Also 5 lead ECG available.
What are the two cardiac stress tests?
Exercise stress test and nuclear stres test
Exercise stress test
Noninvasive
Seeing how well the heart works when under stress (exercice)
Monitor the pt with leads as they exercise. Monitor HR and BP too.
Used for CAD, dysrhythmia, damaged muscle
If pt has chest pain while doing exercise stress test, what do you do?
Stop the test. Means they’re having ischemia from poor perfusion.
Can you do exercise stress test even if pt is immobile?
Yes, they can take medication that mimics stress/exercise.
Nuclear cardiac stress test
Do this after exercise one if more detailed information needed. Or do this if can’t exercise.
Put radioactive tracer in the blood and then take images before and after exercise.
Visualize blood flow and muscle health.
Urine toxicology test
Tests the urine for drugs and chemicals like:
alcohol, amphetamine, barbiturates, benzo, cocaine, marijuana, opioids
Rx drugs, illegal drugs, etc.
Can be screened for OD, dependency, drug treatment, employment, athletic performance enhancements
Must be clean catch (wash hands, wipe genitalia, void in toilet first and then cup)
Test results ready in 24 hrs.
Can use urine dip stick. Helpful for detecting UTI
Urine culture test
Must be clean catch because high risk of contamination
Checking for bacteria or microbes. If someone has a UTI, we can figure out what abx to use
Can give a broad spectrum abx first to treat common pathogen (e. coli), then do new abx if it didn’t work.
Incubate the sample at body temp for 24 hours.
No growth? no microbes = negative.
Yes growth? further evaluation for which specific microbe, which abx to choose = positive.
Symptoms do not automatically mean UTI
24 hour urine collection
Discard first void
Place larger container in ice or fridge. (void into one container and pour into the larger one). Need to mark/document the time started
Tests for: creatine clearance AND proteins (testing and diagnosing kidney function)
Can add preservative to the urine collection
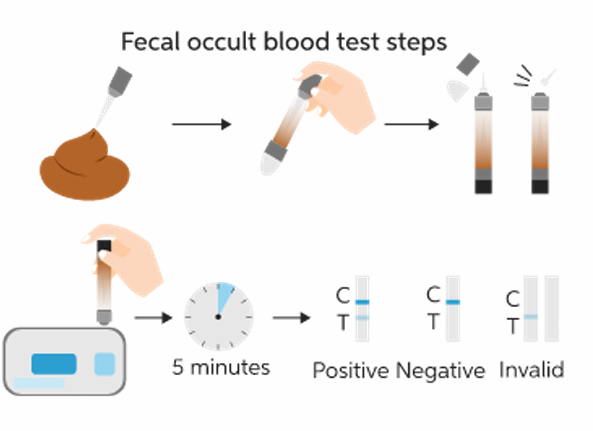
Fecal occult blood test
Tests for hidden blood in stool. 2 methods.
guaiac paper: collect sample and smear guaiac paper on it. If changes color, means there’s blood.
Do if you have unexplained anemia, weight loss, screen colorectal cancer (but guaranteed cancer)
fecal immunochemical test: quicker (5 min), you have a kit like a COVID test. Combine sample with liquid in vile. There’s a control and Test line. If Test line positive - not guaranteed cancer. Needs follow up.
Endoscopy and nursing considerations
Flexible tube with camera goes into mouth up to duodenum.
Allows you to see esophagus, stomach, duodenum.
Diagnose and treat GI issues, do biopsy, remove tumors, stop bleeds.
Use if pt has pain, bloating, hard to swallow, GERD, anemia, bleeding in upper GI.
Pt does need to recover after
Nursing considerations:
education
verify consent (MD must sign. RN cannot sign, can witness).
diet restrictions (NPO for several hrs before procedure)
allergies (meds given to sedate bc invasive, laxatives or enema)
Sore throat or bloating after procedure
EGD
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy aka upper endoscopy.
Esophagus, stomach, duodenum
Colonoscopy and nursing considerations
Nursing considerations:
education (will be passing gas after it’s done)
verify consent
Dietary restrictions (NPO)
Bowel prep (a lot of laxatives or enema)
Allergies (meds for sedation).
Recommended age for colonoscopy now 45 (used to be 50). Trying to identify and diagnose earlier
Should get screened earlier than others if: have fam hx, IBD, Crohn’s, UC, genetic things, lynch syndrome.
Order if pt has abnormal fecal occult test.
Flexible tube with light and camera to visualize the lining. May have to remove stool or inject air (farting).
If sedated, don’t drive or operate heavy machinery for 24 hrs.
Possible cramping/gas. Will have to recover after procedure.