Nucleic Acids
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
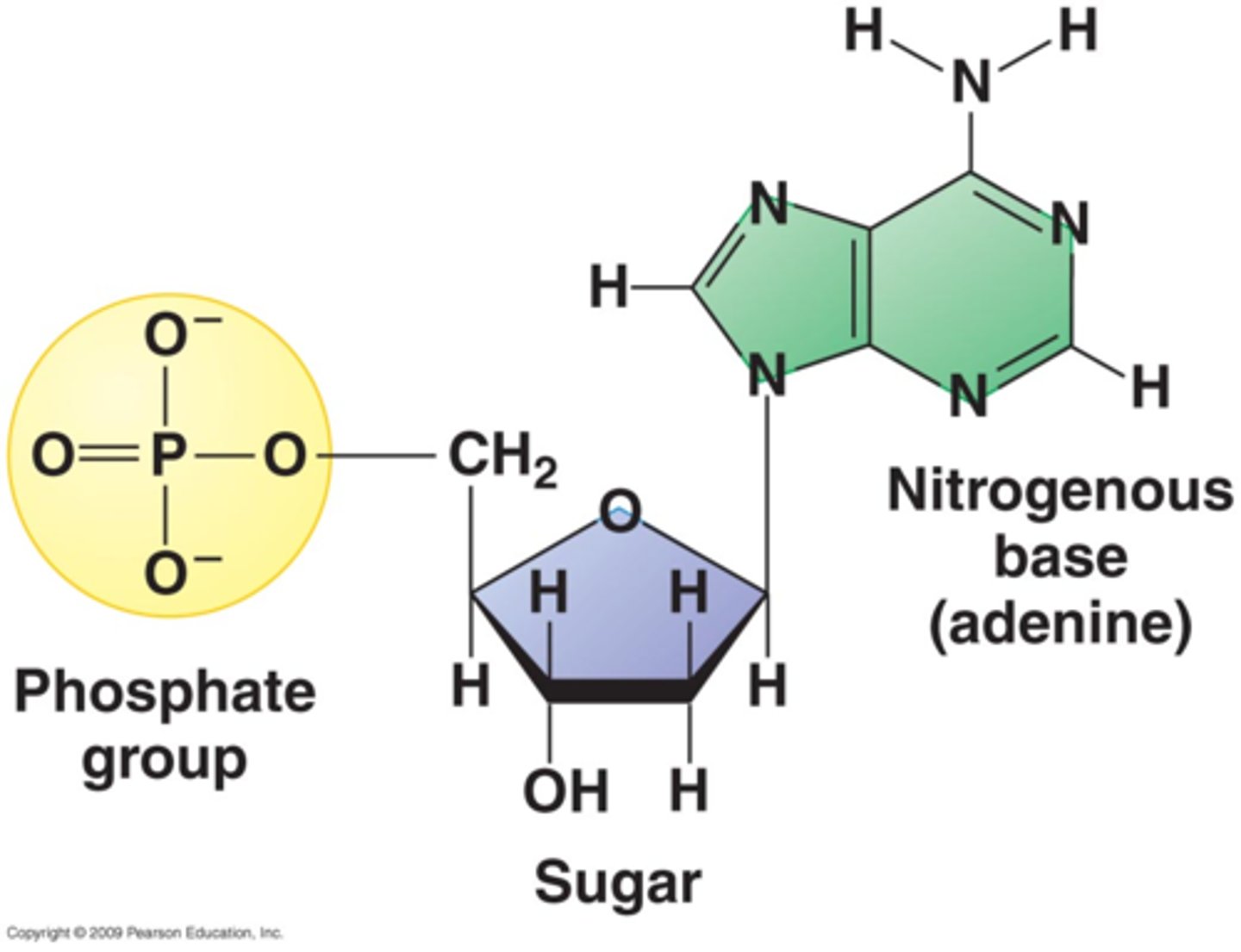
Draw a nucleotide and label the three main parts.
Recognize pyrimidine and purine nucleotides.
Purine: A & G
Pyrimidine: C & T
Explain why the pairing of one purine with one pyrimidine is important to the shape of a DNA molecule.
It was very important that the DNA matched up one pyrimidine with one purine to keep the distance between the deoxyribose backbones constant at a total of three carbon rings between them.
Define "complementary base pairing."
A base in one strand can from a specific hydrogen bonds with another base in the opposite strand across from it
Explain the difference between a nucleotide and a "base."
- Base implies one of the nitrogenous bases( adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine).
- One nucleotide is composed of a base, a deoxyribose sugar, and a phosphate.
- There are four types of nucleotides because there are four types of bases.
Explain how the structure of DNA is important to its function as an information storage molecule.
Genetic information is stored within the chemical structure of the molecule DNA. The molecule consists of:
- Two backbones, which spiral around each other in the well-known double helix formation
- Strings of four chemicals, called "bases", running along the backbones
- Bridges between bases on opposite backbones, called "base pairs"
List three structural differences between DNA and RNA.
1. DNA has the bases adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine; RNA has the bases adenine, uracil, guanine, cytosine.
2. DNA has the sugar deoxyribose; RNA has the sugar ribose.
3. DNA is double stranded; RNA is single stranded.
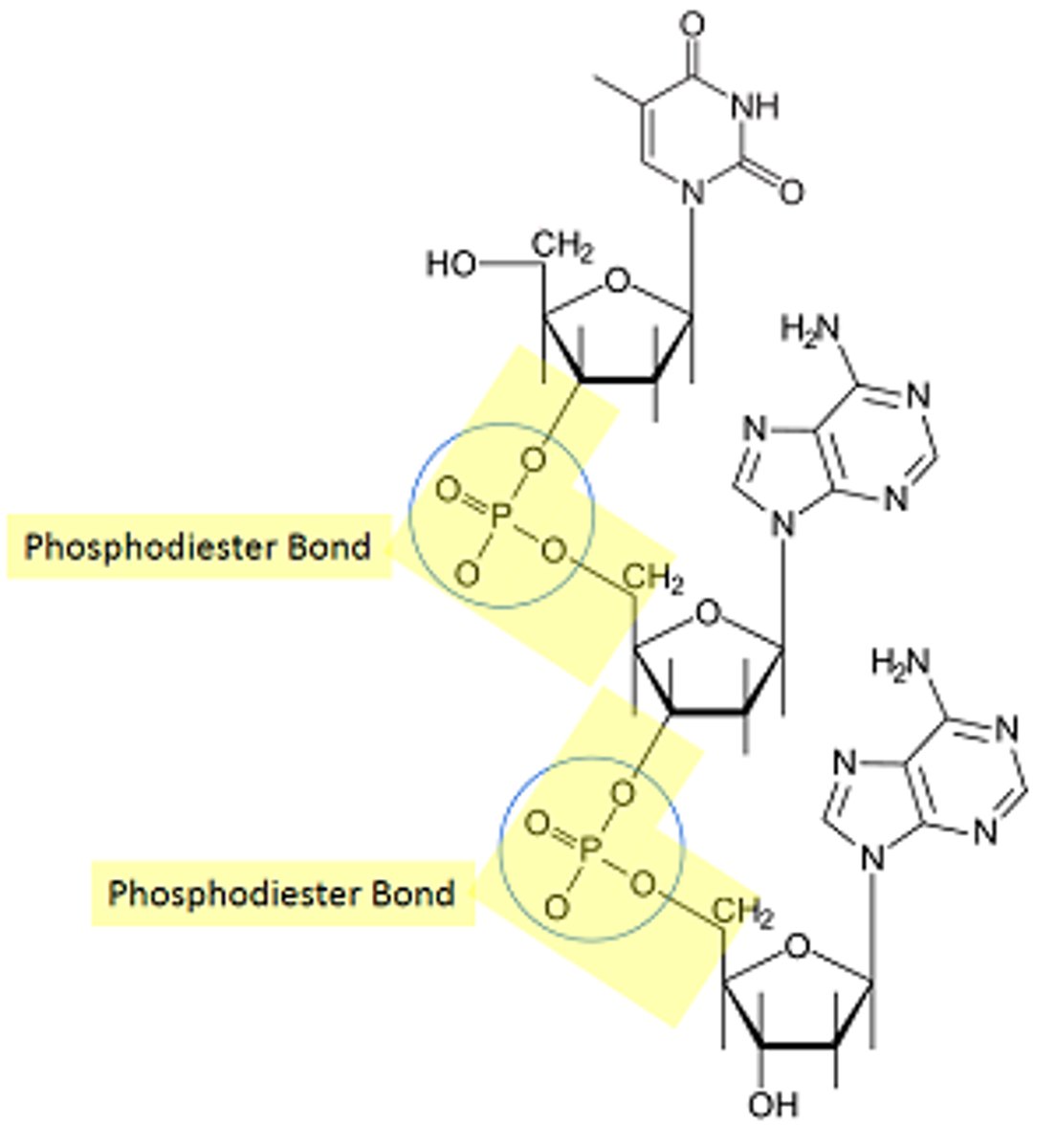
Describe the importance of phosphodiester bonds and hydrogen bonds to the structure of DNA and RNA molecules.
Hydrogen: Internal and external hydrogen bonds stabilize the DNA molecule. The two strands of DNA stay together by H bonds that occur between complementary nucleotide base pairs
Phosphodiester bond: A bond between nucleotides in RNA and DNA molecules.
Calculate the percentage of each of the nucleotides in a DNA molecule if the percentage of one of the nucleotides is known.
If a segment of DNA contains 28 percent T nucleotides, then the percentage of A nucleotides in that segment will be 28 percent.
Describe how a phosphodiester bond is formed between two nucleotides.
A phosphate group linked to two adjacent nucleotides via phosphoester bonds.
Phosphate group attached by phosphoester bond to 5' carbon of one nucleotide becomes linked to a second phosphoester bond to the 3' carbon of the next nucleotide.
- Called a 3'5' phosphodiester bridge.
Predict the effect of increasing temperature on the structure of DNA and RNAmolecules.
As temp increases DNA unwinds, Hydrogen bonds break, and turned into single strands (denaturation)
Explain how the structure of DNA makes it possible for a cell to make exact copies of its chromosomes quickly and with very few errors.
- Before a cell divides, its DNA is replicated (duplicated.) Because the two strands of a DNA molecule have complementary base pairs, the nucleotide sequence of each strand automatically supplies the information needed to produce its partner.
- If the two strands of a DNA molecule are separated, each can be used as a pattern or template to produce a complementary strand. Each template and its new complement together then form a new DNA double helix, identical to the original.
Explain why the two strands in a DNA molecule are described as antiparallel to each other.
To form a stable double helix the strands nut be antiparallel (running in different directions 3' to 5' and 5' to 3') as well as complementary. Each base in one strand can form specific hydrogen bonds with the other strand directly across from it.