Gr.9 Geography Unit 4 - Population Test review
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
population distribution
The way something is spread out or arranged over a geographic area.
demography
statistical characteristics of human populations such as age or income
population density
How many people live in a specific geographical area
natural increase & net migration
natural increase- The difference between births and deaths in a population
net migration- the difference in the number of people immigrating or migrating
Different transportation types
Terminal facility- walking, airports
Public transportation- bus, railways
Private transportation- automobiles, bicycles
refugee
someone who has been forced to flee their country due to war, violence e.t.c
Immigrant
A person who has come to another country to live permanently.
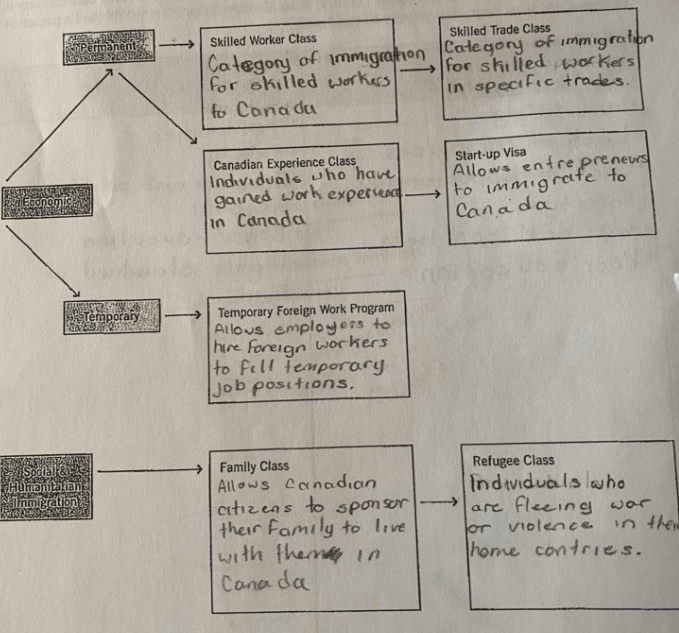
Push and pull factors
reasons which a person should or should not move to another country or stay on their own
urban & rural
urban - areas are areas with a large population
rural - areas with lower population density
immigration & interprovincial migration
moving to a country to live permanently
moving from another province or territory to another.
urban function & urban land use
the different functions and uses of land in an urban area
Residential – 40%, Transportation – 32%, Institutional – 10%, Open space – 7%, Industrial – 6%, Commercial – 5%
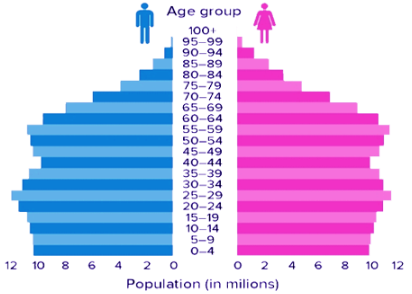
population pyramid
graphical illustration of the distribution of a population by age groups and sex
categories for immigrants to earn points
Language skills points,
Education points
Work experience points
Age points
Arranged employment in Canada points
Adaptability points
settlement patterns
distribution of human activity across an area :
concentrated: population which lives close together
dispersed: population which is spread out,
linear: a group of buildings in a long line
survey system
surveying and collecting data on land used for planning
3 land seperation systems
long lot: long narrow pieces of property
concession system: land comprising a row of lots that spanned the entire length of a new township
section system: a system separating area units
urbanization
the increase of population in an area
multiplier effect:
an increase in economic activity resulting the the growth of services and population
threshold population
the minimum number of people or land before a service or good can be provided
diversified urban center
town or city containing a variety of basic urban functions
land use
different ways land is used
(Industrial, residential,commercial,transportation,recreation, open space)
3 kinds of goods
high-order good: items not frequently bought (e.x cars, appliances)
middle-order good: less frequently bought items (e.x clothing)
low-order good: frequently bought goods (e.x groceries)
residential density
number of residential units within an area
winter-city concept
cities experiencing cold winters which encourage certain system, transportation, buildings, and projects
central business district (CBD)
the commercial and businesses center of a city or town
urban sprawl
the spreading of urban development in a less populated or underdeveloped area
arterial road
high capacity road which carries long distance flows between important centers of activity
rural-urban fringe
area at the very edge of a city right beside countryside
3 kinds of industries
primary industries: industries which harvest and obtain raw materials for manufacturing.
secondary industries: industries which manufacture goods from raw materials.
tertiary industries: industries which provide services and administration for goods.
Secondary Industries location Factors
raw material
water
labor
capital
power
transport
market
raw material
substances available naturally which are processed to obtain finished goods
manufacturing
any industry which makes raw materials into finished goods usually carried out by labor or machinery
what are basic and non basic industries
basic industries: bring money into the economy (Car making factory, consumer goods)
non-basic industries: recycles money in the economy (Hospitals, diners, service companies)
extractive industries
industries involved with extracting raw materials. (Oil, minerals)
goods
produced objects which demands exist for