History Taking Exam (Lectures)
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
What is a poor historian?
Patient response that has led to an unsatisfactory interview (blame on the patient)
What is the most important source of diagnostic information?
The clinical history
Does the patient or provider bear the most "historian" responsibility
Provider
When conducting a patient visit what are considered the units of observation and quantities of measurement?
- signs & symptoms = observation
-words & numbers = measurement
What does it mean to have objectivity during patient interactions?
Removing your own beliefs, prejudices & preconceptions; eliminating bias
- w/ accuracy & validity
When actively listening you should separate the patients theory from ?
their symptoms
What is precision in a medical interview?
Characteristic relating to the distribution of observations around the "real value"
! precise words have diagnostic value !
What is an example of a symptom being very sensitive but not specific?
Sensitive - most patient with pneumonia have a cough
Not specific bc/ many disease states have a cough
What is an example of a symptom being relatively specific but not sensitive?
Specific - nocturnal mid-epigastric pain relieved by eating secondary to a duodenal ulcer
Not sensitive bc/ many patients with duodenal ulcer don't have that symptom
A complete symptom complex should be?
Objective
Precise
Sensitive & Specific
**basis for diagnosis and therapy**
How can a thorough history advance your differential diagnoses (aka hypotheses) ?
It should help rule out, support, or confirm w/ physical exam/work-up
Sensitivity & specificity are irrelevant if you (the instrument) lack what ?
Objectivity & precision
- these also help reduce false + and false - histories from the patient
Why is reliability ( aka different observers obtaining same results) sometimes challenging ?
Patients learn to "package" a story with various symptoms (embellish, omit, forget, & recall new info), and have their own beliefs about their illness
A patients primary symptom data enhances what aspect of history taking?
Objectivity
When obtaining the the chief complaint (CC) what kind of questions should u be asking?
Open-ended
What is an Iatrotropic stimulus (give common examples)
Why the patient decided to seek medical attention. -symptom worsening, anxiety about symptoms, new physical finding, or need for a routine exam
When u ask about the HPI you should move from open-ended questions to what kind of questions?
Direct and specific questions (who,what, when, how...) this will achieve precision in symptom description
What do we use to collect the HPI?
OPPQRST
Once the hypothesis is well established (via open-ended questions) what type of questions build the case for a particular diagnosis?
Close-ended to provide detail
Should the interview contain more open-ended or closed-ended questions?
OPEN :)
Type of questions to AVOID :
- leading Q's
- rapid-fire Q's
- medical jargon Q's
Why would you need to use confrontation w/ a patient during their history?
To clarify something they said that was contradictory
What are reticent patients and how can u overcome the challenge they pose?
Patients who say little to nothing
-try rearranging your open-ended question
What are rambling patients and how can u overcome the challenge they pose?
Tell u irrelevant info
-redirect them to their actual concern via your summation
What are vague patients and how can u overcome the challenge they pose?
Difficult to figure out what they're describing
-offer them useful descriptors
What should a patients past medical history (PMHx) disclose to you?
The total picture of their health/illnesses, behavior & lifestyle
If someone says they have no other medical conditions what should you ask to confirm?
"What medications do you take daily" ?
What should you ALWAYS ask female patients when taking their PMHx?
Gynecologic/obstetric history
Do you document the LNMP/LKMP as the first or last day of period?
First day !
How do you document Gravid status?
G_P_A_
G - gravida ( # of pregnancies)
P - para ( # of births)
A - premature terminations
Explain what it means if a women is "G2P2" ?
She has had 2 pregnancies and 2 deliveries after gestational period of 24 weeks
How is smoking recorded?
pack years!
Calculate the pack years of a person who has smoked 2 packs a day for 3 years
6 pack years
What does asking about patients safety measures evaluate?
Their risk-taking behavior
How many generations of family history do u need to obtain?
At least 3
What can use as identifying data to keep track of patients family history when documenting?
A genogram which is basically a family tree (pedigree) labeling each person w/ disease states or deceased
The ROS is complaint-specific UNLESS…
You're doing a full head to toe exam (or ur doing our ROS exam)
During ROS, what order do you document pertinent positives and negatives?
First list all pertinent positives, followed by the negatives (paragraph form)
What are the objectives/goals of the ROS?
To identify active problems not yet discussed, and associate additional symptoms with the current illness
What's the general format of an oral presentation
1. State patient name, age, race, gender
2.state chief complaint with OPPQRST
3. Give further descriptive findings
(pertinent +/- & PMHx)
What are the 7 standards of critical thinking?
Clarity
Accuracy
Precision
Relevance
Depth
Breadth
Logic
What's an example of a CYA order?
cover your a$$
Tell patient to go to the ER if their signs or symptoms worsen (be specific with signs & symptoms)
What's the purpose of a SOAP note in an ambulatory setting? An in-patient setting?
Ambulatory - episodic or problem-specific visits
In-patient - document patient progress/condition
* rarely used to record entire MH or new patient visit
What should you AVOID in a problem focused progress note?
Confusion
Redundancy
Omission of info
What does SOAP stand for
Subjective
Objective
Assessment
Plan
Subjective (SOAP)
a patient's description of the problem or issue
-must document if a caregiver, parent, etc is the one giving the info
What percent of the assessment is based on history alone?
75%
What is included in the subjective portion of a SOAP note?
CC, HPI, pertinent ROS, fam, social, psych, cultural, & specialized hx relating to the CC
Objective (SOAP)
Vital signs, physical exam, lab findings, and procedures or interventions
Short hand for documenting lab values
XD
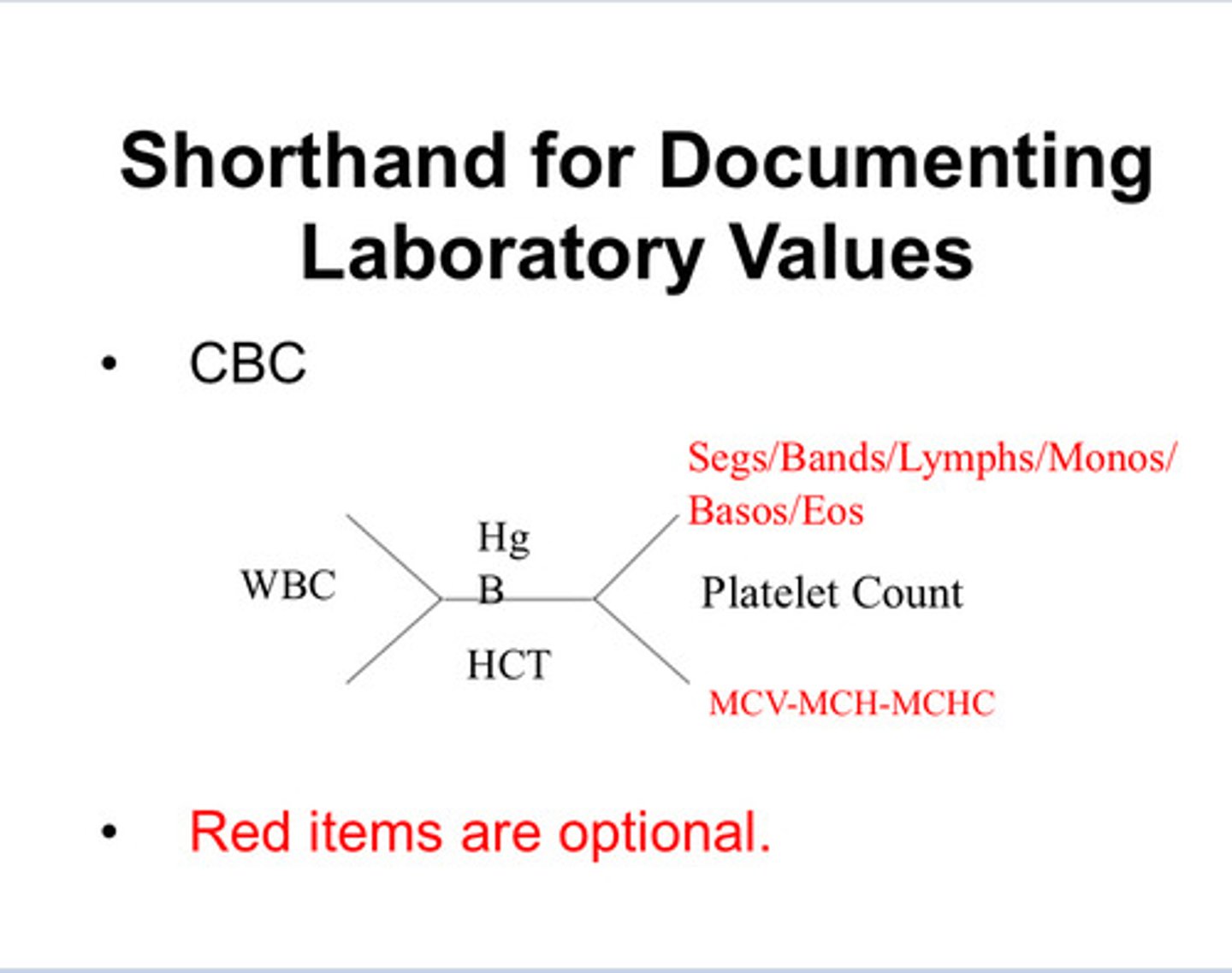
Primary Assessment (SOAP)
Diagnosis (what you think it is)
Differential diagnosis (DDx)
List of possible conditions not yet ruled out
-list from most likely —> least likely
What do you do if unsure about the diagnosis?
Use a presumptive diagnosis such as:
symptom, complaint, condition, problem
** do NOT use rule out as dx**
VINDICATE (universal DDx)
Vascular
Inflammatory
Neoplasm
Degenerative & Deficiency
Intoxication
Congenital
Autoimmune & Allergic
Trauma
Endocrine
Secondary Assessment (SOAP)
Listing all additional issues noted (elevated BP, obesity, hepatomegaly, etc)
When there is no certain diagnosis for a patient presenting with chest pain how should you document it?
chest pain… if u used the medical term “angina” it’d insinuate you made that specific diagnosis
ICD-XX-CM coding uses
Determines level of reimbursement, forecast healthcare needs, evaluate facilities & services
What codes are used in conjunction during electronic billing process?
ICD-XX-CM and CPT (procedural) codes
CPT cat 1 (procedural & medical practices) 6 sections
1. Eval & management
2. Anesthesiology
3. Surgery
4. Radiology
5. Path & lab
6. Medicine
Plan (SOAP)
tests, referrals, pharm therapy, pt edu, f/u instructions
What is the "cornerstone" of PA profession ?
Patient education
What must you document you provided to the patient in regards to patient education?
-medical conditions/illness or dx
-preventative measures/risk factors
-f/u info
What could cause u legal issues/ lawsuits ?
-Not documenting on a symmetrical body part consistently in the hx and PE
-not f/u on abnormal labs/studies
-coding for reimbursement only (fraud !)
INFO NOT RECORDED =
INFO LOST (didn't happen!)
Dependent & Demanding (DD) patients
-Initially appear compliant
-impresses the urgency of their request
-if their need is not met they withdrawal and blame u
** SUS DD if they make u feel that ur the only one who has ever listened
How to manage a dependent & demanding patient
-specify limits
-avoid making hard-to-keep promises
-emphasize their responsibility
-remind them of ur limited time
-don't take credit for remission (blame for relapse)
Orderly & Controlled patients
-punctual, compliant, and meticulous
-sickness threatens loss of control
-usually take notes or has diary to share findings
-important to give them autonomy and + feedback
-often similar personality to provider
How to manage orderly and controlled patients
-take an orderly & systematic approach to interview
-explain EVERYTHING and don't leave loose ends
-summarize often and take notes
-if u don't know, say so and describe a plan for finding out
Dramatic patients
-may charm, fascinate, frustrate, and anger u
-attention hog & resent ur other duties/patients
-personal inquiries about your social life, over the top compliments
What are other ways to describe a dramatic patient
histrionic, hysterical, manipulative, seductive
How to manage a dramatic patient
-remain calm, gentle, and firm
-use frequent summaries to remain in control
-remain descriptive not judgmental
-identify patients strengths & feed them back
Long suffering masochist patients
-reject help ( hx of continual suffering, disappointment, and adversity)
-disregard their own needs to help others
-no tx will help them (when one symptom disappears another will pop up)
-doesn't respond to reassurance, optimism, or hope
How to manage long suffering masochist patient
-avoid being overly optimistic
-don't focus on their strengths
-avoid insensitive or patronizing remarks
Guarded, paranoid patients
-white coat syndrome
-often talk about mistakes of past HC professionals -blame their problem on others
-become anxious, suspicious, and quarrelsome under stress (makes u feel guilty by association)
How to manage guarded or paranoid patients
-remain friendly & courteous
-explain dx and plan for tx clearly
-identify ur role and limitations
-acknowledge their suspicious attitude
-clarify ur understanding while indicating u don't necessarily agree
Superior style patients
-very self confident, smug, vain, grandiose
-think they're entitled to the best of everything
-demand "senior" clinician
-try to control the visit
-respond with anger and hostility
How do u deal with a superior or entitled style patient?
Acknowledge their POV and avoid arguing back
Somatization
the expression of psychological distress through physical symptoms
How to deal with a patient who somatisizes
-obtain a complete medical history & PE
-avoid vague references
-speak of the body not the mind
-speak in physiologic context when discussing stress/tension
Managing an anxious patient
-be unhurried and calm
-empathize
-be specific and descriptive in your findings & what u expect from the patient
-let them know anxiety is normal in this setting
How to manage an angry patient
-recognize and acknowledge their anger
-acknowledge your error if u made a mistake
-help them recognize ways they can deal with anger-provoking situations
How to manage a depressed patient
-identify or acknowledge the state they're in
-ask ( giving patient floor for open discussion)
-evaluate and stratify their risk for suicide to get them appropriate help
What 2 things are paramount in pediatric population?
Privacy and comfort
Why do we start with open-ended questions in a pediatric exam?
To size up their maturity, behavior, reason for visit, and parental concern
Importance of prenatal visit
-relay important medical info and trust/respect
-lays groundwork for guidance and care of future child
Additional info that should be gathered during infant and toddler visit
-pregnancy complications
-detailed fam hx
-crying/sleeping, bowel and bladder habits
-immunization status
-developmental stages/temperament
What is a pre-verbal child's illness gaged on?
Their interaction! U can gauge the severity of illness- are they running around, laughing, playing? Crying, lethargic?
What can parents provide in a medical interview?
Accuracy and precision
Dealing w/ teens
-Establish trust ( don't take instant BFF approach)
-let them know ur convo is confidential
Avoid yes/no questions in what population?
Peds (mainly teens)
The 5 P's of sexual history taking
Partners (# & gender)
Practices (oral, anal, intercourse)
Past STDs/HIV
Pregnancies (hx and plans)
Protection (use contraceptives?)
CAGE (sus alcohol addiction questionnaire)
Cut down ?
Annoyed w/ other peoples comments?
Guilty?
Eye opener?
* 2 or more +associated w/ addiction*
Rule of thumb for questioning about sensitive topics
Start out general (very open-ended) and then get more specific
Diagnoses having high association with abuse
Pregnancy and somatization disorder
General rule of thumb for delivering news on death and dying
- In-person appointment w/ patient & loved one
-Use simple, clear language; don't leave room for misinterpretation