Chemistry (mr mcdermott)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/20
Earn XP
Last updated 2:21 PM on 1/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
Define first ionisation energy
The energy required when one mole of gaseous
atoms forms one mole of gaseous ions with a single positive charge
atoms forms one mole of gaseous ions with a single positive charge
2
New cards
Show first ionisation energy with hydrogen
H(g) --> H+ + e-
3
New cards
Define second ionisation energy
The energy required when one mole of
gaseous ions with a single positive charge forms one mole of gaseous
ions with a double positive charge
gaseous ions with a single positive charge forms one mole of gaseous
ions with a double positive charge
4
New cards
State the 4 factors affecting ionistion energy
1. Atomic radius
2. Nuclear charge
3. Shielding
4. Electron pair repulsion
2. Nuclear charge
3. Shielding
4. Electron pair repulsion
5
New cards
What happens to ionisation energy across a period?
INCREASES- The nuclear charge increases, causing a greater pull on the electrons and therefore more energy is required to remove electrons. There is a decrease between group2 and 3 as the p shells start to fill
6
New cards
What happens to ionisation energy down a group?
DECREASES- due to the shielding of the outer electrons from the nucleus and so the attraction is weaker and they are more easily removed.
7
New cards
Explain atomic emission spectra
Ground state--> absorb heat and become "excited"--> they then become less excited --> they emit energy in fixed amounts (light)
8
New cards
How does ionisation energy show electron configuration?
From right to left you can see the levels which reflect the shells. This shows with group and period an element is in
9
New cards
State the 4 subshells and how many electrons they contain
s- 2
p-6
d-10
f-14
p-6
d-10
f-14
10
New cards
Define orbital
A region within an atom that can hold up to two electrons with opposite spins
11
New cards
What is the shape of the s and p subshells?
s- spherical
p- dumbbell
p- dumbbell
12
New cards
How do electrons fill subshells?
They fill singly then into pairs with opposite spins ("bus theory")
13
New cards
What are the 2 conditions in subshell filling
1. 4s fills and empties before 3d
2. Cu and Cr are 4s1
2. Cu and Cr are 4s1
14
New cards
Which elements are in which block?
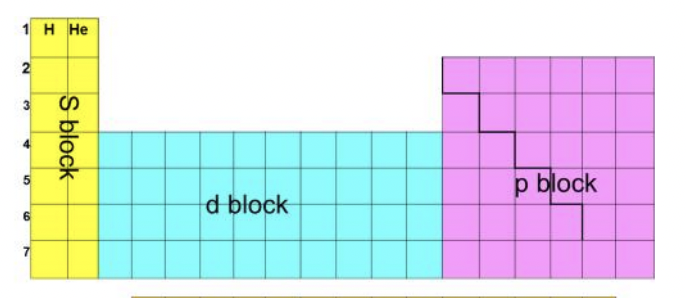
15
New cards
Define periodicity
The repeating pattern of physical or
chemical properties going across the periods
chemical properties going across the periods
16
New cards
Explain the trends in melting and boiling points in terms of bonding
Metallic bonding- strong bonds-->high melting and boiling points
Ionic bonding- strong bonds-->high melting and boiling points
Simple covalent- weak bonds--> low melting and boiling points
Macromolecular- strong bonds--> high melting and boiling point
Ionic bonding- strong bonds-->high melting and boiling points
Simple covalent- weak bonds--> low melting and boiling points
Macromolecular- strong bonds--> high melting and boiling point
17
New cards
Define ionic bonding
Electrostatic attraction between two oppositely charged ions
18
New cards
Define covalent bonding
Electrostatic attraction between two nuclei and a shared pair of elctrons
19
New cards
Describe the trend of ionic radii down the groups
The radii increases and there are more shells
20
New cards
What is a dative covalent bond?
When the shared pair of electrons in the covalent bond come from only one of the bonding atoms
21
New cards