Genes and Health
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
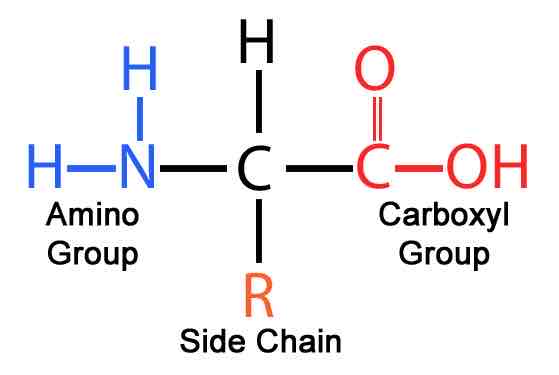
What is the general structure of an amino acid?
R-CH(NH2)-COOH
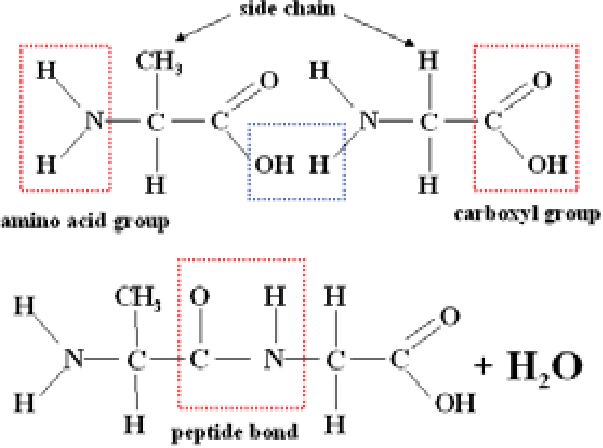
What is a dipeptide?
A peptide with 2 amino acids
What is a polypeptide?
A polypeptide with many amino acids
What role does water play in the production and breakdown of dipeptides?
Water is produced during the condensation reaction. Water is broken down during the hydrolysis reaction
Define protein
A molecule made up of amino acids
What is the R group?
The side group that changes depending on the amino acid
What is a peptide bond?
A covalent bond that links amino acids together to form a protein
What is the primary structure
The amino acid sequence
What is the secondary structure
The form a protein assumes after having folded up
What is the tertiary structure
The three dimensional structure of the entire polypeptide chain
What is the quaternary structure
The arrangement of multiple polypeptide chains that produce a complete protein
What is a conjugated protein
A protein with another chemical group attached
What is a globular protein
A protein that is water soluble and shaped like a sphere after folding
What is a fibrous protein
Long strands of polypeptide chains that have cross linkages due to hydrogen bonds
How is a peptide bond formed?
Condensation reaction.
OH removed from Hydroxyl group. H removed from amine group.
How have mammals adapted for a large surface area to maximise gas exchange?
Many alveoli and capillaries surrounding alveoli
How have mammals adapted for a thin diffusion difference to maximise gas exchange?
Alveoli and capillaries are made of flat squamous tissue
How have mammals adapted to have a concentration gradient to maximise gas exchange?
Breathing and circulation of blood maintains a high gradient between the alveolar air space and bloodstream
What are the anatomical adaptations in a mammal to maximise gas exchange?
Large surface area, high concentration gradient, thin exchange surface
What is the formula for flicks law?
Rate of diffusion= surface area x concentration difference/ diffusion distance
How would an increased thickness of gas exchange surface due to thicker mucus affect the rate of diffusion?
Molecules have to travel further so rate of diffusion decreases
How would the rate of diffusion be affected by a reduction in the concentration gradient between the alveolar air space and capillaries?
Fewer particles so less chance of them moving to a lower concentration so rate of diffusion would decrease
How would rate of diffusion be affected by damage to alveoli resulting in a reduction of their numbers?
A reduced surface area as less space for them to diffuse across so rate of diffusion decreases.
What do goblet cells do in the respiratory system?
Secrete mucin and create a protective mucus layer
What do cilliated epithelial cells do in the respiratory system?
Propel mucus up the airway to remove particulate material
Define epithelial
Cells that line the internal and external surfaces of the body
Define goblet cells
An epithelial cell that produces mucus
Define mucus
A substance that is produced by goblet cells and acts as a protective barrier