Nervous System Histology and Physiology
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
the nervous system (NS) is branched into the ______ NS and the _______ NS
central, peripheral
the central nervous system is composed of the
brain and spinal cord
brain
interprets and stores information and sends orders to muscles, glands, and organs
spinal cord
pathway connecting the brain and the peripheral nervous system
peripheral nervous system
transmits information to and from the central nervous system
the two branches of the peripheral nervous system are the _______ NS and the _______ NS
autonomic, somatic
the two divisions of the autonomic nervous system are the _______ division and the _______ division
parasympathetic, sympathetic
the two branches of the somatic nervous system are the _____ systems and the ______ systems
sensory, motor
autonomic nervous system
automatically regulates glands, internal organs and blood vessels, pupil dilation, digestion, and blood pressure
somatic nervous system
carries sensory information and controls movement of the skeletal muscles
parasympathetic division
maintains body functions under ordinary conditions; saves energy (REST AND DIGEST)
sympathetic division
prepares the body to react and expend energy in times of stress (FIGHT OR FLIGHT)
sensory system (afferent)
carries messages from senses to CNS
motor system (efferent)
carries messages from CNS to muscles and glands
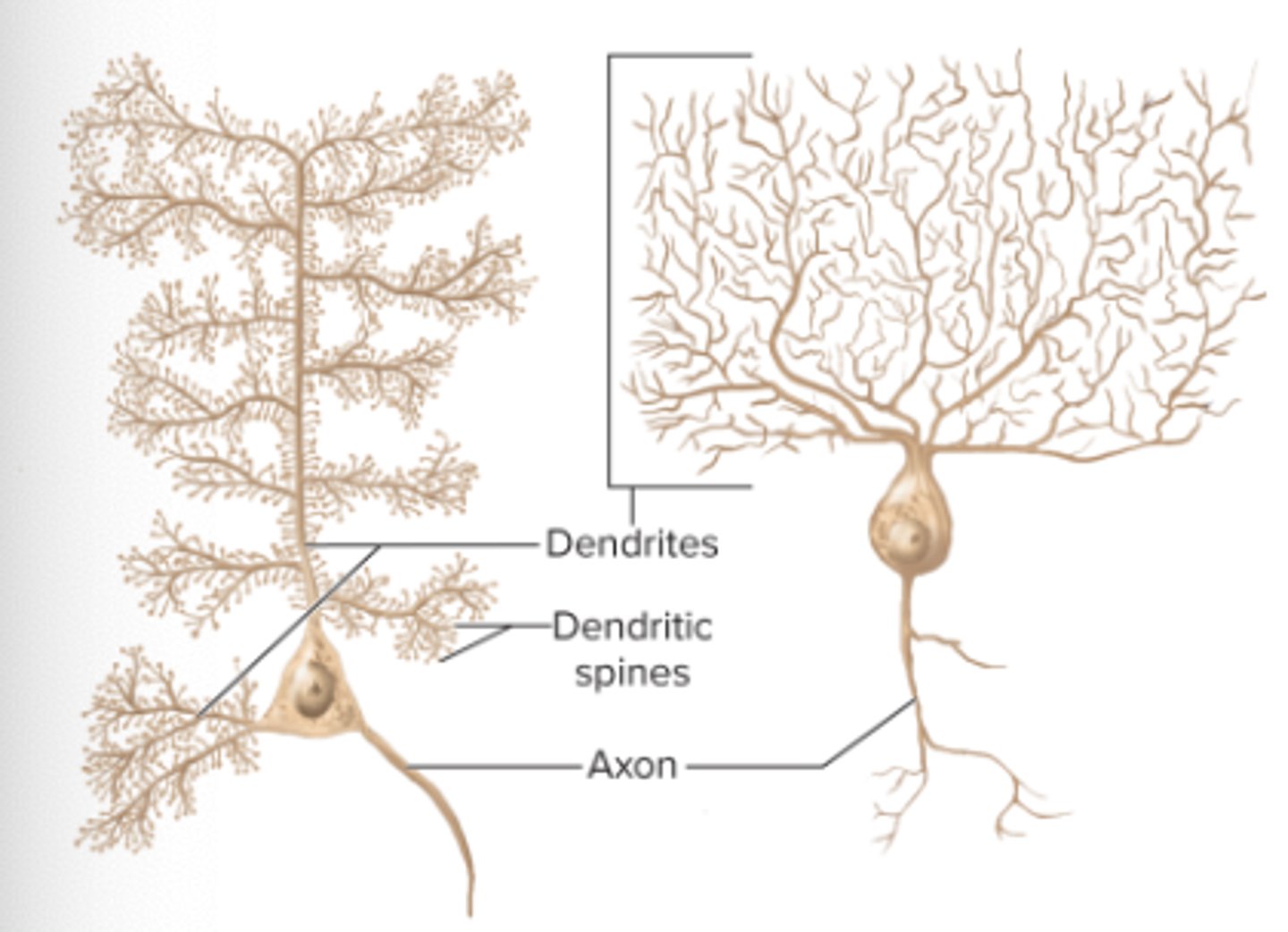
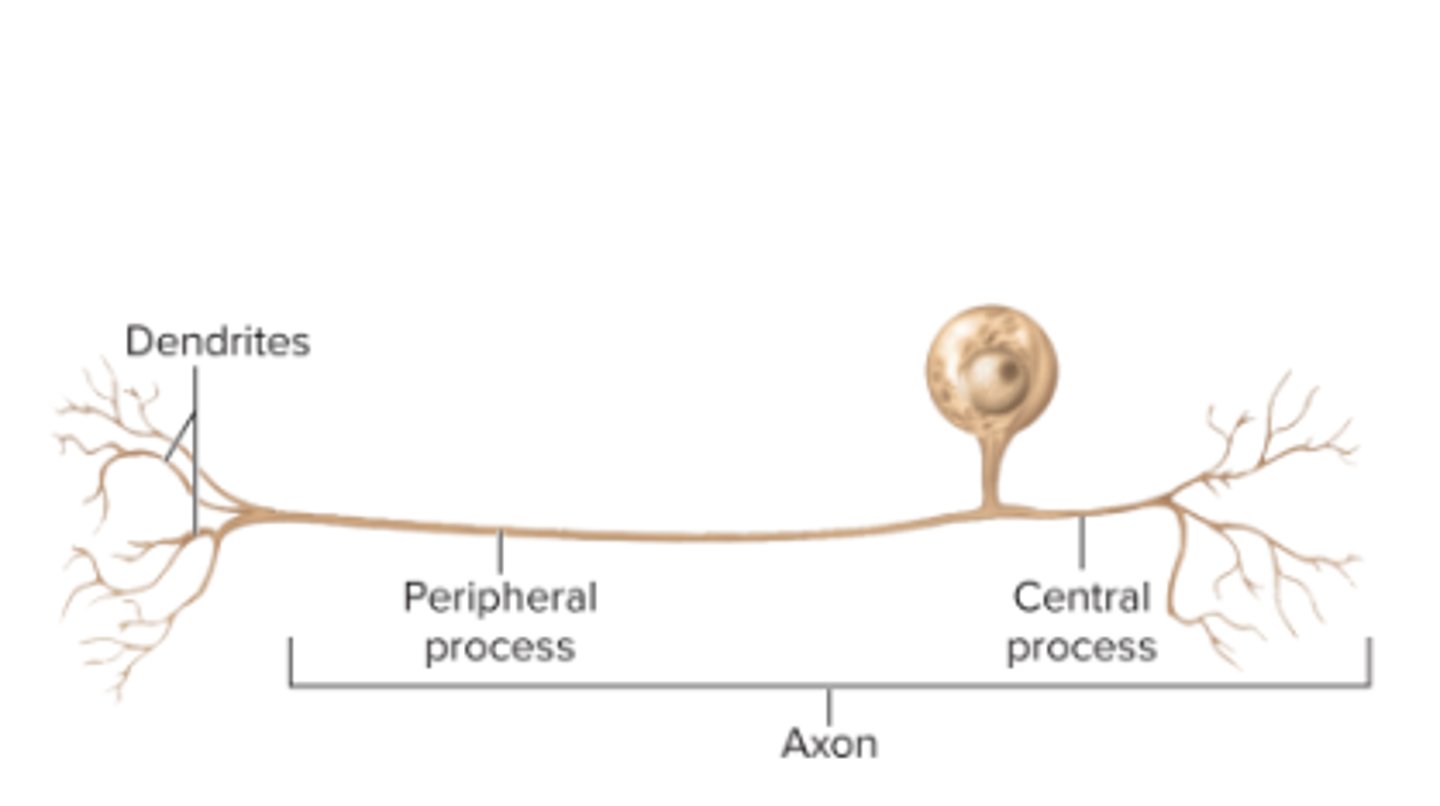
dendrites
extrude from cell body; receive signals
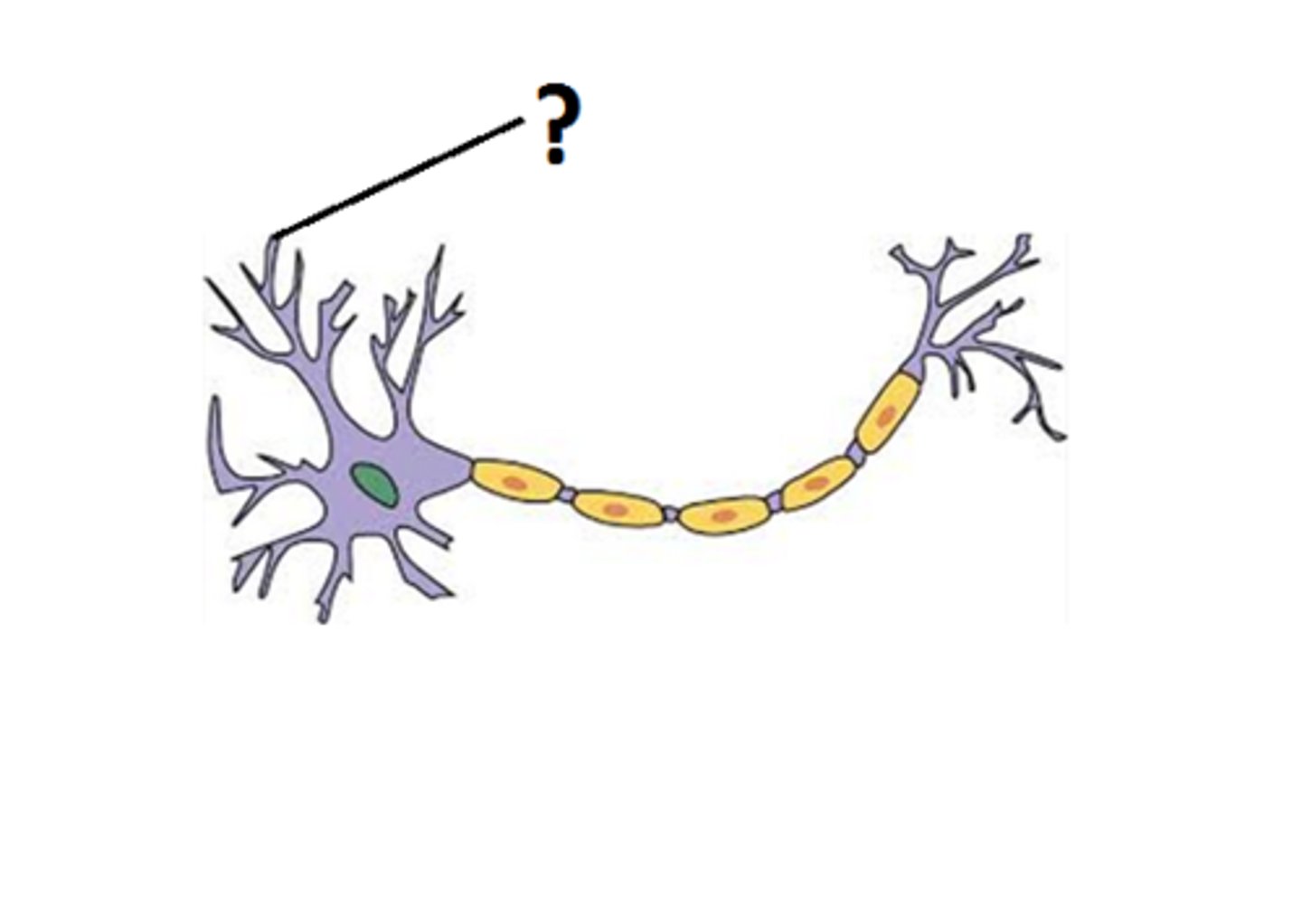
cell body
control center
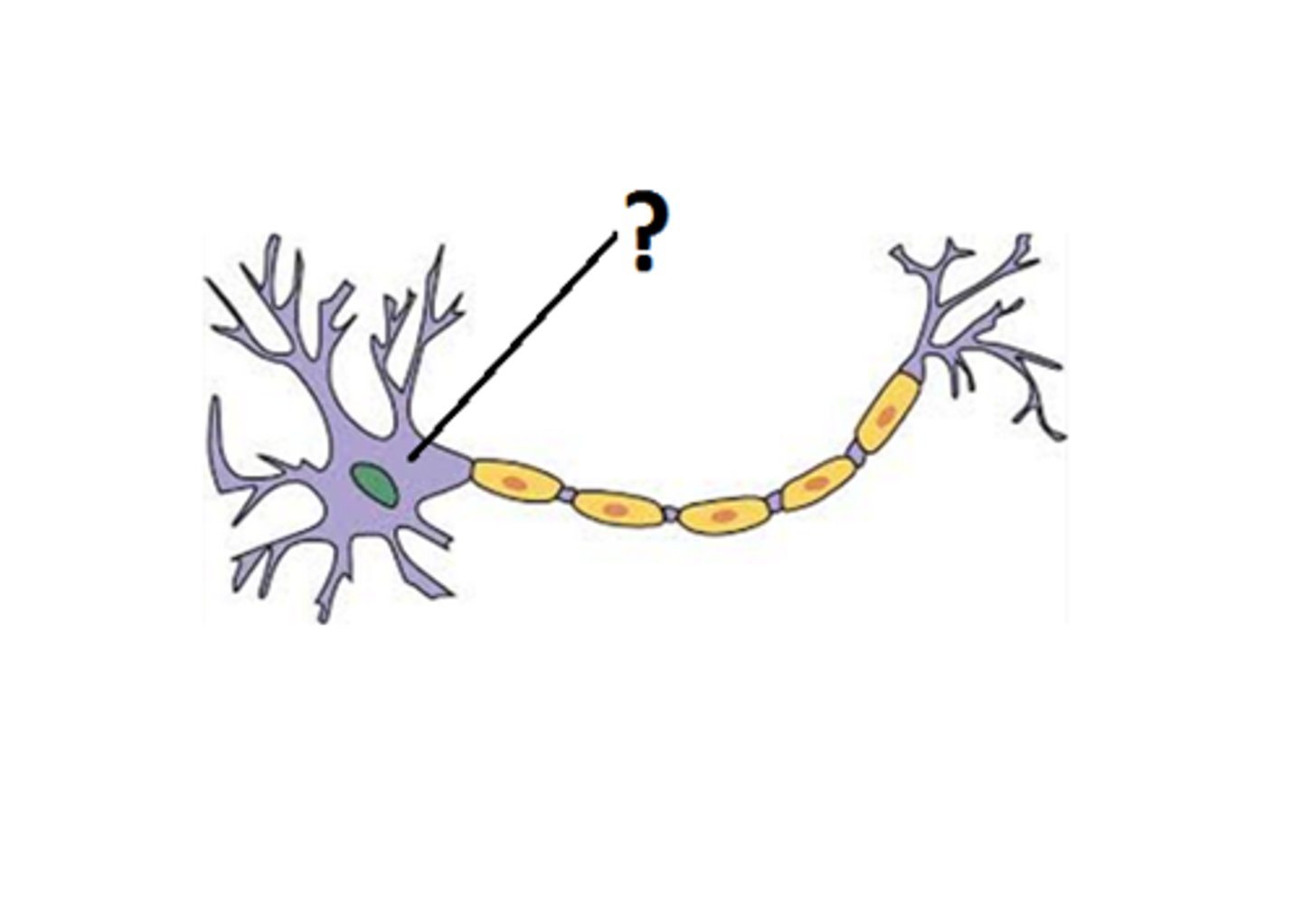
axon hillock
controls initiation of action potential
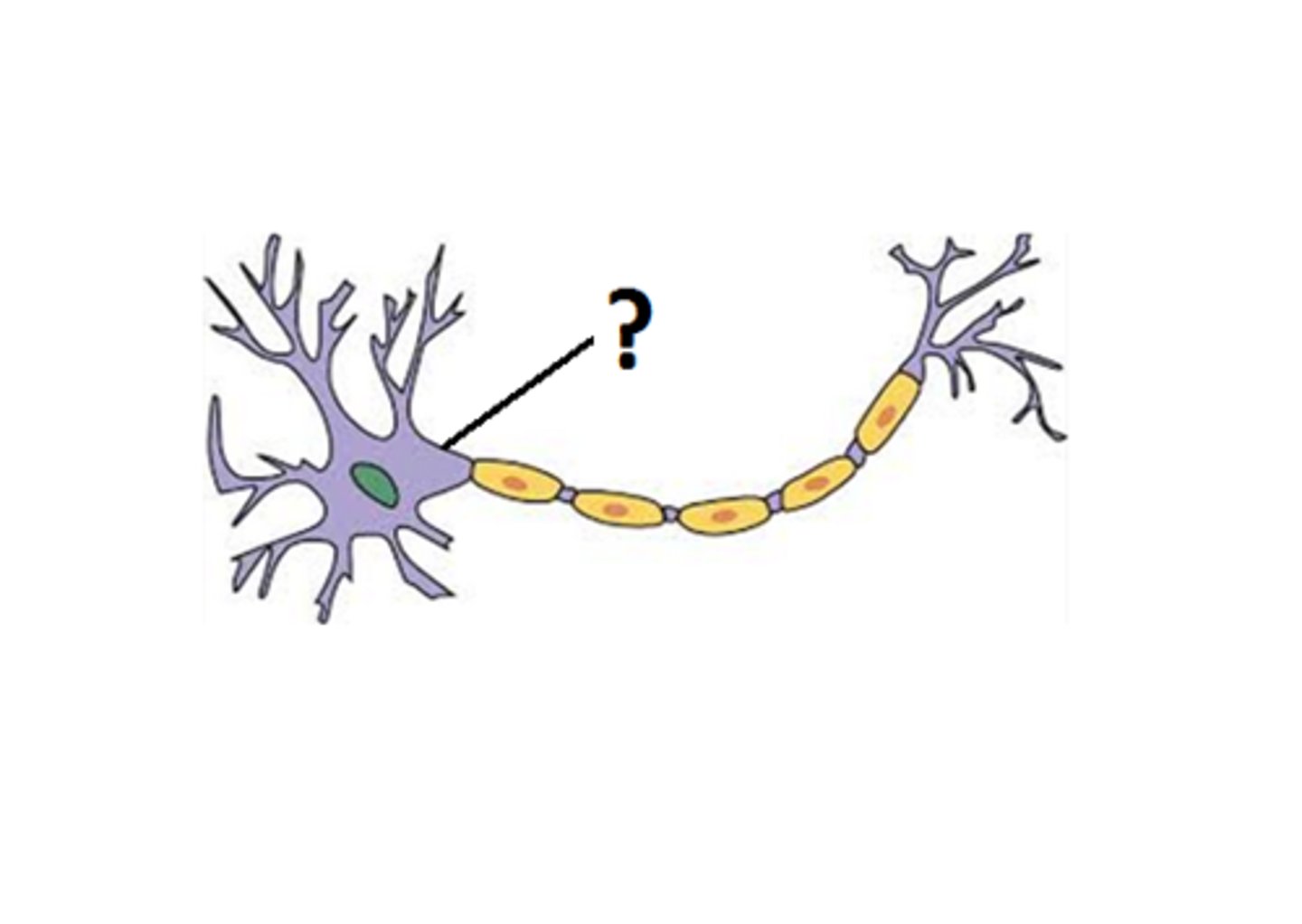
axon
conduction of nerve signal (action potential)
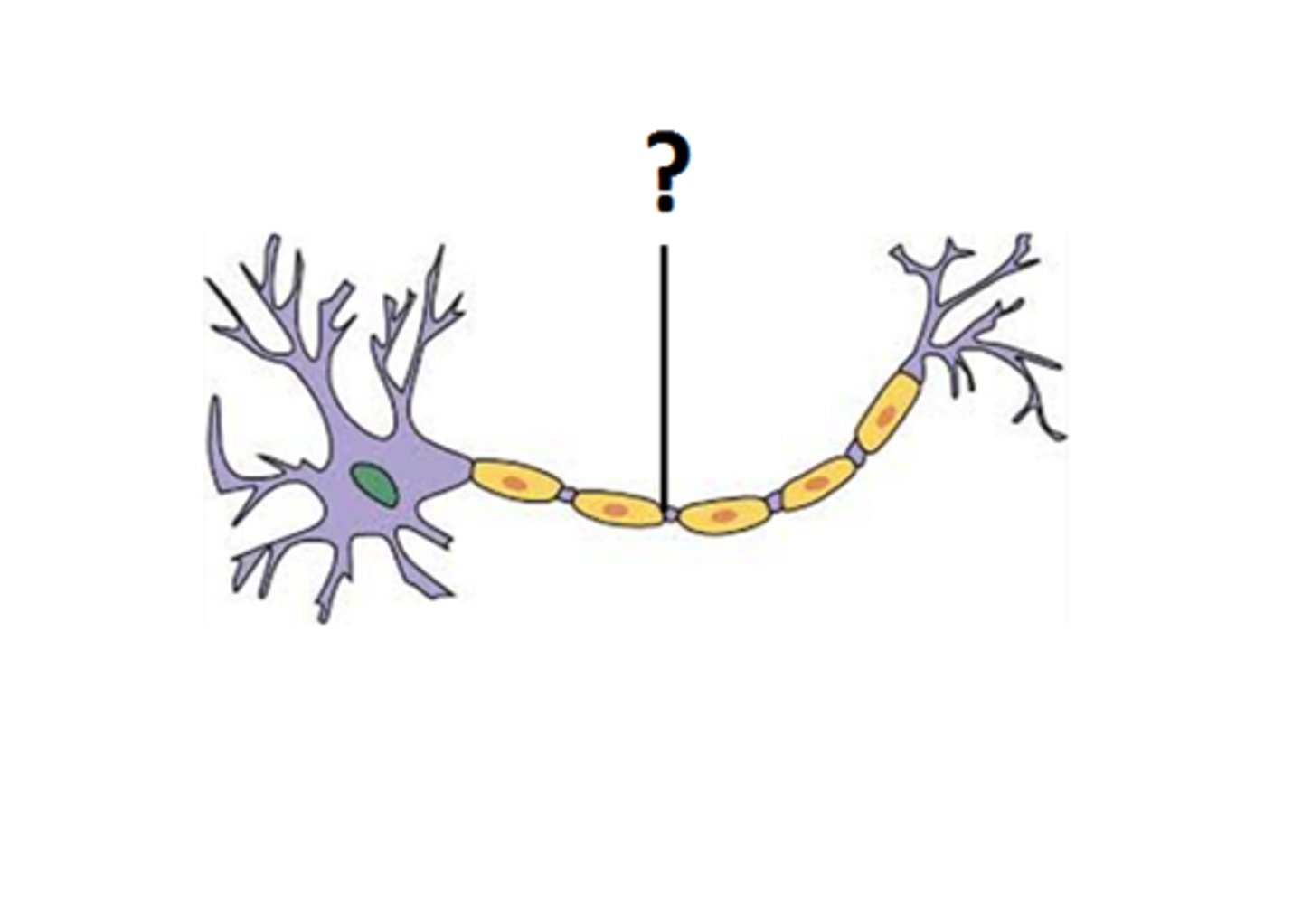
axon terminal
signal output; forms junction with next neuron (synapse)
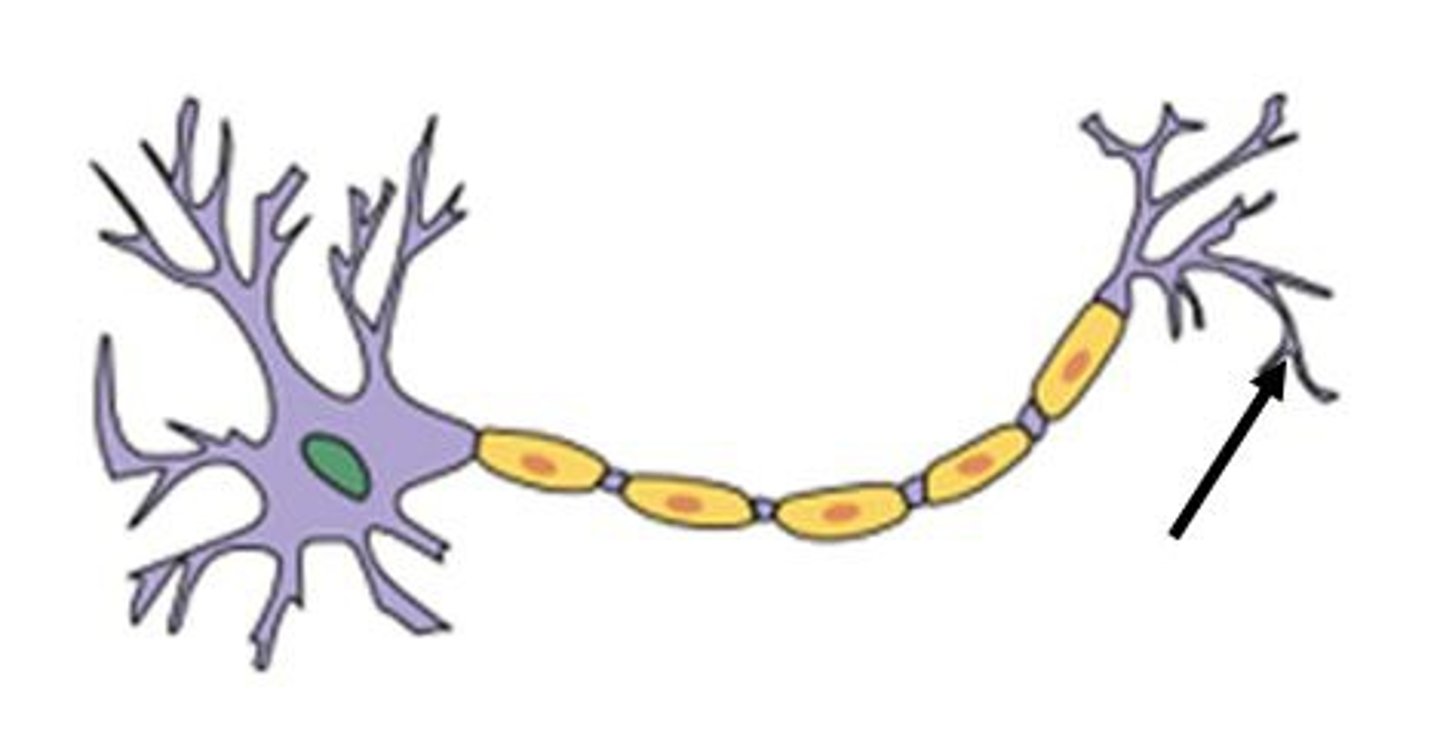
multipolar neuron
-one axon
-multiple dendrite
-MOST COMMON (composes most neurons of brain and spinal cord)
bipolar neuron
-one axon
-one dendrite
-found in olfactory cells, some neurons of retina, sensory neurons in ear

pseudo-unipolar neuron
-one process from cell branches into a T shape
-carries signals to spinal cord for touch and pain
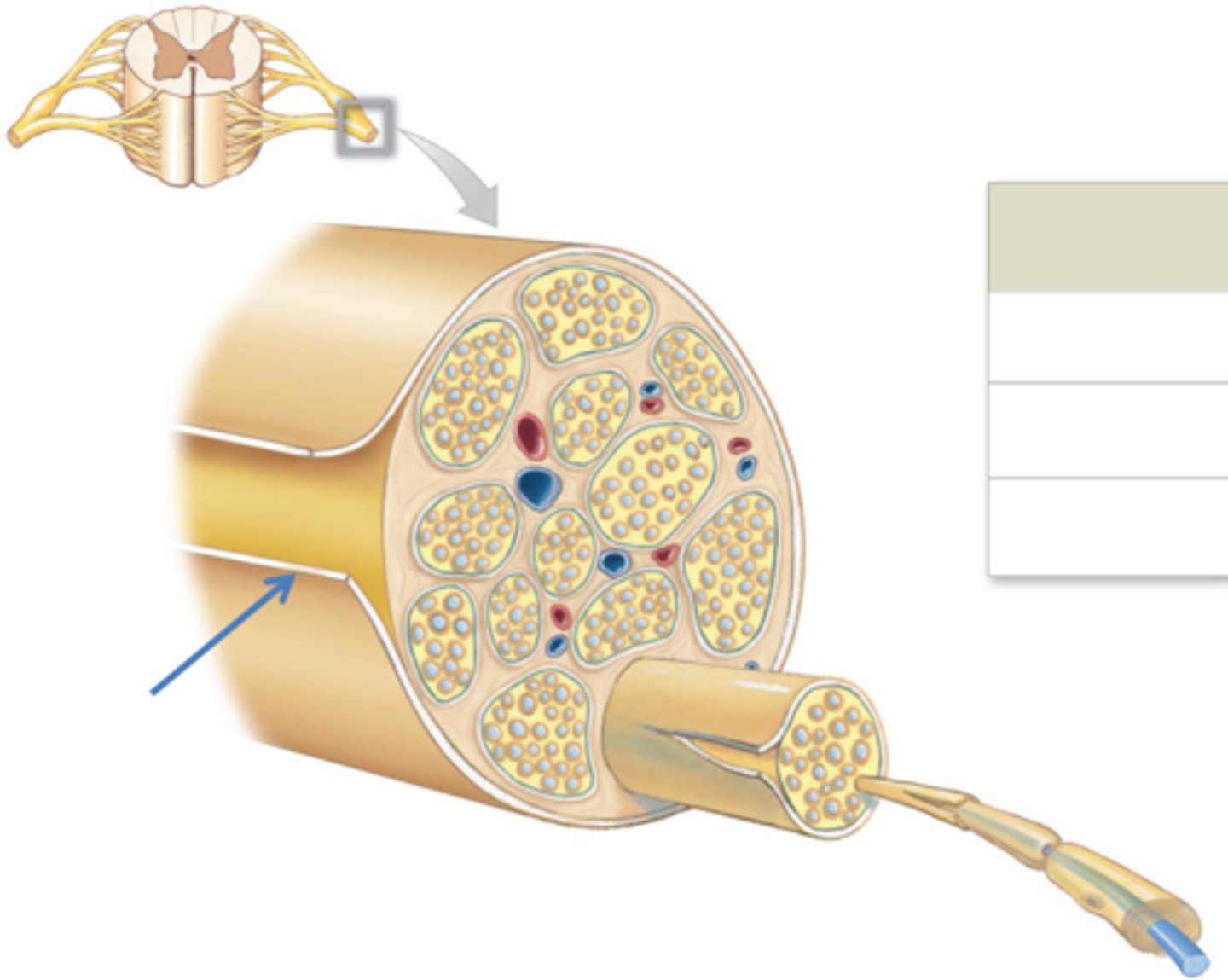
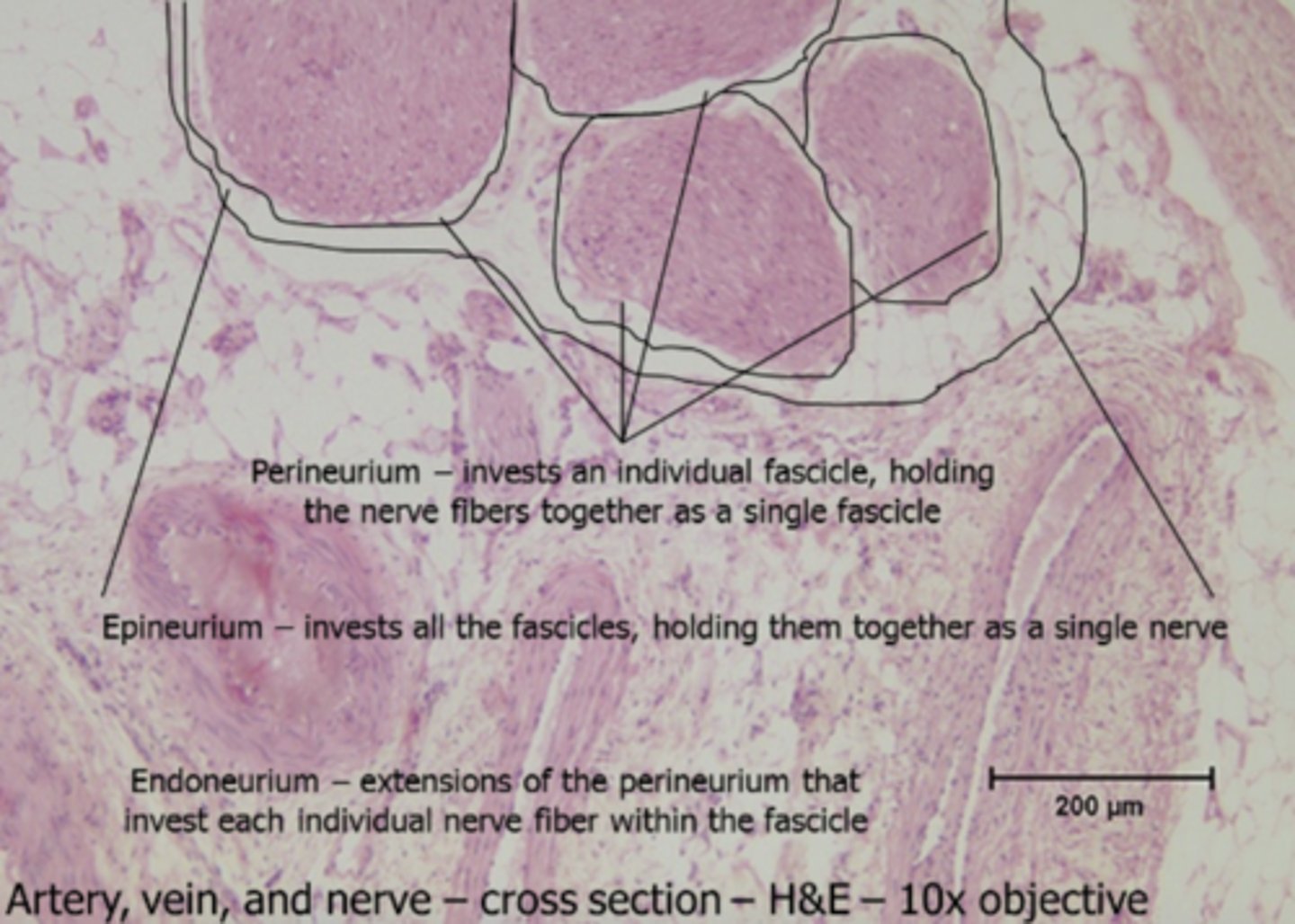
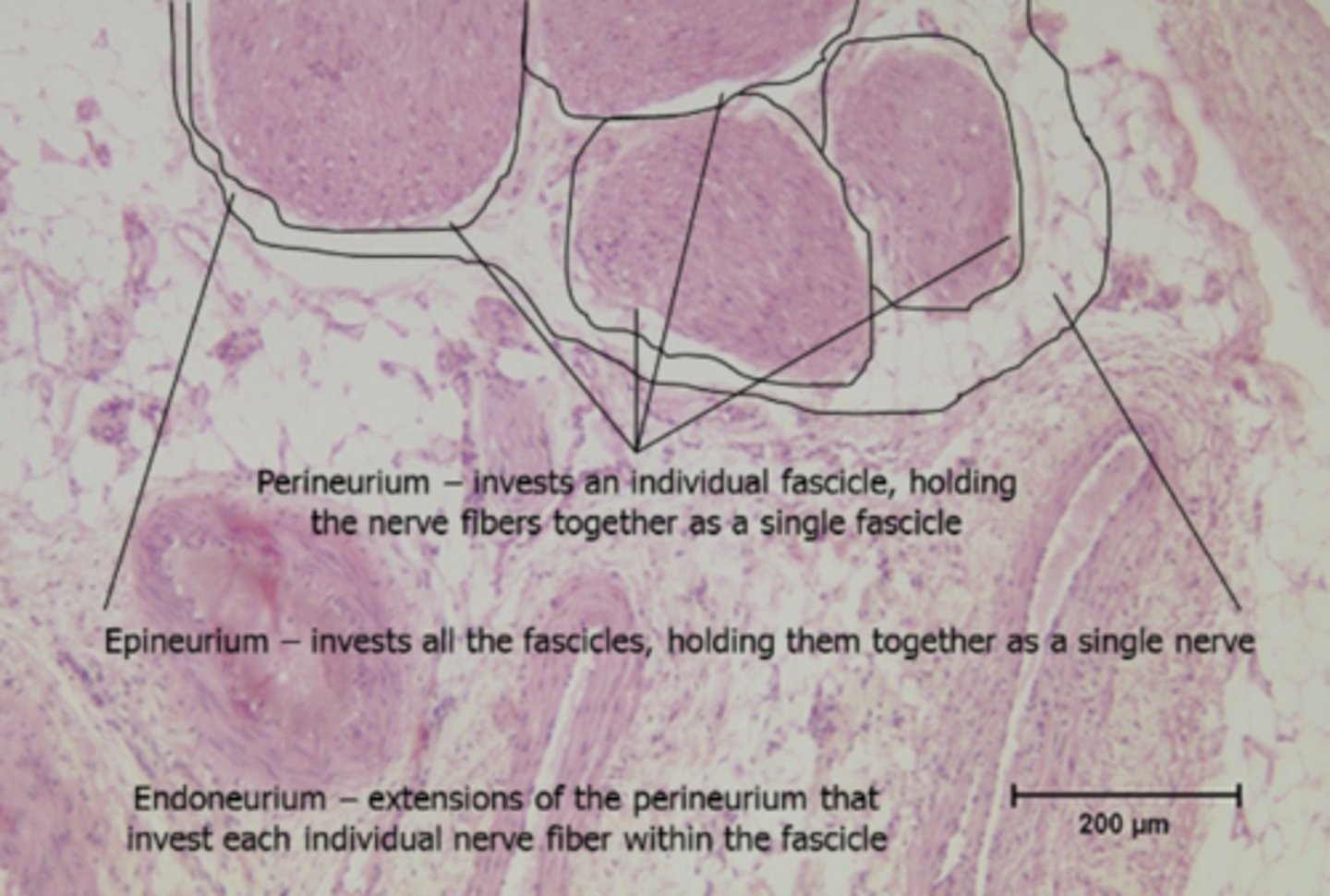
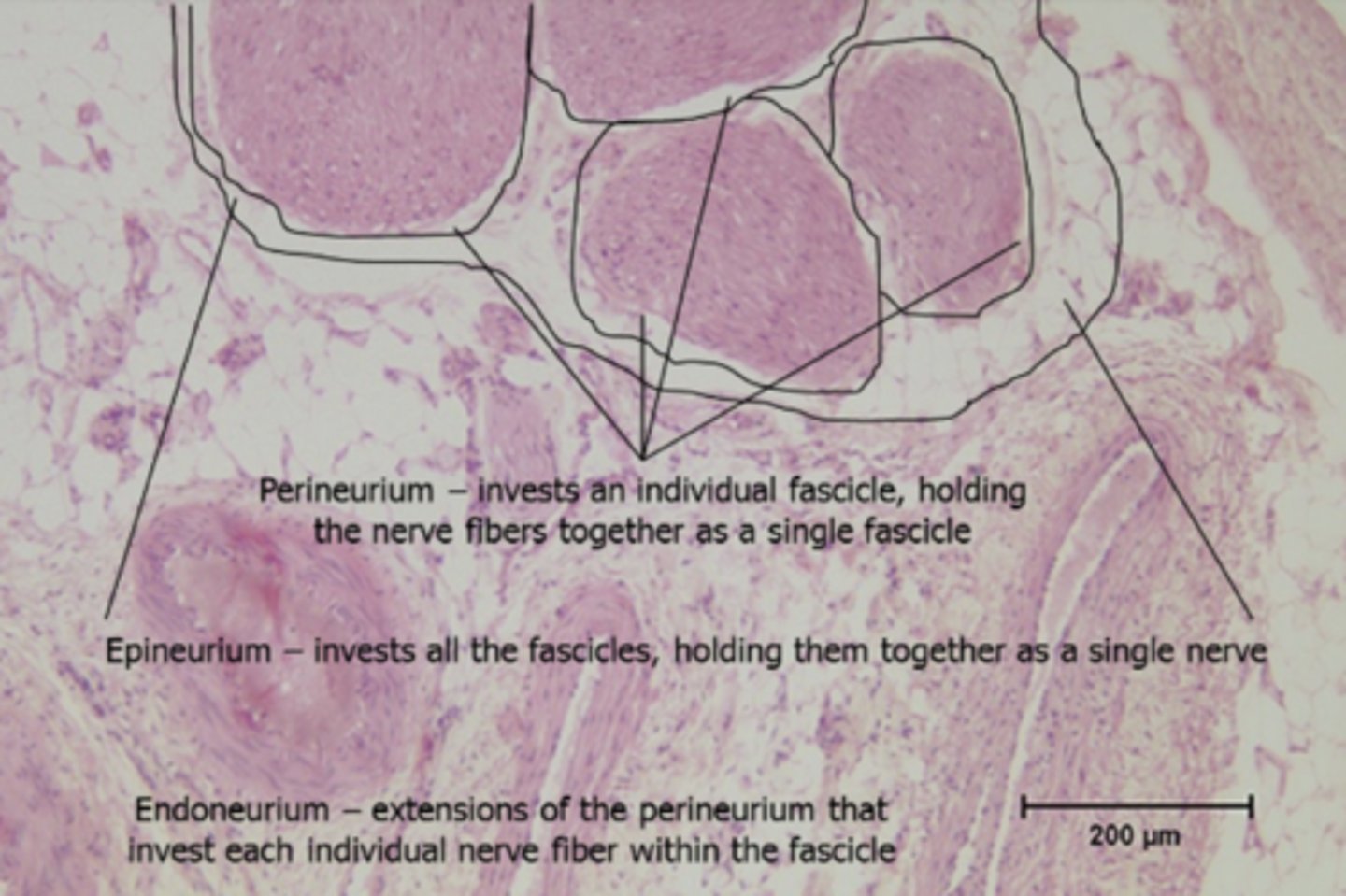
epineurium
connective tissue layer that surrounds ENTIRE NERVE
epineurium histology
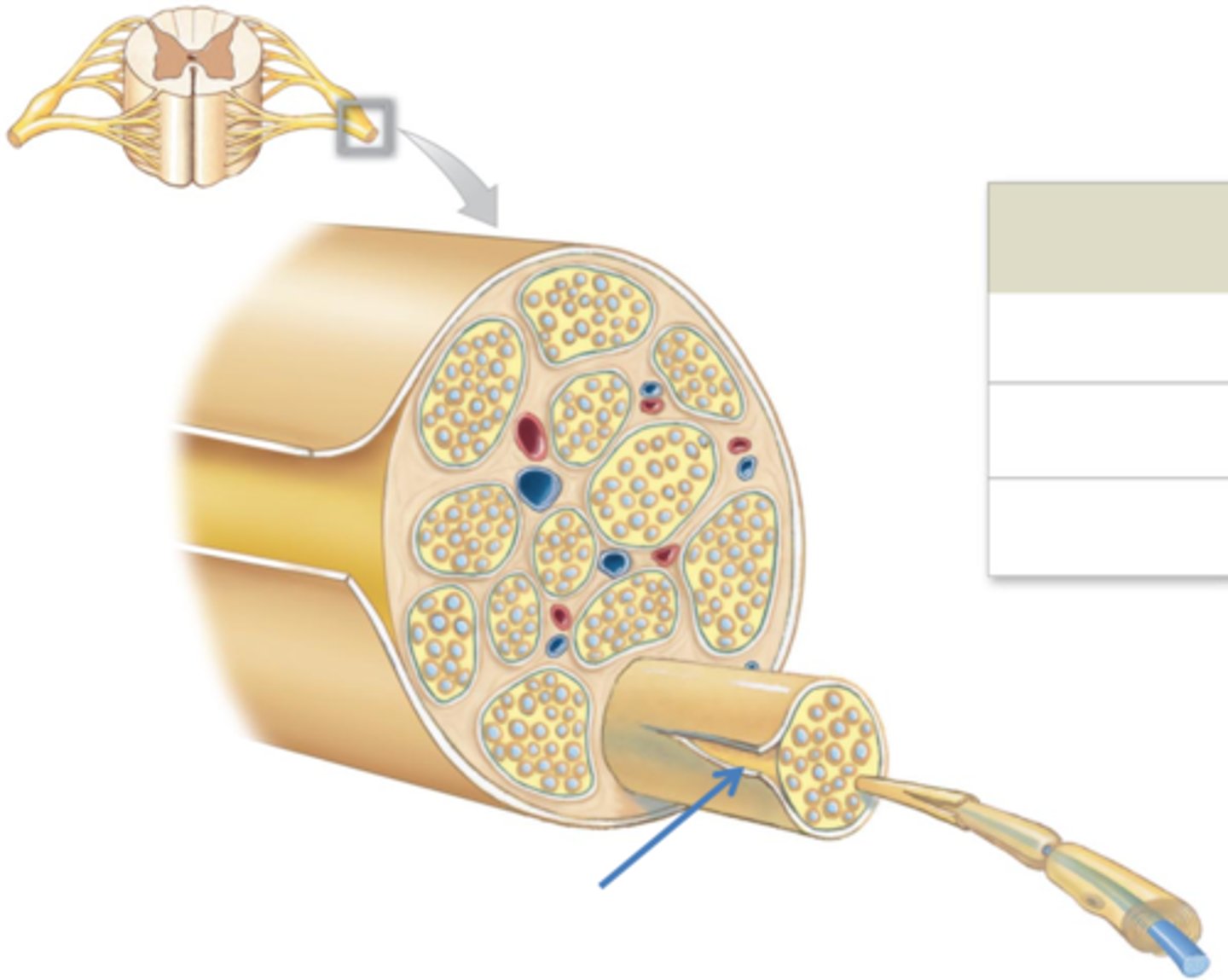
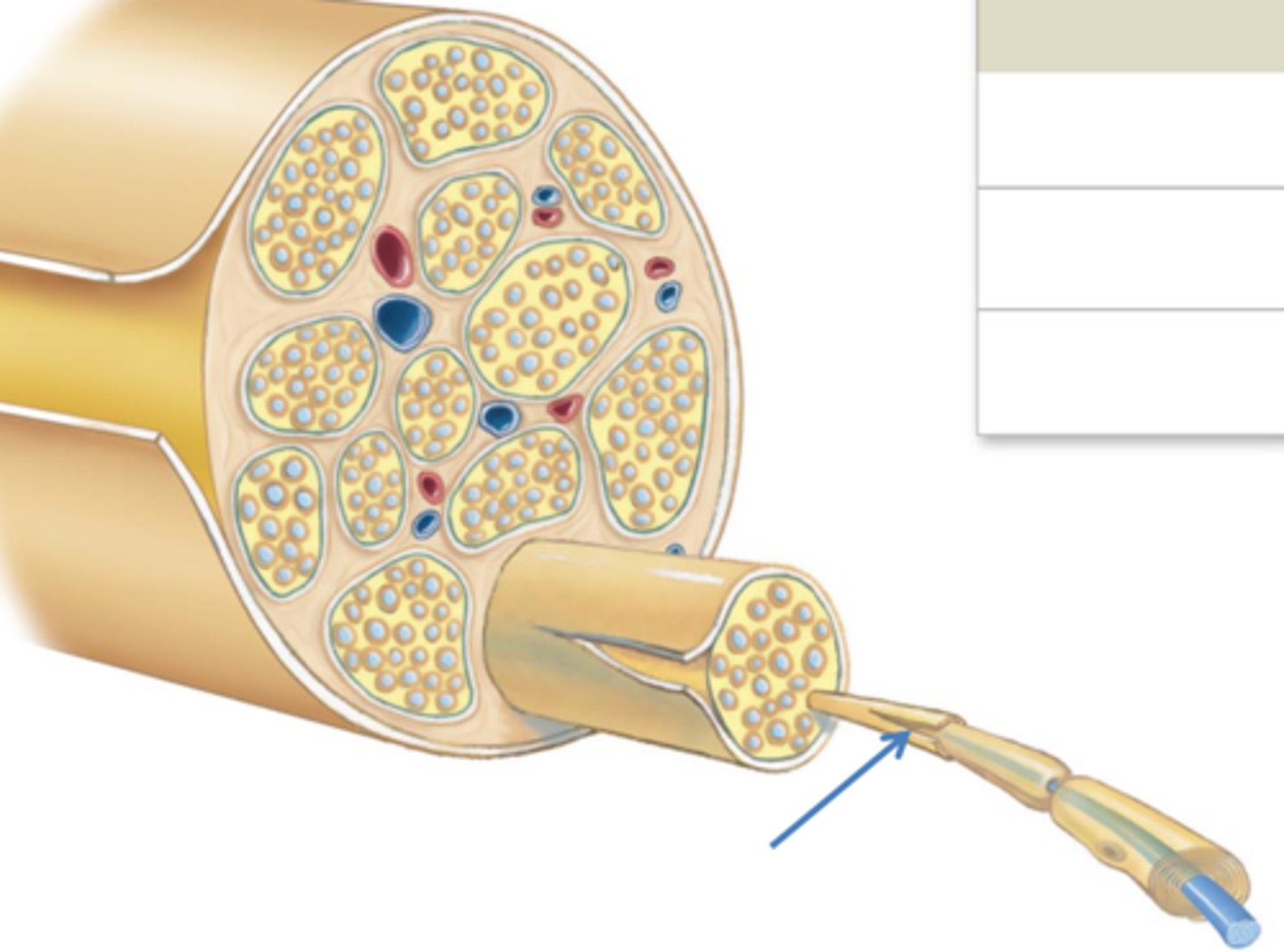
fascicle (middle black box in picture)
bundle of nerve fibers

fascicle histology

perineurium
connective tissue layer that surrounds the FASCICLE
perineurium histology
endoneurium
connective tissue layer that surrounds INDIVIDUAL AXON
endoneurium histology
myelination
Axons are covered in myelin sheath for insulation and to speed up electrical signals.
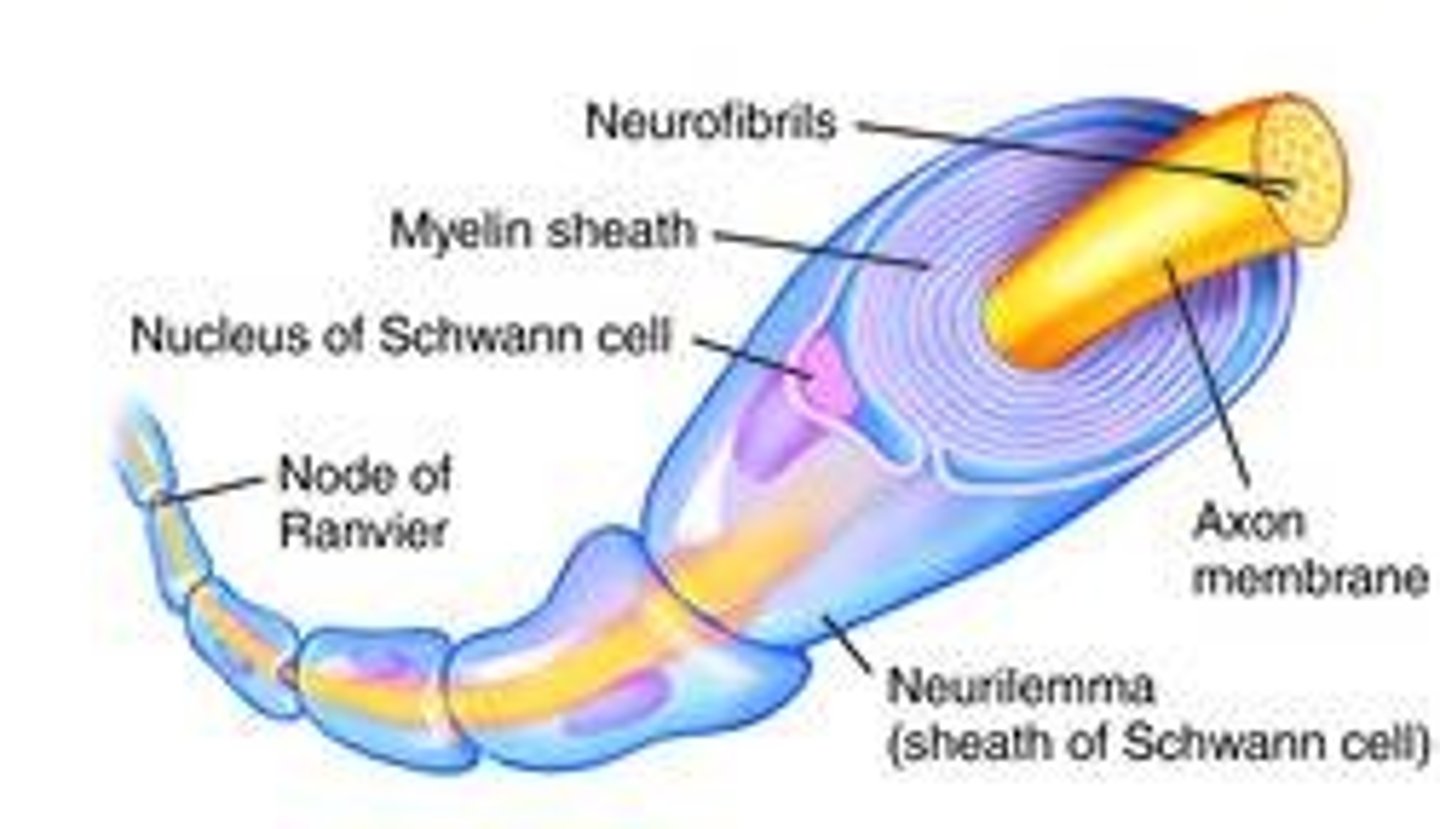
nodes of ranvier
gaps in the myelin sheath
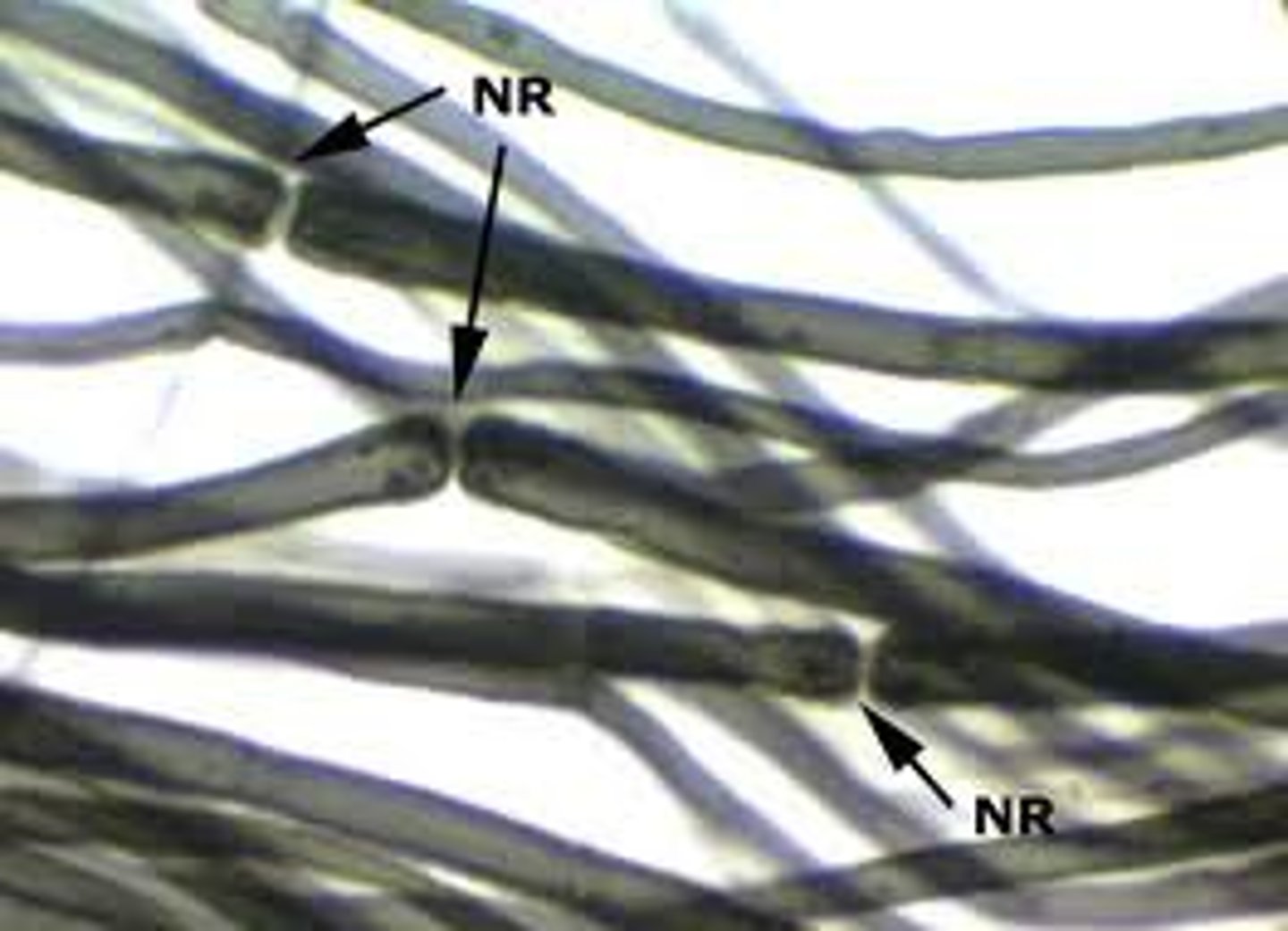
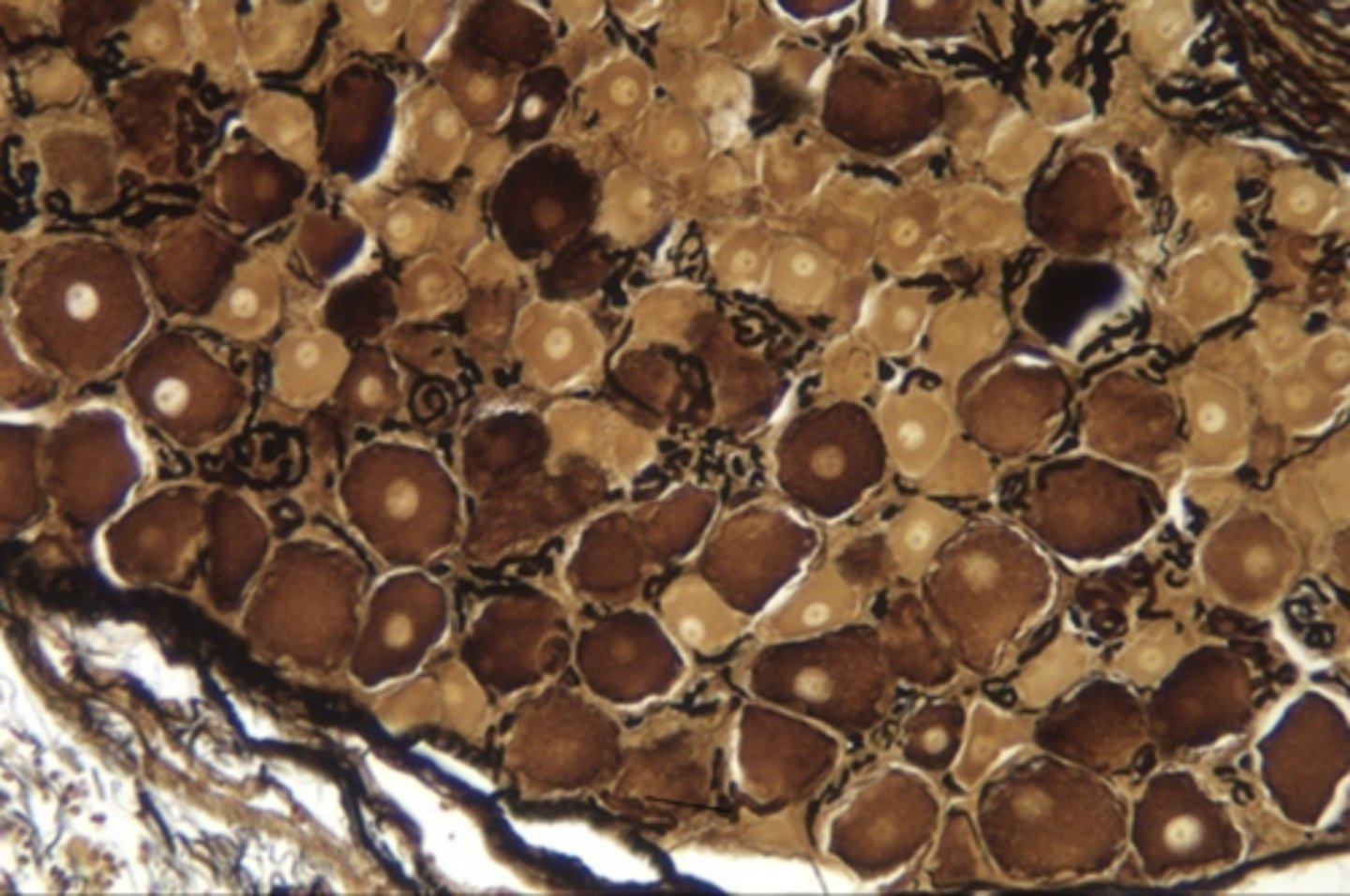
nerve histology (longitudinal section)

nerve histology (cross-section)

dorsal root ganglion
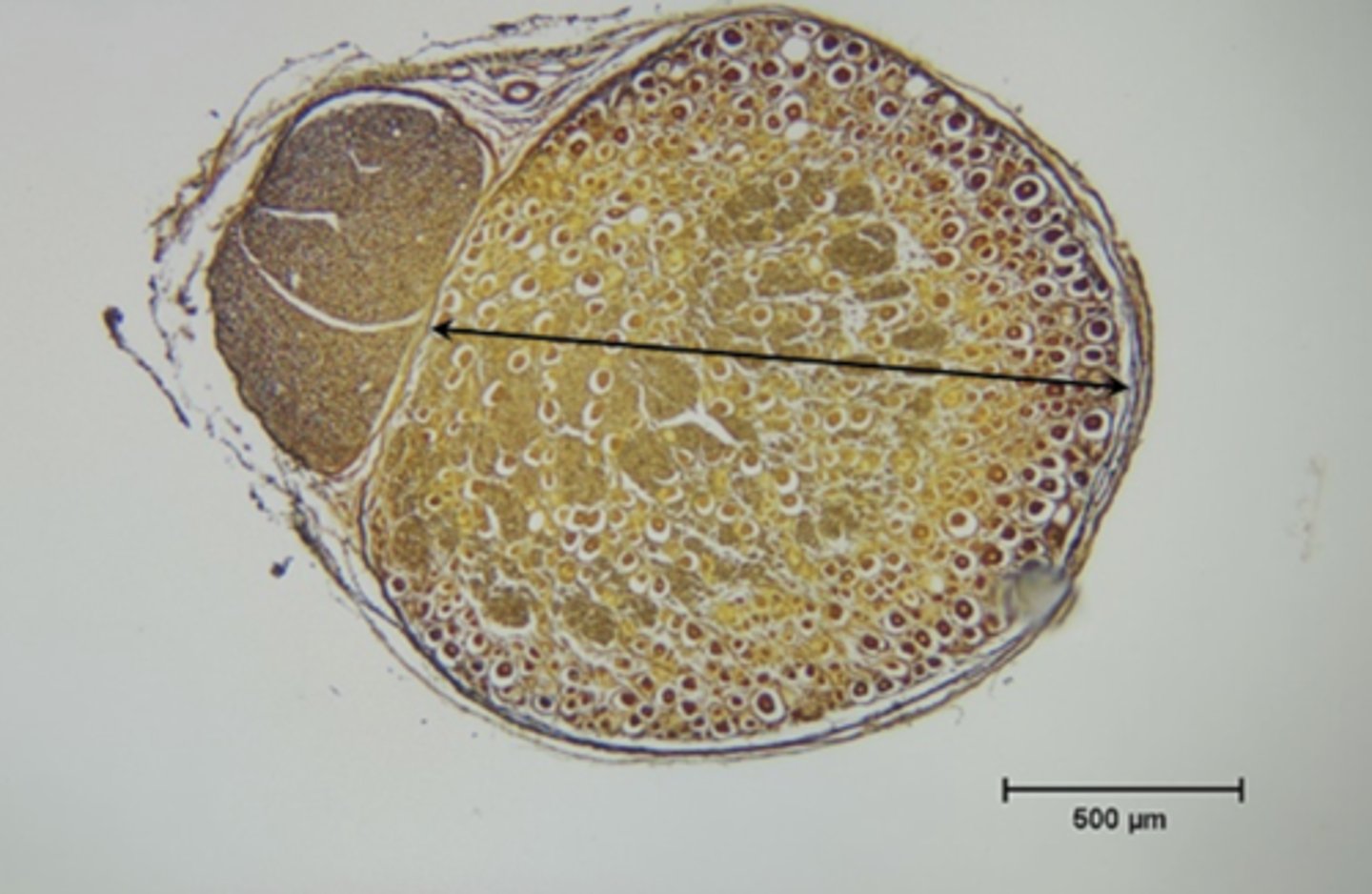
dorsal root ganglion (higher objective)
action potential
-firing of a neuron
-brief, transient reversal of membrane potential (voltage) that sweeps along the membrane of a neuron
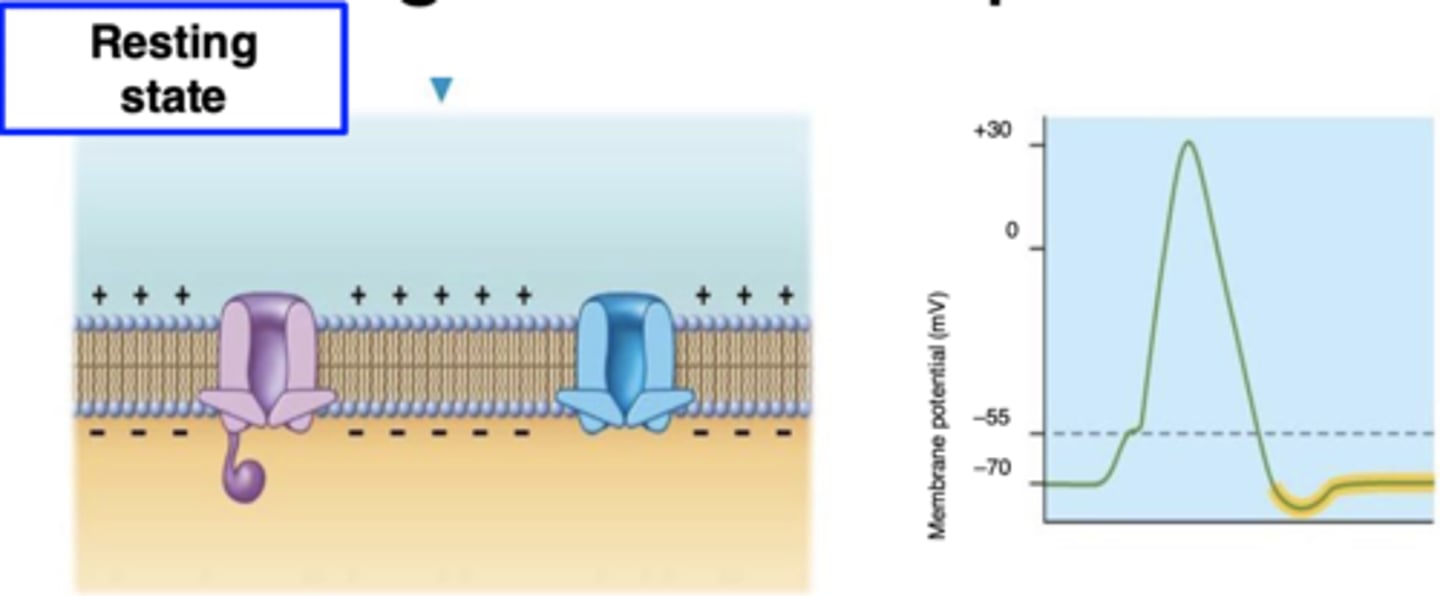
resting membrane potential (RMP)
- -70 mV
-voltage across the membrane in neuron that is NOT FIRING
-2 K+ IN and 3 Na+ OUT
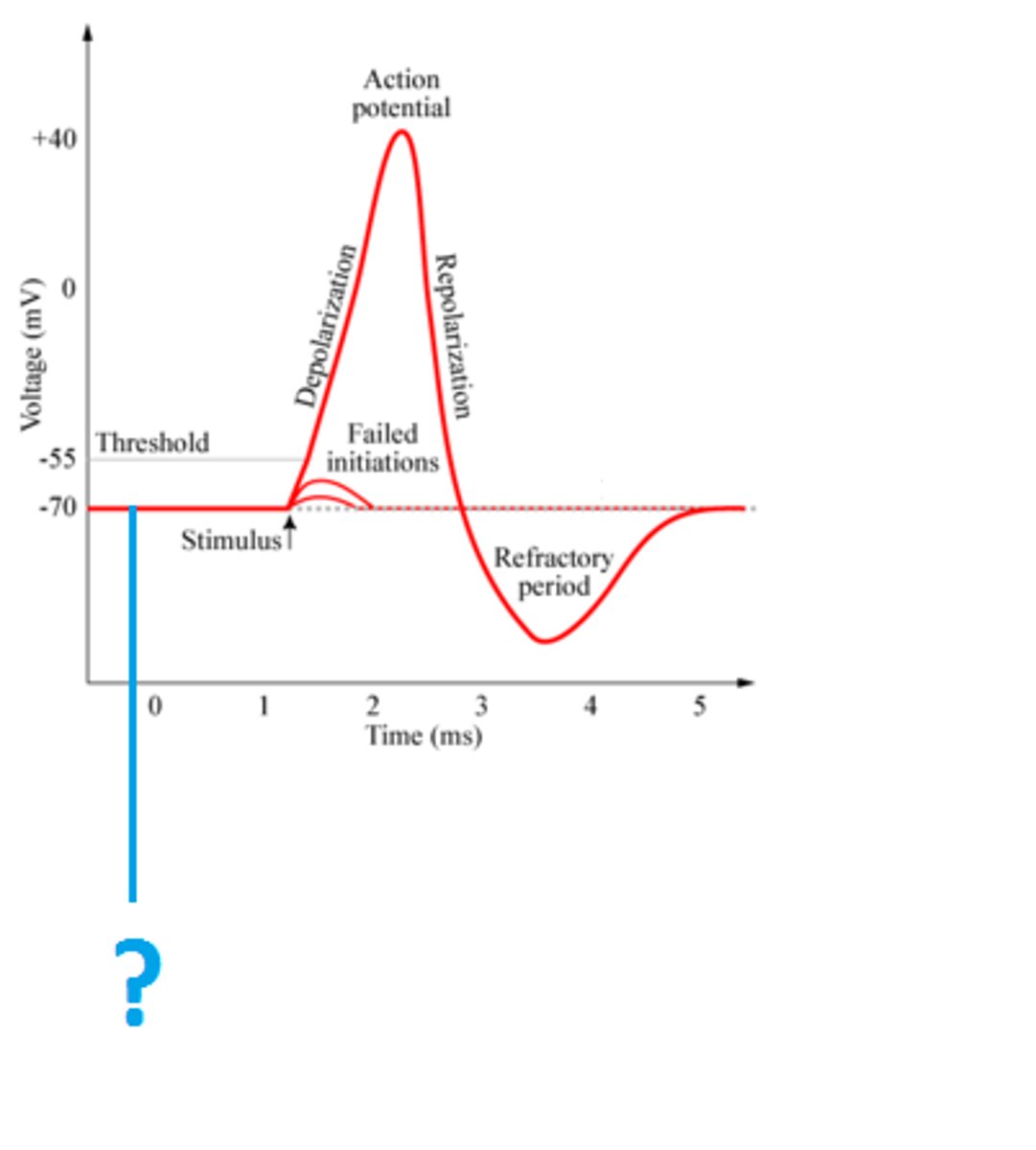
threshold potential
- -55 mV
-point at which voltage-gated ion channels begin to open
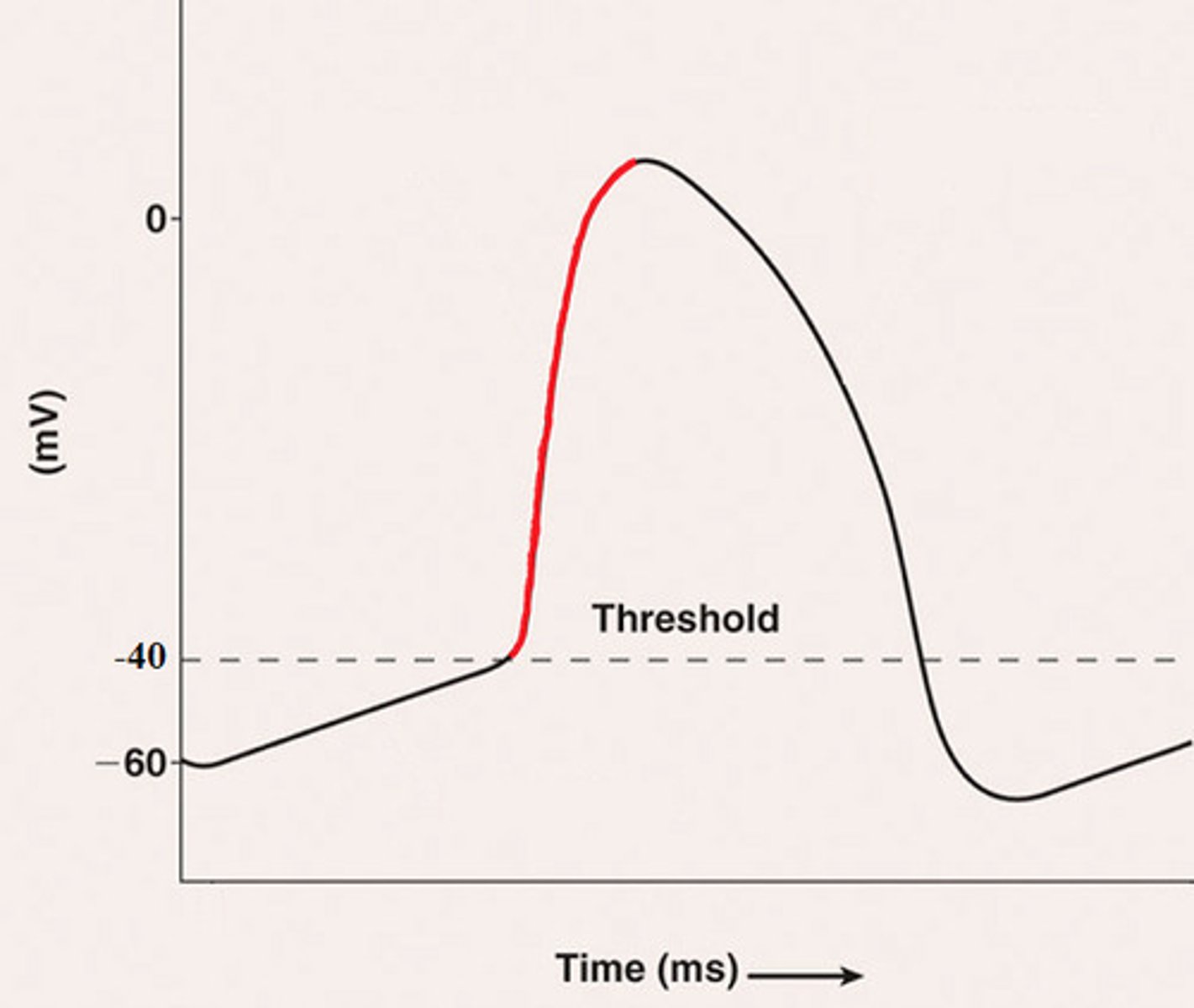
depolarizing phase
- -55 to +40 mV
-the membrane potential rapidly INCREASES as Na+ FLOWS IN
repolarizing phase
- +40 mV to -70 mV
-membrane potential rapidly DECREASES as K+ FLOWS OUT
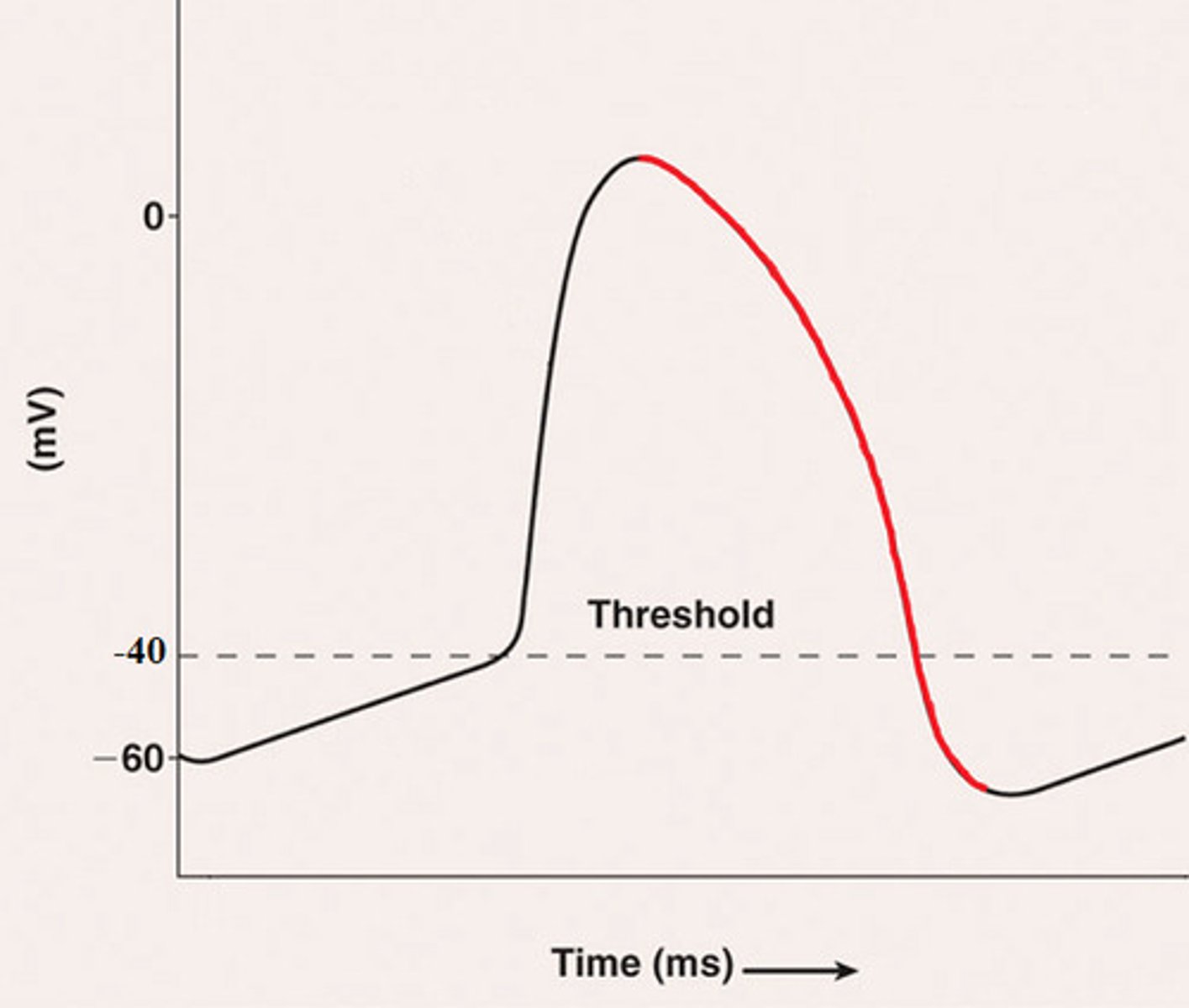
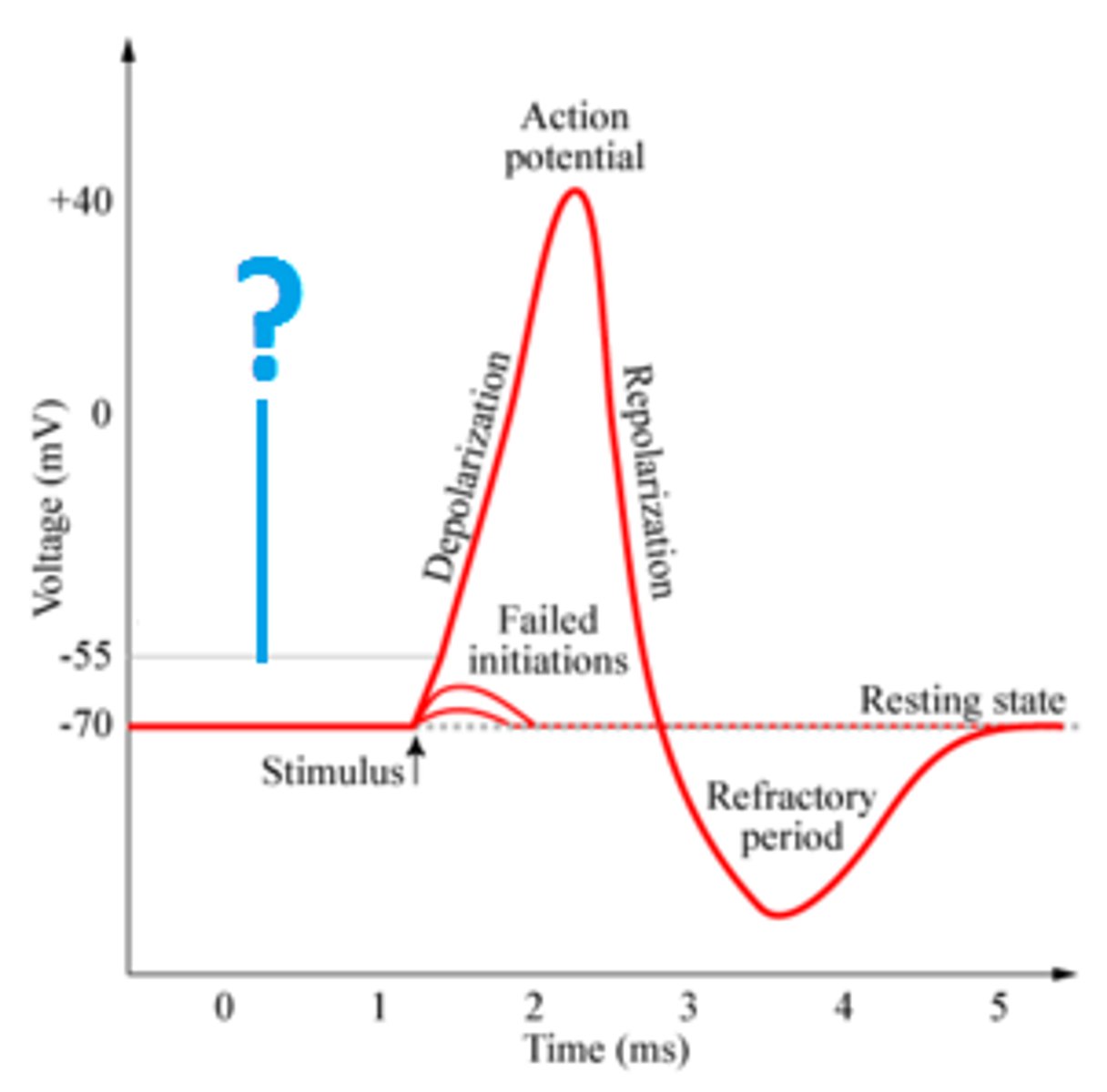
hyperpolarization phase
- -70 to -80 mV
-the membrane potential rapidly DECREASES as K+ FLOWS OUT
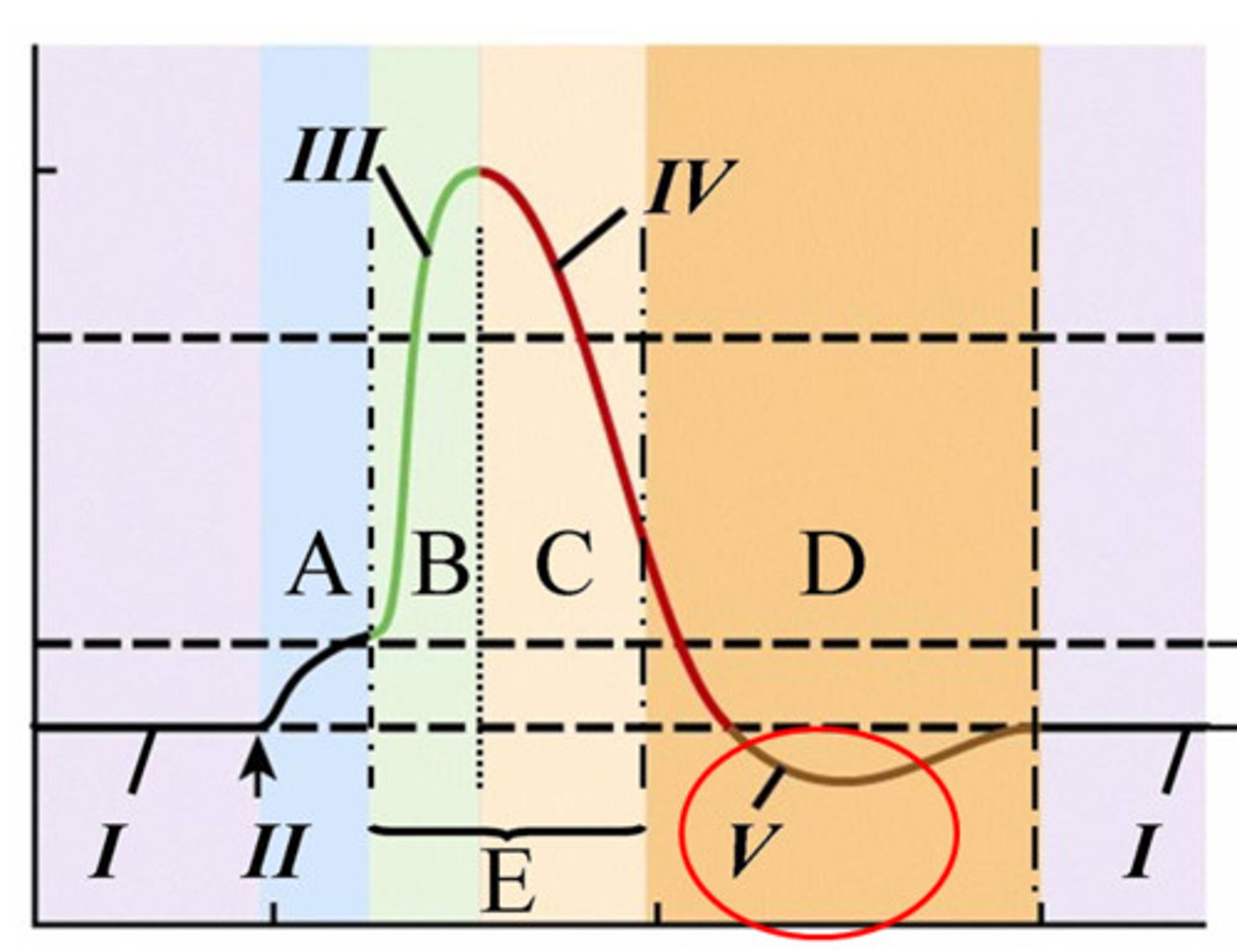
return to RMP
membrane potential rises again to RESTING (-70 mV)
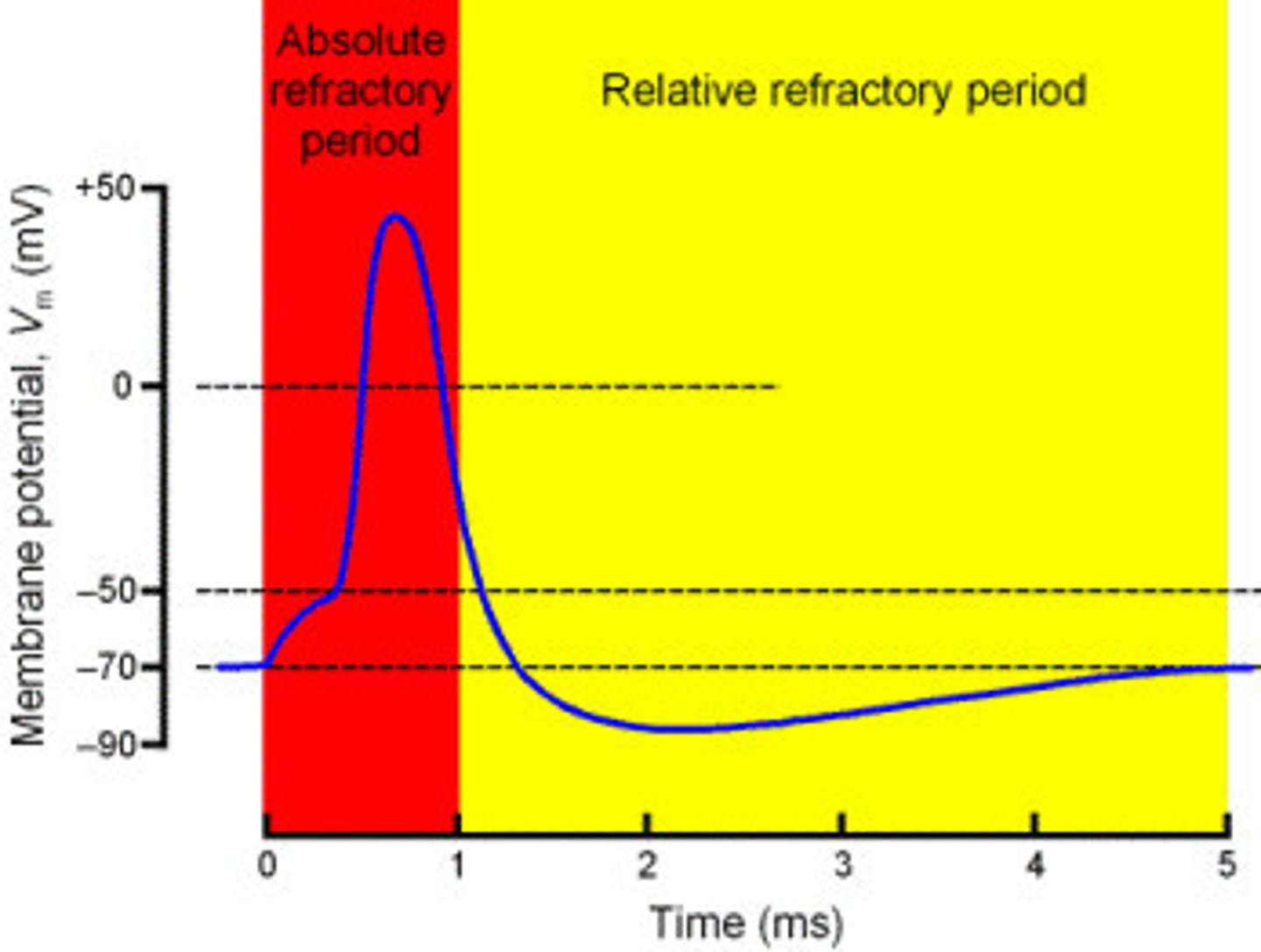
absolute refractory period
-nerve CANNOT BE STIMULATED due to Na+ FLOWING IN no matter how great the stimulus
-occurs during DEPOLARIZATION AND MOST OF REPOLARIZATION
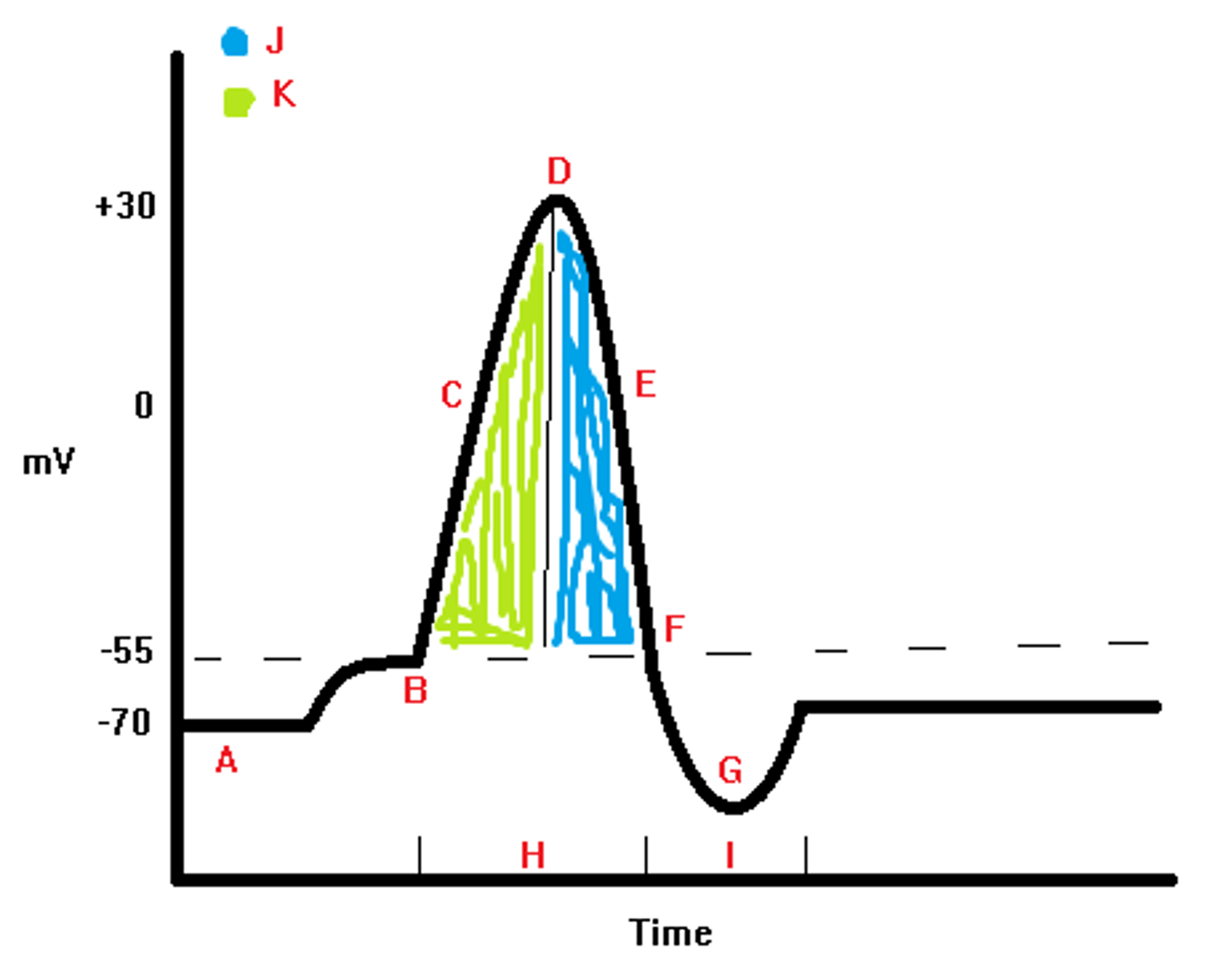
relative refractory period
-interval of time in which 2nd action potential CAN be initiated
-BUT stimulus must be GREATER THAN BEFORE
-Na+ are CLOSED
-K+ flows OUT
-membrane becomes more NEGATIVE
compound nerve
A nerve composed of several neurons, each having different properties with respect to irritability and conduction velocity
compound nerve action potential
cumulative action potentials of all the neurons in the nerve
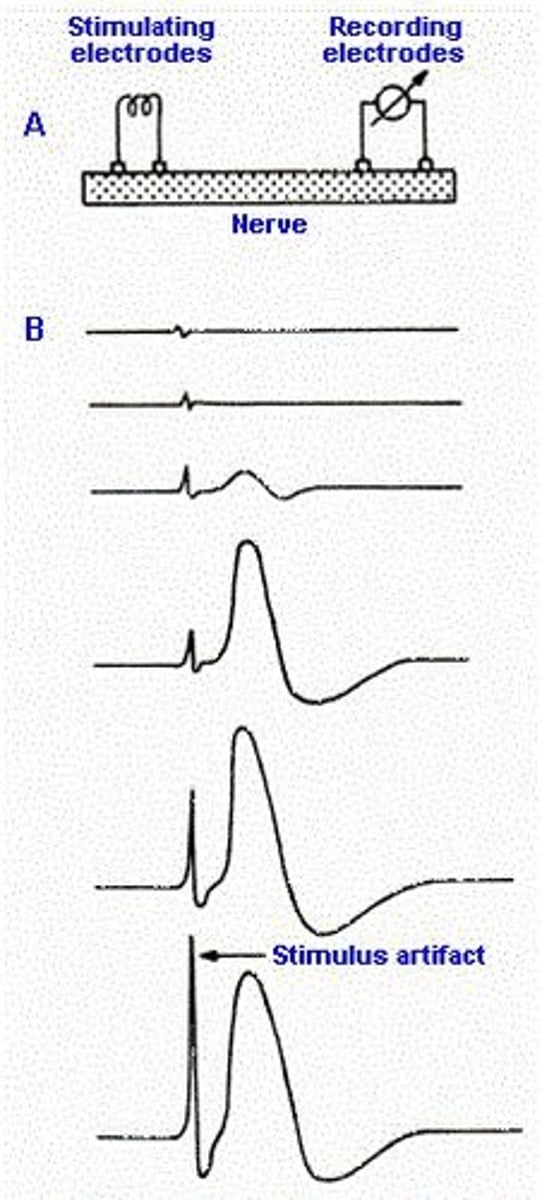
AXON SIZE
Large axons have _______ threshold
lower
DISTANCE FROM ELECTRODE
The ________ axon will reach threshold first
closer