Macro Unit 2 IDs
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total value of all final goods and services produced with in a country in a specific time period. (Within the country only) GDP= C (consumption)+I (investment) + G (government spending) + Xn (net exports)
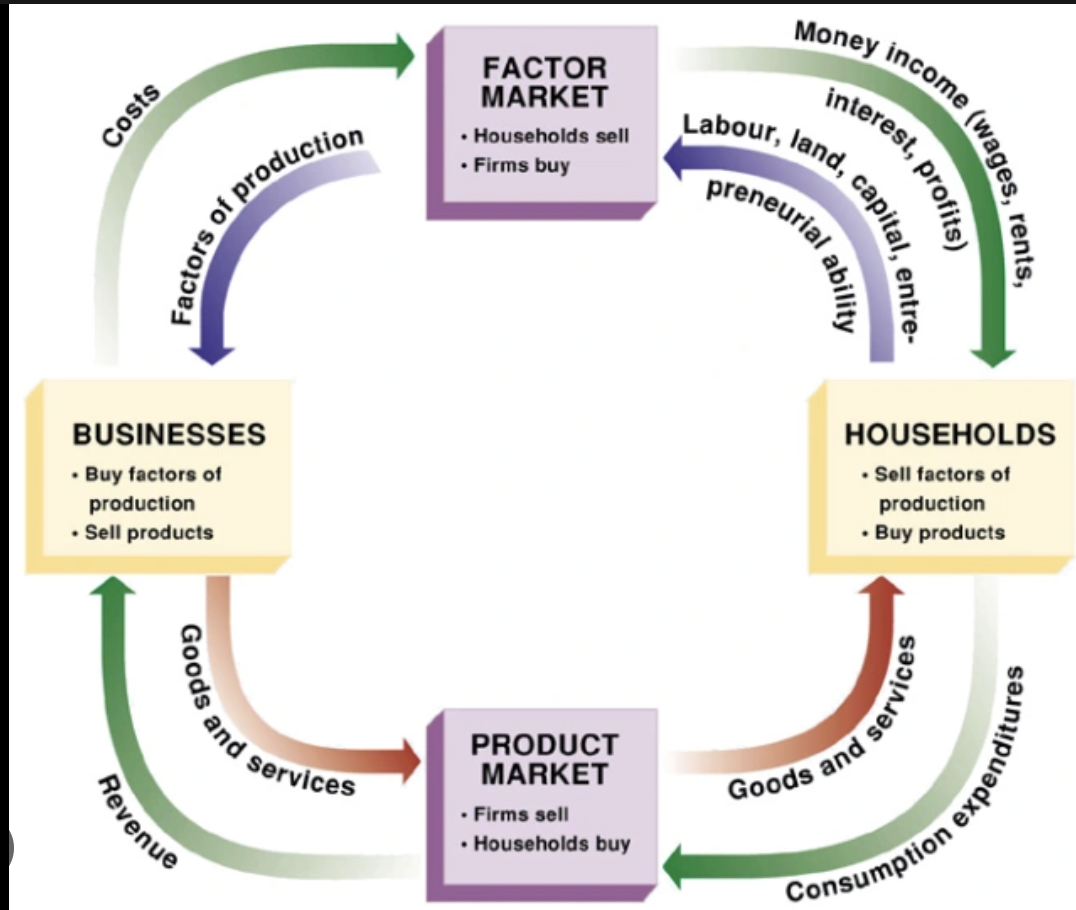
CIrcular Flow Model
A graphic representation of how different units of the economy interact.
Gross National Product
An estimate of total value of goods and services produced by the country’s residents both at home and abroad. (Includes things made out side of the country) GNP= GDP + NR (net income from assets abroad)
Factors of Production
Labor, land, capital, and entrepreneurship
Product Market
When the consumers exchange goods and services with products
Resource Market
When businesses purchase the resources they desire to produce the goods consumers demand.
Consumption
The final purchase of a good or service
Expenditures Approach
A method of calculating gross domestic production (GDP) by summing the amount spent on final goods and services within an economy during a particular period, usually a year. GDP= C (consumption)+I (investment) + G (government spending) + Xn (net exports)
Income approach
An approach to calculating GDP that involves adding up all of the income earned through the factors of production; GDP= W (wages) + R (rents) + I (interest) + Pr (profits)
Value added approach
An approach to calculating GDP by determining the value of goods and services and subtracting the good and services there were used in generating that output. GDP= Value of production - Value of intermediate good.
Economic Wellbeing
Consists of the material living conditions that people experience and their access to goods and resources
Intermediate Goods
Ones used to produce final goods ~ Used to calculate GDP using the Value-added approach
Final goods
Ones sold to the consumer who will actually use it.
Nonmarket Transactions
Domestic activities such as cooking, cleaning, and childcare make up a large share of economic activities
Underground Economy
the part of a country's economic activity that is unrecorded and untaxed by the US government; the black market.
Unemployment Rate
The percentage of the labor force not working. 4% or under is ok unemployment rate anything over is bad.
Labor Force
People who are able to and willing to work
Frictional Employment Rate
Times when people are not working due to transitions such as a move from school to work. (Why it is ok to have a 4% unemployment rate)
Structural Unemployment Rate
Occurs when there is a mismatch between the jobs that are available and the people looking for work. such as the decline of a particular industry
Cyclical Unemployment
Happens when the demand for goods and services in an economy decreases, forcing companies to lay off workers in an effort to cut costs.
Seasonal Unemployment
Occurs when people are unemployed at particular times of the year when demand for labor is lower than usual, like people who work at spirit halloween
Labor Force Participation Rate
Compares the size of the labor force with the number of people who could potentially be part of the labor force
Full Employment Rate
A condition where anyone who wants to work can get work
Natural Rate of Unemployment
The accepted unemployment rate ~ 4% or under
Inflation
An overall rise in the price of goods and services
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
A measure that tracks the average change in price of a gap of consumer goods and services.
CPI= (Cost of market basket in year/Cost of market basket in base year) x 100
Inflation Rate
The rate of increases in price over a given period of time

Real Variables
The actual value of a good/service including inflation
Deflation
An overall drop in the price of goods and services
Disinflation
A marginal reduction in the inflation rate over a short period of time
Demand-Pull Inflation
When demand for goods or services rises faster than the supply of those goods and services.
Aggregate Demand
The total demand for all finished goods and services that consumers want at current prices
Ad= C (consumption) + I (investment) + G (government spending) + (X (total exports) - M (total imports))
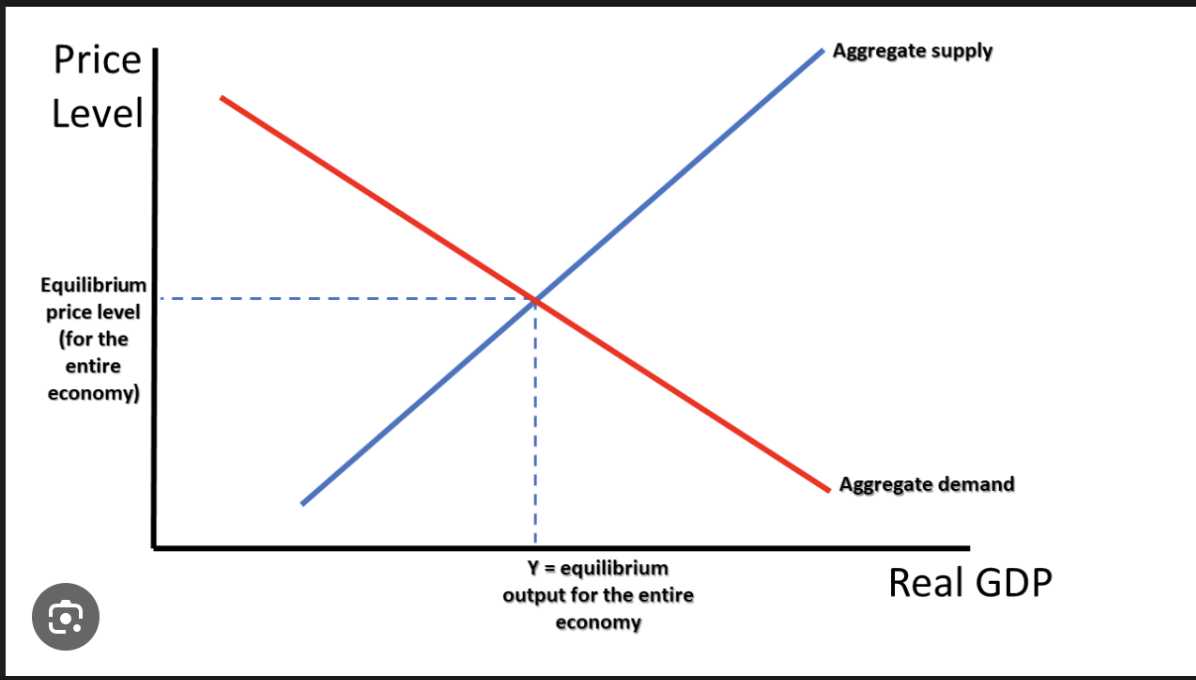
Aggregate Supply
The total amount of goods and services suppliers want to supply at those prices.
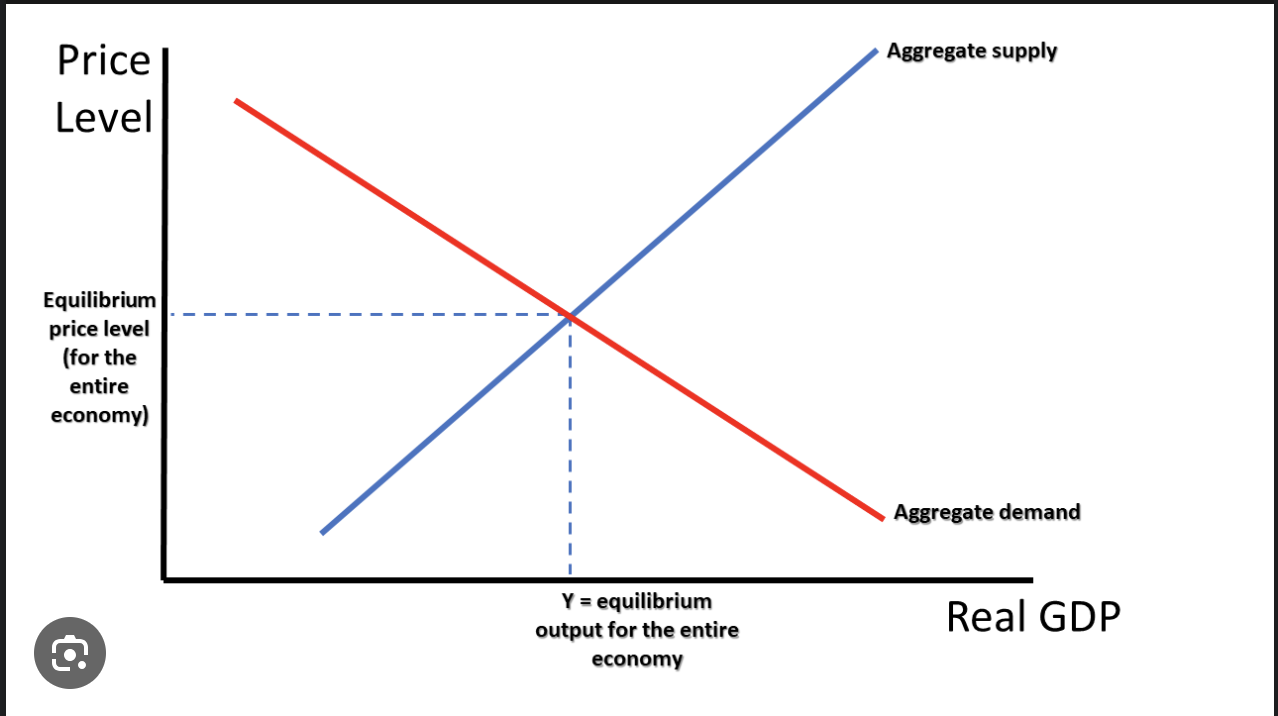
Cost-Push Inflation
occurs when overall prices increase (inflation) due to increases in the cost of wages and raw materials
Inflationary Spiral
When inflation leads to more inflation
Nominal GDP
Quantifies the total value in money of all goods produced in a year.
Nominal GDP = C (consumption) + I (investment) + G (govermnet spending) + (X (net export) - N (net import))
Real GDP
Quantifies the total value in money of all goods produced in a year, including deflation/inflation
Real GDP = Nominal GDP/GDP Deflator
GDP Deflator
Measures the change in prices of goods and services, including those exported to another country.
GDP Deflator = (Nominal GDP/Real GDP) x 100
Real GDP Per Capita
A measure of a country’s output per person. Calculated by dividing a country’s GDP per person
Recession
A significant decline in economic activity
Expansion
A phase of increasing employment, economic growth, and pressure for price increases
Peak
The maximum growth stage of the economy
Contraction
A phase that is generally characterized by increasing unemployment, decreasing economic activity, and declining economic output.
Trough
The lowest point in economic activity
Recovery
The eventual upward direction of the economy following the trough
Depression
A prolonged recession
Output Gap
The difference between the economy’s actual output and the potential output
Actual Output
What has been achieved in reality
Potential Output
How much the economy could ideally produce if it used all its resources including employees, natural resources, equipment, and technology