Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Overview
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
90 Terms
Chronic Productive Cough
Cough producing mucus lasting over specified duration.
Airway Inflammation
Swelling and irritation of bronchial airways.
Mucus Plugging
Blockage of airways by accumulated mucus.
Bronchospasm
Smooth muscle constriction causing airway narrowing.
Air Trapping
Inability to fully exhale air from lungs.
Hyperinflation of Alveoli
Excessive air in alveoli due to trapping.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
A group of lung diseases causing airflow blockage.
Chronic Bronchitis
Productive cough for 3 months over 2 years.
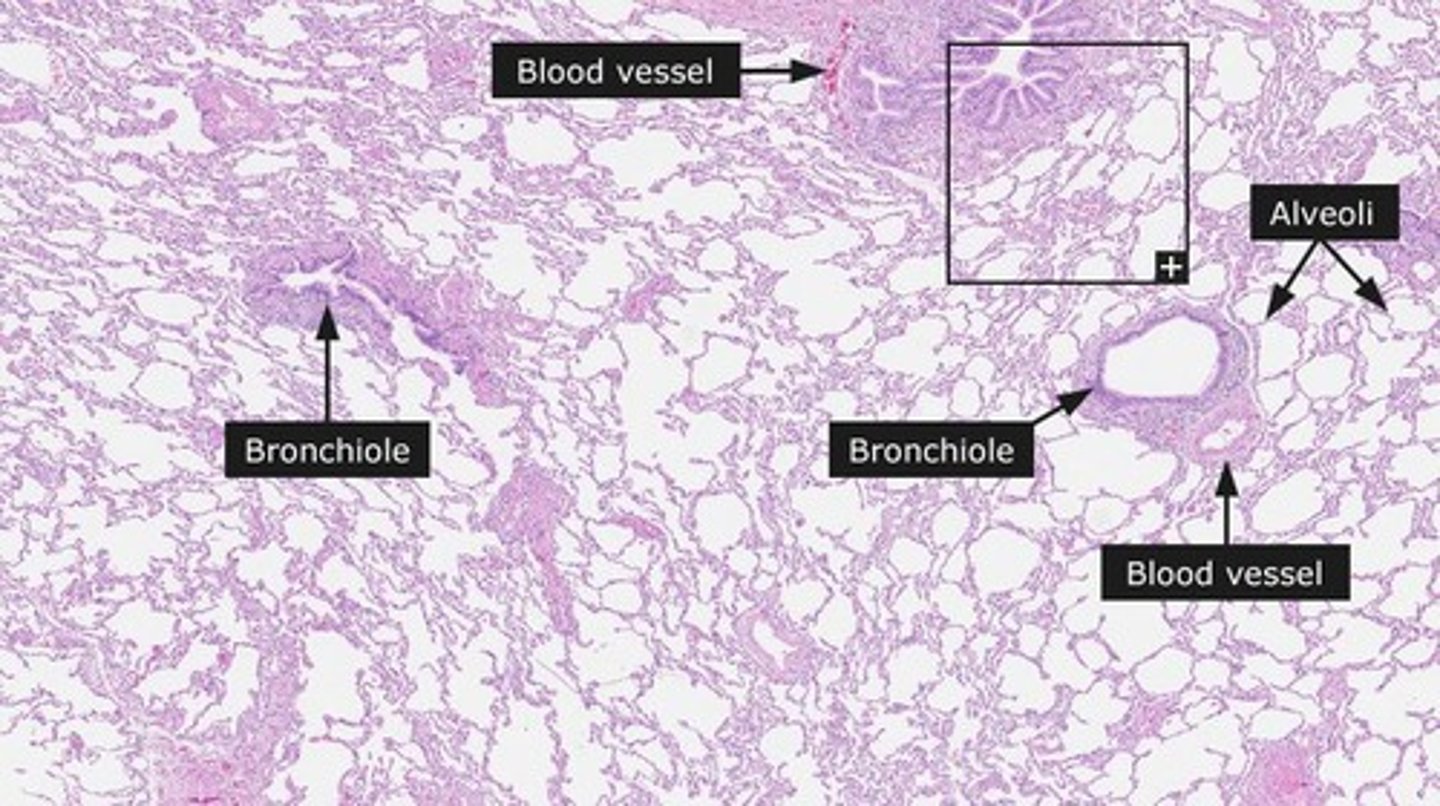
Emphysema
Permanent enlargement of air spaces distal to bronchioles.
Obstructive Lung Diseases
Diseases causing obstruction of airflow in lungs.
Centrilobular Emphysema
Weakening of respiratory bronchioles, linked to smoking.
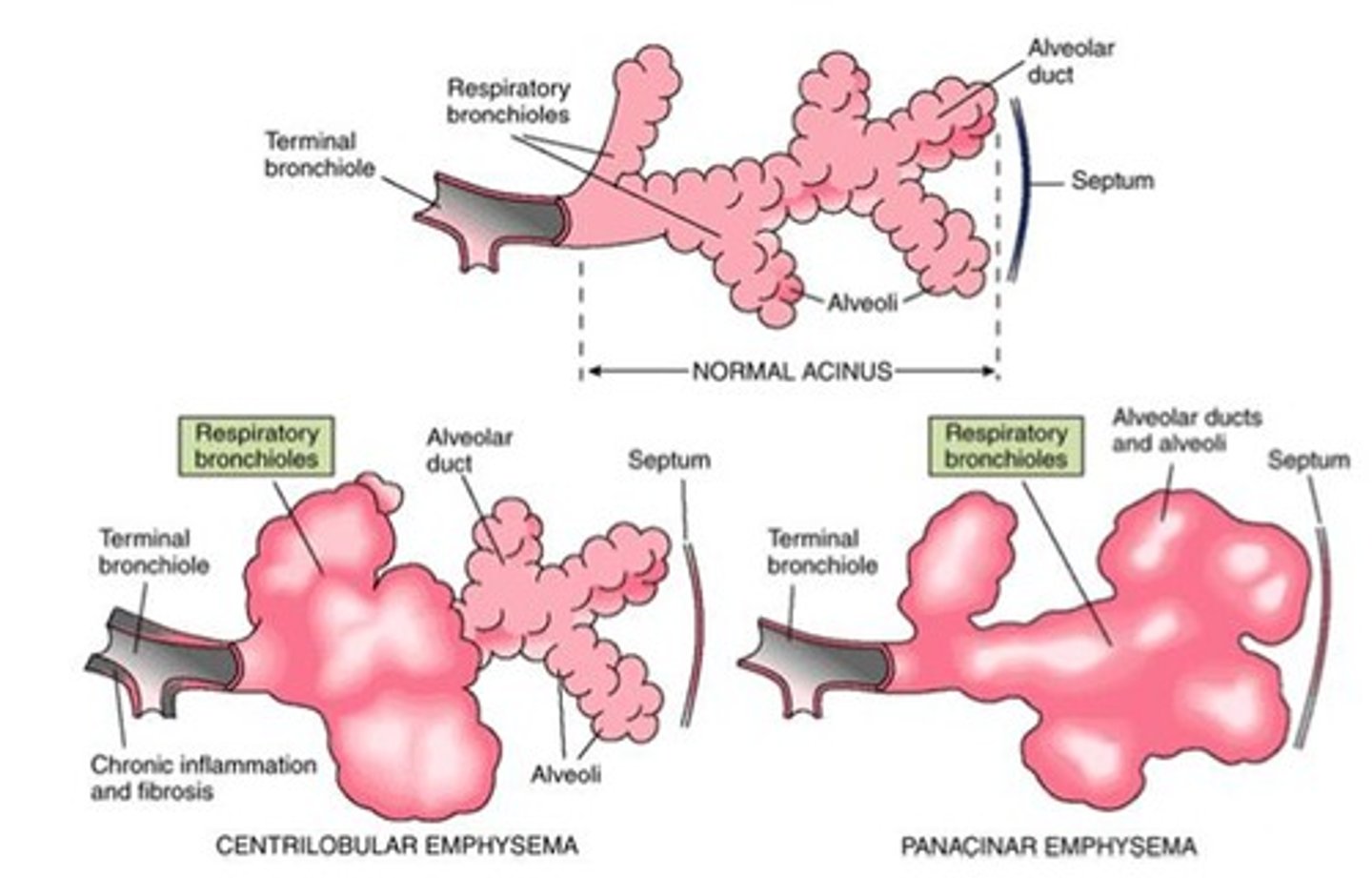
Panacinar Emphysema
Dilation affecting all alveoli distal to bronchi.
Destruction of Pulmonary Capillaries
Loss of blood vessels in lung tissue.
Lung Parenchyma Loss
Reduction of functional lung tissue.
Elastic Recoil Loss
Decreased ability of lungs to return to normal.
Increased Lung Compliance
Lungs stretch more easily but lose recoil.
Increased Residual Volume
Higher amount of air remaining after exhalation.
Total Lung Capacity
Maximum volume of air lungs can hold.
Cigarette Smoking
Primary risk factor for developing emphysema.
Chronic Inflammation
Persistent immune response causing lung tissue damage.
Anatomic Alterations
Structural changes in lungs due to disease.
Panacinar Emphysema
Abnormal enlargement of air spaces distal to bronchioles.
Alveolar-capillary Surface Area
Significantly decreased in panacinar emphysema.
Location of Panacinar Emphysema
Commonly found in lower lung parts.
Alpha1-antitrypsin Deficiency
Often associated with severe emphysema cases.
Centrilobular Emphysema
Type of emphysema affecting central parts of lobules.
Chronic Bronchitis
Excessive bronchial secretions leading to airway obstruction.
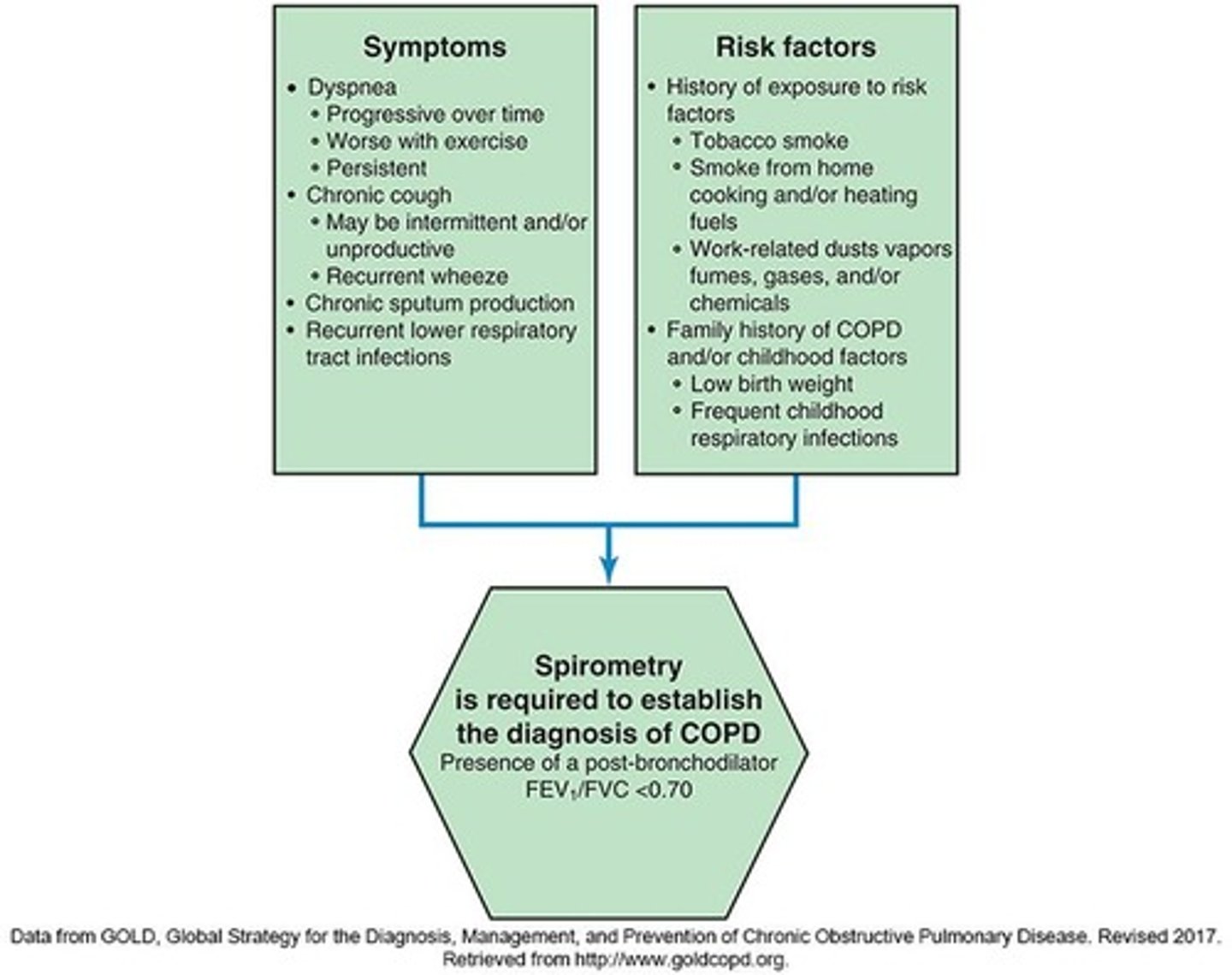
COPD Definition
Preventable, treatable disease with airflow limitation.
COPD Causes
Primarily caused by cigarette smoking and inflammation.
Airflow Limitation in COPD
Not fully reversible and usually progressive.
Small Airways Disease
Obstructive bronchiolitis contributing to COPD airflow limitation.
Parenchymal Destruction
Destruction of lung tissue, primarily in emphysema.
Structural Changes in COPD
Includes airway narrowing and loss of alveolar attachments.
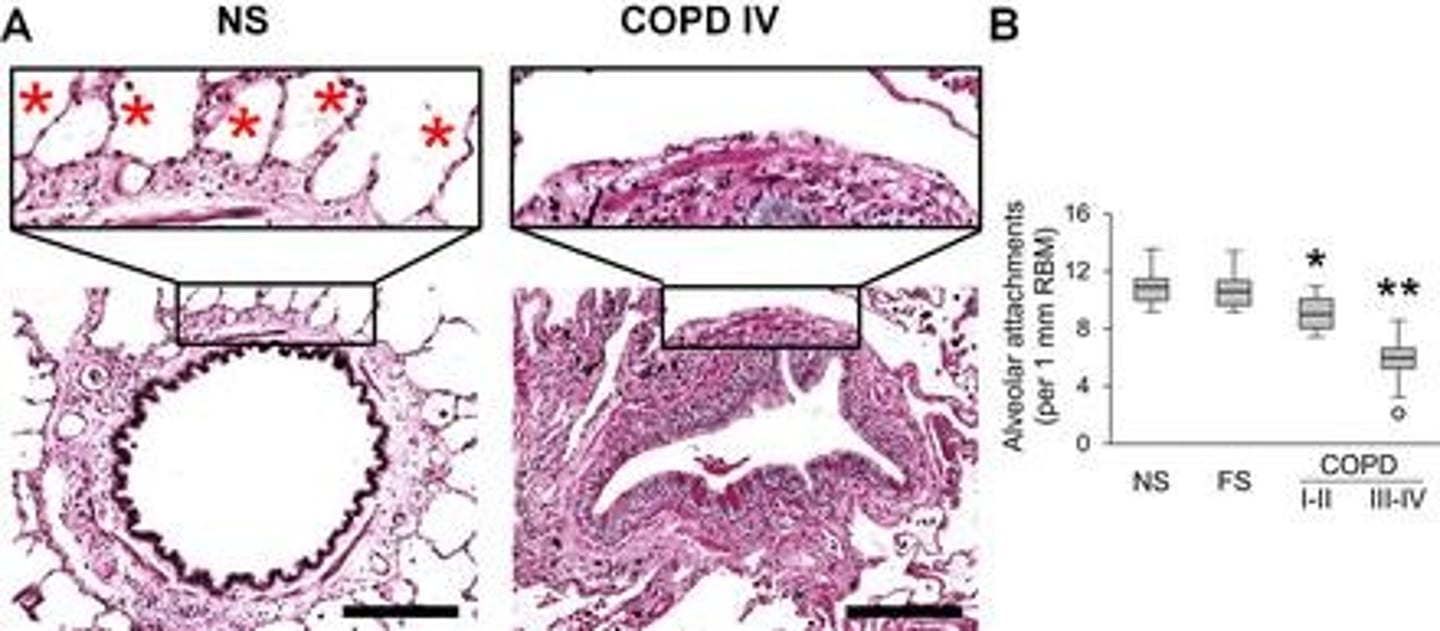
Lung Elastic Recoil
Decreased ability in COPD patients during expiration.
Mucociliary Dysfunction
Impaired clearance of mucus in COPD.
Systemic Inflammation
COPD leads to non-pulmonary consequences like cachexia.
Epidemiology of COPD
10-15 million Americans affected by COPD.
Under-diagnosis of COPD
Most authorities agree COPD is frequently missed.
Risk Factors for COPD
Includes genetic factors like alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency.
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Function
Protects lung tissue by inactivating elastase.
Elastase
Enzyme that damages lung tissue when unchecked.
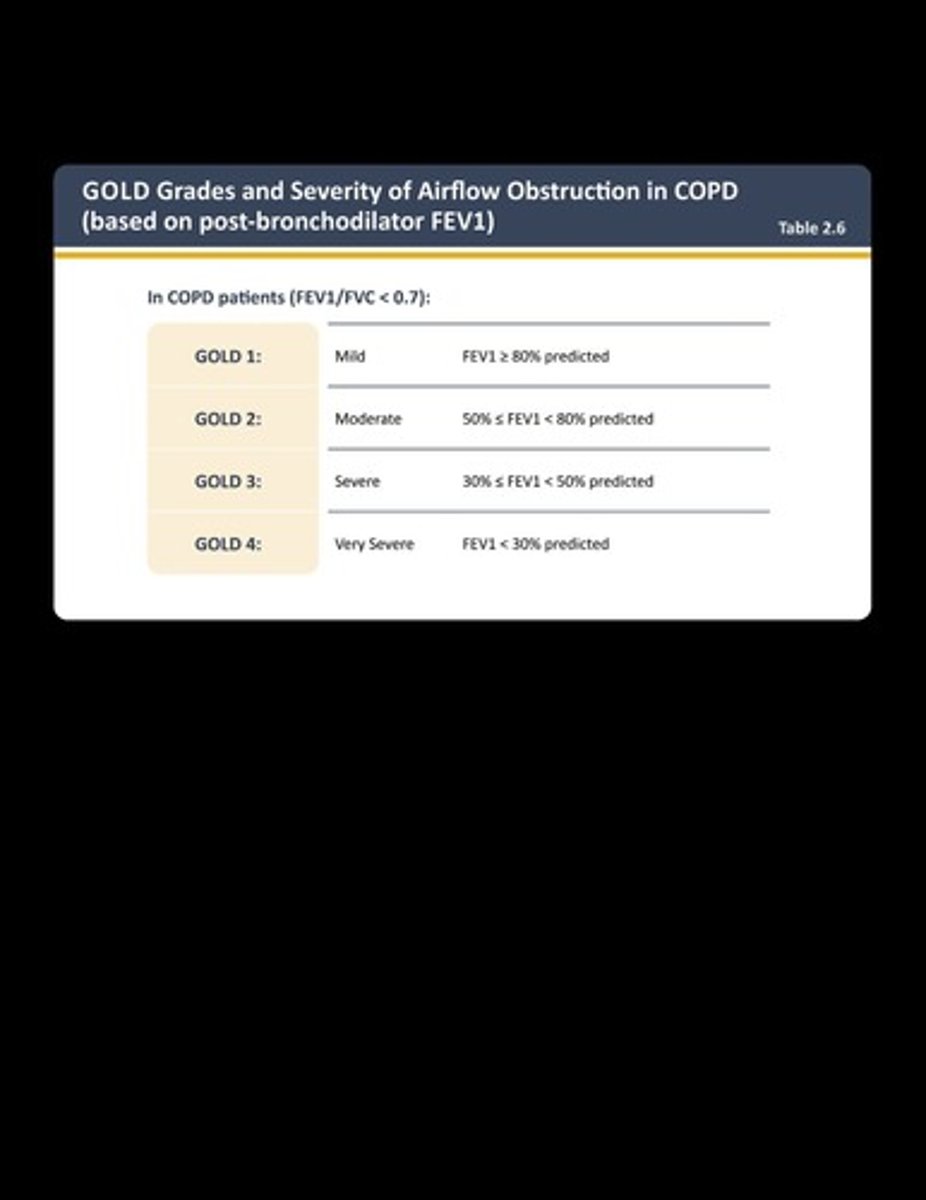
GOLD Staging
Measures severity of COPD based on symptoms.
Systemic Consequences of COPD
Includes cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis, and depression.
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, a progressive lung disease.
GOLD
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease guidelines.
Age and Gender
Older age and female gender increase COPD risk.
Lung Growth Factors
Factors affecting lung development during gestation and childhood.
Socioeconomic Status
Poverty linked to increased COPD risk factors.
Exposure to Particles
Inhalation of harmful particles contributing to COPD.
Tobacco Smoke
Primary risk factor for COPD from various smoking forms.
Occupational Exposures
Exposure to dust and chemicals at work increases risk.
Indoor Air Pollution
Pollution from burning fuels in poorly ventilated spaces.
Outdoor Air Pollution
Environmental pollutants with minor effect on COPD risk.
Asthma
Chronic condition linked to increased COPD susceptibility.
Chronic Bronchitis
Long-term inflammation of the airways, a COPD risk factor.
Severe Respiratory Infections
Childhood infections linked to reduced lung function later.
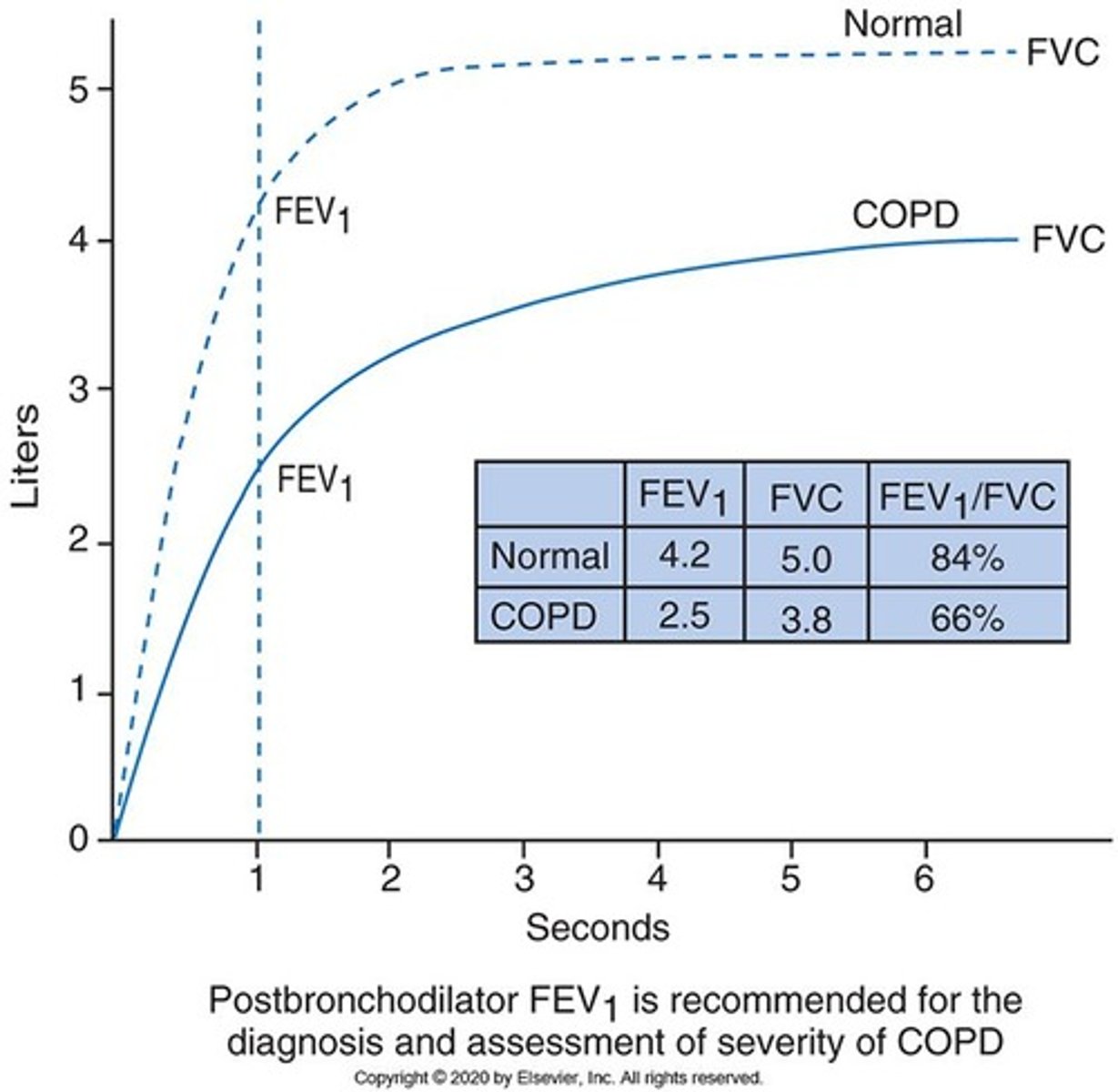
Spirometry
Pulmonary function test essential for diagnosing COPD.
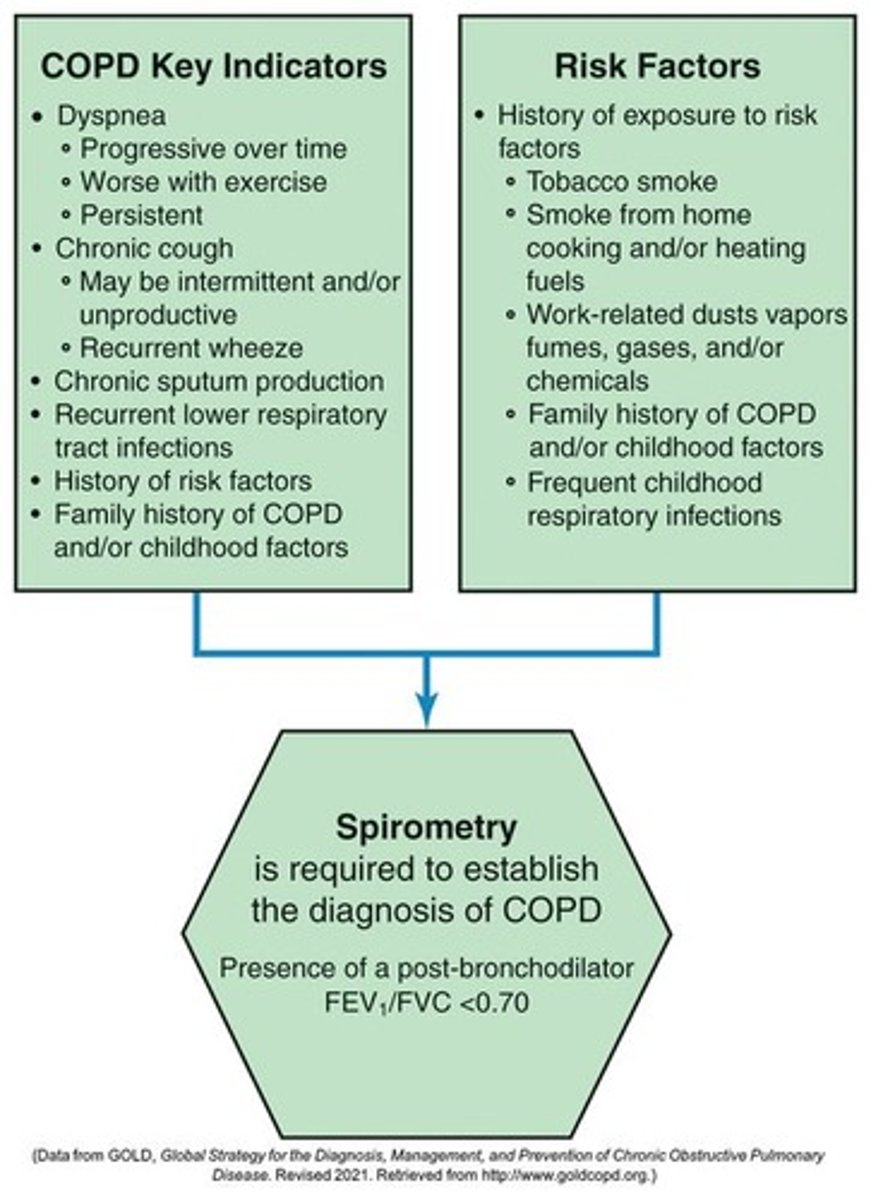
Assessment of Airflow Limitation
Evaluates airflow using FVC, FEV1, and FEV1/FVC ratio.
FVC
Forced Vital Capacity, total air exhaled after deep breath.
FEV1
Forced Expiratory Volume in one second measurement.
mMRC Dyspnea Scale
Questionnaire assessing breathlessness severity in COPD patients.
COPD Assessment Test (CAT)
Tool to evaluate symptoms and impact of COPD.
COPD Exacerbation
Acute worsening of respiratory symptoms requiring treatment.
Exacerbation Severity Levels
Classified as mild, moderate, or severe based on treatment.
High Exacerbation Risk
Two or more yearly exacerbations indicate high risk.
COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease affecting airflow.
Comorbidities
Additional diseases worsening COPD condition.
Cardiovascular disease
Heart-related conditions impacting COPD patients.
Skeletal muscle dysfunction
Weakness affecting muscles in COPD patients.
Metabolic syndrome
Cluster of conditions increasing heart disease risk.
Osteoporosis
Bone density loss, common in COPD patients.
Depression
Mood disorder prevalent among COPD sufferers.
Anxiety
Mental health condition affecting COPD management.
Lung cancer
Malignancy often associated with COPD.
Chest x-ray
Imaging to rule out other lung diseases.
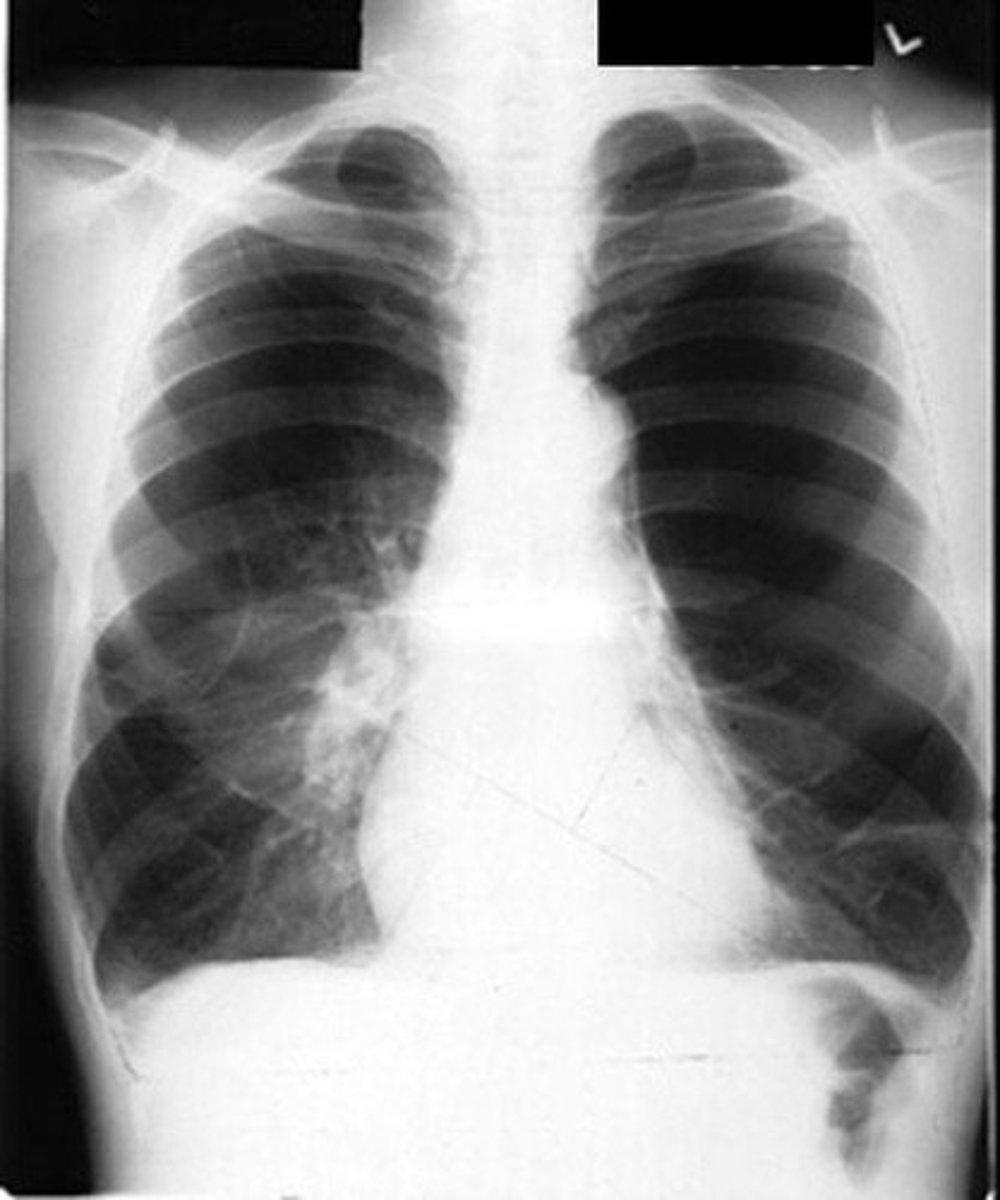
Chest CT
Detailed imaging for assessing lung conditions.
Lung Volume Testing
Measures lung capacity and airflow obstruction.
DLCO testing
Assesses gas exchange efficiency in lungs.
Oximetry
Measures blood oxygen saturation levels.
ABG
Arterial Blood Gas test for respiratory function.
Exercise Testing
Evaluates physical capacity and COPD severity.
Alpha1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
Genetic condition affecting lung function.
Chronic Bronchitis
COPD type with excessive mucus production.
Emphysema
COPD type characterized by alveolar damage.
Pink Puffer
Emphysema patient presentation with breathlessness.
Blue Bloater
Chronic bronchitis patient with cyanosis.
PaO2
Partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood.
PaCO2
Partial pressure of carbon dioxide in blood.
Cor pulmonale
Right heart failure due to lung disease.
Still learning (6)
You've started learning these terms. Keep it up!