intro to psych final - Dr. Bright (GCC)
1/151
Earn XP
Description and Tags
begins with vocab for chp 14-18, includes names and other vocab he told us to study
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
152 Terms
how do you minimize a stigma?
by seeing someone first as a person, but secondly as someone with a disorder
comorbidity def
meeting criteria for more than one mental disorder
psychopathology def
study of mental, emotional, and behavior disorders
maladaptive def
when a mental disorder causes significant disruption and distress
example of maladaptiveness
too much depression may keep you from completing assignments and day-to-day activities
DSM
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (of mental disorders)
what causes mental disorders?
biological and/or psychosocial factors
schizophrenia def
chronic serious mental illness causing disordered cognitions and behaviors
5 symptoms of schizophrenia
psychotic symptoms, delusions, hallucinations, disorganized thought, catatonia
delusions of schizophrenia (3)
persecution, influence, erotomanic
what does the persecution delusion of schizophrenia make others believe
“everyone’s out to get me” OR “people are trying to poison my food"!”
what does the influence delusion of schizophrenia make others believe
someone is putting those thoughts into their head (i.e. GOD)
what does the erotomanic delusion of schizophrenia make others believe
“i am destined to be with this person”
most common form of hallucinations
voices and visuals
leading cause of schizophrenia
stress and vulnerability
3 mood disorders we discussed
depression, seasonal affective disorder (SAD), and bipolar
depression def
extreme and prolonged sadness / hopelessness
biopsychosocial
looking at the whole person to determine why something happened (not just one thing)
suicide phone number
988
seasonal affective disorder (SAD)
depression during certain seasons
job of phototherapy
regulate circadian rhythms and melatonin
bipolar disorder
mood swings between depression and mania
3 types of anxiety disorders
generalized anxiety disorder, specific phobia, panic disorder / attack
generalized anxiety disorder
patient has 3+ symptoms for >6 months
specific phobia
excessive and irrational fear of usually 2+ things (more common in females)
panic disorder / attack
sudden physiological distress with no identifiable trigger
trigger for a panic attack (usually)
agoraphobia
post-traumatic stress disorder
flashbacks and more common in women
obsessive compulsive disorder
recurrent disturbing thoughts compelling you to act repeatedly to decrease anxiety
dissociative identity disorder / multiple personality disorder
one person possesses 2+ distinct personalities
antisocial personality disorder (PD)
lack empathy, manipulative, under-aroused, seeks stimulusex
example of antisocial PD
adhd. can lead to juvie, then to apd, then to prison
borderline PD
affective instability, lack a strong sense of self and self-control
psychoanalysis
free association and resistance: YOU TALK, they listen
dream analysis
reveals unconscious messages during therapy
behavior therapy
one person on couch and one on chair (larry the cucumber)
aversion therapy
uses classical conditioning to link a bad habit with discomfort
example of aversion therapy
to stop biting nails, paint them so they taste bad when you bite them
systematic desentization
rank a list of fears, relax, and work through them
reciprocal inhibition
you can’t be both anxious and relaxed
VR exposure or vicarious desensitization
something to distract from a fear
example of VR exposure
fear of roller coasters: ride a slow ride, but progressively increase
operant therapy
no reward = extinction
example of operant therapy
sticker chart to get people to do the right thing, when they do, they get a prize
2 types of humanistic therapies
client centered and existential
client centered humanistic theory
facing client during therapy, genuine empathy
existential therapy
therapy based on choice and personal responsibility
cognitive therapy
seek to change disordered thinking
all-or-nothing thinking
believing one event applies to all (this is BAD!)
key to psychotherapy success
therapeutic alliance
therapeutic alliance
rooted in active listening, empathy, reflection of feelings, etc
example of therapeutic alliance
AA meetings and sponsors
tardive dyskinesia
longterm antipsychotic drug usage
reference group
someone you want to be like
cognitive dissonance
clashing attitudes, behaviors
example of cognitive dissonance
healthy person eats LOTS of desserts
proxemics
personal space and culture govern how close is comfortable for interactions of individuals
social loafing
being part of a group reduces individual effort
group sanctions
rewards given by a group to control behavior
group think
emphasis on loyalty to group does not allow people to say what they really think
excommunication
blocking or unfriending someone when they don’t conform to your ideas
brainwashing
coercive attitude change involving environmental control, isolation, manipulation, and abuse
coersive
against your will
% of childhood attachments (3)
65% secure, 25% avoidant, 10% ambivalent / anxious
T or F: childhood attachment affects adulthood relationships
TRUE
secure childhood attachment leads to…
trusting, longer relationships
avoidant childhood attachment leads to…
skepticality, noncommittal, fears
ambivalent/anxious childhood attachment leads to…
anxiety, jealousy, borderline personality disorder, questioning
evolutionary psychology / mate selection
men seek youth & beauty, women seek maturity & $$
bystander effect
everyone assumes someone else will help out
when are you more likely to help someone
when you’re empathetic towards them
men vs women: helping others
men: more daring, women: more relational
industrial organizational (IO) psychologists
enhance workplace culture, emphasize job satisfaction
job analysis
vocational interest tests, structured interviewing
example of job analysis
myers briggs test, ASVAB
job satisfaction examples
flex-time, sincere gratitude, intrinsic motivation, shared decision making
theory X vs theory Y
X = tight control, no development
Y= giving responsibility, control
example of theory Y
facing the giants scene
environmental psychology
social and physical environments effect behavior
example of environmental psychology
noise and light pollution
attentional overload / social numbing
people enter social dilemmas with individual/immediate needs
forensic psychology
influences behavior- jury, witness, etc. in law enforcement
what leads to peak performance
flow (fully focused) experience (like the meme)
teratogen
environmental factors that cause congenital problems (usually with childbirth)
example of teratogen
alcohol, smoking, drugs, health problems (diabetes)
sleep disorders (4)
narcolepsy, apnea, night terrors, insomnia
narcolepsy
fall asleep suddenly / unexpectedly
apnea
breathing frequently stops and lightly wakes you up
negative of apnea
can lead to sudden infant death syndrome in babies
night terrors
stage 4 total panic; wake up with little memory of why
insomnia
difficulty falling / staying asleep
causes of insomnia
poor diet, screens
brain scanning procedures (4)
MRI, PET scan, EEG, CT scan
MRI
3D image of brain using strong magnetic field
PET scan
shows glucose consumption to identify active parts of brain
EEG
measures electrical activity on brain surface
CT scan
reveals effects of strokes, tumors, traumatic brain injuries

label: F
lens
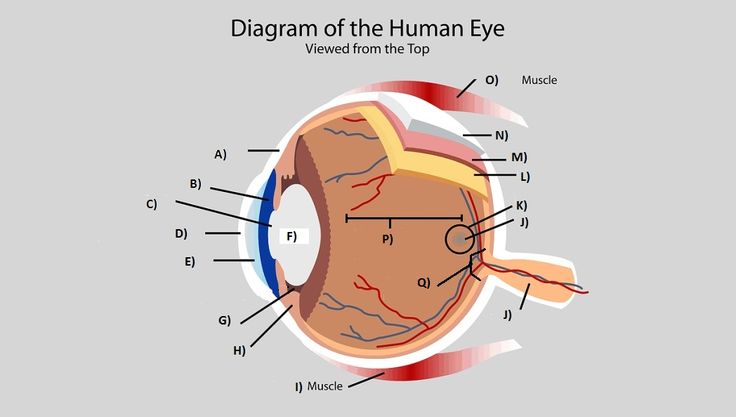
label: B
iris