Organic Chemistry Reactions
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Nucleophilic Substitution of Alkyl Halides
What type of reaction is this?
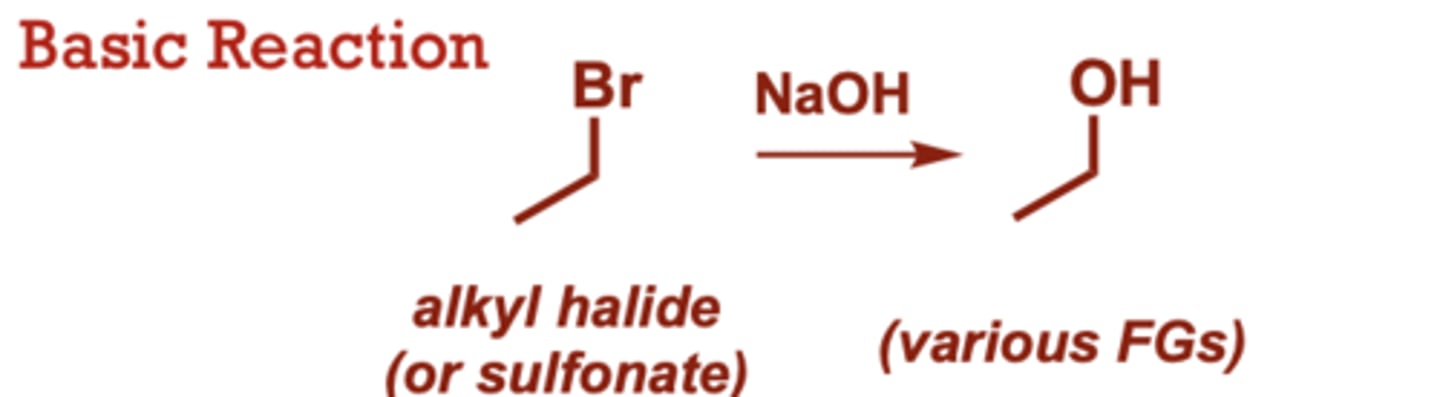
dehydrohalogenation
What type of reaction is this?
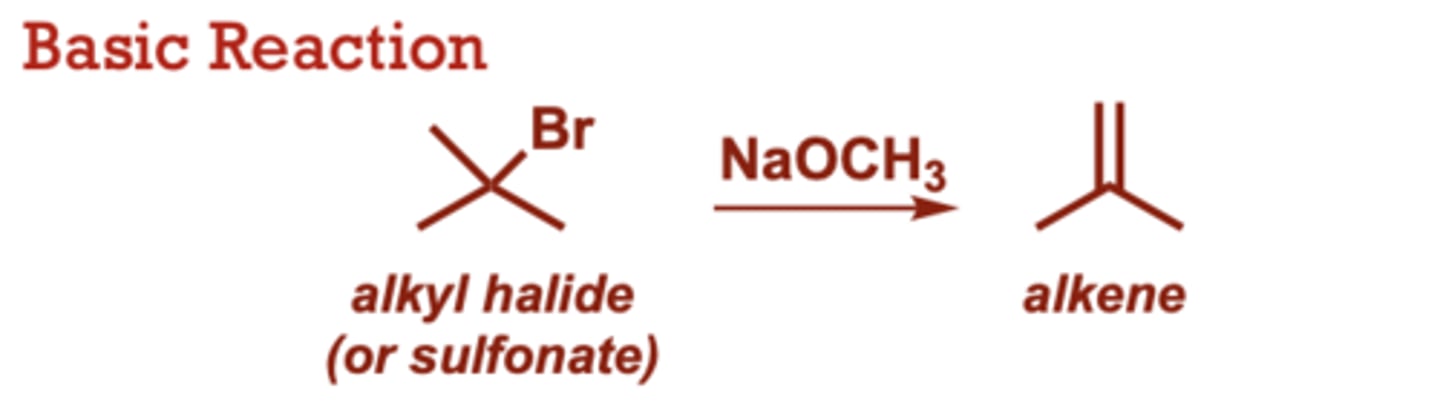
dehydration of alcohols
What type of reaction is this?
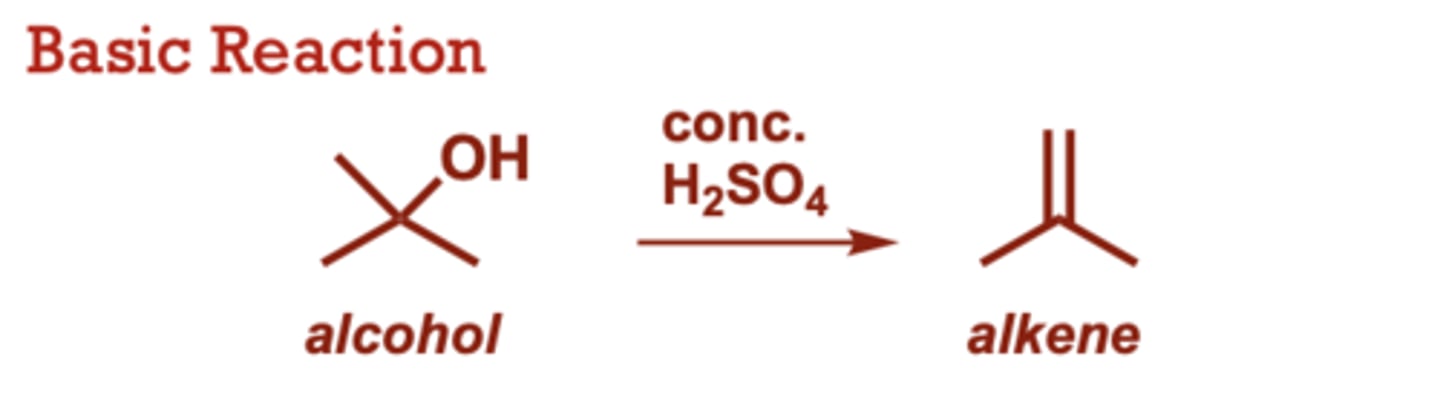
hydrohalogenation of alkenes
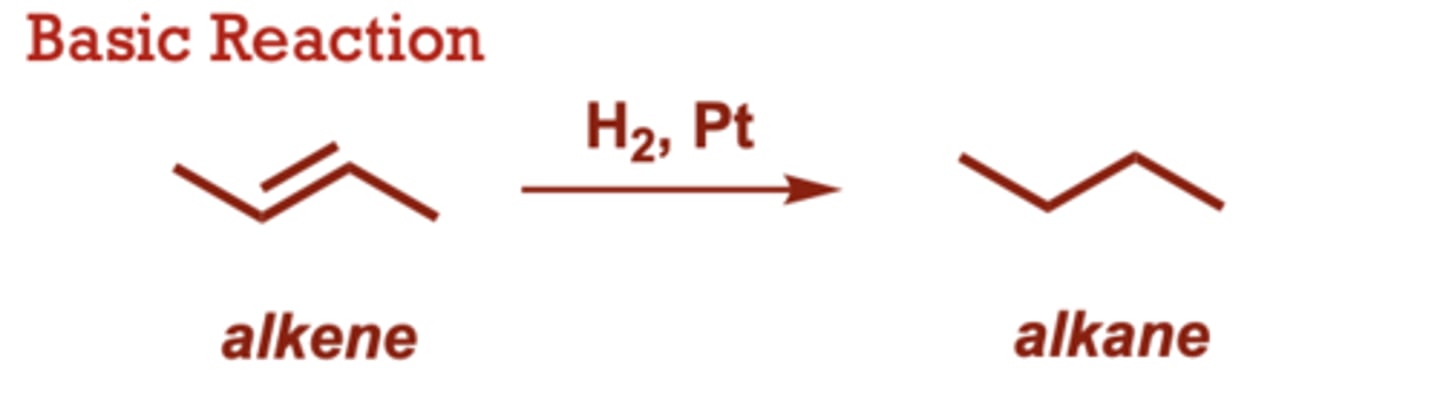
What type of reaction is this?
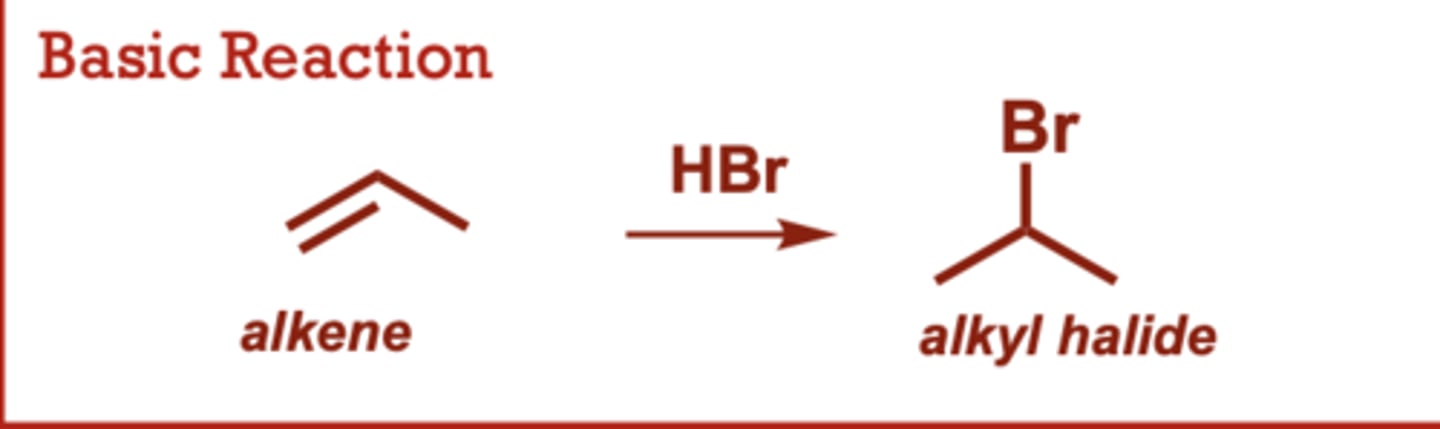
acid-catalyzed hydration of alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
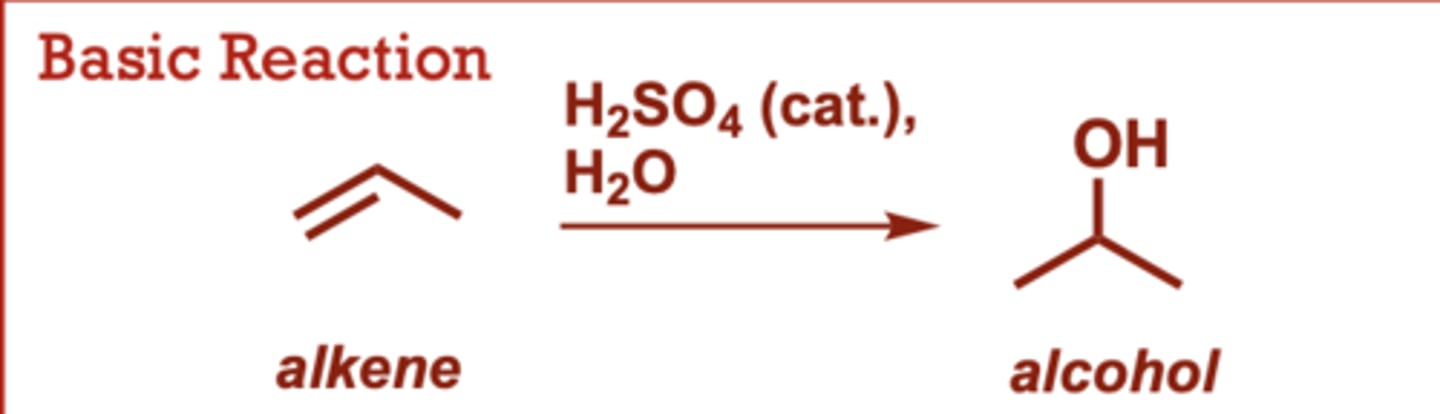
oxymercuration-demurcuration of alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
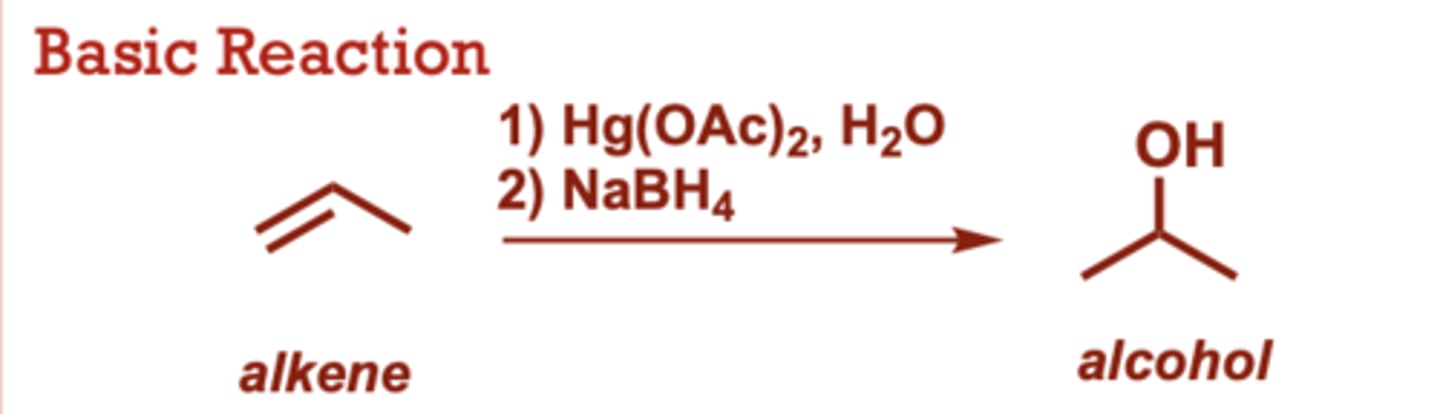
hydroboration-oxidation of alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
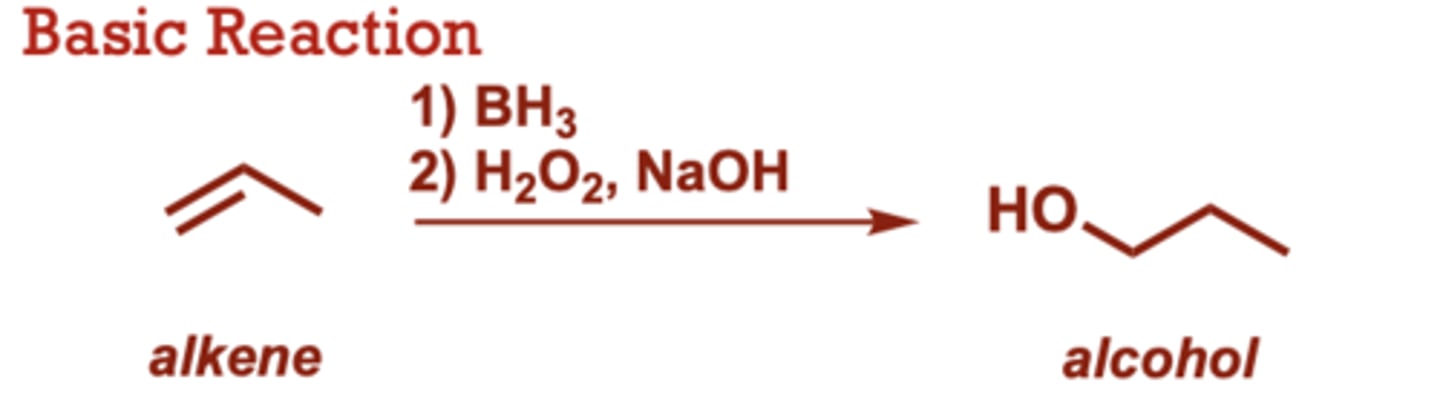
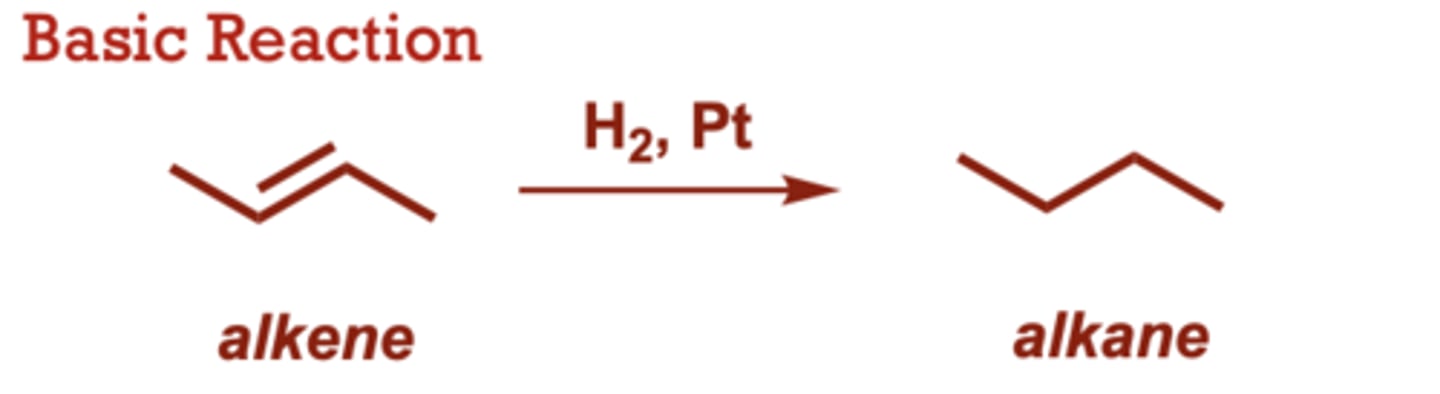
catalytic hydrogenation of alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
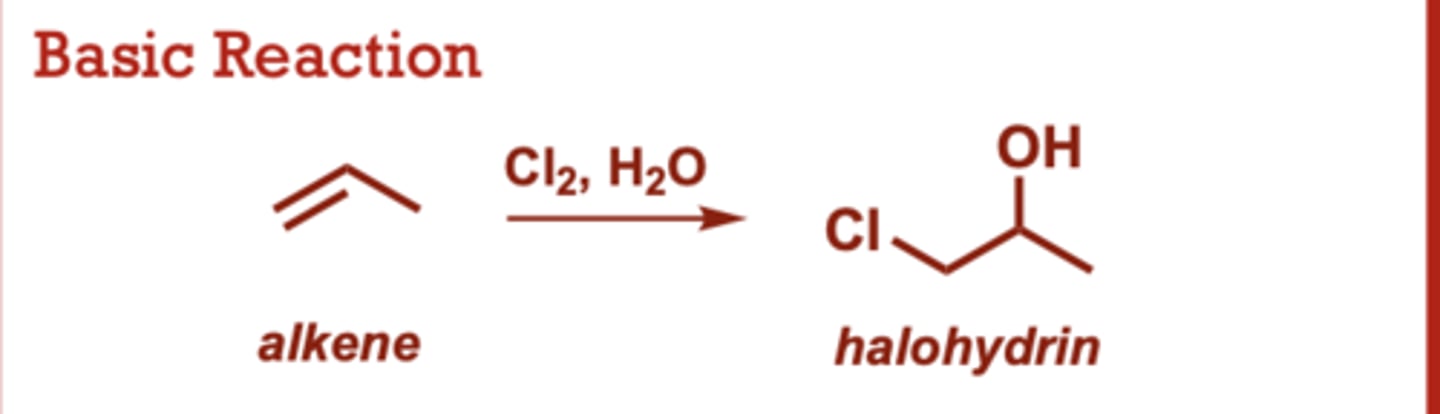
halohydrin formation from alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
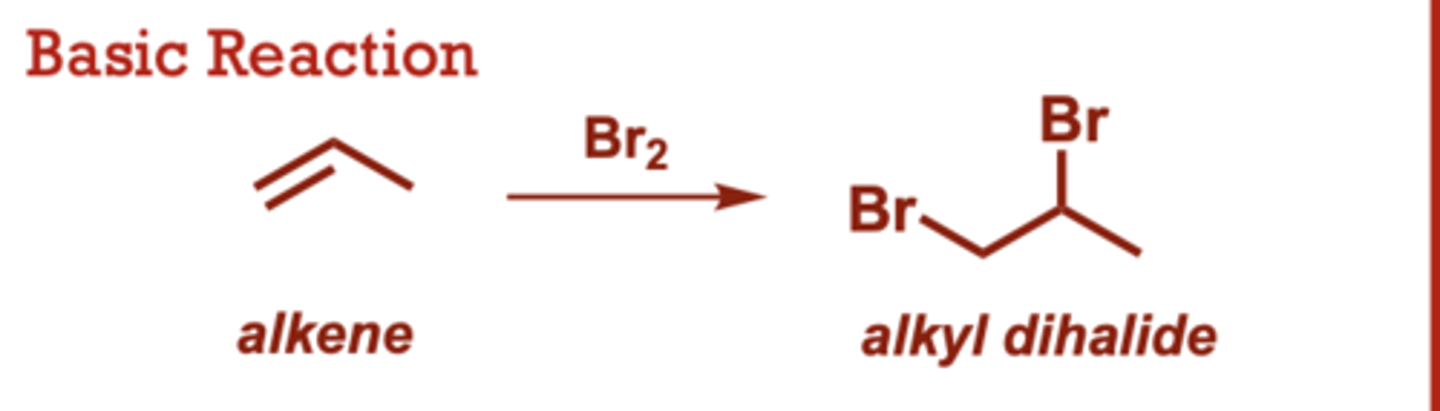
dihalogenation of alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
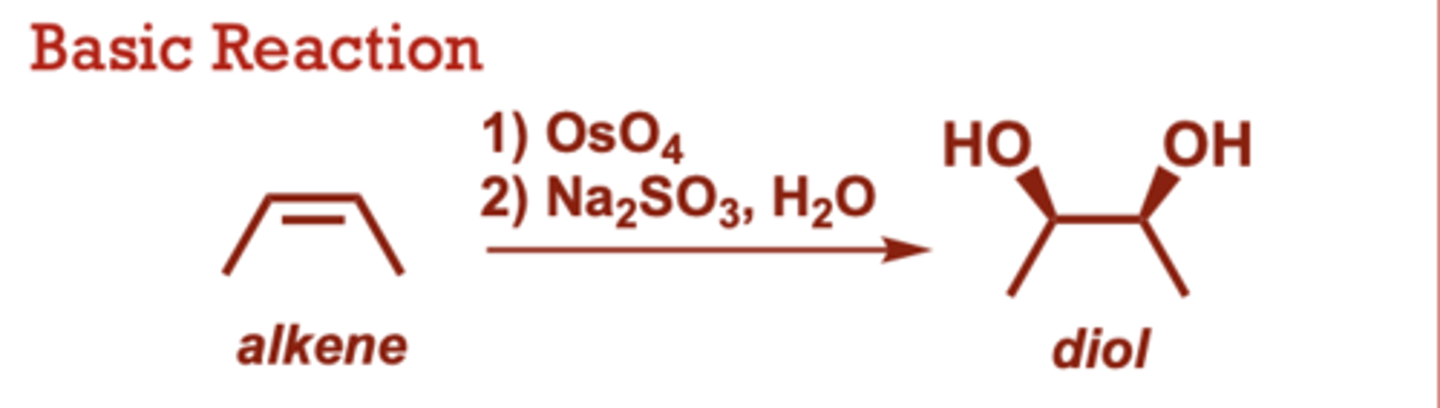
anti-dihydroxylation of alkenes
What type of reaction is this?

syn-dihydroxalation of alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
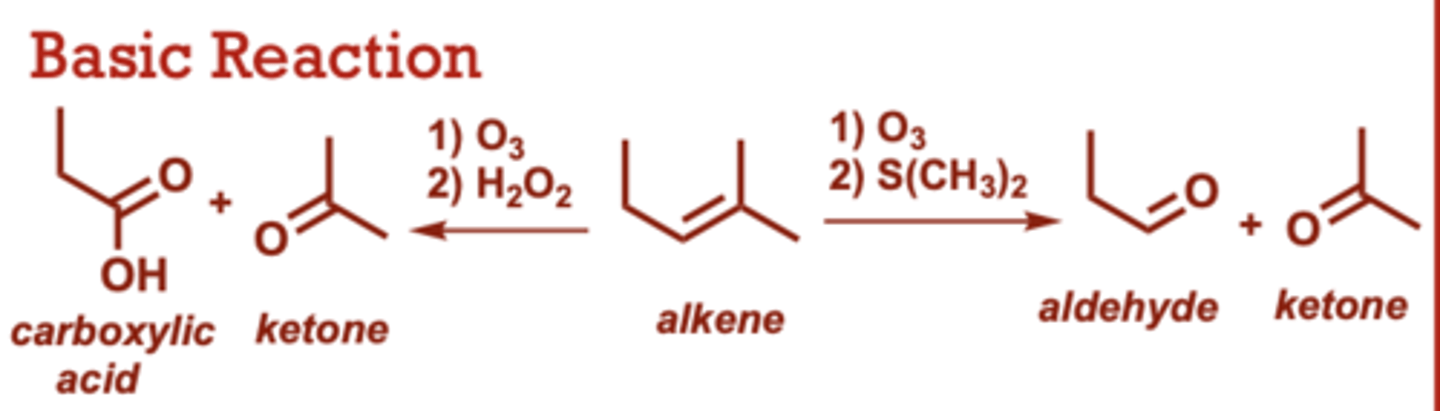
ozonolysis- reduction/oxidation
What type of reaction is this?
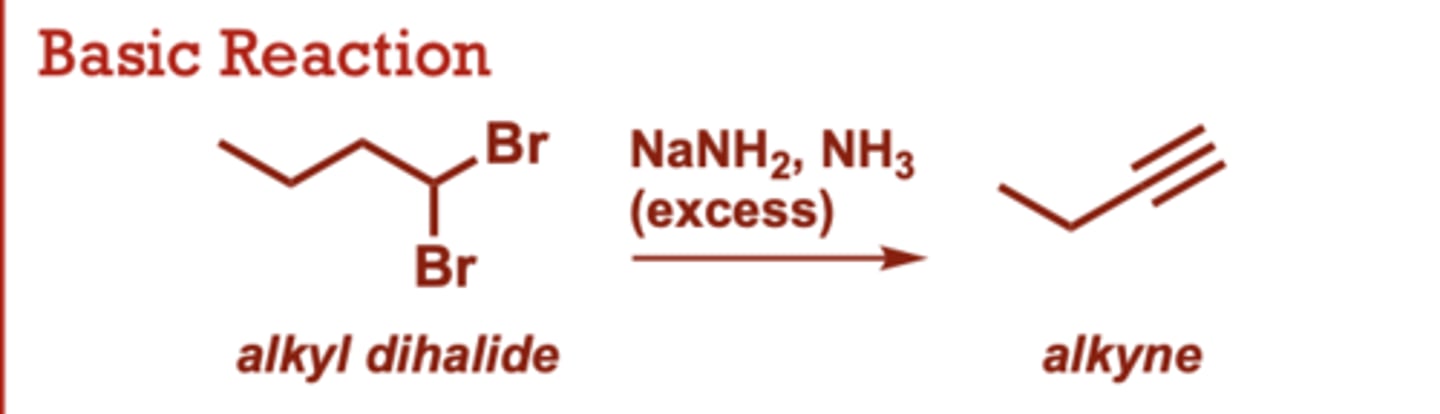
Preparation of Alkynes from Alkyl Dihalides
What type of reaction is this?
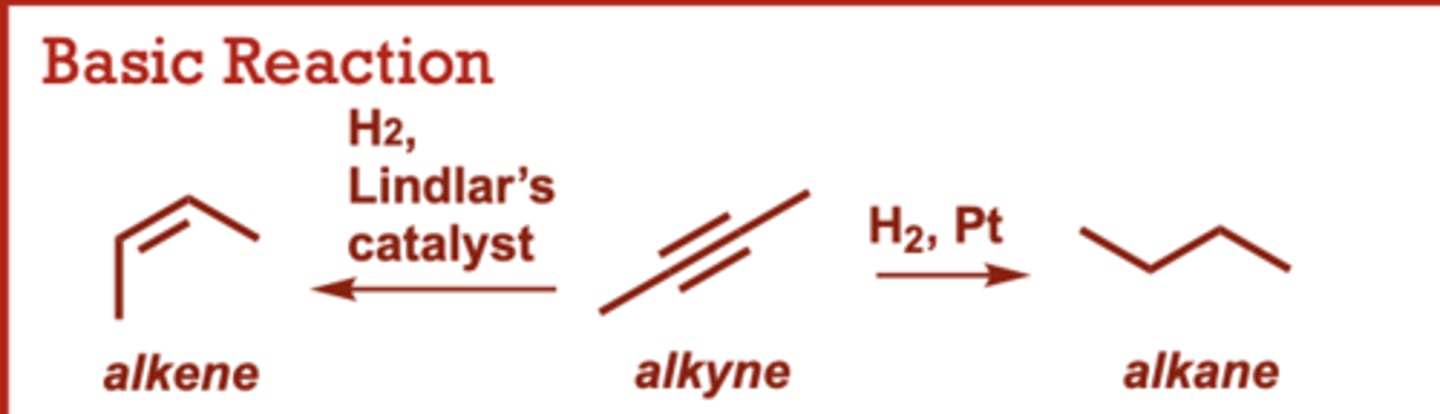
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?
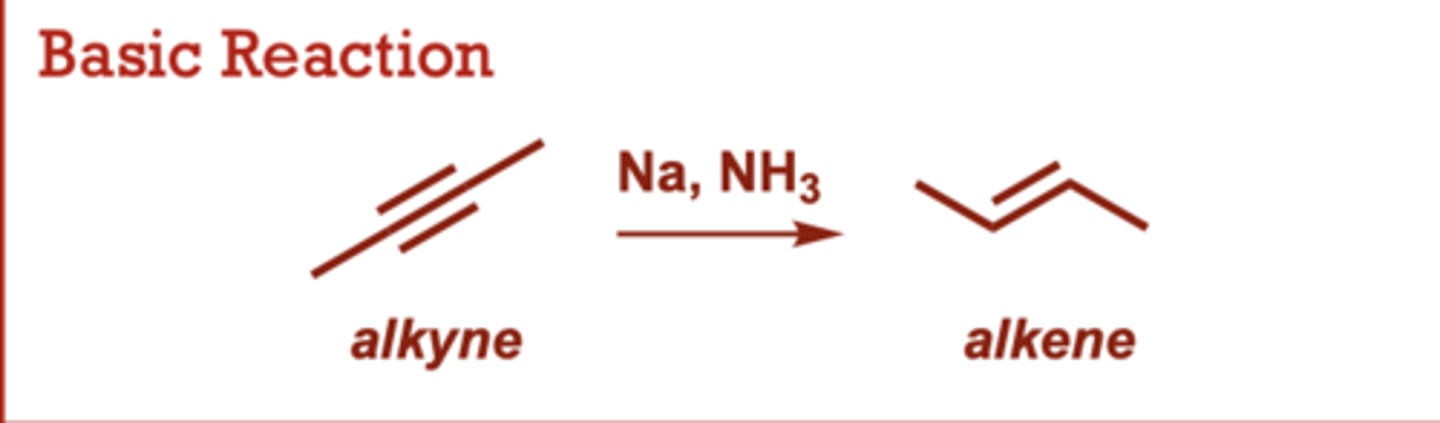
Dissolving Metal Reduction of Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?
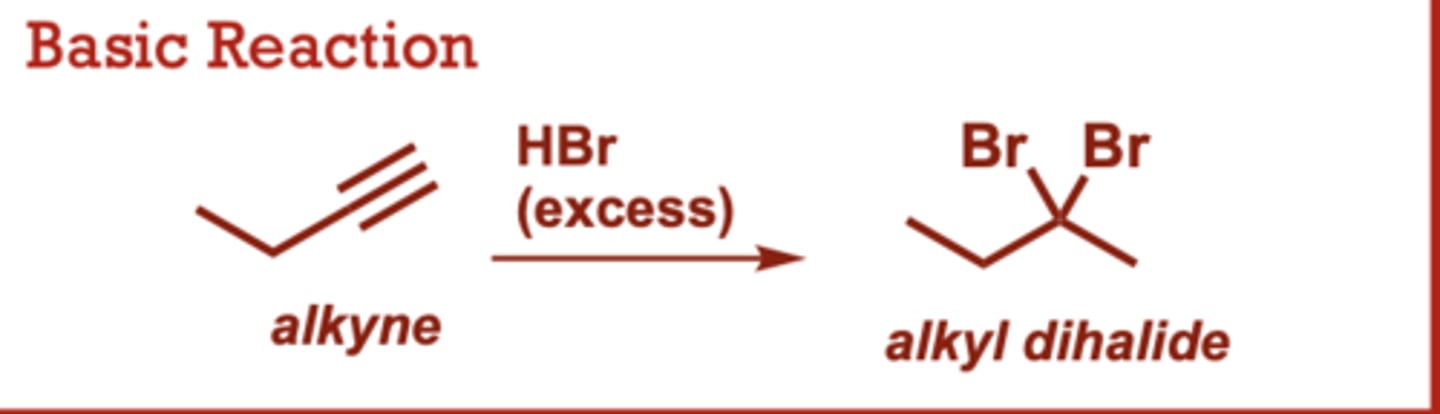
Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?
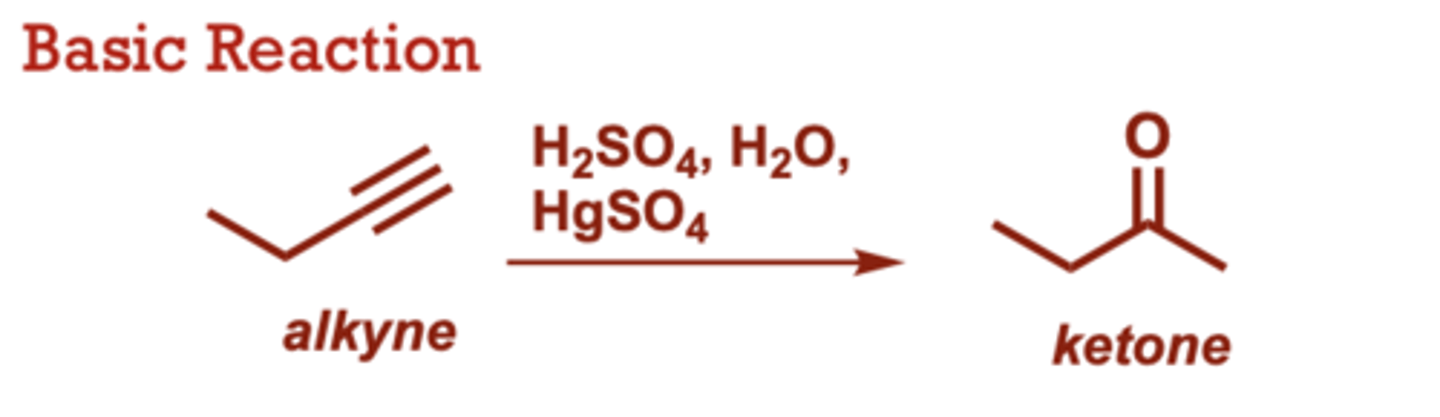
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?
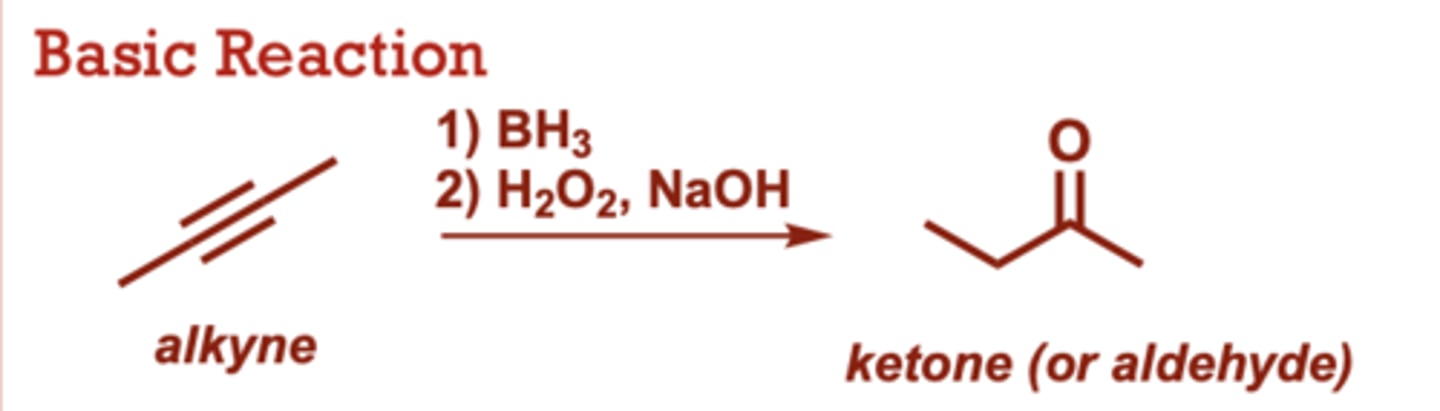
Hydroboration/Oxidation of Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?
Halogenation of Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?
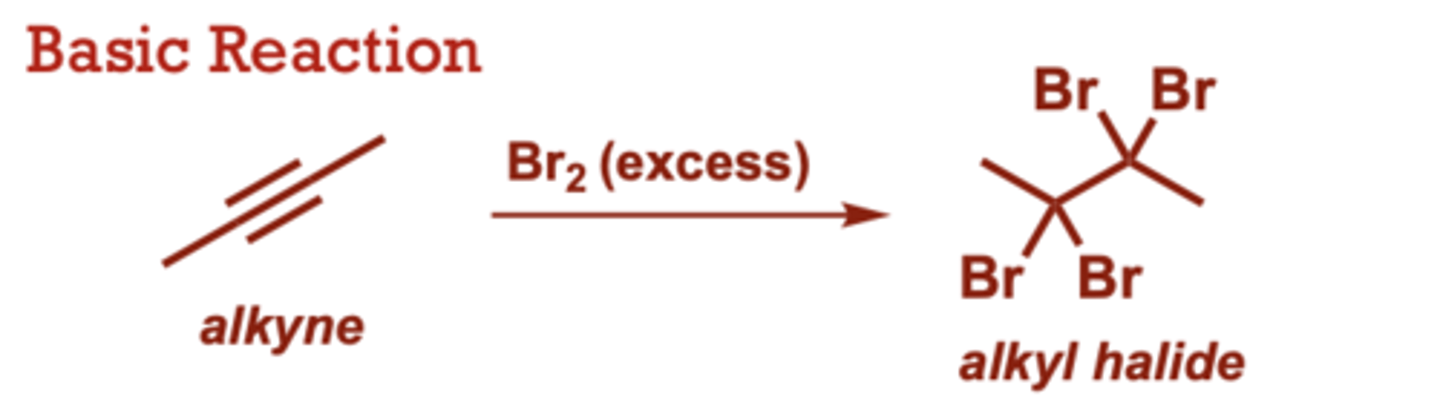
Ozonolysis of Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?

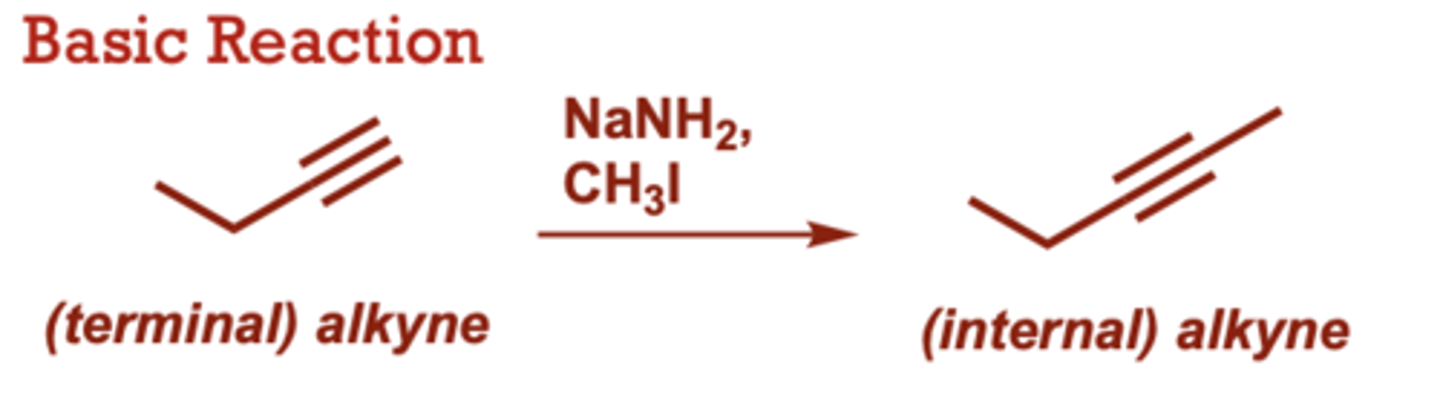
Alkylation of Terminal Alkynes
What type of reaction is this?
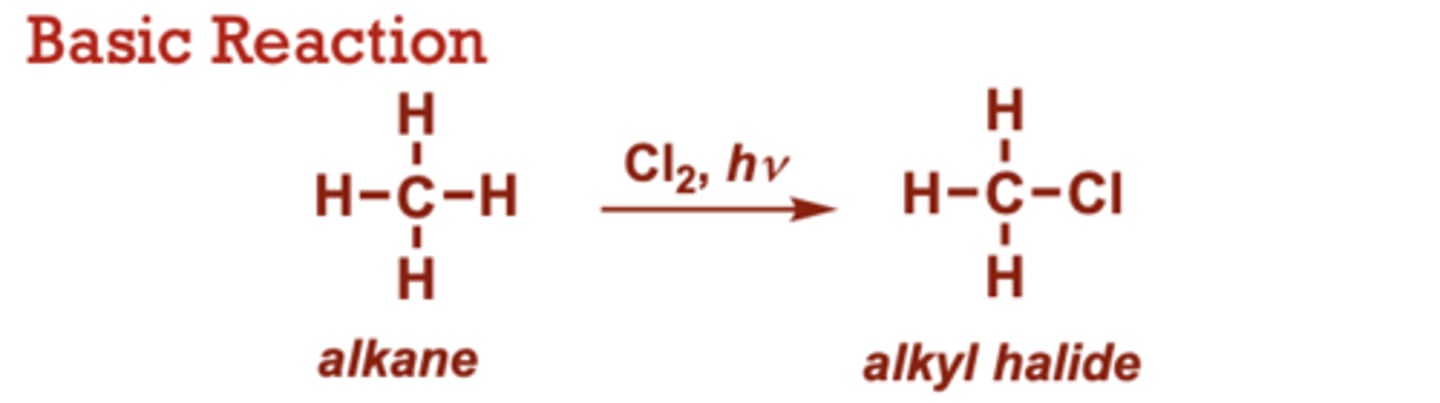
Radical Halogenation of Alkanes
What type of reaction is this?
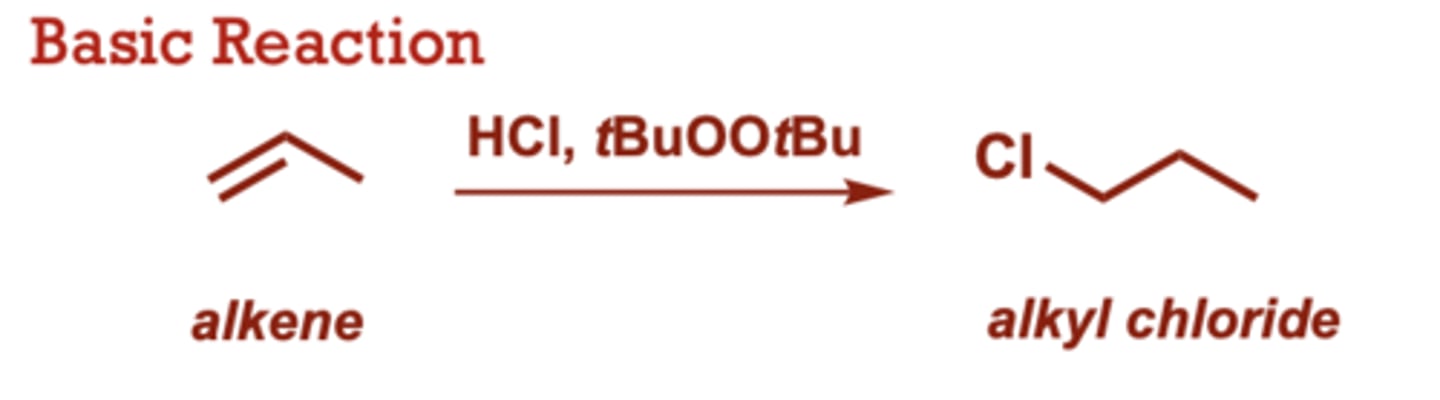
Radical Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes
What type of reaction is this?
Radical Allylic Halogenation
What type of reaction is this?

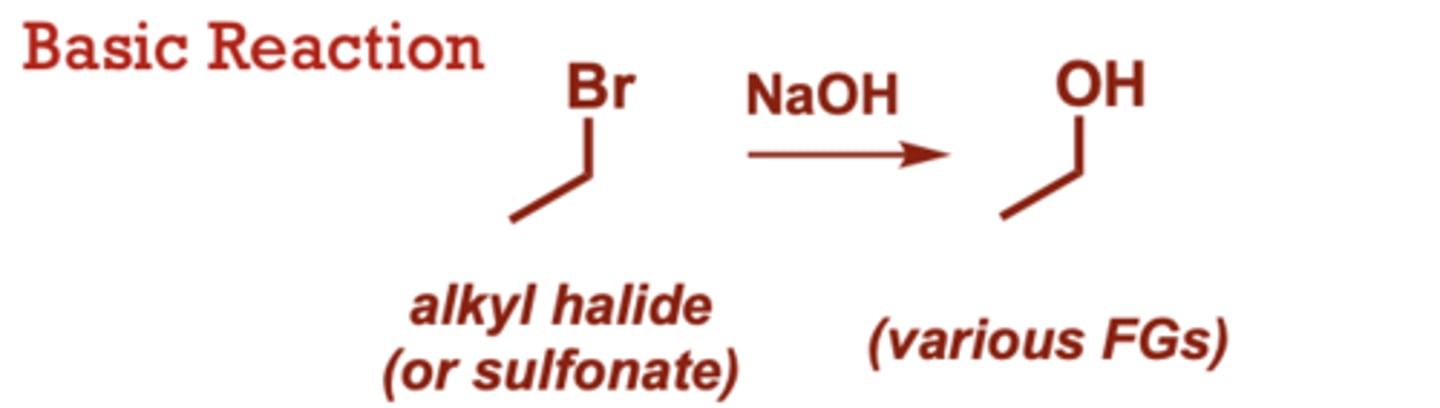
What conditions do nucleophilic substitutions of alkyl halides occur in?
Cl, I (in place of Br), Many other nucleophiles
can be used.
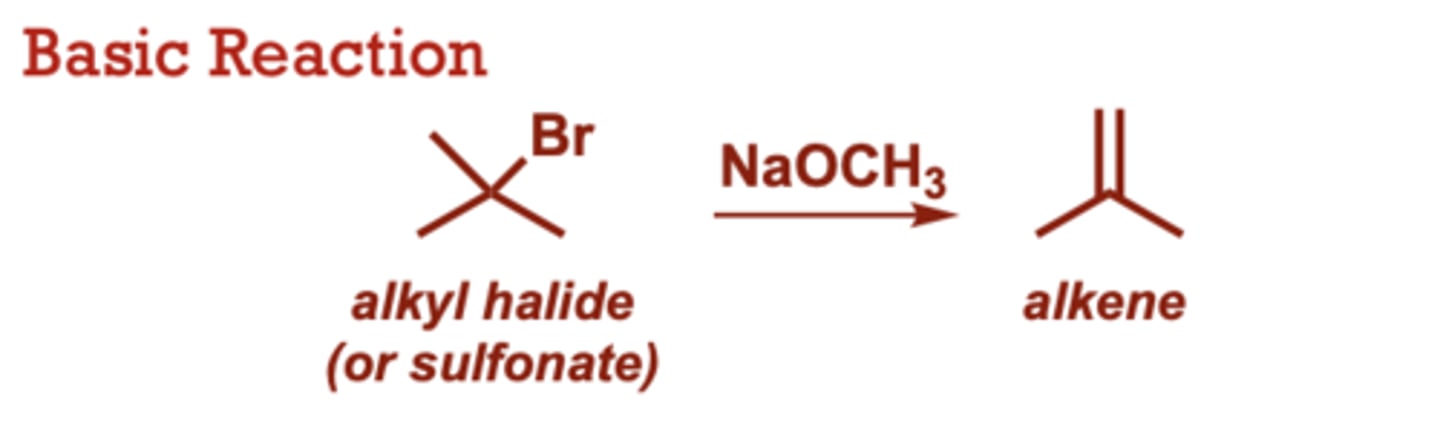
What conditions do dehydrohalogenation occur in?
Various other strong or
weak bases possible (in
place of NaOCH3).
What conditions do dehydration of alcohols occur in?
HNO3, H3PO4, HClO4 or
other strong acids may be
used (in place of H2SO4).
• Water should be 'excluded'.
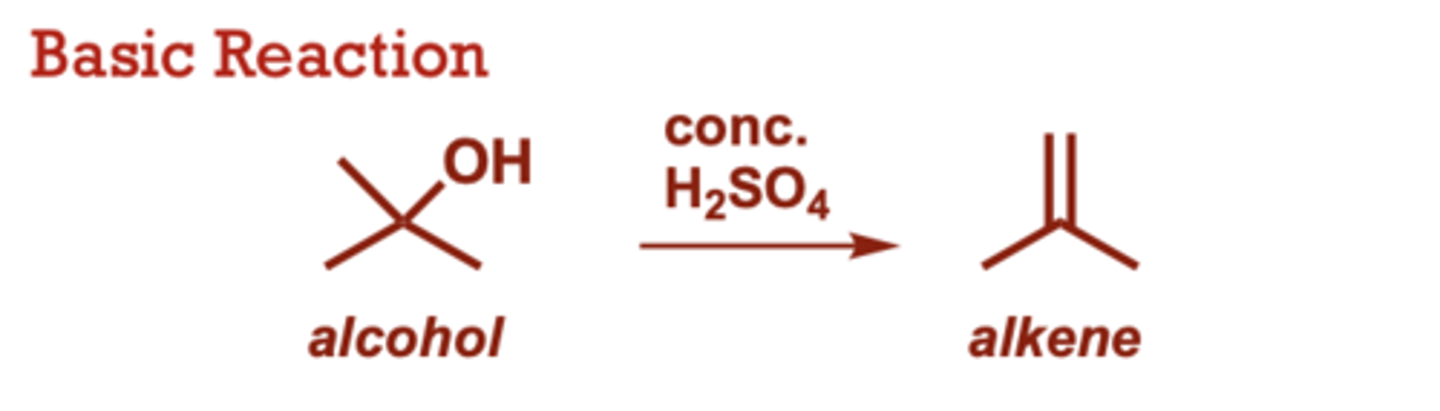
What conditions do Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes occur in?
HCl or HI may also be used
(in place of HBr) to make
other alkyl halides
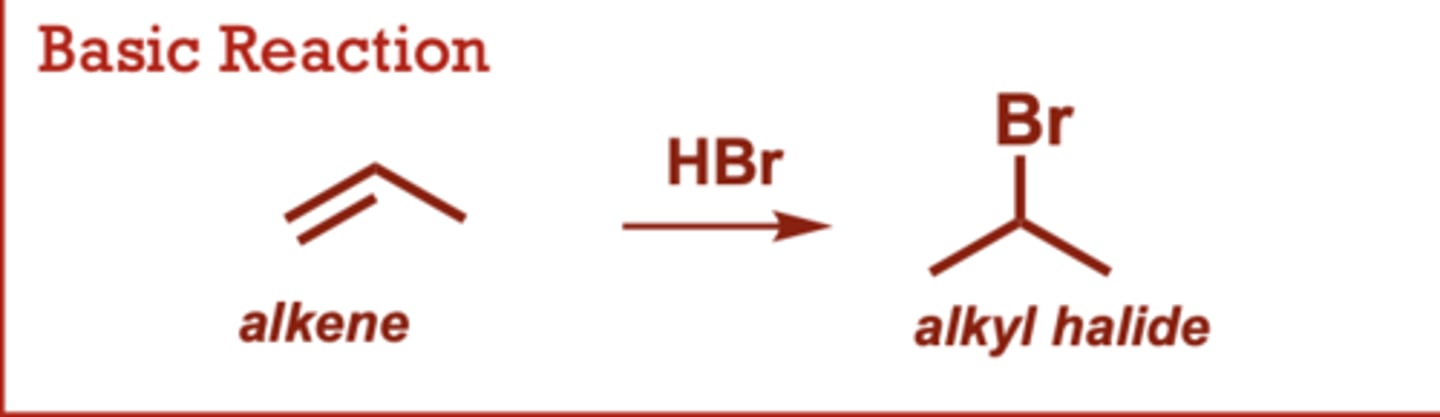
What conditions do Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes occur in?
HNO3, H3PO4, HClO4 or
other strong acids may be
used (in place of H2SO4) to
generate H3O+
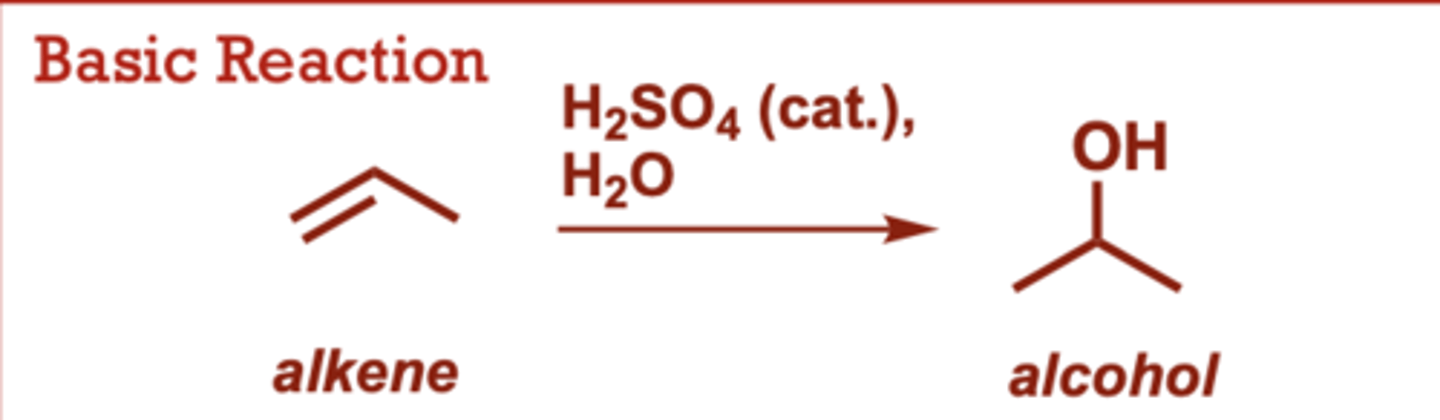
What conditions do Oxymercuration-Demurcuration of Alkenes occur in?
1) Hg (OAc)2, H2O
2) NaBH4
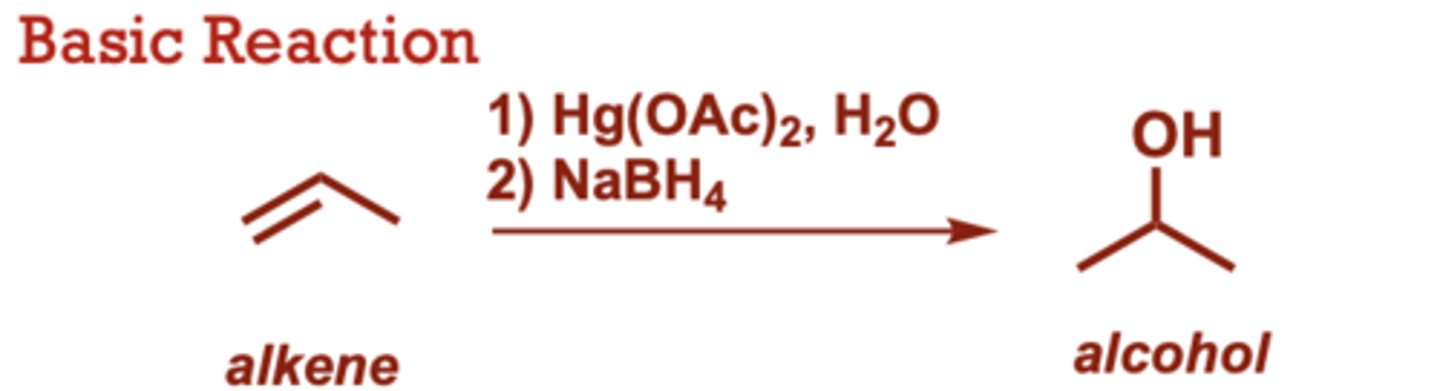
What conditions do Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkenes occur in?
R2BH can also be used in
place of BH3 (where R is an
alkyl group)
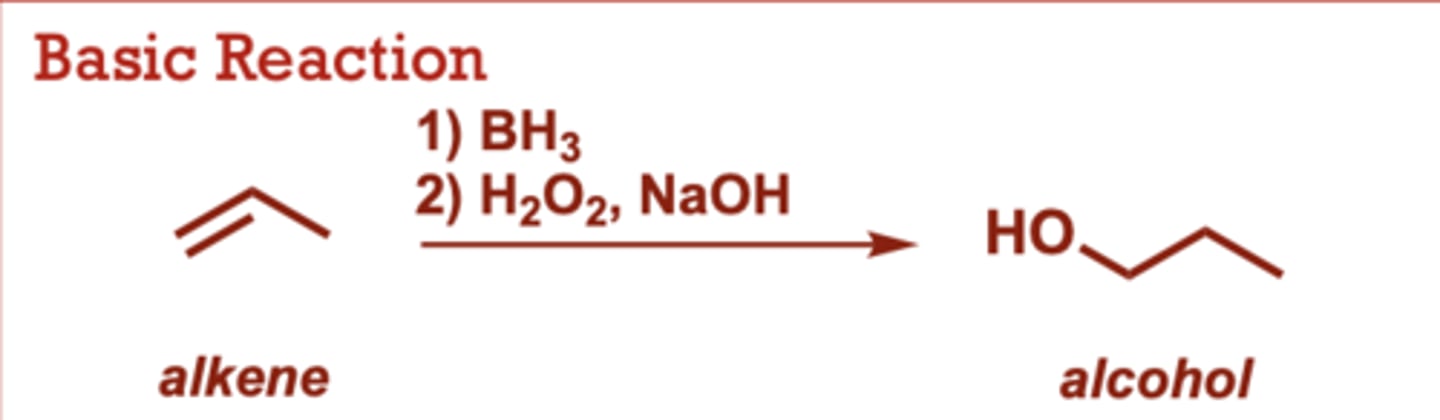
What conditions do Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes occur in?
H2, Pt (of Pd)
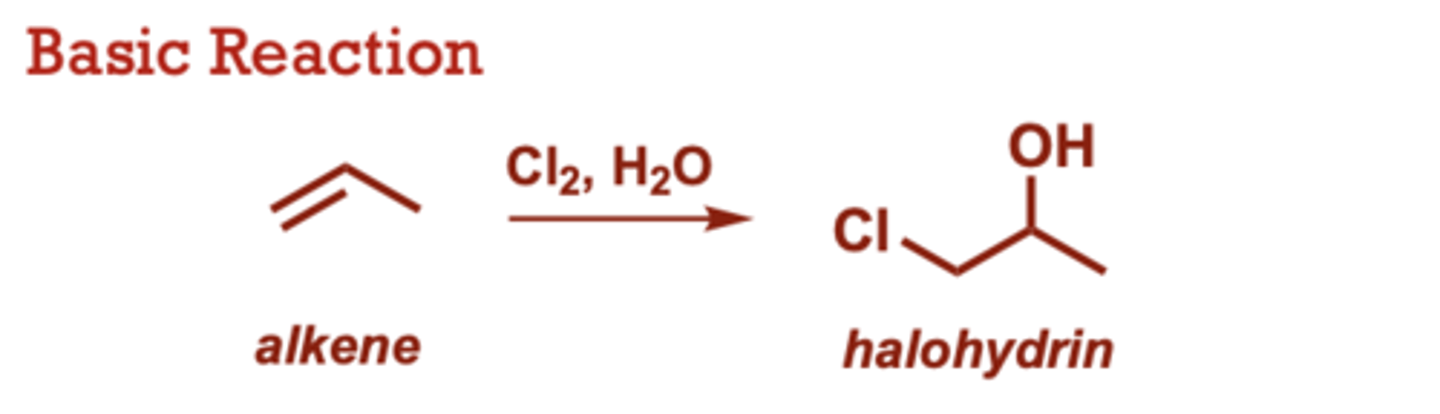
What conditions do Halohydrin Formation from Alkenes occur in?
Br2 can be used (in place of
Cl2) to generate
bromohydrin instead of
chlorohydrin.
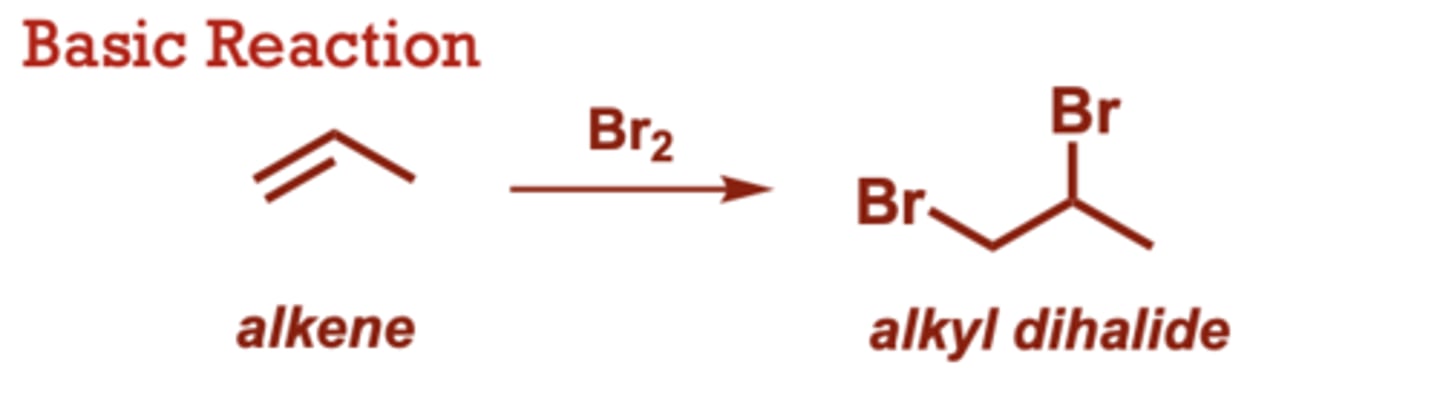
What conditions do Dihalogenation of Alkenes occur in?
Cl2 can be used (in place of
Br2) to generate dichlorides
What conditions do Anti-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes occur in?
Other peroxyacids
(CF3CO3H, mCPBA, etc.)
possible in step 1 in place of
CH3CO3H.
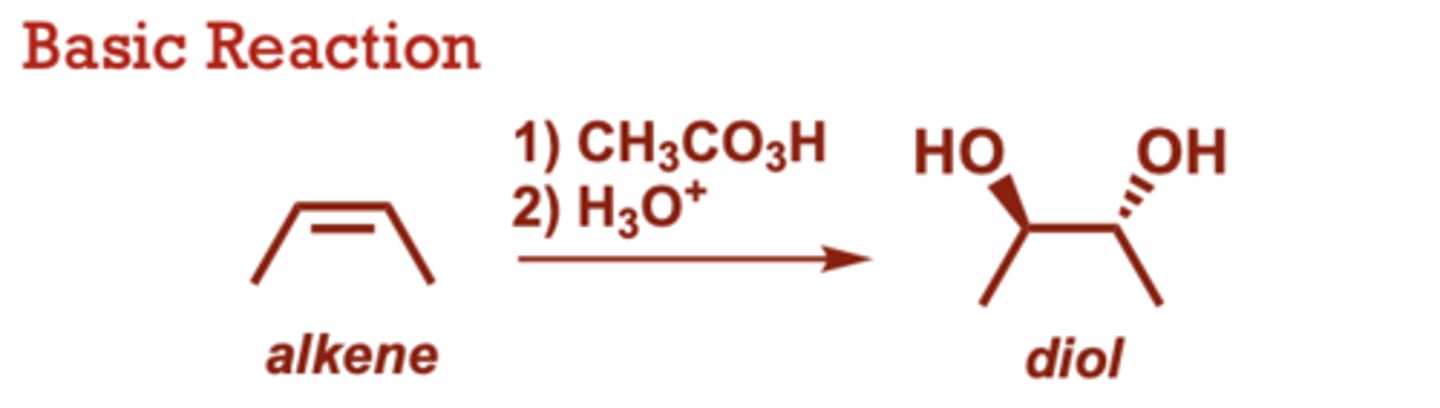
What conditions do Syn-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes occur in?
Catalytic OsO4 with NMO
can also be used (in place
of OsO4).
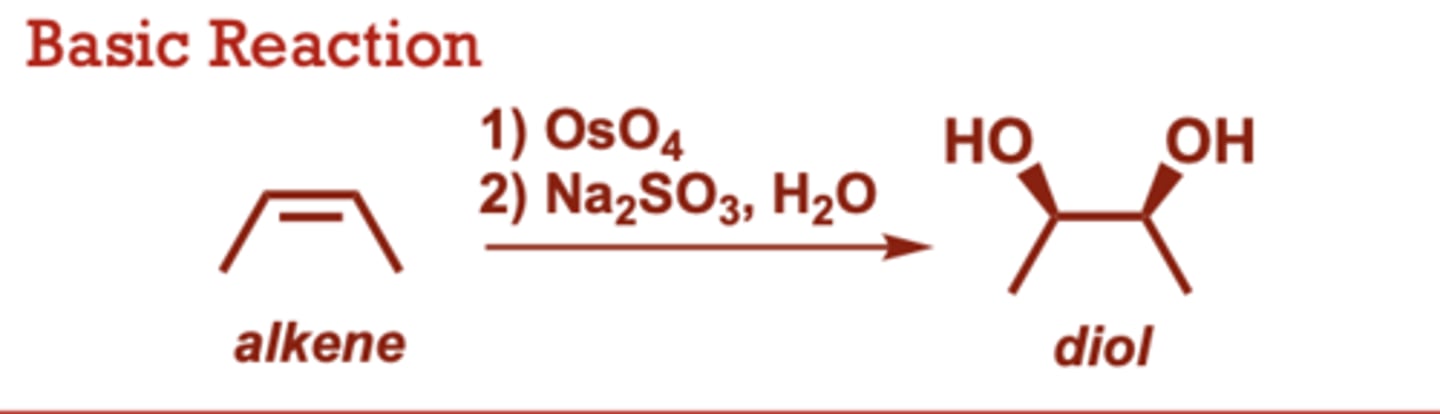
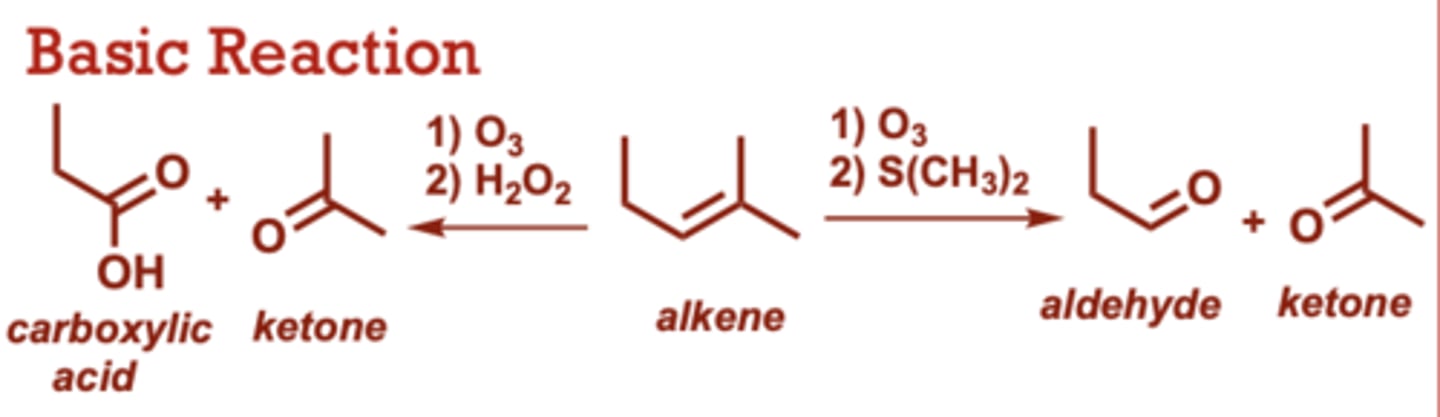
What conditions do Ozonolysis-Reduction/Oxidation occur in?
1) O3
2) H2O2
(alkene to carboxylic acid+ ketone)
1) O3
2) S(CH3)2
(Alkene to aldehyde+ ketone)
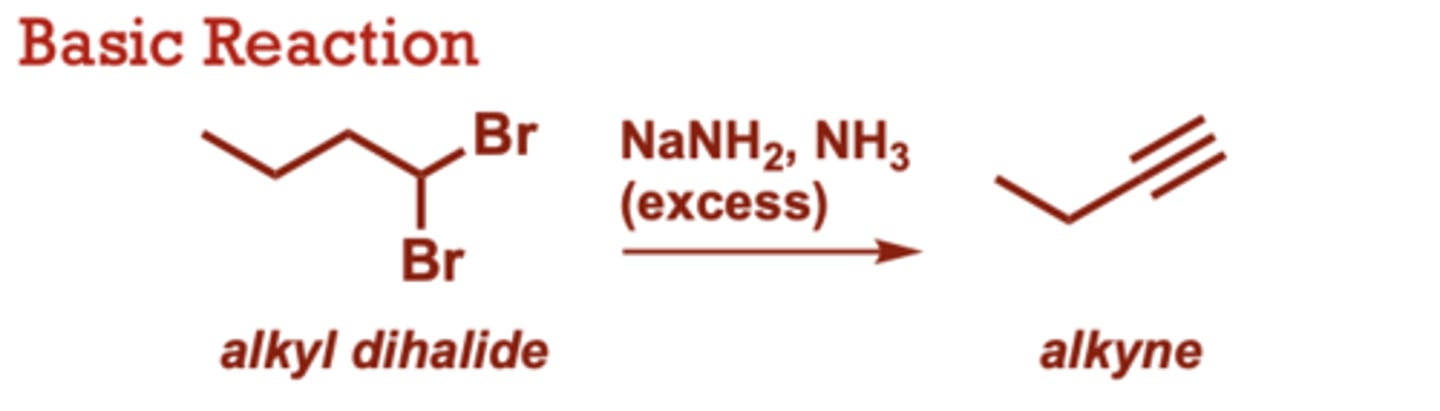
What conditions do Alkynes from Alkyl Dihalides occur in?
NaNH2, NH3 (excess)
Alkyl Dihalide to an alkyne
What conditions do Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkynes occur in?
Pd/C catalyst possible in
place of Pt.
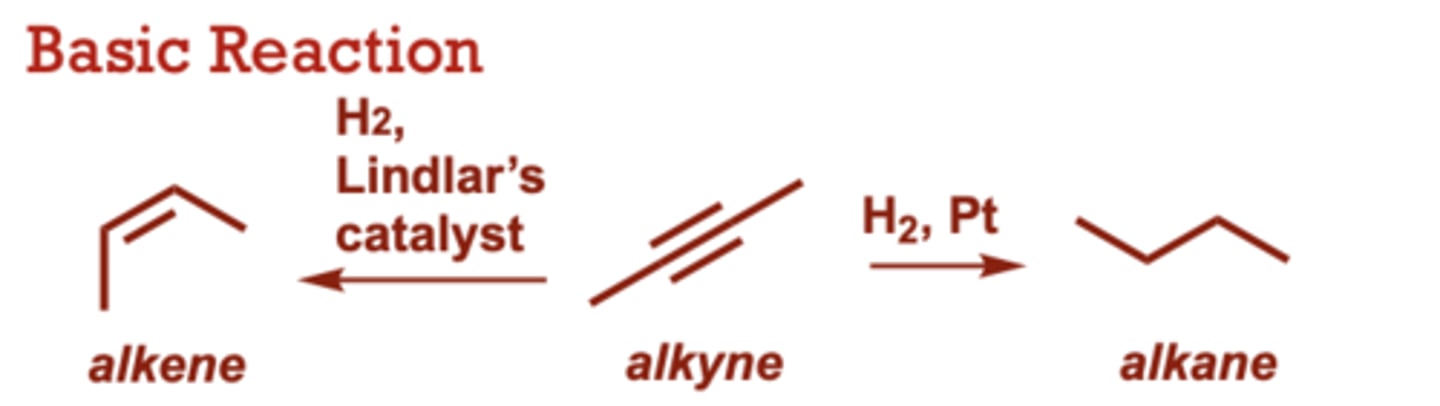
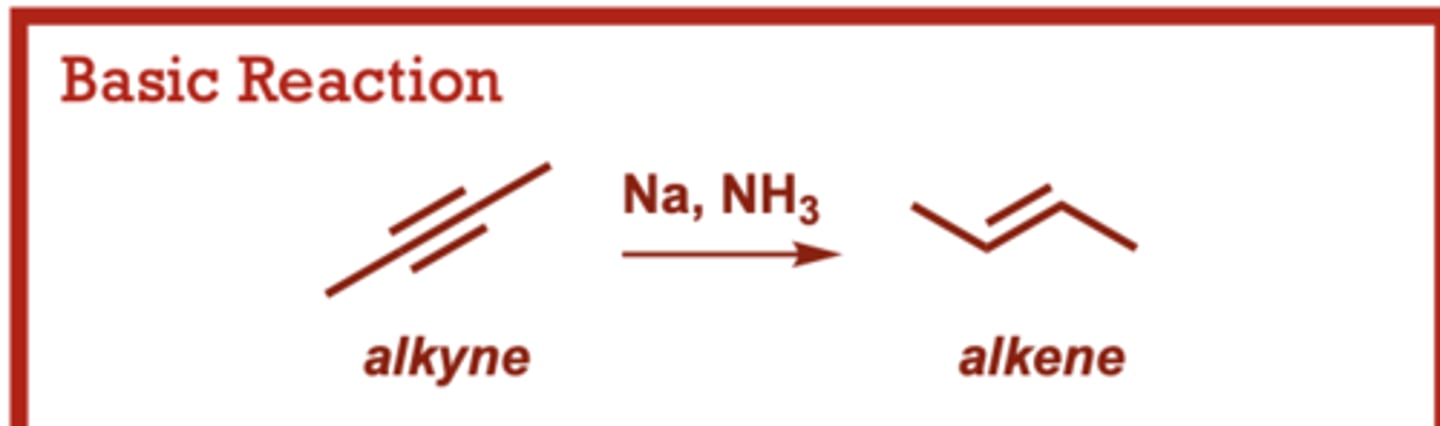
What conditions do Dissolving Metal Reduction of Alkynes occur in?
Na, NH3
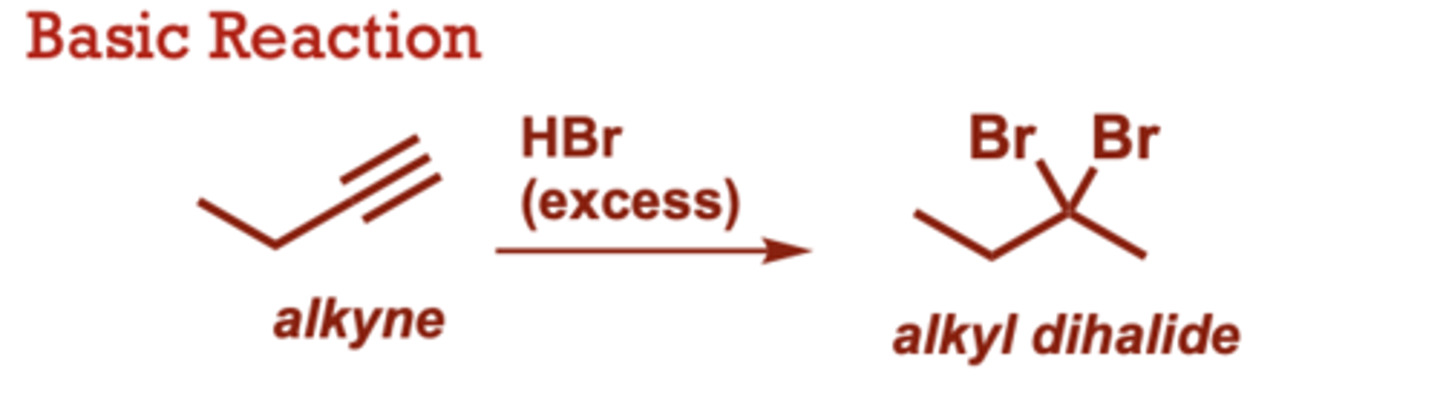
What conditions do Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes occur in?
HBr
(excess), HCl or HI (in place of HBr)
provides the corresponding
dichloride or diiodide.
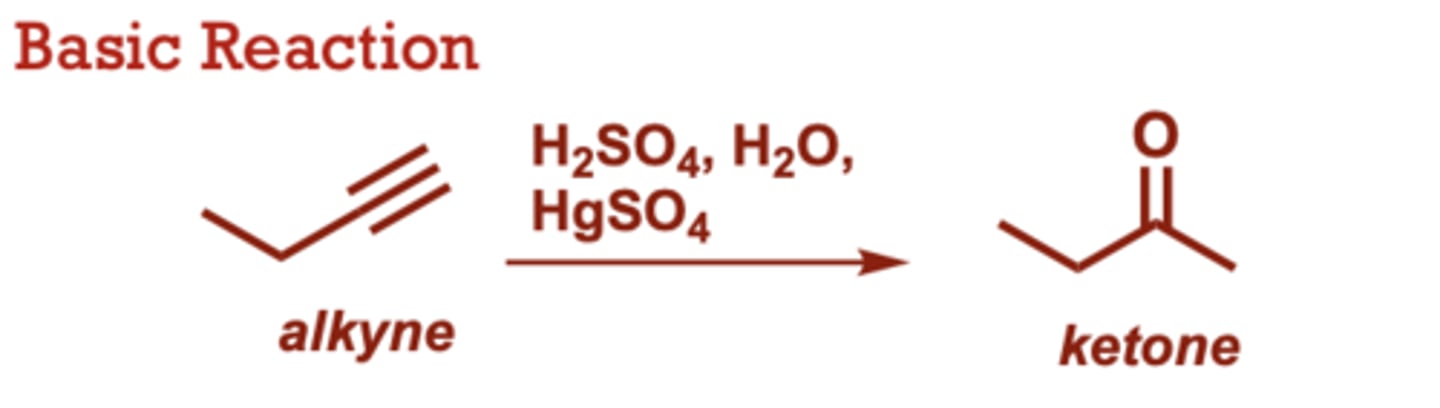
What conditions do Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkynes occur in?
H2SO4, H2O,
HgSO4
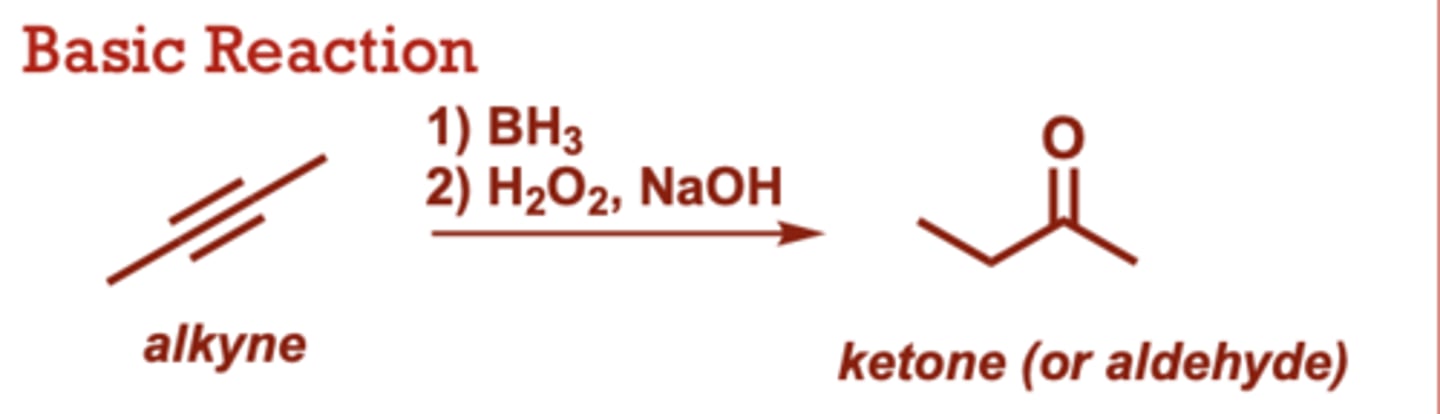
What conditions do Hydroboration/Oxidation of Alkynes occur in?
1) BH3
2) H2O2, NaOH
R2BH can also be used in
place of BH3 (where R is an
alkyl group)
What conditions do Halogenation of Alkynes occur in?
Br2 (excess), Cl2 (in place of Br2) provides
the corresponding
tetrachloride.
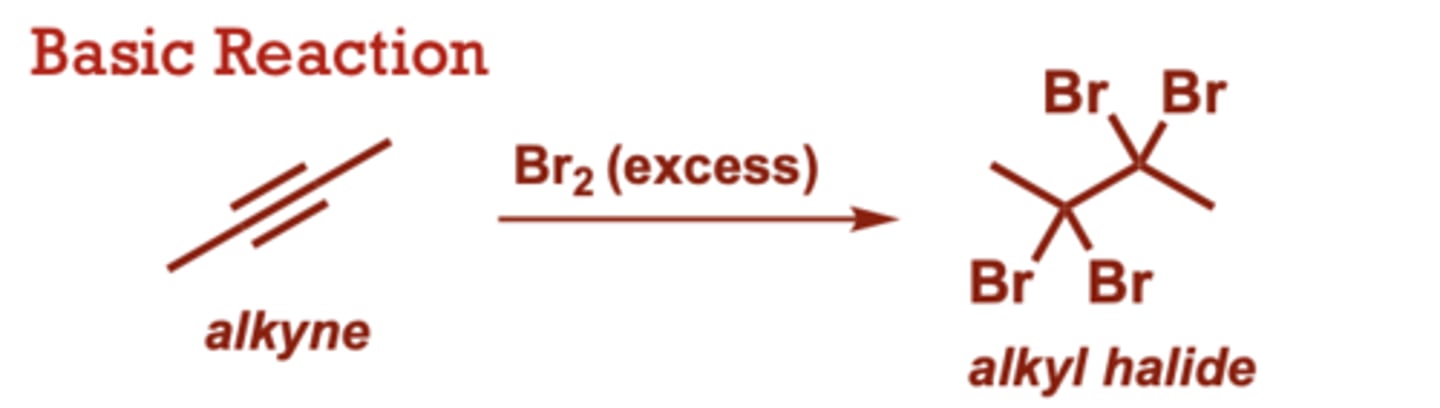
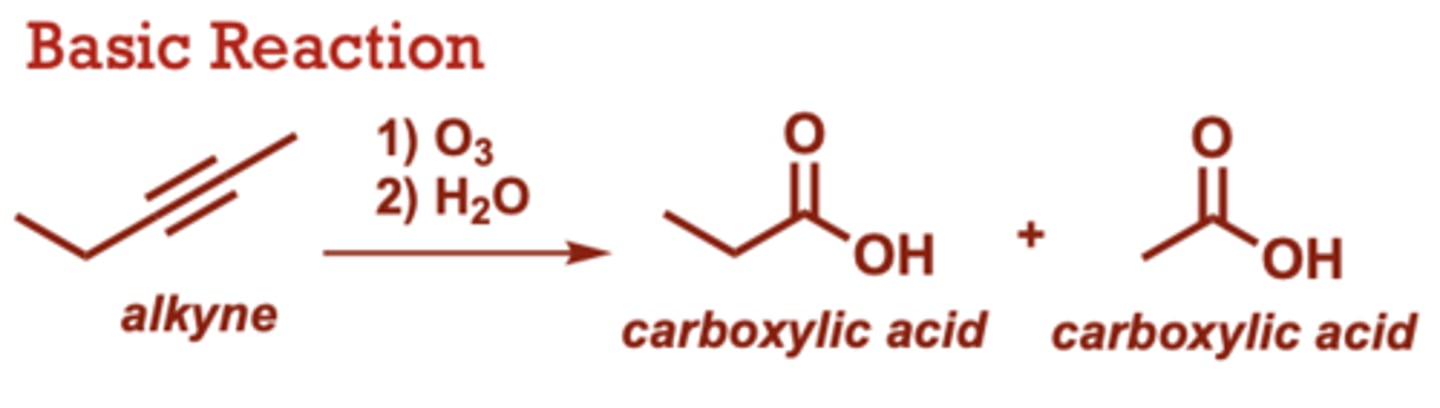
What conditions do Ozonolysis of Alkynes occur in?
1) O3
2) H2O
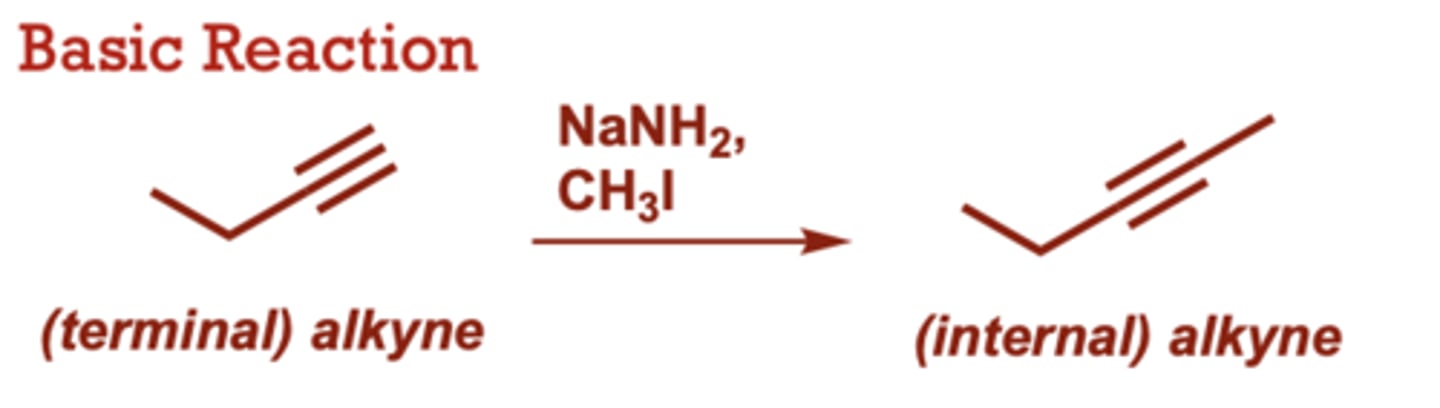
What conditions do Alkylation of Terminal Alkynes occur in?
NaNH2,
CH3I
A variety of primary alkyl
halides can be used (in
place of CH3I)
What conditions do Radical Halogenation of Alkanes occur in?
I2, Br2, or F2 may be used
(in place of Cl2) to give the
corresponding halides.
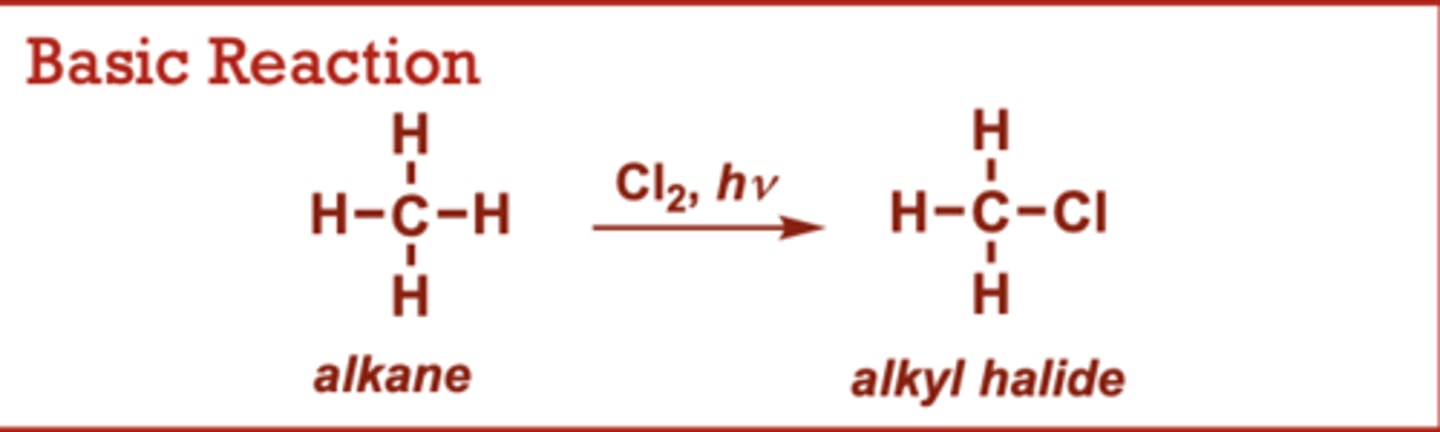
What conditions do Radical Allylic Halogenation occur in?
NBS, (heat)

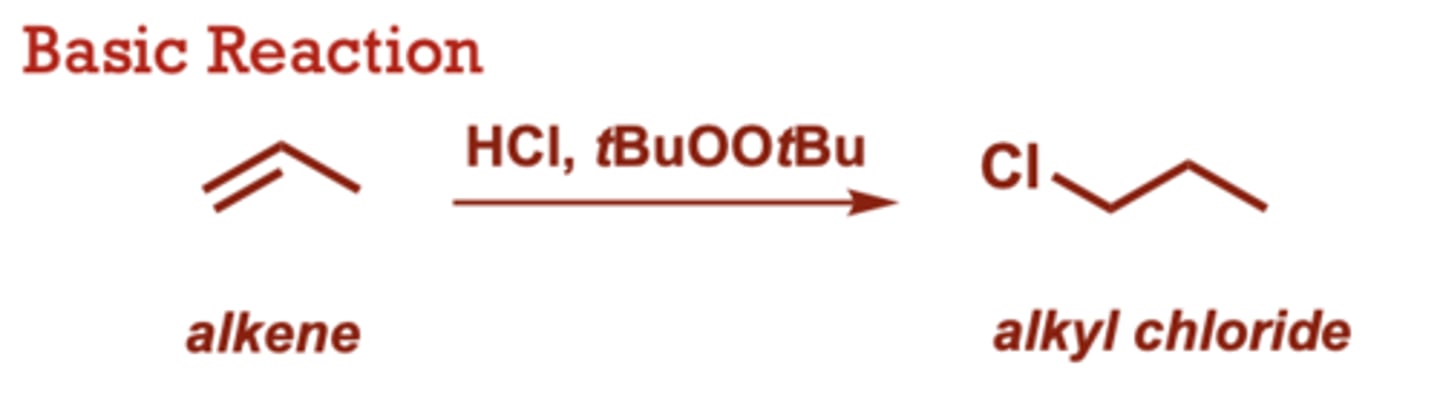
What conditions do Radical Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes occur in?
HCl, tBuOOtBu
ROOR (where R is other
alkyl or acyl) and AIBN may
also be used as radical
initiators.
When do nucleophilic substitutions occur?
SN2 proceeds in one
mechanistic step with
inversion of configuration.
SN1 proceeds through a
carbocation intermediate
(possibility for 1,2 shifts).
Preferred mechanistic
pathway depends on
several factors (reactant
sterics, nucleophilicity,
solvent, carbocation
stability, etc.)
When do Dehydrohalogenation occur?
E2 proceeds in one
mechanistic step.
E1 proceeds through
carbocation intermediate
(possibility for 1,2 shifts).
Site of deprotonation
depends on several factors
(mechanistic pathway, base
sterics, solvent, strength of
base used, substrate
conformation, etc.)
When do Dehydration of Alcohols occur?
Requires protonation of the
alcohol by acid, to convert
into a leaving group.
• With primary alcohols, the
reaction proceeds by E2
mechanism (no carbocation
intermediate).
• "Concentrated" (conc.) is
important. Water can't be
totally excluded, but should
be minimized to avoid
reversal of the reaction.
When do Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes occur?
The major product arises
from the more stable
carbocation intermediate
formed in the initial
protonation.
• Follows Markovnikov’s rule
• The intermediate may
undergo 1,2-alkyl or 1,2-
hydride rearrangement prior
to attack by the halide
When do Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes occur?
Water is typically used as
solvent (in large excess).
• Mechanism is catalytic in
Bronsted acid.
• Follows Markovnikov’s rule
• The intermediate
carbocation may undergo
1,2-alkyl or 1,2- hydride
rearrangement.
When do Oxymercuration-Demurcuration of Alkenes occur?
This is a two-reaction
sequence.
• Water attacks the more
electrophilic carbon of the
mercurinium intermediate.
• Follows Markovnikov's rule,
but there is no carbocation
intermediate (and no
possibility for 1,2-shifts).
When do Hydroboration-Oxidation of Alkenes occur?
This is a two-reaction
sequence.
• Boron bonds to the less
substituted alkene carbon,
whereas hydride attacks the
more electropositive alkene
carbon.
• You only need to know the
mechanism for the first
reaction (hydroboration).
• This reaction provides the
anti-Markovnikov product.
• No carbocation intermediate
When do Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes occur?
More substituted alkenes
react more slowly, with
tetrasubstituted alkenes
often failing to hydrogenate.
• Both hydrogens are added
simultaneously, to the same
face of the alkene (syn
addition).
When do Halohydrin Formation from Alkenes occur?
Water typically used as
solvent (in large excess).
• Water preferentially attacks
at the more electrophilic
carbon of the halonium ring
(more substituted carbon,
better stabilized partial
positive character).
When do Dihalogenation of Alkenes occur?
Formation of the bromonium
or chloronium intermediate
is concerted (no carbocation
intermediates).
• Halide anion attacks the
more electrophilic carbon of
the halonium ring.
When do Anti-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes occur?
This 2-step reaction
sequence involves
epoxidation followed by
acid-catalyzed epoxide ring
opening.
• Results exclusively in an
anti diol.
• SN2 ring opening occurs
selectively at the more
electropositive epoxide
carbon.
When do Syn-Dihydroxylation of Alkenes occur?
This is a 2-step reaction
sequence.
• Results exclusively in a syn
diol (both hydroxy groups
delivered to the same face
of the alkene).
When do Ozonolysis-Reduction/Oxidation occur?
Gives 2 moles of carbonyl
product(s) for every mole of
alkene starting material.
• S(CH3)2 in the second step
can give aldehyde or ketone
products.
• Aldehydes cannot be
products if H2O2 is used the
2nd step. H2O2 rapidly
converts any potential
aldehydes to carboxylic
acids.
When do Preparation of Alkynes from Alkyl Dihalides occur?
Involves 2 sequential E2
reactions.
• Halogens can be situated
on the same carbon
(geminal) or adjacent
carbons (vinical).
• Useful for the synthesis of
terminal alkynes, but not
internal alkynes.
When do Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkynes occur?
Lindlar’s catalyst results in
the ‘cis’ alkene product (syn
delivery of only one
equivalent of H2).
When do Dissolving Metal Reduction of Alkynes occur?
Provides the trans alkene
resulting from anti addition
of two H atoms across the
triple bond.
When do Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes occur?
Use of 1 equiv of HX
provides the vinyl halide as
the major product.
• Both HX additions follow
Markovnikov's rule (halogen
add to the more substituted
carbon)
• Internal alkynes exhibit poor
regioselectivity.
When do Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkynes occur?
Unlike alkene hydration,
HgSO4 is required to
accelerate the reaction.
• Carbonyl group is
generated at the more
substituted alkyne carbon
(Markovnikov selectivity).
• Proceeds through an enol
intermediate which
tautomerizes to the ketone.
When do Ozonolysis of Alkynes occur?
Gives 2 moles of carboxylic
acid product(s) for every
mole of alkyne.
• If the staring material is a
terminal alkyne, the reaction
generates CO2 as a
product.
When do Alkylation of Terminal Alkynes occur?
Reaction does not proceed
with secondary or tertiary
alkyl halides.
• Acetylene can be alkylated
twice (with excess base and
alkyl halide).
When do Radical Halogenation of Alkanes occur?
Heat is needed to
initiate homolytic cleavage
of the dihalide.
• Can give complex mixtures
of regioisomers.
• Use of excess dihalide
reagent often results in
multiple halogenations.
When do Radical Allylic Halogenation occur?
Heat is required to
initiate homolytic cleavage
of NBS.
• NBS allows you to minimize
the amount of Br2 present
during the reaction (large
amounts of Br2 would result
in dihalogenation of the
alkene).
• HBr (a byproduct of the H
abstraction step) reacts with
NBS to form a small amount
of Br2.
When do Radical Hydrohalogenation of Alkenes occur?
• Initiator starts the reaction
by facilitating the generation
of a halide radical.
• The more stable
(substituted) radical
intermediate is formed from
the alkene.
• This reaction provides the
anti-Markovnikov product.