Business Finance WW4. AU4
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
working capital
current assets - current liabilities
working capital ratio
current assets / current liabilities
receivable turnover ratio
net credit sale / avg accounts receivable
day sales outstanding
365 / receivable turnover ratio
inventory turnover ratio
COGS / average inventory
days in inventory
365 / Inventory turnover ratio
cash conversion cycle
days in inventory + day sales outstanding - days payable outstanding
operating cycle
days in inventory + day sales outstanding
cost of discount foregone
opportunity cost when the customer does not pay within the cash discounted period

stretching of payables
avg accounts payable
increase in accounts payable
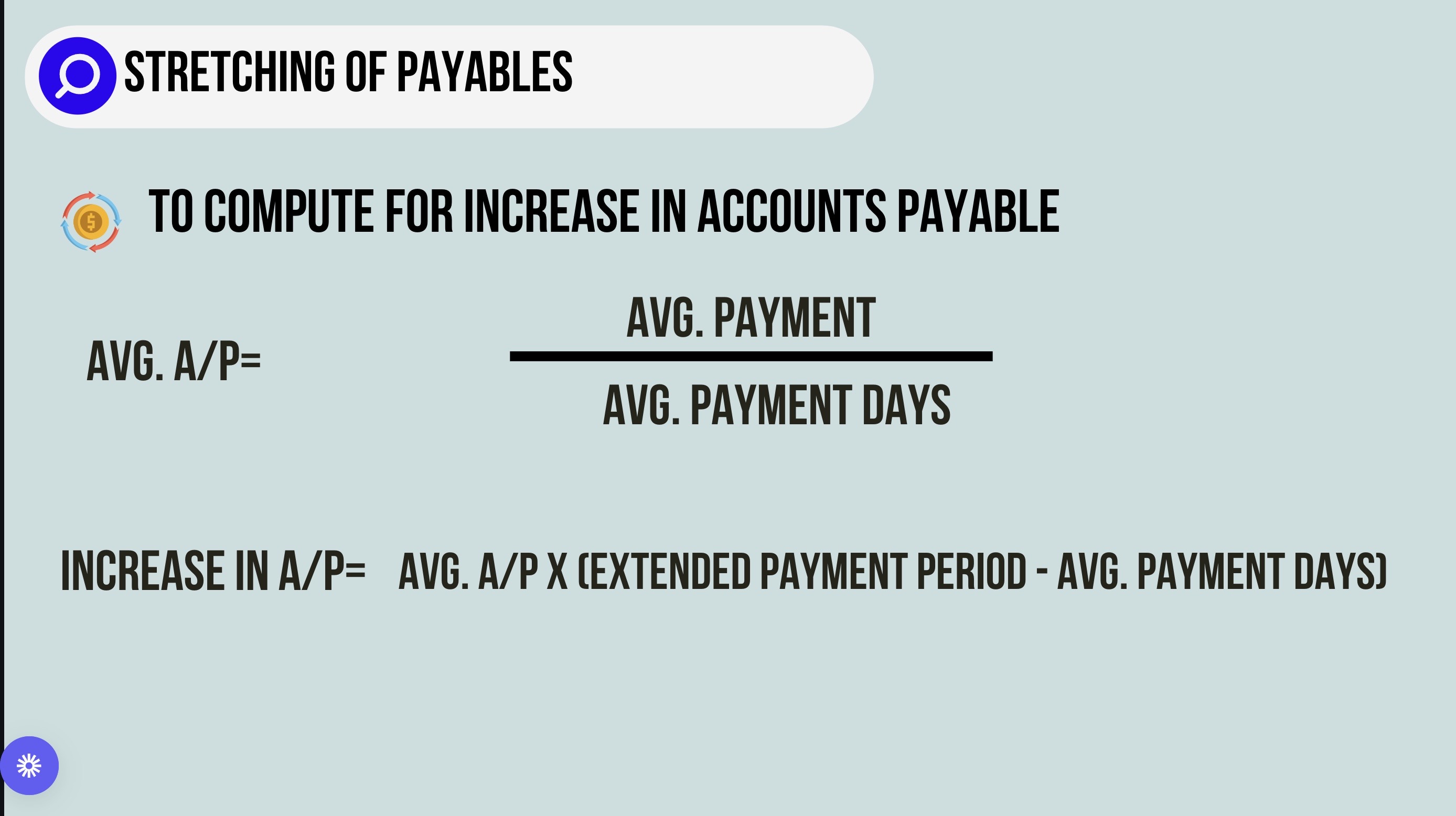
average accounts payable
avg payment / avg days of payment
increase in a/p
avg a/p x (extended payment period - avg. payment days)
economic order of quantity
ideal quantity of units a company should purchase to meet demand while minimizing inventory costs such as holding costs, shortage costs, and order costs
Q= EOQ units
D = Demand in units (annually)
S = Order Cost (PER PURCHASE)
H = Holding costs or Carrying Cost (per unit, per year)
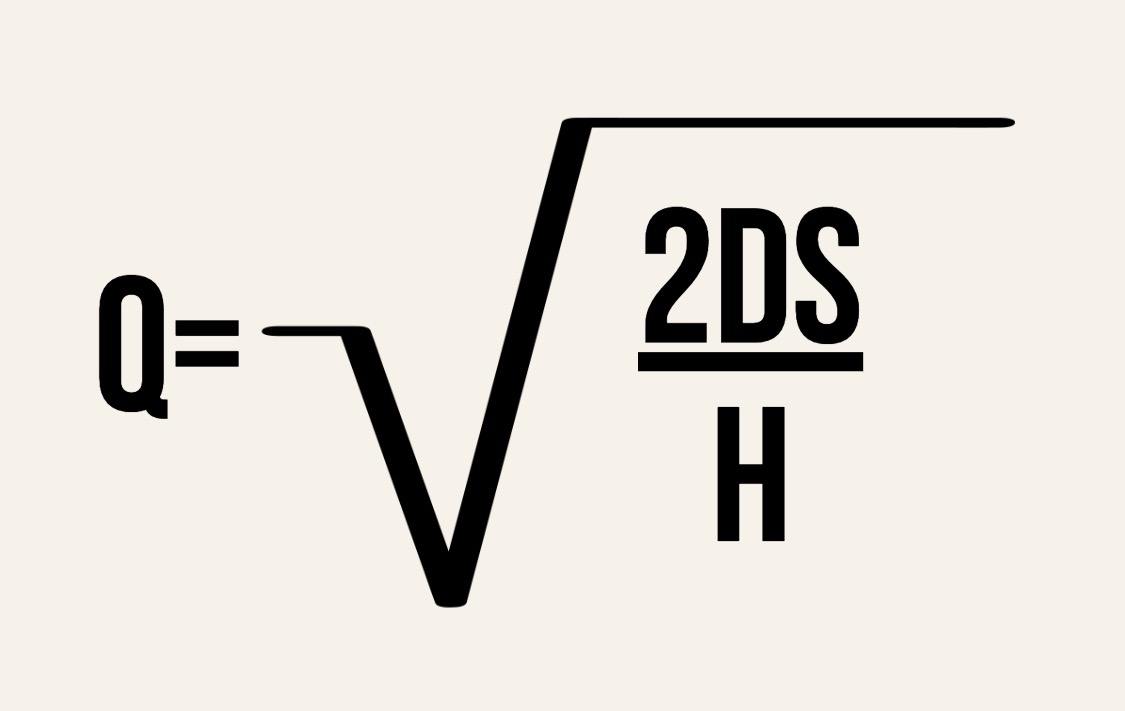
holding costs
[FOR EOQ]
multiply the number after “order of x units at a price of” by the carrying cost
demand in units
[FOR EOQ]
phrases like “annual requirement of x” or “places an order of x units.”
make sure to convert it to annual
cost of commercial paper
compute for amount of interest
use the EAR formula

amount of interest
[FOR cost of commercial paper, cost of factoring a/r,
Face Value x Interest Rate x days / 360
EAR cost of commercial paper
EAR = Effective Annual Rate
I: Interest
IC: Issue Costs
FV: Face Value
DM: Maturity Days

cost of factoring accounts receivable
compute for amount of interest
compute for factoring fee
compute for factor’s holdback
compute for net proceeds
compute for cost of factoring receivableS

net proceeds
[2ND TO LAST STEP OF COST OF FACTORING ACCOUNTS RECEIVABLE]
= Total A/R - (Amount of Interest + Factoring Fee + Factor’s Holdback)
cost of debt
Interest Rate of the long-term debt x (1-corporation’s income tax rate)
cost of preferred shares
dividends per share / market value per preferred share
cost of common shares
expected cash per dividend share / market value per ordinary share + dividend growth rate
weighted average cost of capital
(E/V + Re) + (D/V x Rd x (1-Tc))

add-on interest
based on outstanding loan balance and whatever interest is added to the principal payment
discounted interest
what you get when discount amount is deducted from the principal amount