BIO 1M03 Final Exam + Test 2 content
1/340
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
341 Terms
What is adaptive radiation?
The rapid production of many descendant species from a single lineage
What are the three hallmarks of adaptive radiation?
1. They are a monophyletic group
2. They speciated rapidly
3. They diversified ecologically into many niches
What are extrinsic factors?
Favorable new conditions in the environment
What are intrinsic factors?
Evolution of key morphological, physiological or behavioral traits
What is ecological opportunity?
The availability of more or new types of resources
What is the example of adaptive radiation from lecture?
The anolis lizards
What is the escape-and-radiate coevolution hypothesis?
proposes that species diversify through an evolutionary "arms race" between consumers and producers
What is the Cambrian explosion?
Sudden diversification of new species and evolutionary change
What is a fauna?
A collection of animal species
What triggered the Cambrian explosion?
Higher oxygen levels
Evolution of predation
New niches beget more new niches
New genes, new bodies
What is the Burgess Shale?
The Burgess Shale is a 508-million-year-old fossil deposit in Canada, preserving diverse Cambrian organisms with exceptional detail, offering key insights into early animal evolution and biodiversity.
What are hominids?
Large bodied animals with long arms, short legs and no tail
What are the different ways hominids walk?
Different types of primates (gorillas, chimps, bonobos) fist-walk when on the ground
Humans are bipedal and walk upright on two legs
When did human evolution begin?
7 million years ago
How many "human species" are estimated to have evolved?
20 early human species
What are the three major hominin groups?
Early hominins, australopithecines, homo genus
When did early hominins evolve? What were their key traits?
4.4-7 million years ago. small cranial capacity, small canines, many ape like traits but some human like traits
When did australopithecines evolve? What were their key traits?
1.4-4.4 million years ago. Some ape like traits. Had shifts in the spine, hip and legs towards human like features
When did homo genus evolve? What were their key traits?
2.4 - 1.4 million years ago. Higher cranial capacity, used tools, first to control fire,
What synapomorphy defines the hominins?
Bipedalism
What animals are humans most related to according to DNA sequence data?
Chimpanzees, bonobos and gorillas
What four groups did researchers organize hominins into?
Gracile australopithecines
Robust australopithecines
Early Homo
Recent Homo
What traits were present in the hominin evolution timeline between 4.5-1 mya?
Small bipeds with small teeth
What traits were present in the hominin evolution timeline between 2.7 - 1mya?
small bipeds with big teeth (probably ate plants)
What traits were present in the hominin evolution timeline at 2.3 mya?
Larger braincase, reduced cheek teeth
What traits were present in the hominin evolution timeline at 1.8 mya?
Even larger braincases, used fire to cook food, stone tools
What traits were present in the hominin evolution timeline at 400-24 kya?
Last hominin species to live with our species
Heavily built, large brains, low foreheads, powerful haws, large brow ridges, small chins
What traits were present in the hominin evolution timeline at 195 kya?
Reduced brow ridges, flat faces, largest braincases
How was natural selection involved in the evolution of hominins?
Thought that natural selection was responsible for the ability to reason and communicate, triggered by increased tool and language use
What is the out-of-Africa hypothesis?
Homo sapiens evolved traits in Africa then dispersed throughout the world, and Homo sapiens evolved independently of earlier European and Asian species of Homo
Where did Homo Neanderthalensis reside?
Europe and the Middle East
Where did Homo Erectus reside?
Asia
Where did the first wave of Homo Sapiens migrate to?
East and South towards Australia
Where did the second wave of Homo Sapiens migrate to?
Europe and mainland Asia
Did Homo Sapiens interbreed with other species as they migrated? What evidence supports this?
Yes they did
1-4 % of genomes of indigenous Europeans and Asians is derived from Neanderthals
Why did hominins evolve to become bipedal?
1. Lower surface area exposed to sun (less heat stress)
2. Hands free to carry food or tools and forage better
3. Long-distance migration, follow migrating prey
Describe the position of foramen magnum
Enters skull from below in fully bipedal hominins
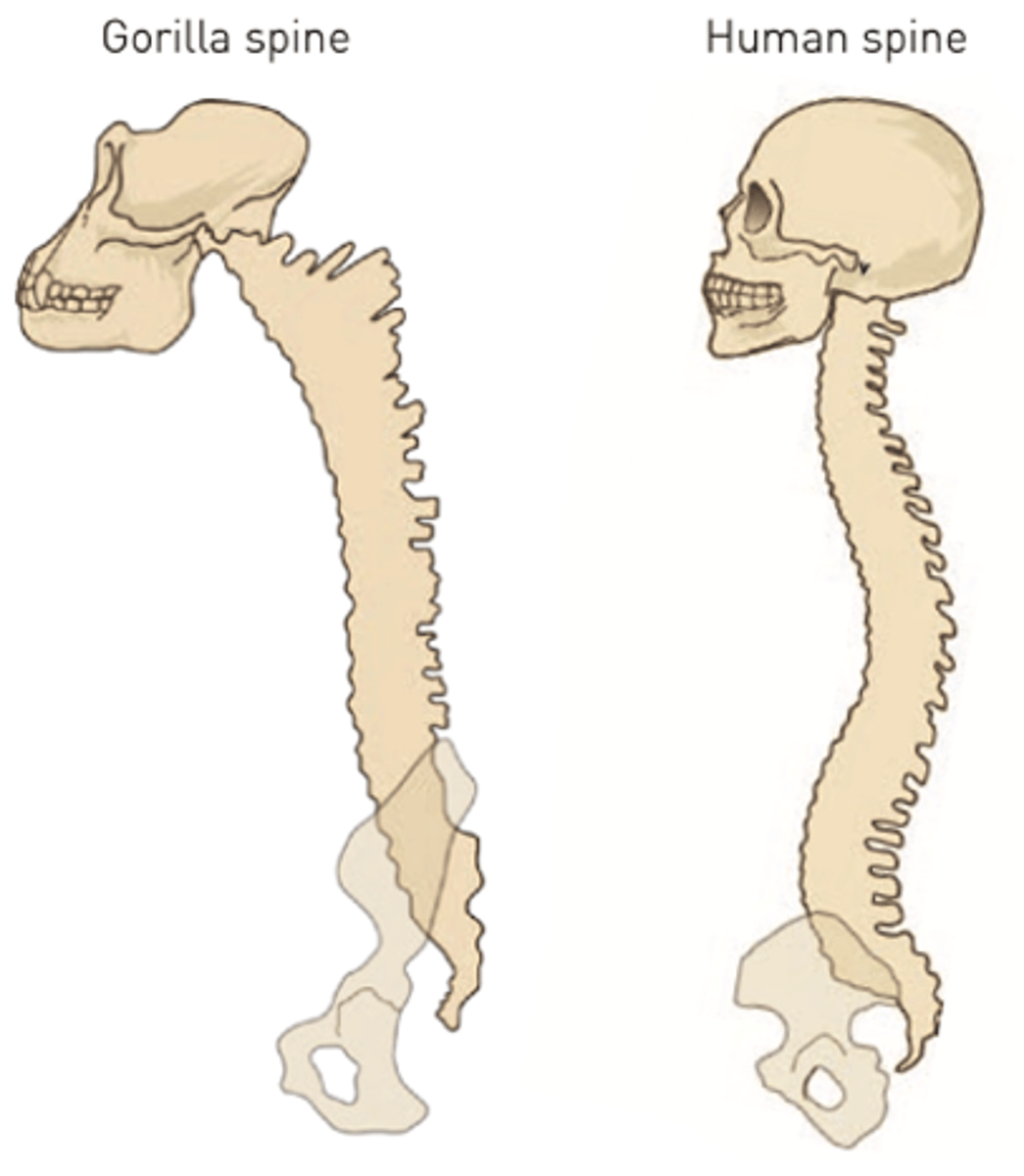
What were the major modifications in the shape of the hominin pelvis?
Bowl-shaped to support upper body and provide better balance for upright posture
What were the major modifications in the feet of hominins?
Lost opposable great toe
Large heel, arched foot, ridged lever vs grasping
Propel forward, absorb forces of bipedal walking
What were some of the advantages of increased brain size?
Sophisticated tool manufacture and use
Foraging and hunting techniques more complex and effective
Cooperative social skills, social learning
What was a cost associated with larger brains?
Energy expensive
What occurred when brain size increased regarding brain development?
Took much longer than our descendants
Dependent on parental care for much longer
What were the sexual dimorphisms and differences in parental care in homo sapiens?
Males are 15% larger
There is greater parental care:
- More food sharing
- Division of labor
- Pair-bond mating
What is the FOXP2 gene? Why is it important?
It is the language gene. Essential for human speech
What evolved in homo sapiens to allow for better speech?
Hyoid bone positioned to allow tongue movements in speech
What is altruism? How might this affect evolution?
Benefiting another individual at one's own expense
Reciprocation: benefitting others feeds back to benefit you
Cheaters (take and not reciprocate) are punished
What are some pieces of evidence for cooperative hunting?
Injuries due to hunting
Healing from wounds that would have required care from others in the social group
What are some examples of how humans are still evolving today?
- Coevolution with pathogens
- Effects of C-section on evolution of head size
- Spread of lactose tolerance mutation
- Human skin pigmentation
- Resistance to malaria
Describe the evolution of human skin pigmentation?
Over 350 genes associated with skin color (MC1R gene has allele for lighter and darker pigmentations)
Where is UV radiation most intense?
Equator
Where does natural selection favor darker skin pigmentation?
Near the Equator
What are some selective agents of skin pigmentation?
Skin cancer
Folate
Vitamin D
What are the two main types of skin cancer?
Melanoma and Non-melanoma
Which type of skin cancer is more common? Which is more fatal?
Non-melanoma is more common
Melanoma is more fatal
What is folate? Why is it important?
An essential nutrient, cannot be synthesized and must be obtained from diet
Necessary for DNA repair and synthesis
Deficiencies decrease reproductive success in women (chance of improper fetus development) and men (chance sperm do not develop and mature properly)
How does UV radiation effect folate?
Causes breakdown in blood folate
How is vitamin D obtained? Is it synthesized in the human body? What is required?
Vitamin D is obtained through diet
Can be synthesized in our bodies, pathway requires UV light
What is vitamin D important?
Necessary for calcium absorption
Regulates immune function
Correlations between Vitamin D deficiencies and cancer
Describe the fitness trade-off regarding human skin pigmentation?
Darker skin pigmentation means more protection from UV damage, but reduces vitamin D synthesis
Who is usually affected by malaria?
young children and pregnant women
How is malaria transmitted to humans? What occurs when in the body?
mosquitos. Replicates within RBCs and causing them to burst open and release more
How has selection affected the resistance to malaria?
Favored modifications of RBCs that reduce the success of malaria. (sickled cell shape due to HbS mutation).
What happens if an individual is homozygous for HbS?
Develop sickle cell anemia
What happens if an individual is heterozygous (HbS/HbA)?
Strongly protected against malaria
What is balanced polymorphism?
A steady state when both alleles persist in the population
When is lactase production halted?
After weaning
What is pastoralism?
the domestication of animals around 5-10 kya
How did selection affect pastoralist populations?
Lactase production continued after the age of 2 due to dominant mutations that kept the lactase gene active
What are mismatches to modernity?
Biology cannot keep pace with cultural and rapid environmental change
What is the hygiene/old friends hypothesis?
Gut-associated microbes are essential for normal development and improved health
What happened when modern medicine and hygiene practices were introduced?
Removed some coevolved microbes, leading to immune system dysregulation. Worms evolved to dampen inflammatory responses. Without them, immune responses can be over-reactive
What is the relationship between contraception and breast cancer?
Women who delay having children through contraception are more susceptible to breast cancer because they have more menstrual cycles. Each menstrual cycle, breast tissue goes through many rounds of mitosis, which means more room for replication error
What is degenerative disease?
Disease caused by a deterioration of the body
What affect does age have on selection intensity?
Decreases as we age
What is antagonistic pleiotropy regarding reproduction and lifespan?
It is the genetic coupling of traits, and increased reproduction reduces lifespan
What is the evidence behind the cost of reproduction in humans?
Alleles associated with increase reproductive performance raise the risk of cancer later in life
How did cancer evolve?
Through mutation and clonal competition.
What do successful clones of cancer lead to?
Metastasis and drug resistance
What happens when less malignant clones are removed through chemotherapy?
Removes competition, allows aggressive clones to expand
What do lower chemotherapy doses do?
Maintains competition and slower malignancy
Why is AMR significant?
Leading cause of death
Why is AMR a problem?
Pathogens evolve resistance quickly, and Horizontal gene transfer spreads the resistance genes rapidly, accelerating AMR evolution
What does overuse of antibiotics cause in AMR?
causes selection for multidrug-resistant pathogens
How can resistance development be slowed in AMR?
Using lower effective antibiotic doses
What is a biotic factor?
A living organism
What is an abiotic factor?
Nonliving aspects
What is a population?
Individuals of the same species in the same place at the same time
What is the size feature of a population?
total number of individuals present in the same area at the same time
What is the range feature of a population? What drives the range feature?
Area over which a population is spread (driven by abiotic and biotic factors)
What is the density feature of a population?
Size divided by range
What is the random spatial distribution?
Individuals in the population are placed random with no clear pattern. Equal chance of occupying any position
What is the clustered spatial distribution? What causes it?
When individuals are grouped together in various locations.
Caused by clustering of resources or if proximity enhances fitness
What is the uniform spatial distribution?
Individuals are distributed evenly , due to territories, limited resources or predation
What is the lime swallowtail butterfly?
Native to Asia, a butterfly that spread around South America. Eat the leaves of citrus trees
What is sessile?
adult forms stay attached to one place; generally don't move
What is the formula for the mark-recapture method?
N = (C/R) M
N = population size
C = total caught on day 2
R = # of M recaptured
M = marked on day one
What is the Asian vulture crisis? Why did it occur?
The rapid decline of 3 species of Gyps vultures.
Caused by traces of veterinary drug diclofenac found in the kidneys. Caused visceral gout in vultures, leading to renal failure then death
What are the four factors that determine population size?
Birth, Death, Immigration, Emigration
What is the equation for the change in population?
Change = (B-D) +(I-E)
What is the equation for change in population over time?
Delta N / Delta t