TV4001 - VPH - Risk Factors & Analysis
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Performing a risk-based approach
We wish to control Salmonella in milk
Where does salmonella come from?
Risk factors therefore include?
What next?
Anything to do with the gut (gut contents, manure, faeces, ingesta)
RF
Faeces on hides/surfaces
Not hand washing after toilet or animal handling
Cross contamination of environment
Animals with visible faeces being milked
Not washing knives btw skin cuts
Raw and cooked food prepped in same area
Use the risk factors as a control method e.g. wash hands, clean areas → Control the RF = Control the hazard
Product-based inspection
What does it entail?
What are some issues with the method?
basing all inspection on the end-product
Issues
Not representative for entire chain
Lots of expenny sampling to be effective
At mercy of labs - labs can be questionable
Reactive → see something a remove it from food chain but doesn’t get to the reason why it occurred or how to prevent it
Risk-based inspection
Overview?
What steps are involved?
ID all necessary control measures first, and inspect them to see if they are appropriate
Is preventative approach, not reactive
Determining food-borne disease risk factors
To determine food-borne disease risk factors, national food control
systems rely on various techniques and programmes including?
Epidemiological surveillance (determines RF for food-borne disease by linking dz with origin through outbreak investigation) → OzFoodNetwork
Contaminant monitoring programs (e.g. FSANZ)
Environmental Consideration e.g. water source/quality, old mining land, pollutant residues, manure run-off etc.
Product & Producer history - certain products have certain risks or have resident bacteria anyway
Non-compliance frequency in companies
Assessing risk
A risk assessment must identify?
Specificity of addressing risk aspect?
Risk on a hazard / disease-specific basis where possible
Must identify the risk for any given hazard / disease of concern separately, not simply address
the overall risk i.e. Bacteria risk vs Salmonella risk
Qualitative Risk Assessment
What is it based on?
Data that is inadequate for numerical risk estimations BUT when conditioned by prior expert knowledge and ID of attendant uncertainties allosw ranking or separation into descriptive categories of risk i.e. Low/Medium/High
Quantitative Risk Assessment
How does it work?
Making a mathematical model to link aspects of epidemiology of a disease
Expressed numerically
Quantitative Risk Assessment
A model like this incorporates X?
Features of each?
Deterministic
Outcome of model determined by initial conditions and specified set of equations e.g. population growth
Opposite of random
Stochastic
Incorporates uncertainty and randomness into the model to account fir variability in the system’s inputs and parameters
Generates multiple possible outcomes
Quantitative Risk Assessment
Issue in regards to results?
results, which are also expressed numerically, invariably present significant
challenges in interpretation and communication
What is BIRA?
What does this department do?
Biosecurity Import Risk Analysis
Range of risk analyses in response to import good requests into AUS, particularly if these goods have not been imported b4 or imported from somewhere new.
Covello–Merkhofer risk analysis model
Steps involved (broad)
Hazard ID - separate from risk assessment
Risk assessment in stages
Risk management and communication combo with risk assessment and hazard ID = Risk analysis
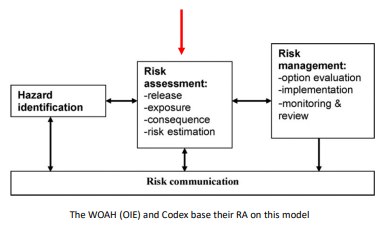
Covello–Merkhofer risk analysis model
Risk assessment steps - the stages include?

Covello–Merkhofer risk analysis model
Risk assessment steps - Release Assessment
Features of note?
ID the Hazard via Source and Mechanism Release → From a facility? Imported goods? Infected animal?
Assess probability of release → Likliness of release under conditions
Amount & Frequency of Release → Quantitiy released? How often?
Covello–Merkhofer risk analysis model
Risk assessment steps - Release Assessment is followed by?
What is this integrated with?

Once risk is estimated, what next?
What is considered acceptable?
With measure implementation, what are some ways to implment it? What are some concerns with measure implementation?
Process to decide what measures are done to address ID risks
Measures to protect AUS biosecurity while also minimising negative effects on trade
Implement with new laws (difficult but sometimes needed)
Implement with non-regulatory options
E.g. Quality assurance schemes at farm level, consumer education, Packaging for safe handling in the home
Implementation concerns
Hard to select the most apt control measure - outcome altered by legal, ethics, economic, social factors
Following implementation of measures based on risk estimation, what next?
Monitoring: Observing if control measures work or make an unintended bad outcome aswell
What does ALOP stand for?
Appropriate Level of Protection
BIRA
There are two main types of risk analyses used by it, what are they?
• a BIRA which is conducted through a regulated process provided for in the
Biosecurity Act and the Biosecurity Regulation
• a non-regulated risk analysis (e.g. scientific reviews of exisitng policy)
The principal aim of BIRA is to provide?
importing countries with an objective and defensible method of assessing the disease risks associated with the importation
A BIRA can identify conditions that must be satisfied to?
manage the level of biosecurity risk to achieve Australia’s “appropriate level of protection” (ALOP)
BIRA and ALOP
If the biosecurity risks associated with the importation, do not achieve Australia’s ALOP, what is done?
If the risks cannot be reduced to good levels, what happens?
risk management measures are proposed to reduce the risks to an acceptable level
Goods aren’t imported until suitable measures are ID’d
ALOP & SPS Agreement
What does this entail?
SPS measures are used to?
WTO members are entitled to maintain a level of protection apt to protect life or health within their territory (i.e. ALOP)
Manage risk to achieve ALOP
AUS ALOP is contained in what law?
Where is it applied?
Biosecurity Act 2015
In Risk analyses by Department of agriculture, water and environment
AUS ALOP
Example involving FMDv
How to do so?
ALOP is to remain free of FMDv
Insist on apt level of protection from imported goods that may harbor virus
AUS will want certain measures applied to imports that may threaten free FMDv status
Methodology
Importance of framing the risk question?
What should we consider in terms of the risk question?
The risk is clearly defined
Consider
Specific hazard of concern (e.g. Campylobacter or bacteria?)
Vector/vehicle of the hazard
Specific risk that’s being assessed
Time frame being observed
Methodology
Framing the risk question and specificty requires a balance, describe this
sensitive question may be more inclusive but can be interpreted in different ways; if too
specific may miss relevant cases