Foundational Music reading skills final exam
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
How to find the tonic of a key with sharps
find the last sharp and go up a half-step
How to find the tonic of a key with flats
take the last flat and go back a flat
How to find the tonic of a minor key
go down 3 half steps from the major tonic
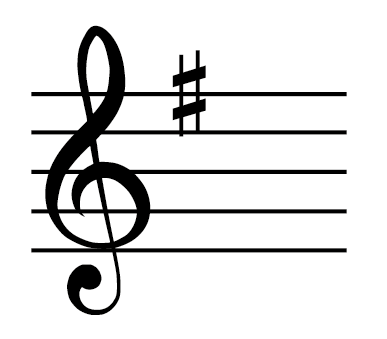
Key with one sharp
G major/E minor
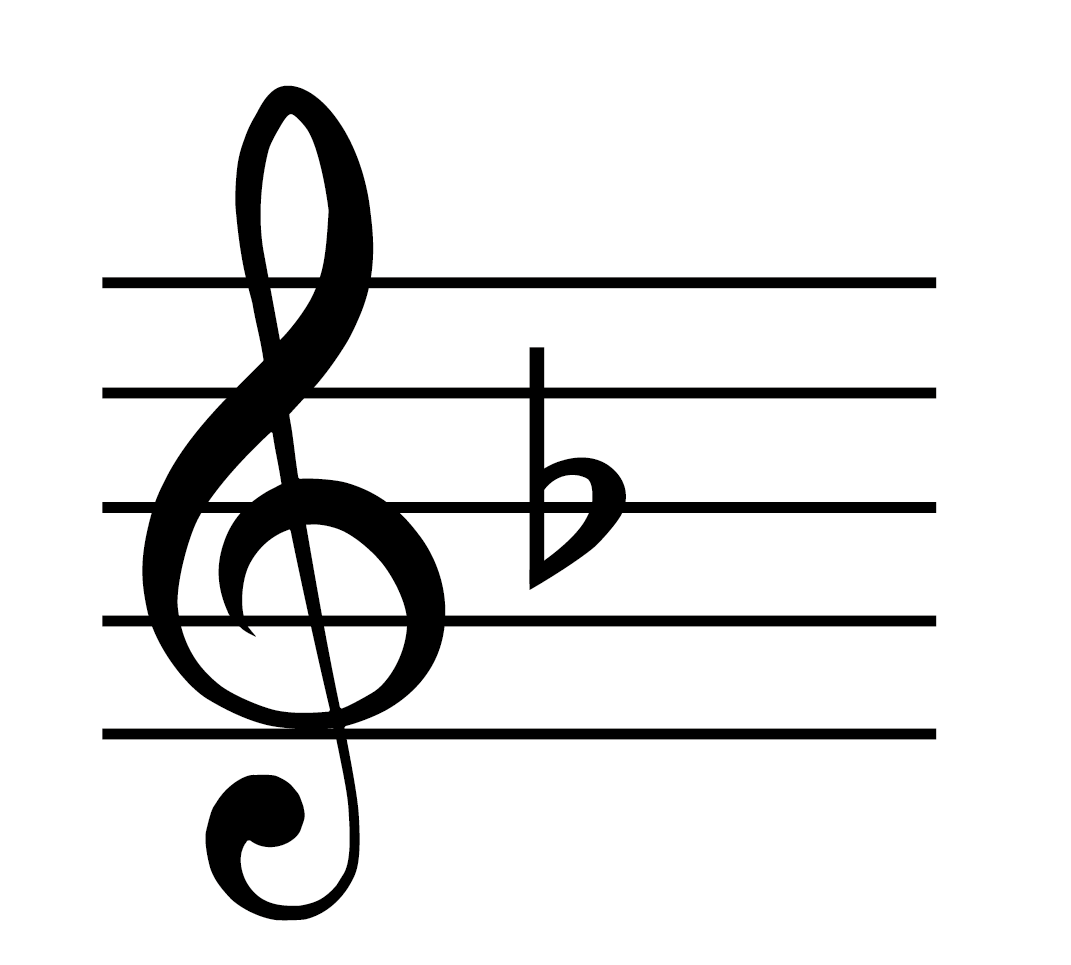
Key with one flat
F major/d minor
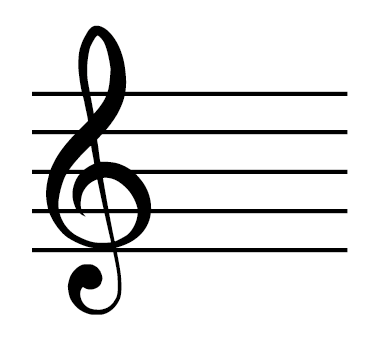
Key with no accidentals
C major/A minor
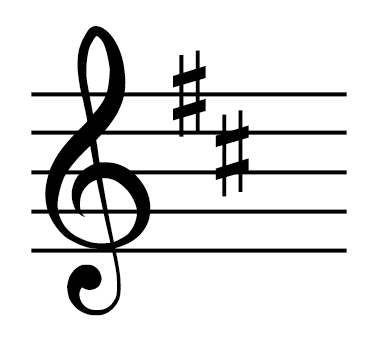
Key with two sharps
D major/B minor
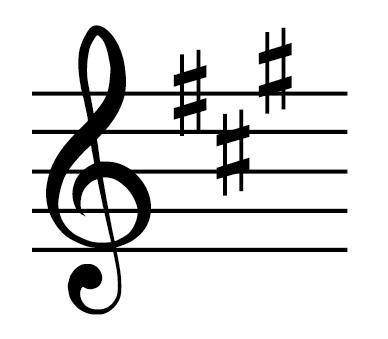
Key with three sharps
A major/F# minor
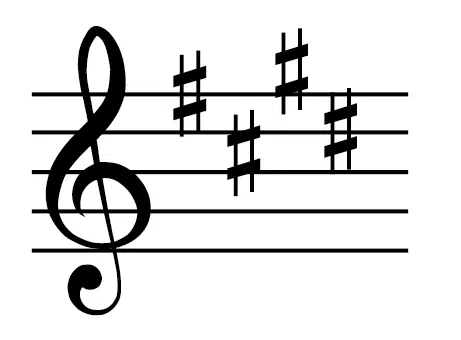
Key with four sharps
E major/C# minor

Key with five sharps
B Major/G# major
Key with six sharps/flats
Gflat+F# major/Eflat+D# minor
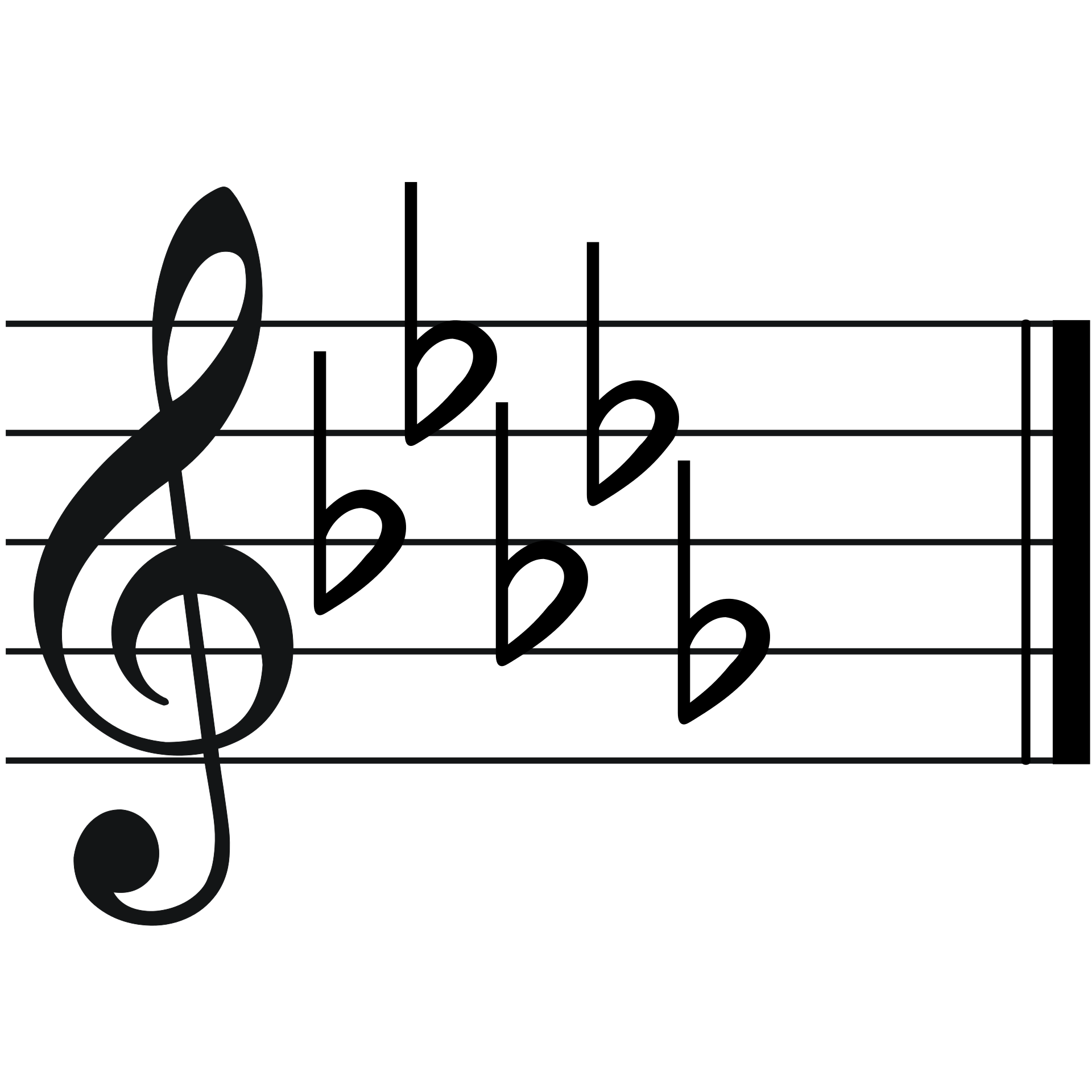
Key with five flats
Dflat major/bflat minor
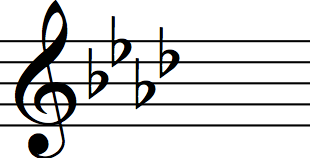
Key with four flats
A flat major/F minor
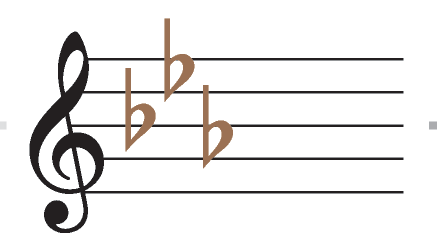
Key with three flats
E flat major/C minor
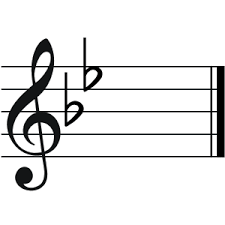
Key with two flats
B flat major/G minor
Order of flats
B-E-A-D-G-C-F
Order of sharps
F-C-G-D-A-E-B
the name for scale degree 1
Tonic
The name for scale degree 2
Supertonic
The name for scale degree 3
mediant
Name for scale 4
Subdominant
Name for scale degree 5
Dominant
name for scale degree 6
Submediant
name for scale degree 7
Leading tone (for major), and sub-tonic (for Minor)
What is the formula for a Major scale
1w2w3h4w5w6w7h1
What is the formula for a minor scale
1w2h3w4w5h6w7w1
What is a relative key pairings
A major key and relative minor key that share the same key signature
Relative keys
different tonics and same key signature
Parallel Keys
Same tonic and different key
Natural Minor
the way the minor scale sits naturally
Harmonic Minor
when you take the natural minor scale, and raise the sub-tonic a half-step to make it a leading tone
Melodic Minor
When you raise scale degrees 6 and 7 up a half-step, scale degrees 5, 6, and 7 will sound major, but scale degree 3 will sound minor. Is usually used only in ascending scales and will return to the natural minor on the descending scale.
What is a simple meter
A meter that has a top number of 2,3,4 —> 2/4, 3/4, 4/4. The top number is how many beats, and the bottom number is what kind of note. And it is divided by 2.
What is a compound meter
A meter that has a top number of 6, 9, 12 and divided by 3 to find the beat, 6 → 2, 9 —> 3, 12 —> 4. Top number is the division of beats, and the bottom is the top of note.
What is the defining characteristics of an interval
The size of the interval and the quality (M, m, d, A)
What is a simple interval
A interval that’s size is between 1-8
What is a complexed interval
A interval that’s size is more than 8
How many half-steps in an octave
12 half-steps
How to make an interval compound
Add 7 to the size of the interval
How to make an interval simple
subtract 7 from the size of the interval
How do you make a interval augmentive
Add 1hs to a major interval, 2hs to a minor interval, 1hs to a perfect interval, and 3hs to a diminished interval
How to make an interval diminished
subtract 1hs from a minor interval, subtract 1hs from a perfect interval, 2hs from a major interval, and 3hs from an Augmentative interval
What is the size of two octaves
15 because you only count the tonic once
What happens to the quality of the interval when you make it compound or simple
The quality stays the same
Unision
abbreviation is p1
interval type 1
zero half steps
Minor second
abbreviation is m2
type of interval is 2
one half step
Major 2nd
Abbreviation is M2
type of interval is 2
two half steps
Minor 3rd
abbreviation is m3
type of interval is 3
3 half steps
Major 3rd
Abbreviation is M3
type of interval is 3
4 half steps
Perfect 4th
Abbreviation is P4
type of interval is 4
5 half-steps
Tritone
Abbreviation is A4/d5
interval type is 4/5
6 halfsteps
Perfect 5th
abbreviation is P5
interval type is 5
7 half-steps
minor 6th
Abbreviation is m6
interval type is 6
8 half-steps
Major 6th
Abbreviation is M6
interval type is 6
9 half-steps
Minor 7
Abbreviation is m7
interval type is 7
10 half-steps
Major 7th
abbreviation is M7
interval type is 7
11 half-steps
Octave
abbreviation is P8/8ve
size is 8
12 half-steps
How to count half-steps
start counting when you move
How to count size of an interval
start on the first note
Harmonic Interval
the pitch relationship between two notes that are played simultaneously
Melodic Interval
the distance between two pitches played in sequence, one after the other, as in a melody
What is the root position of a chord?
When the first factor is the bottom of the chord (5/3)
What is first inversion of a chord?
When the third factor is the root of the chord (6 or 6/3)
What is second inversion of a chord?
When the fifth factor is the root of the chord (6/4)
What is the formula for a major chord
M3 + P5
What is the formula for a minor chord?
m3 + P5
What is the formula for a diminished chord?
m3 + d5
What is the formula of a Aug Chord?
M3 + A5
What is a chord?
A harmony with three or more notes
How to invert an interval?
The quality changes (except for Perfect), the size changes, and the note order changes—> The Sum needs to be nine. For example, a Major 7th would convert to a minor 2nd because 9-7 equals 2.
What is a marco chord?
Chords identified by letter names, I.E G(chord that it is)/B (the lowest tone)
What is marco analysis?
When a chord is identified by it’s letter names —> to root position —> writtens as 1st factor/the lowest tone