Econ 13: Ch 14: Negative externalities
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is one type of market failure?
externality -
What’s externality?
the impact of one person’s actions on the well-being of a bystander
When does an externality occur?
an exchange between a buyer and seller has an impact on a third party who’s not part of this exchange
Eg. Environmental damages like air pollution caused by economic production
What’s a spillover?
Externality, aka spillover, can have negative or positive impact on third party
How can we improve market outcomes, in the presence of externalities?
the government
What’s a social cost?
the total cost by society from a particular activity or decision
formula: total cost = Private cost + Social cost
What are private costs?
The cost of production, eg. labor cost, materials, etc.
What’s pollution cost?
cost towards society
What happens if the government forces companies to pay for the pollution cost? W/ tax
The cost of production increases, the supply decreases.
Prices increase, quantity decreases
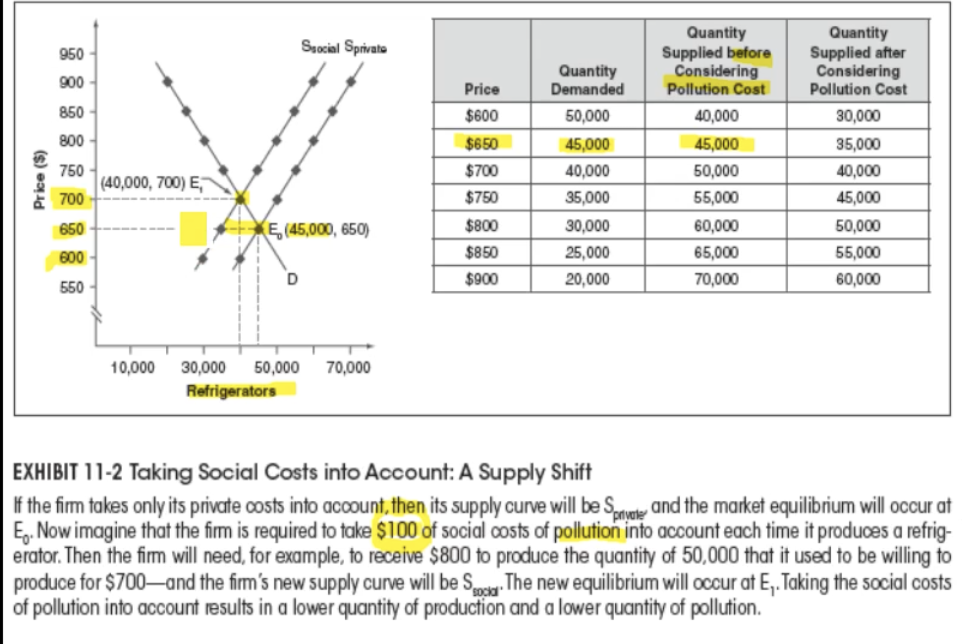
Ex: If a firm puts a $100 social cost on refrigerators, what happens w/ the supply and demand?
Supply decreases, cost of production increases
quantity supplied decreases, price of good increases
some of the burden of the social cost is given to customers and some taken by producers
What happens when a social cost is imposed on the producers
Money is used to help the environment the company is hurting
The producers have smaller quality
Both helping the environment
What are two policies towards externalities?
Command and control regulations
Market-oriented environmental tools
What’s the command-and-control regulation?
set limits to pollution emissions or pollution control tech that must be used
eg. laws that specify allowable quantities of pollution
What was wrong with the command-and-control regulation?
no incentive to pollute less
offer limited flexibility to where n how pollution will be reduced
there’s politically motivated loopholes
What’s market-oriented environmental tools?
provides incentives so that people will solve the pollution problem on their own
What are the 3 tools that the market-oriented environmental tools use?
pollution charge
marketable permits
better defined property rights
What are market oriented policies?
uses taxes, markets, and property rights so that ppl who impose negative externalities will face the social cost
What’s the pollution charge
Tax imposed on the quantity of pollution that a firm emits
If the cost of (preventing) pollution < tax, companies have the incentive to…
companies have the incentive to spend the money to lower the pollution through new technology
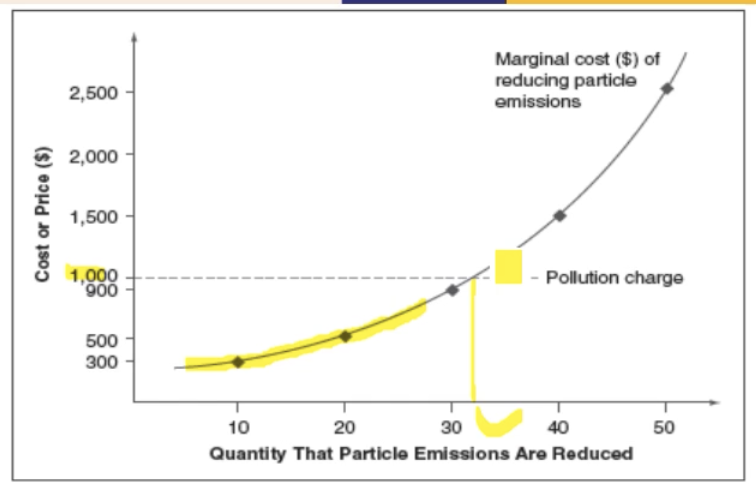
If the cost of (preventing) pollution > tax, then companies have the incentive to…
companies have the incentive to continue polluting and just pay the tax
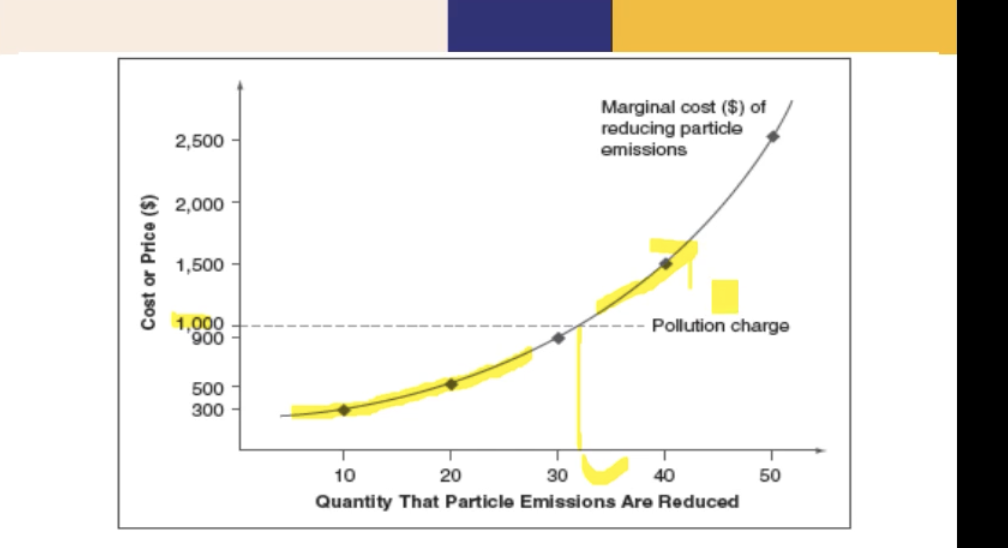
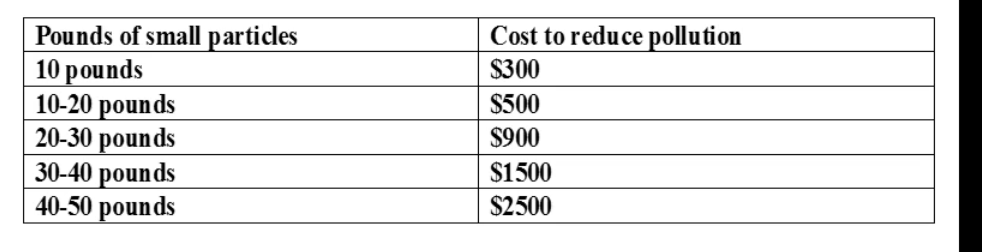
If pollution charge is $1000 per 10 lbs, what pounds of small particles will firms choose to pay the pollution charge or the cost to reduce pollution?
From 10 - 30 pounds, firms should pay the cost to reduce pollution
From 31 - 50 pounds, firms may pay the pollution charge
What is good about the pollution charge,
the pollution charge encourages companies to pay the cost to reduce pollution (to a certain amount of pounds) and whatever they choose to pay for the pollution charge goes towards the government to help the environment.
What are marketable permits?
permit that allows firms to emit a certain amount of pollution
What incentive does Market Permits provide to firms
You can sell your marketable permit, which incentivizes firms to reduce pollution so they can sell non-used permits to other firms and earn more money
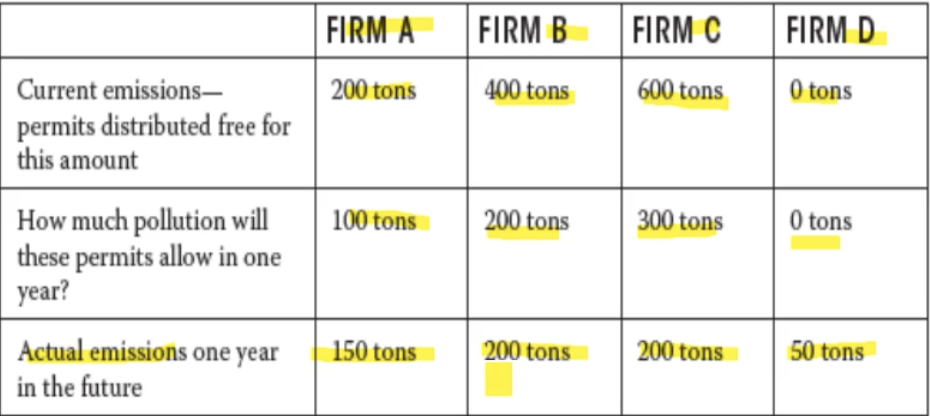
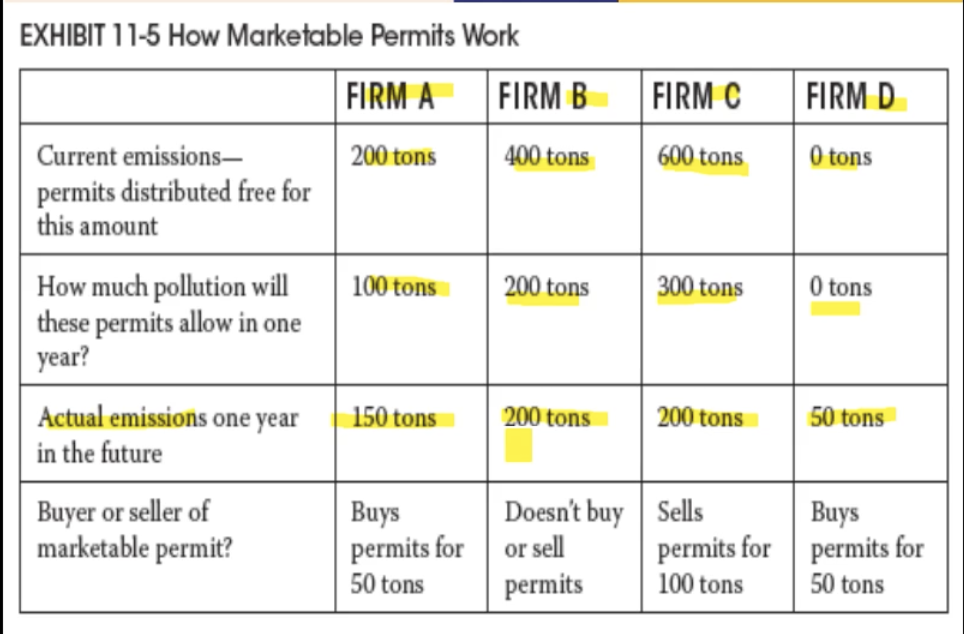
Each firm is given a market permit for two years, how much they can produce in one year, and how much they predict they will use in that on year. What happens when a firm exceeds or uses less than what their permit allowed them to. Hence, firm A and D
Firm A & B polluted 50 tons more than they were allowed
Firm C used 100 less than they were allowed
Firm A & B each buy 50 tons of a permit from firm C
What are better defined property rights?
compensate those who were negatively affected by pollution.
All parties negotiate till they reach an agreement on rights and compensation
Why do we need environmental policies?
The benefits of environmental regulations outweigh the costs
What are the benefits of U.S. environmental laws
ppl stay healthier n live longer
clean air n water
value of the properties increases
ppl enjoya cleaner environment
What are the costs of U.S. environmental laws
Can be very expensive (billions & trillions)
Why can’t poor countries improve their environmental conditions?
Because they gotta focus first on providing their ppl w/ basic necessities.
What’s the tradeoff between economic output and environmental protection?
higher economic growth & income or higher environmental protection
most countries prioritize production efficiency
A pollution charge gives the trucking industry an incentive to reduce its emissions, as long as the ____________ of reducing the emissions is ____________.
a.
total cost; less than the tax
b.
marginal cost; less than the tax
c.
total cost; equal to the social cost
d.
marginal cost; equal to the social cost
B