Chapter 10: Sugar (carbohydrates)
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
Carbohydrates role
energy source for cells, nucleic acids, ATP, cell walls, important part of glycoproteins (sugar)(see examples)
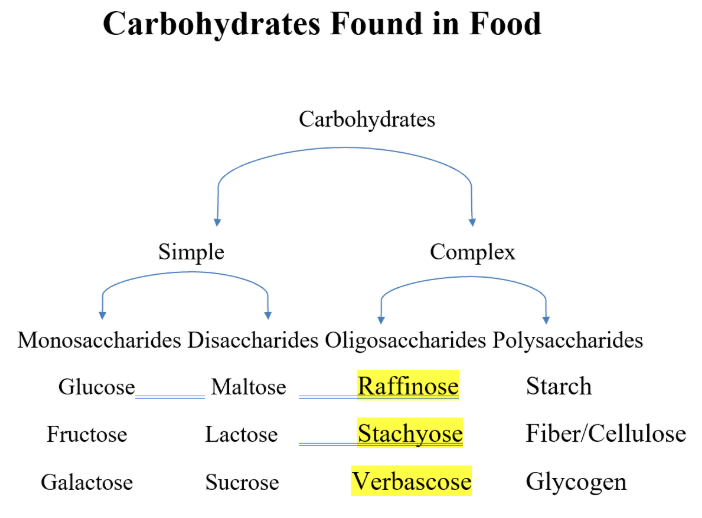
Monosaccharides/ simple sugars
single ring structure that are soluble in water
Disaccharide
double ring structure that are soluble in water
Oligosaccharides
3 to 9 ring structure that are insoluble in water
polysaccharides/ complex sugars
multi ring polymer structures that are insoluble in water but are very stable compounds
carbohydrates found in food
Monosaccharides functional groups
aldose and ketose, they are hydroxyl/ alcohol group
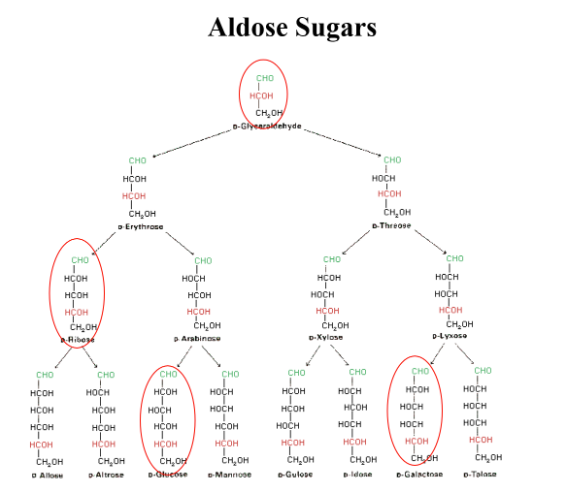
Aldose
contains an aldehyde functional group, 3-6 carbons, all carbons except two end ones are chiral
Glyceraldehyde, ribose, glucose, galactose
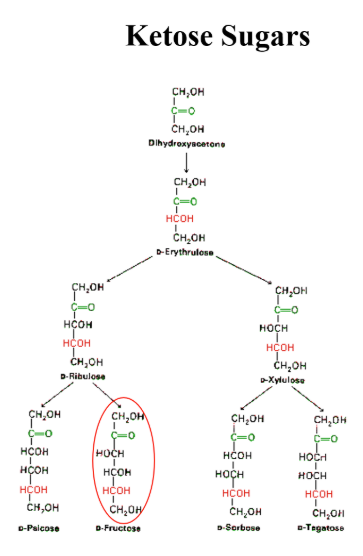
Ketose
contains a ketone functional group, 3-6 carbons, all carbons except two end ones and the carbonyl carbon are chiral
fructose
Only the D-configuration are found in nature (not L)
Only the D-configuration are found in nature (not L)
Anomeric carbon
carbonyl carbon, carbon number is labeled 1 for aldose and number 2 carbon for ketose
Forming hemiacetal bonds
aldehyde or ketone reacts with a hydroxy group on carbon 5
beta (β) configuration
hydroxyl group on carbon 1 is on the same side (cis) as carbon 6
alpha (α) configuration
hydroxyl group on carbon 1 is on the opposite side (trans) as carbon 6
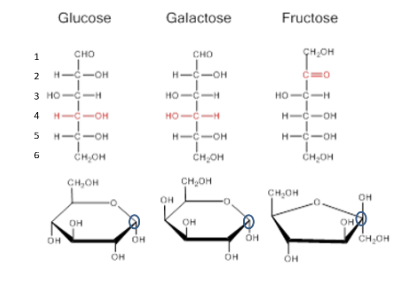
Monosaccharides
single ring structures, very soluble in water, provide energy
Glucose, fructose, galactose
simple sugars/ monosaccharides
all carbohydrate compounds that have two or more monosaccharides will be in the ring structure only.
Simple sugars are very reactive
Because sugars have many hydroxide groups, they are able to react with acidic carbonate groups to form esters
Glycation
non-enzymatic reaction where monosaccharides form a covalent bond with protein molecules such as fibrinogen, collagen, and proteins which denature them, excessive glucose in blood due to diabetes, tested with HbA1c Test
Fructose is 10 times more reactive than glucose
Fructose is 10 times more reactive than glucose
Glycosidic bond
condensation reaction (removal of water) between the anomeric carbon on one monosaccharide and any of the hydroxide groups on the second monosaccharides
Glycosidic linkage
water molecule is removed, anomeric hydroxide is in the alpha position,
Alpha (1,4) bond
1 and 4 hydroxide groups are bonded, a 1, 4 glycosidic bond is formed. If the anomeric carbon is in the alpha position.
Beta (1,4) bond
OH on the anomeric carbon is in the beta position, hydroxide groups on each sugar is on opposite side of each sugar, can be broken by enzymes
Disaccharides
3 most important are sucrose lactose and maltose, chemistry is similar to simple sugars, very sweet
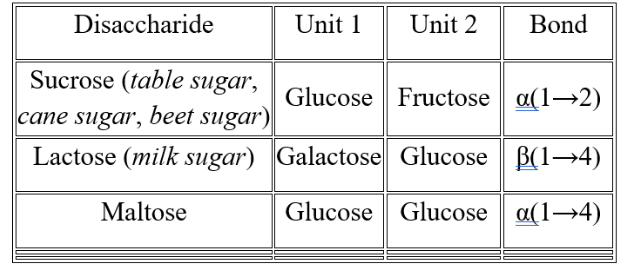
Sucrose
table sugar
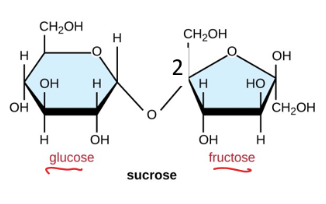
Lactose
sugar found in milk, hard for many adults to digest
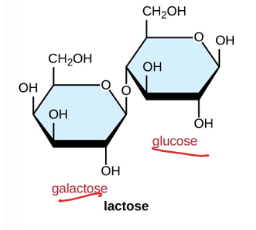
Maltose
found in beer made from barley
Oligosaccharides
tri-saccharides, tetra-saccharides, penta-saccharides, aka soluble fiber because they dissolve in water but cannot be broken down, need special enzymes to break them down so they can be used for energy production
Tri-saccharides (raffinose)
Found in many vegetables especially in grains and beans, breaks down into galactose glucose and fructose, sweetness of 22 compared to sucrose
Tetra-saccharides (Stachyose)
Found in many vegetables, especially peas, beans and soybeans, breaks down into 2 units of galactose, one unit of glucose and fructose, sweetness of 20
Penta- saccharides (Verbascose)
Found in many legumes, 3 units of galactose and one unit of glucose and fructose
Polysaccharides
aka insoluble fibers, insoluble polymers of simple sugars, can only be broken down by specialized enzyme, no sweetness associated with them, (ex. Cellulose, starch, pectin, glycogen)
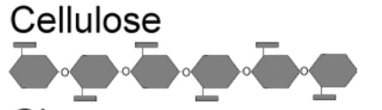
Cellulose
from plant cells walls, connecting bonds are beta (1,4) bands
Starch
storing chemical energy in plants, amylose and amylopectin, formed primarily by plants, , polymer of glucose which means they are insoluble in water
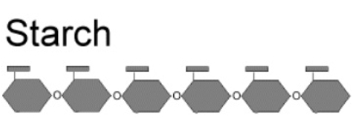
Amylose
linear, few to no branches, aka firm starch, alpha (1-6) bonds,
Amylopectin
branched, aka soft starch, alpha (1-6) bonds,
Pectin
form plant plants cell wall
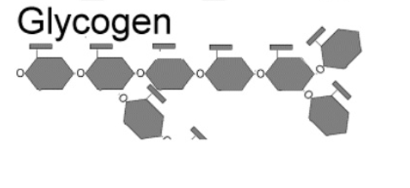
Glycogens
storing energy in the cells of animals especially in working muscles and liver cells, very branched, The long polymer chains are joined by alpha (1,4) bonds and the branch chains are formed by the alpha (1,6) bonds.
Cellulose
polymer of glucose formed by plants, connecting bonds are beta (1,4) bonds, needs specific enzyme to break which most animals and humans do not possess, used by plants to make ridged stems
Pectin
molecule found in plants made from multiple simple sugars bonded in multiple different ways
Blood type
chemical markers made from simple carbohydrates, 3 types: O= give anyone, only receive O, AB= receive anyone, only give AB