Phase Equilibrium
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is phase?
A chemically homogeneous part of a system that is physically distinct and mechanically separable is called a phase
Phase of pure substance
Homogenous. A phase may or may not be continuous
Phase of mixture of gasses
Homogenous
phase of miscible liquids
Homogenous
phase of non-miscible liquids
heterogenous
phase of aqueous solution
Homogenous
Phase of mixture of solids
Heterogenous
component of a system
The least number of independent chemical constituents in terms of which the composition of every phase can be expressed by means of a chemical reaction.
Nitrogen (N2)
Oxygen (O2)
Components = No. of gases present = 2
Phase = 1 = homogenous gaseous mixtures
Rhombic sulfur
Monoclinic Sulfur
Liquid sulfur
Sulfur vapor
Components: 1
Phase: 4
Chemical properties: Same
Physical properties: Different
NaCl Solution
Components = No. of chemical constituents = 2
Phase = 1 (homogenous solution)
NaCl Solution
Solid NaCl
Components: 2
Phase: 2
Water
Ice
Water vapor
Components: 1
Phase: 3
Chemical properties: Same
Physical properties: Different
Rhombic sulfur
Monoclinic Sulfur
Sulfur vapor
Components: 1
Phase: 3
Chemical properties: Same
Physical properties: Different
CaCO3 (s)
Cao (s)
Co2 (s)
Components: 2
Phase: 3
Chemical properties: Different
Physical properties: Different
Degrees of freedom
The least number of variable factors (concentration, pressure and temperature) which must be specified so that the remaining variables are fixed automatically and the system is completely defined
nonvarient
A system with F = 0 is known as nonvariant or having no degree of freedom.
Univarient
A system with F = 1 is known as univariant or having one degree of freedom.
bivarient
A system with F = 2 is known as bivariant or having two degrees of freedom.
phase rule
By means of a diagram it is possible to predict qualitatively the effect of changing pressure, temperature and concentration on a heterogeneous system in equilibrium.
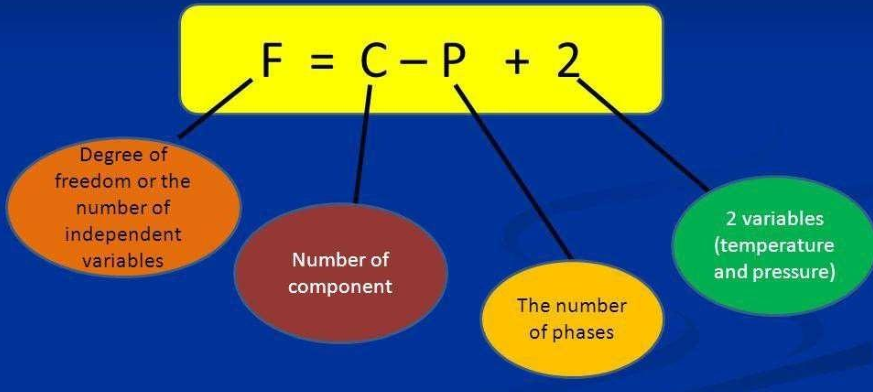
What is Gibb’s phase rule free from?
Gibb’s Phase Rule is free from flaws and limitations
Degrees of freedom o fWater vapor confined to a particular volume
F = 1 - 1 + 2 = 2 (C=1, P=1)
A system comprising a liquid water, in equilibrium with its vapor (DOF)
F = 1 - 2 + 2 = 1
Here, C=1, P=2
Let’s cool liquid water and its vapor until a third phase (ice) separates out (DOF)
F = 1 - 3 + 2 = 0
Here, C=1, P=3