SHOULDER SPECIAL TESTS
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
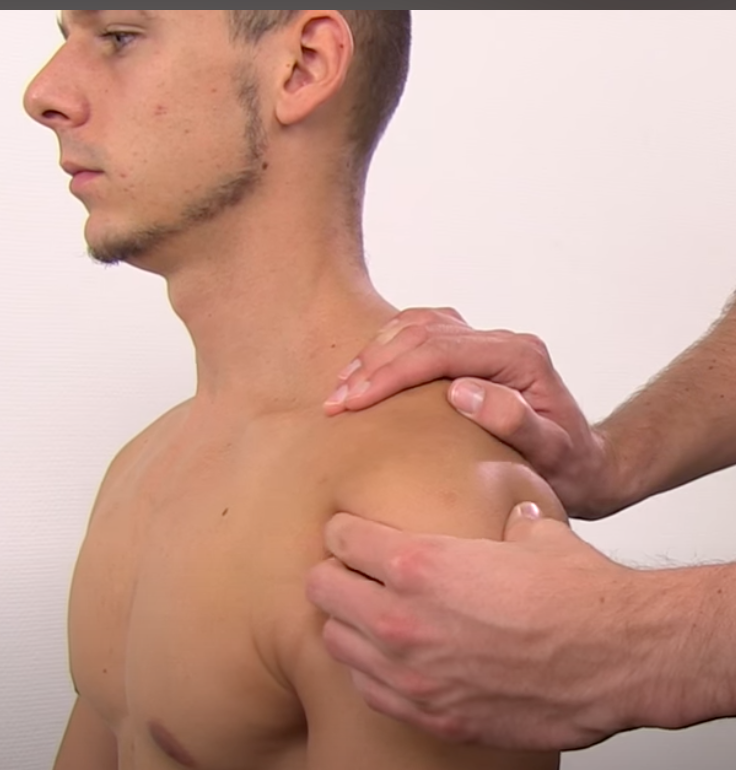
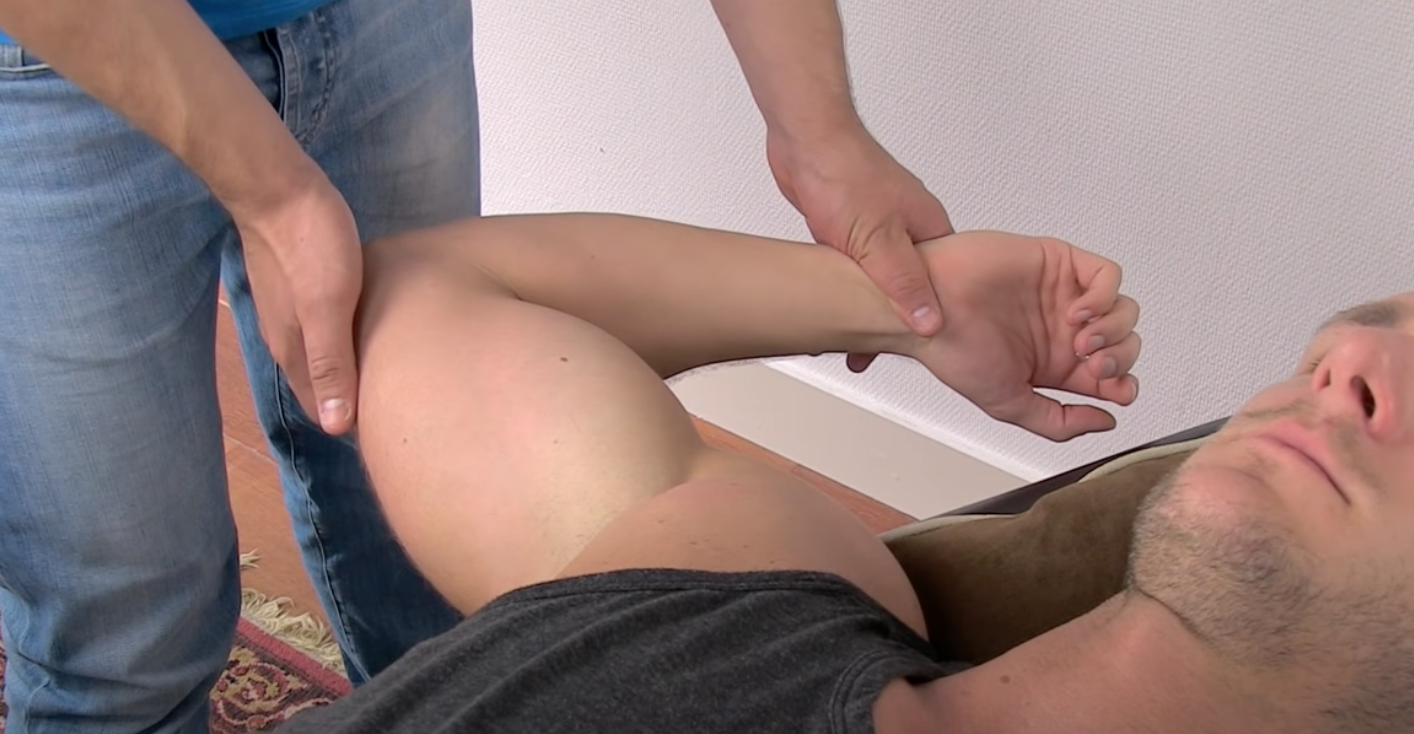
Anterior Instability Tests
_________
Load & Shift test
Forward → Anterior capsule
Backward → Posterior Capsule
(+) when you can redo patient symptoms

Anterior Instability Tests
_______________
Crank Test/ Apprehension Test
(+) if pain or fear of subluxation
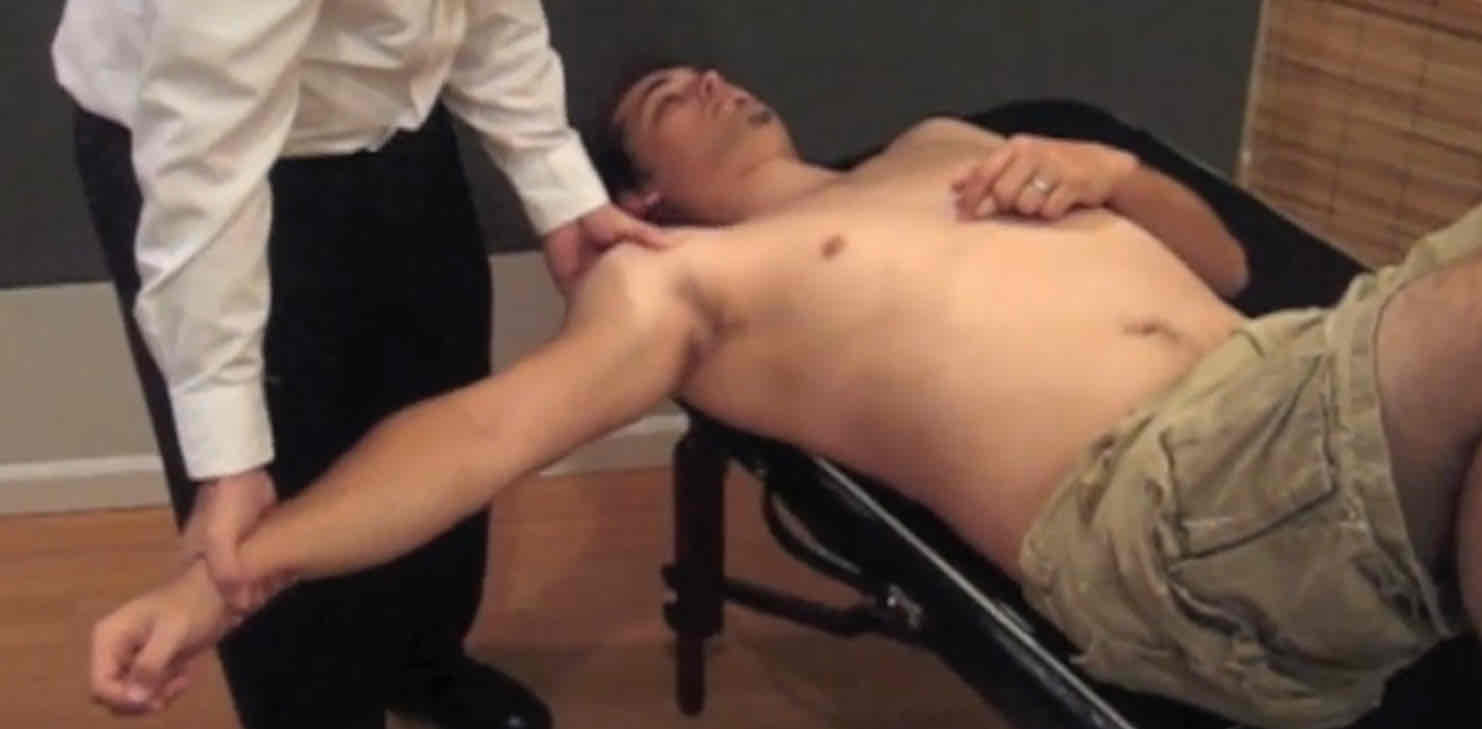
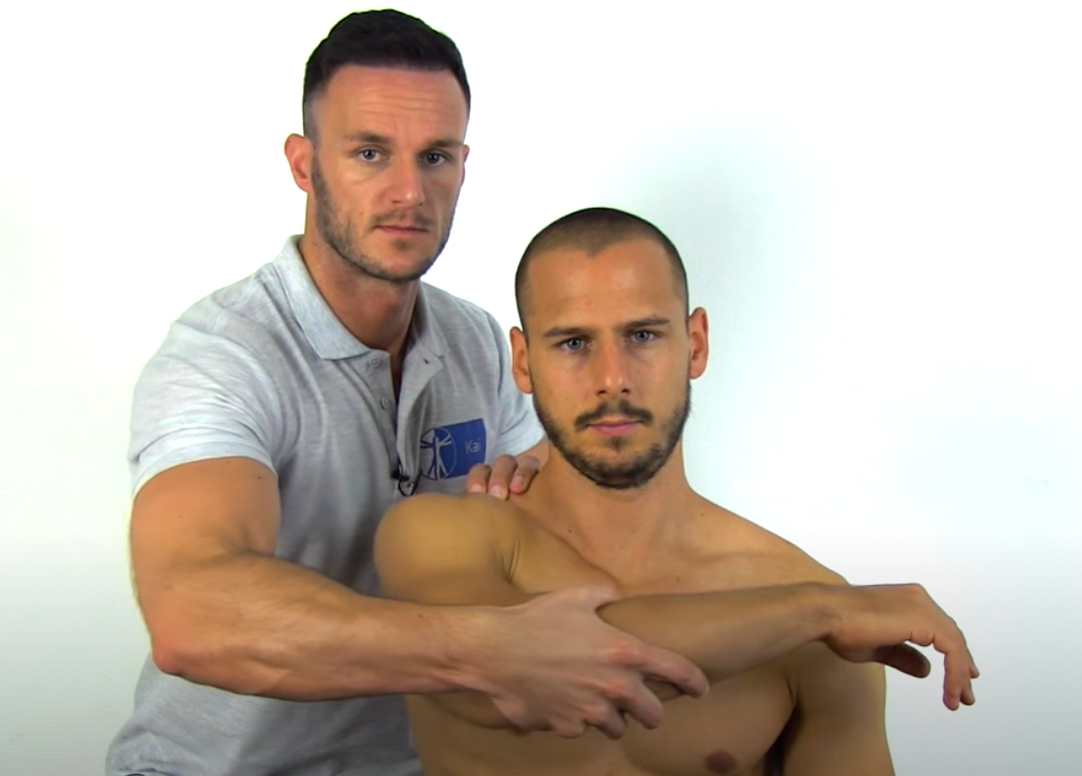
Anterior Instability Tests
__________
Anterior Drawer Test
anterior shoulder laxity ( not pathological)

Posterior Instability Tests
_______
Jerk Test
(+) if there is a sudden clunk during horizontal adduction
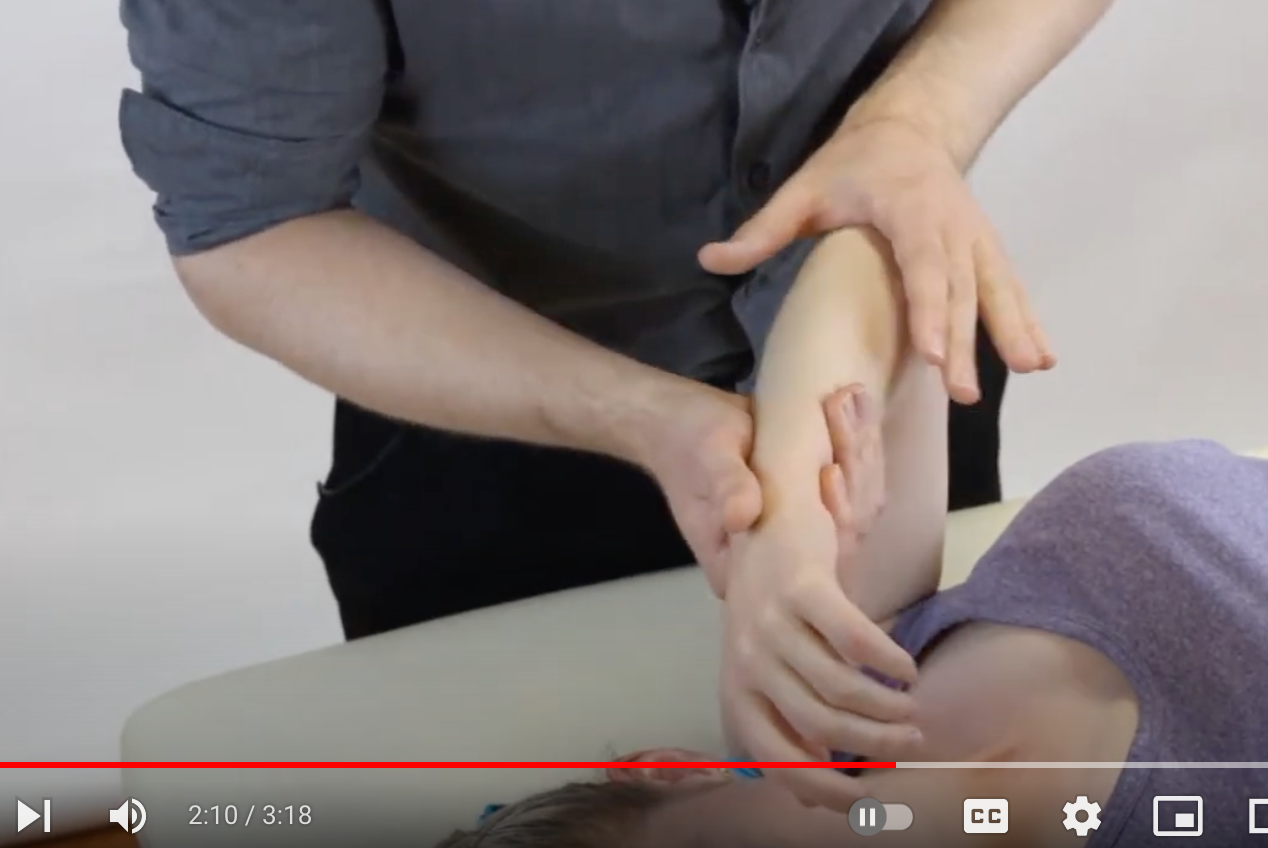
Posterior Instability Tests
_________
Posterior Apprehension Test
(+) if patient looks apprehended
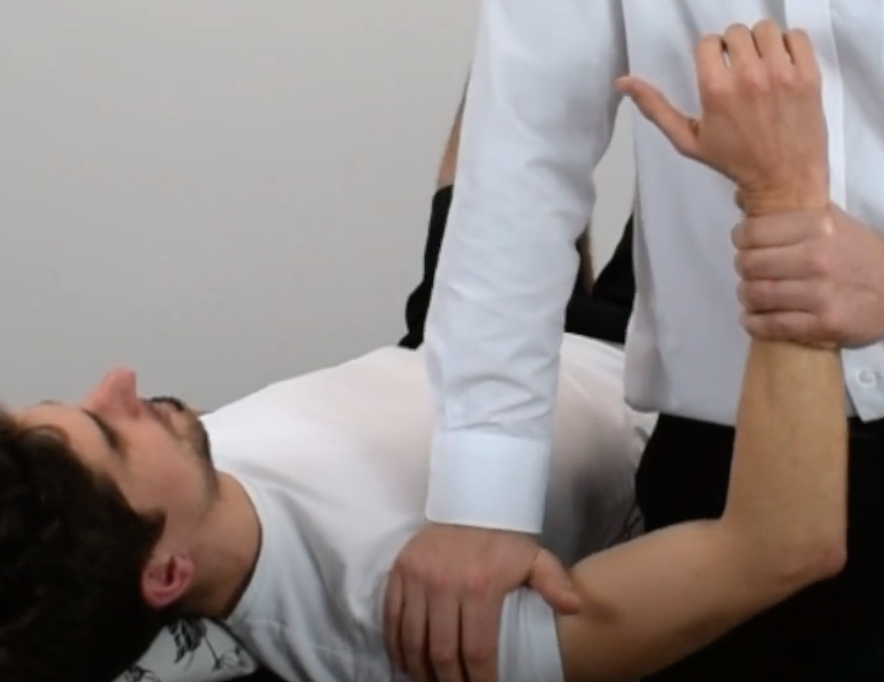
Posterior Instability Tests
Push Pull Test
(+) excessive translation of humeral head
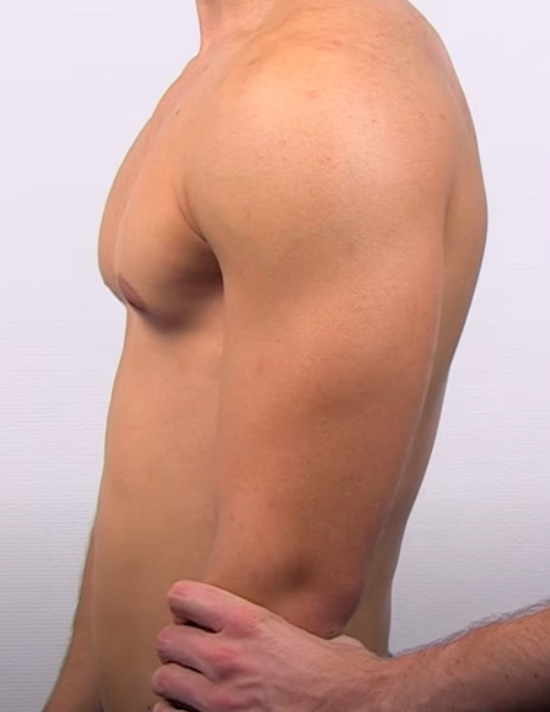
Multidirectional Instability Tests
Sulcus Sign
(+) if there is a little dip on acromion or feeling of subluxation
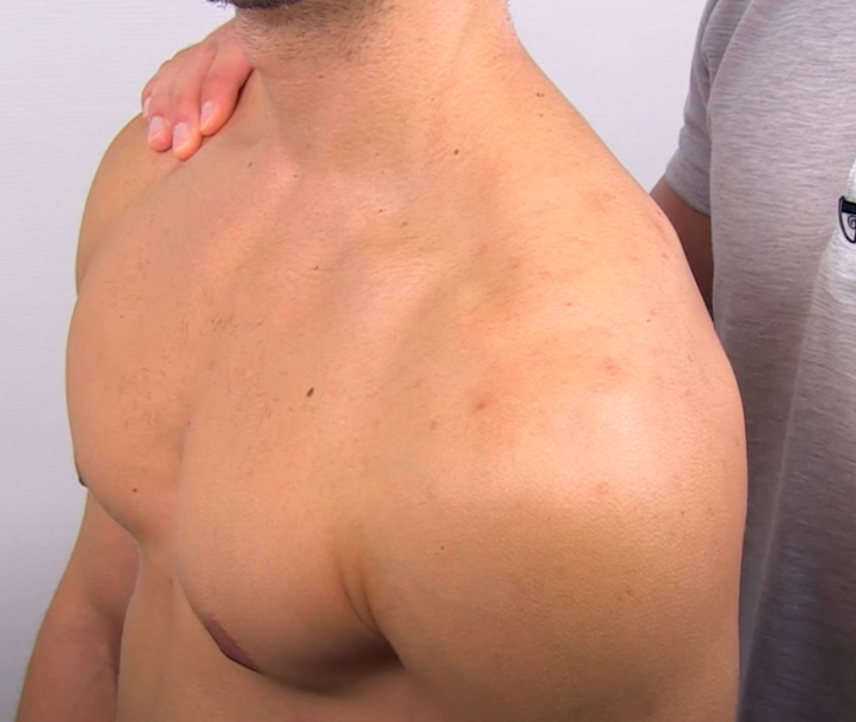
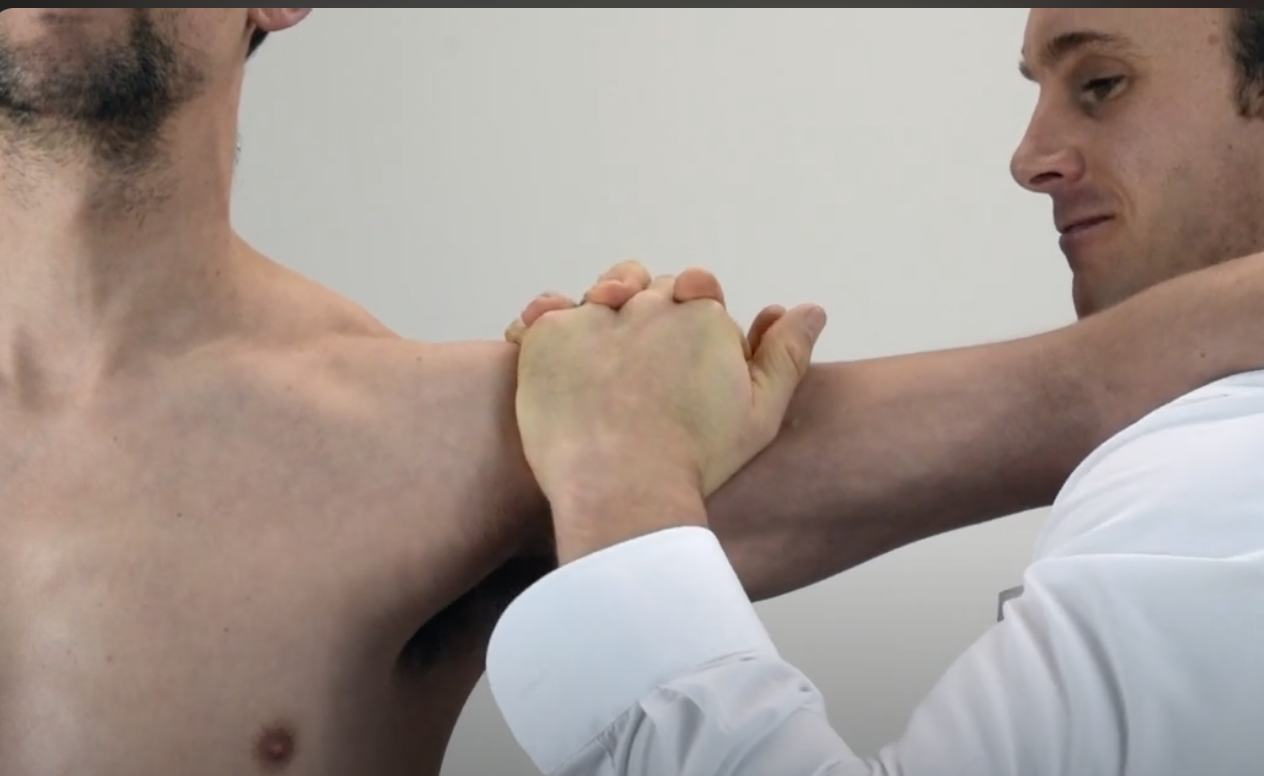
Multidirectional Instability Tests
Feagin Test ( Inf glenohumeral instability)
(+) Excessive laxity or apprehension
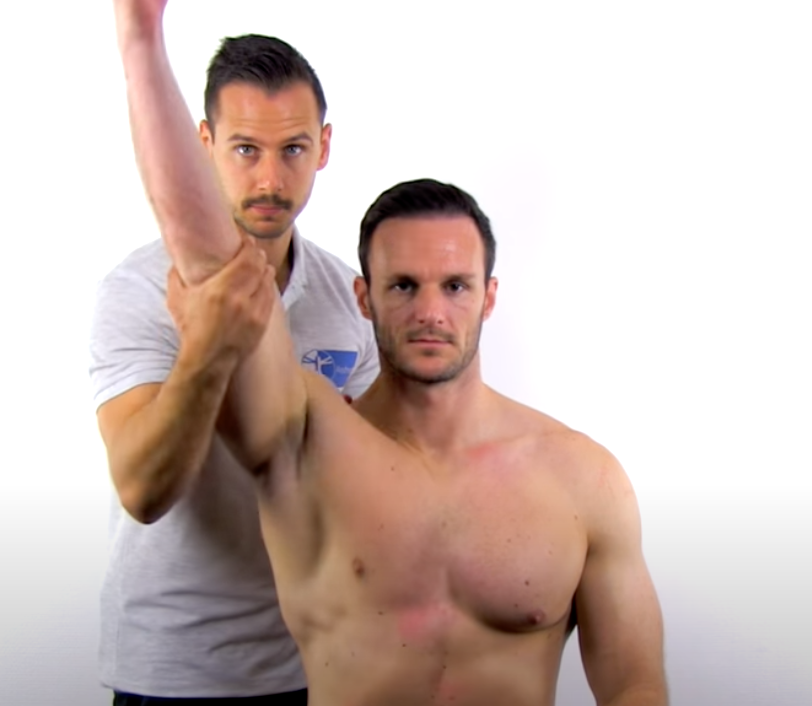

Impingement Tests
arm should be in IR
If done in ER → check AC joint next
Neer Impingement Test
(+)overuse of supraspinatus or biceps tendon
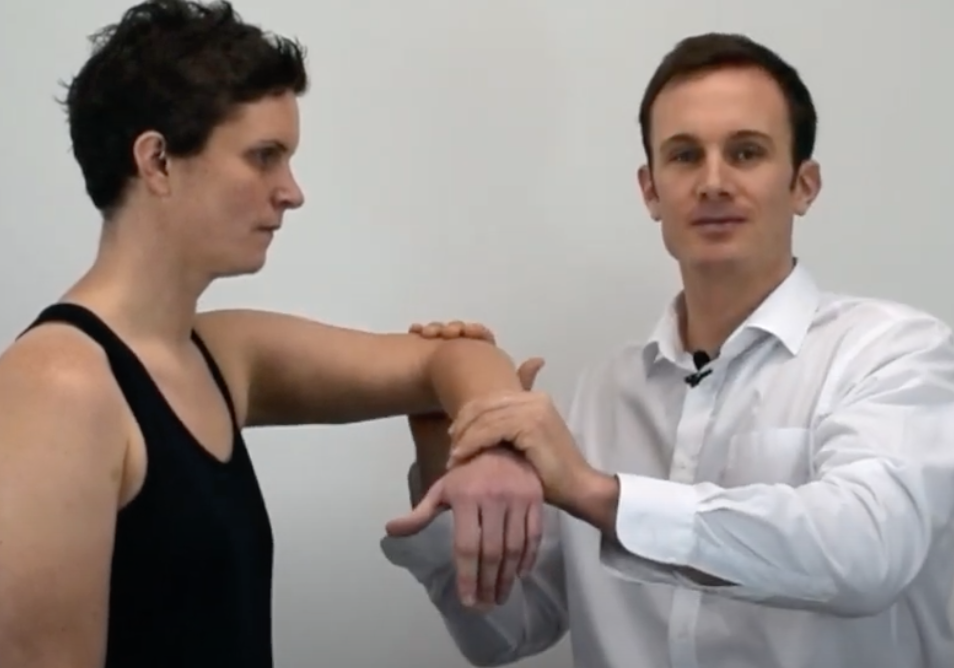

Impingement Tests
Hawkins- Kennedy
(+) Supraspinatus paratenonitis/tendinosis or secondary impingement

Impingement Tests
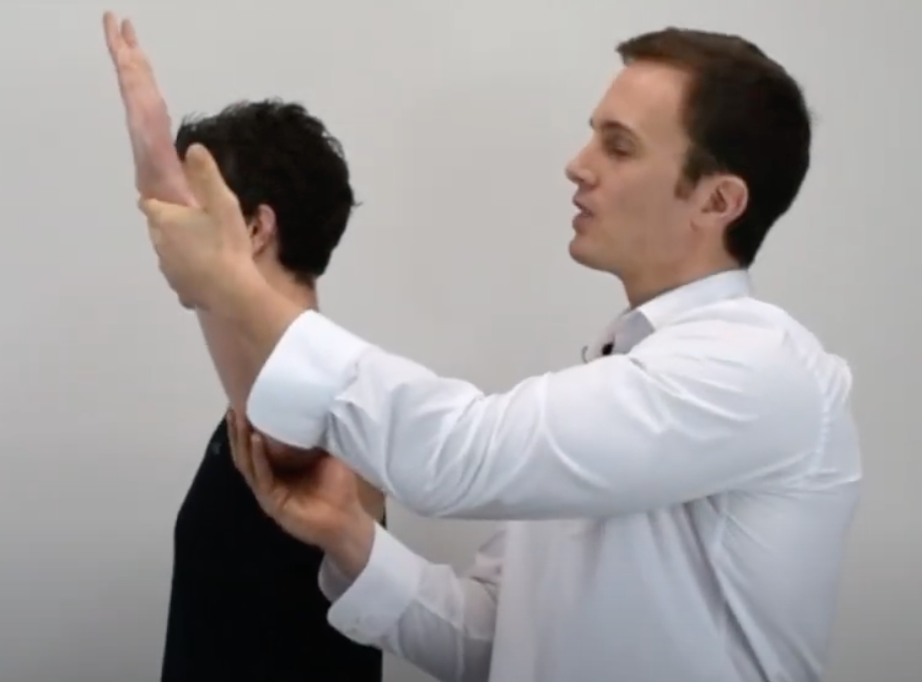
Internal Rotation Resistance Strength Test (ZASLAV)
(+) Internal impingement if good strength on ER but weak in IR
(+) external anterior impingement if weak ER
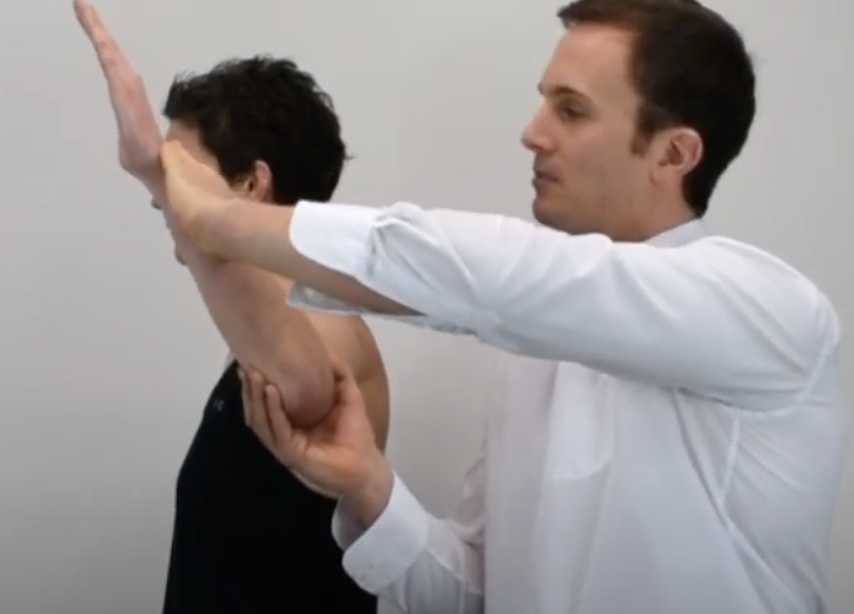
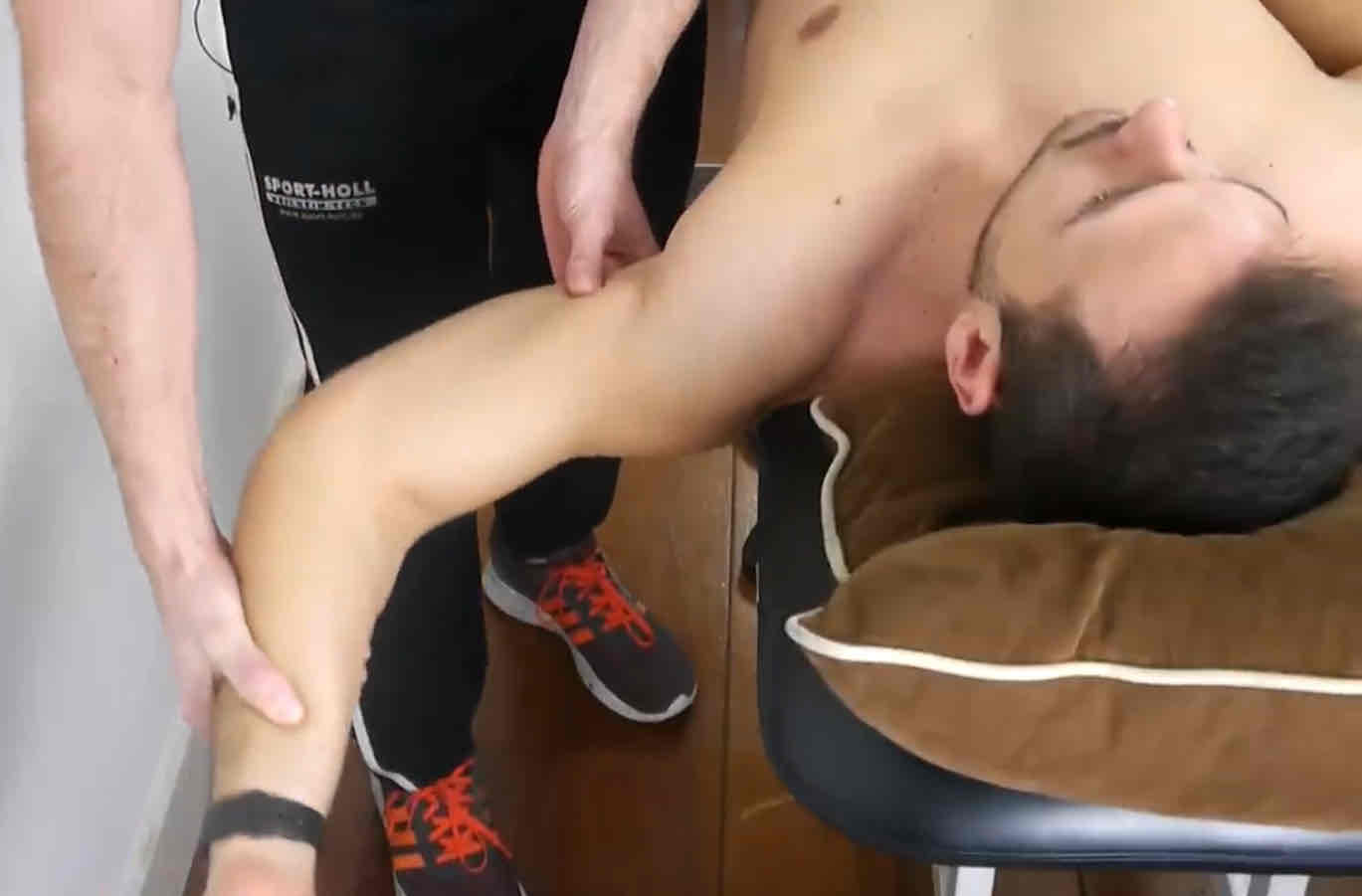
Impingement Tests
Patient in supine, passively abduct shoulder to 90° with 15-20° extension & max ER
Posterior Internal Impingement
(+) localized pain in posterior shoulder
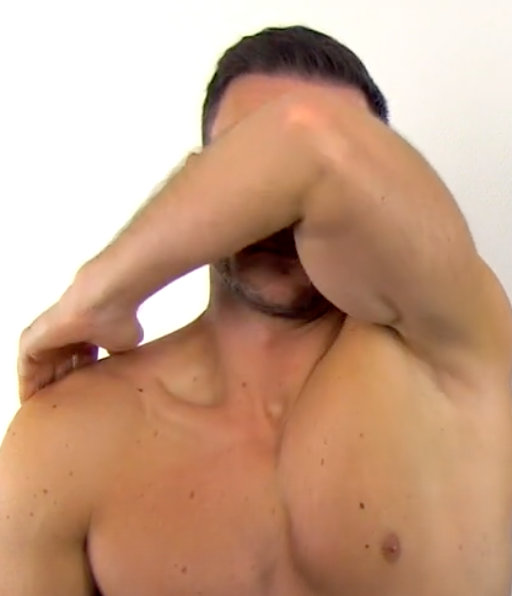

Impingement Tests
Yokum
(+) if familiar pain is reproduced
for Supraspinatus or secondary impingement
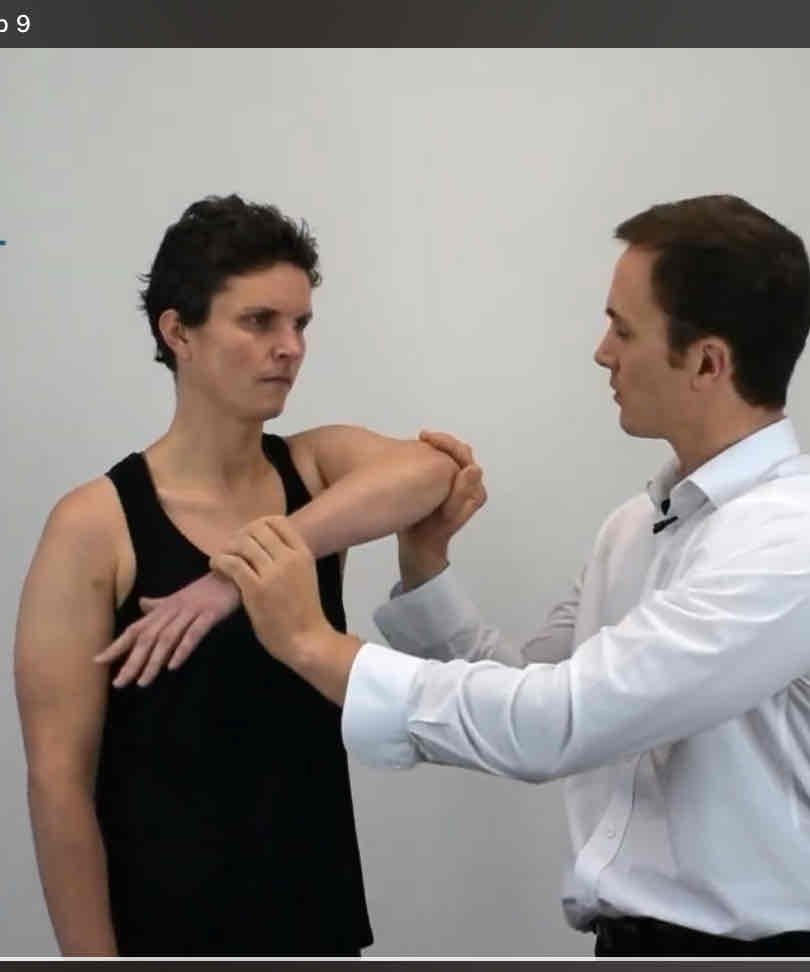
Impingement Tests
same with HK test but add horizontal adduct arm to body 10-20° before doing IR
Coracoid Impingement Sign
(+) if familiar pain is reproduced
for Supraspinatus or secondary impingement
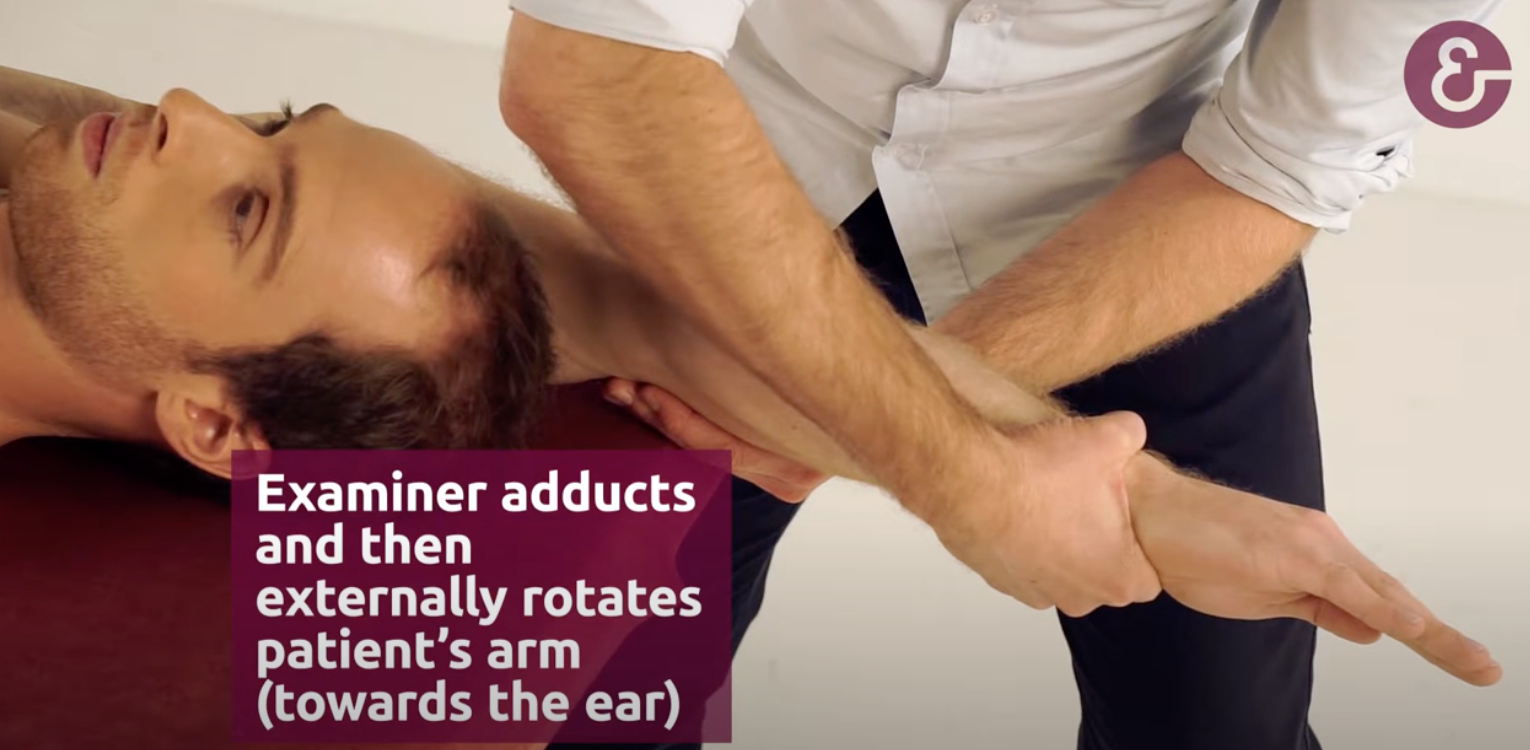
Impingement Tests
Abduct → ER → ADDUCT → IR
Supine Impingement Test
If IR causes pain = impingement & rotator cuff pathology
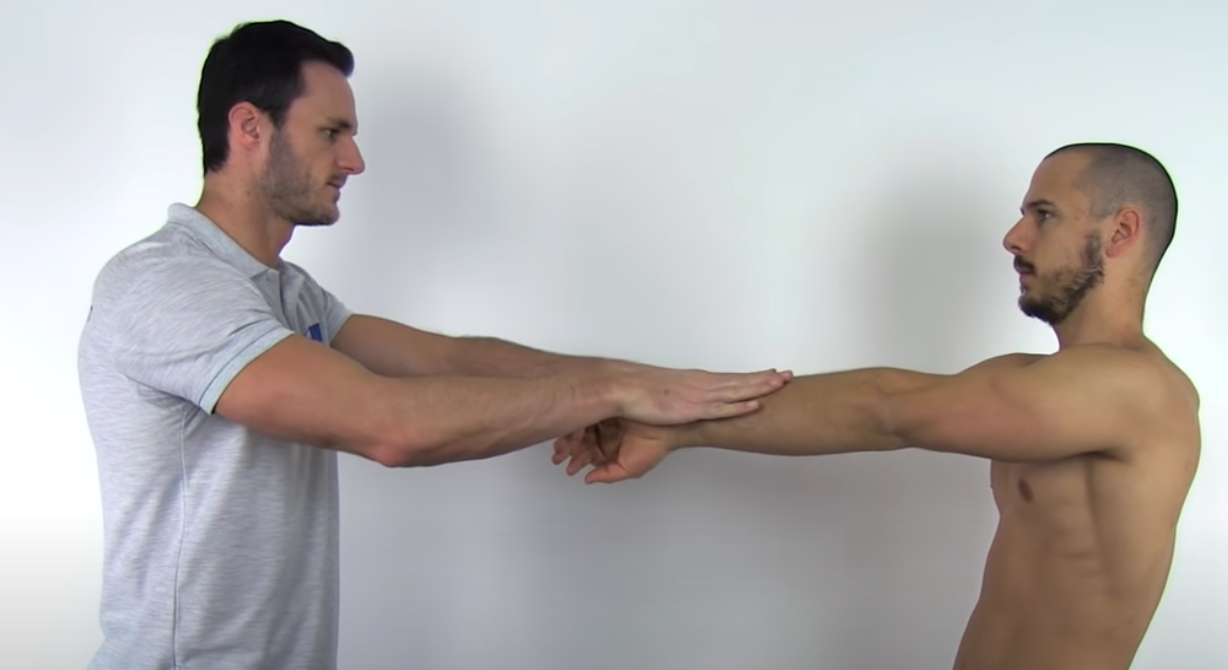

Labral Tear Tests
Position 1: flex and pronate + resistance forearm
Position 2 : flex and supinate + resistance forearm
Active Compression Test of O'Brien
(+) pain or clicking in 1st part of test and decreased in 2nd part = labral abnormality ( SLAP Type 2 / Superior labral lesions)
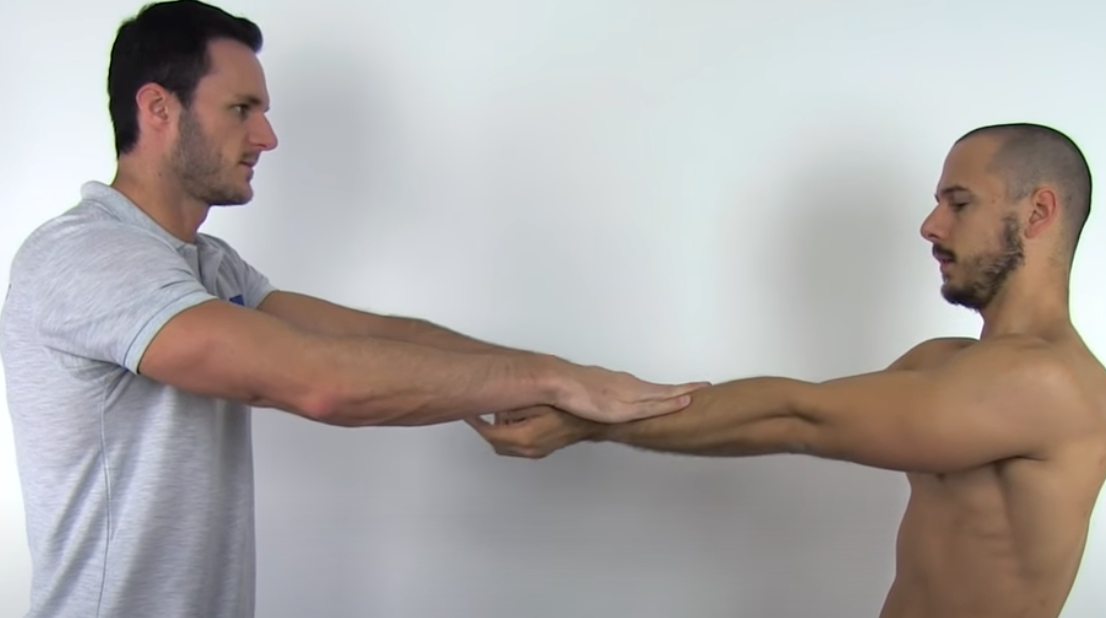

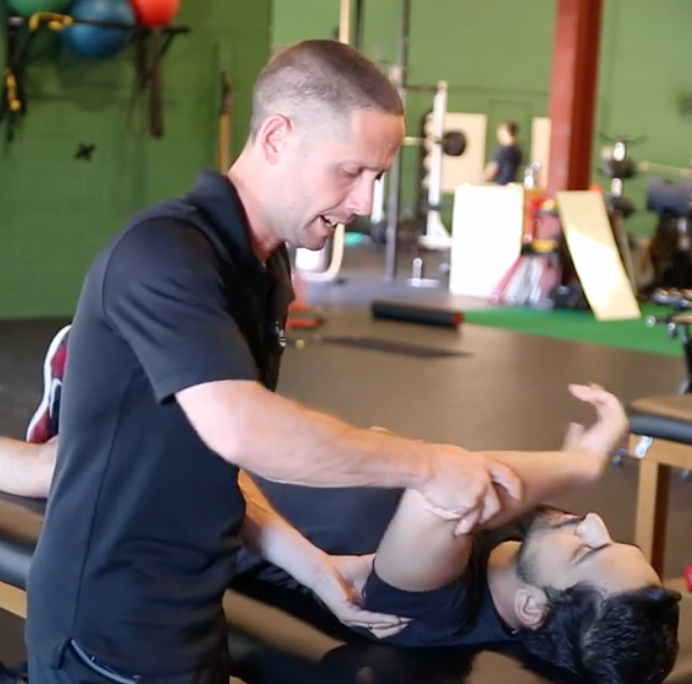
Labral Tear Tests
ikutin arm
Clunk Test
(+) clunk or grinding sound = labrum tear
apprehension = anterior instability
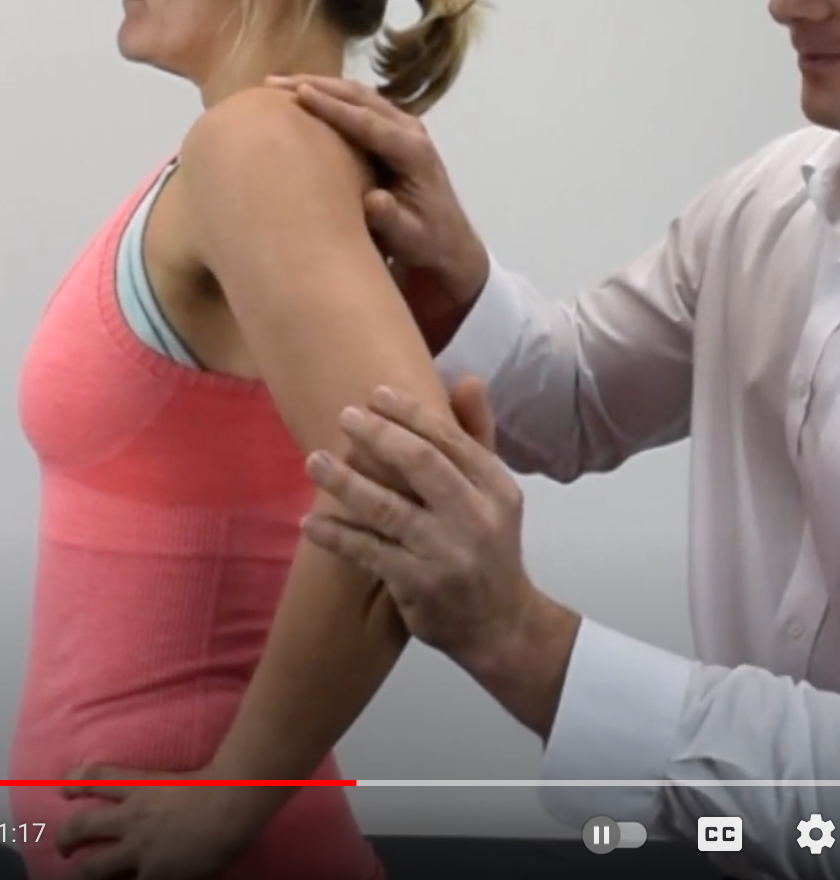
Labral Tear Tests
put anterior/superior force on elbow
Anterior Slide Test
(+) pop or crack / pain in joint line (anterosuperior pain) = SLAP lesion / labrum torn
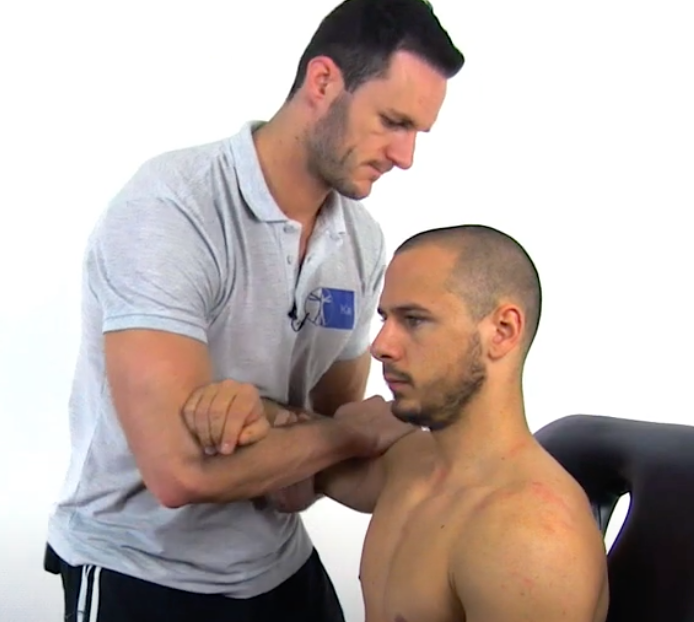

Labral Tear Tests
push glenoid through your body and apply downward/posterior force
Kim Test (Biceps Load Test I)
(+) sudden posterior shoulder pain and click = posteroinferior labral lesion
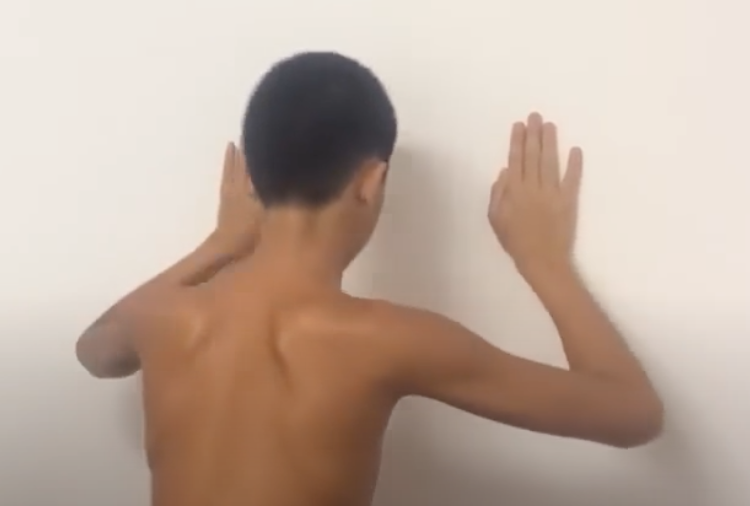

Scapular Dyskinesia Test
Wall push-up for 15-20 times
Wall-Floor Push Up
(+) weakness of scapular muscles or winging in 5-10 push ups

Labral lesion test
Porcellini Test
(+) when pain reduced with or without a change in strength with the second part of the test
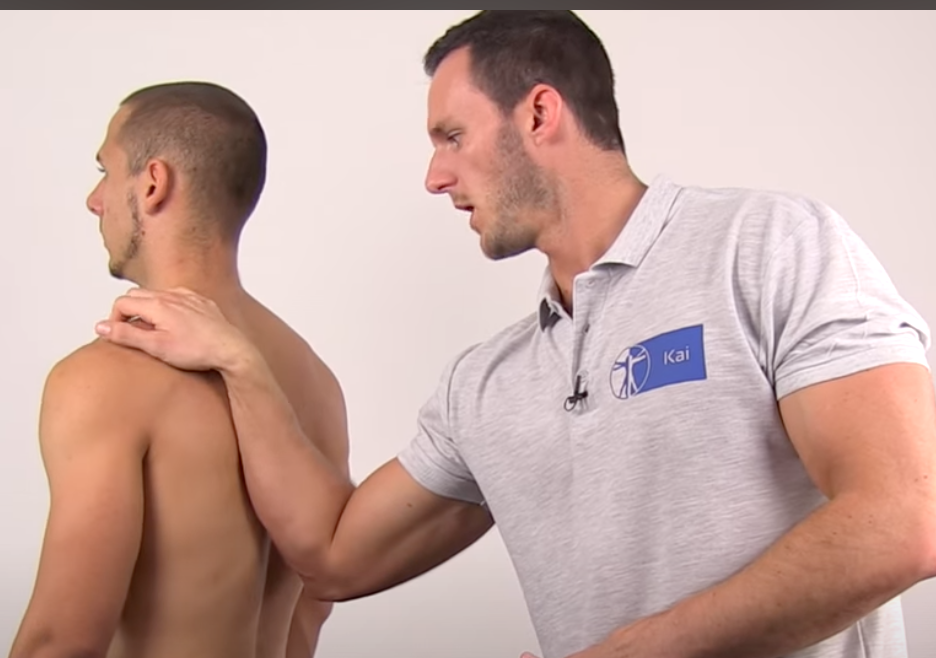
Scapular Dyskinesia Test
Scapular Retraction Test
(+) scapular retraction decreases pain when relocated ( dec pain during empty can) = weak scapular stabilizers
In supine, SICK scapula = scapula is repositioned during forward flexion
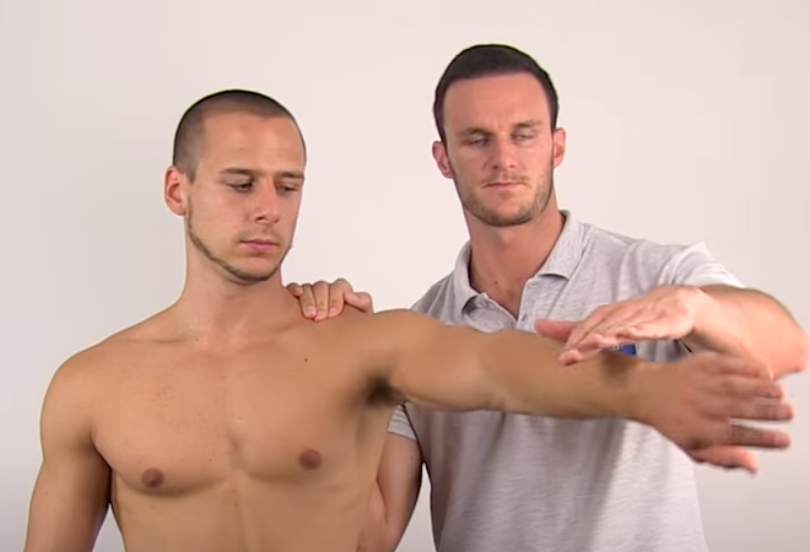

Scapular Dyskinesia Test
Scapular Load Test
(+) if abnormal winging happens
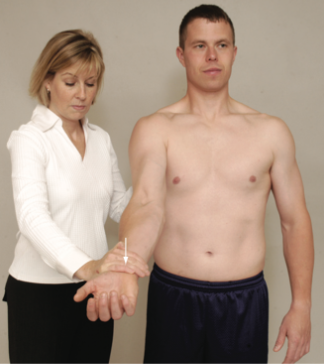
Biceps Test
Speed test
(+) tenderness in the bicipital groove with the arm supinated =of bicipital paratenonitis or tendinosis.
(+) pain, it is positive for SLAP (type II) lesion.
(+) weakness is found on resisted supination, a severe 2nd or 3rd degree (rupture) strain of the distal biceps
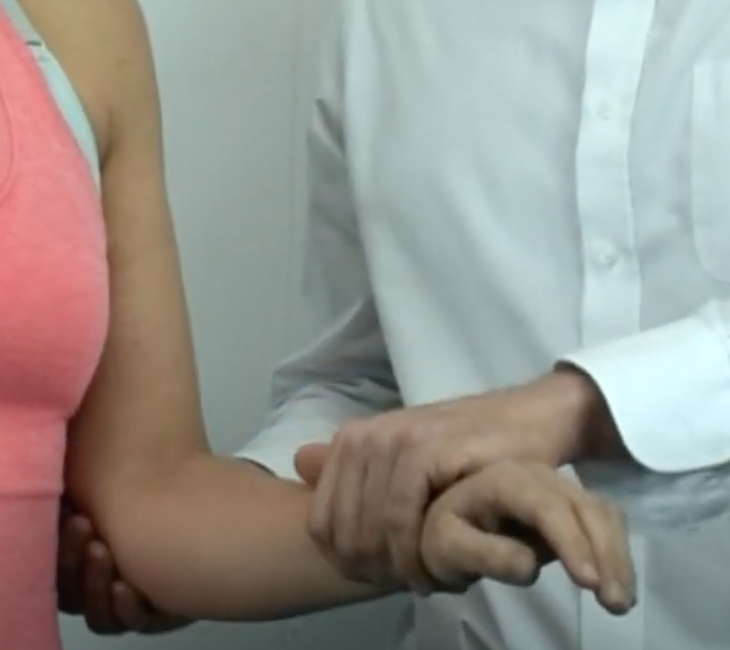

Biceps Test
patient supinates against resistance
Yergason’s Test
(+) when biceps tendon in groove is palpated a “pop out” of the groove if the transverse humeral ligament is torn.
(+) Tenderness in the bicipital groove alone without the dislocation may indicate bicipital paratenonitis/tendinosis.
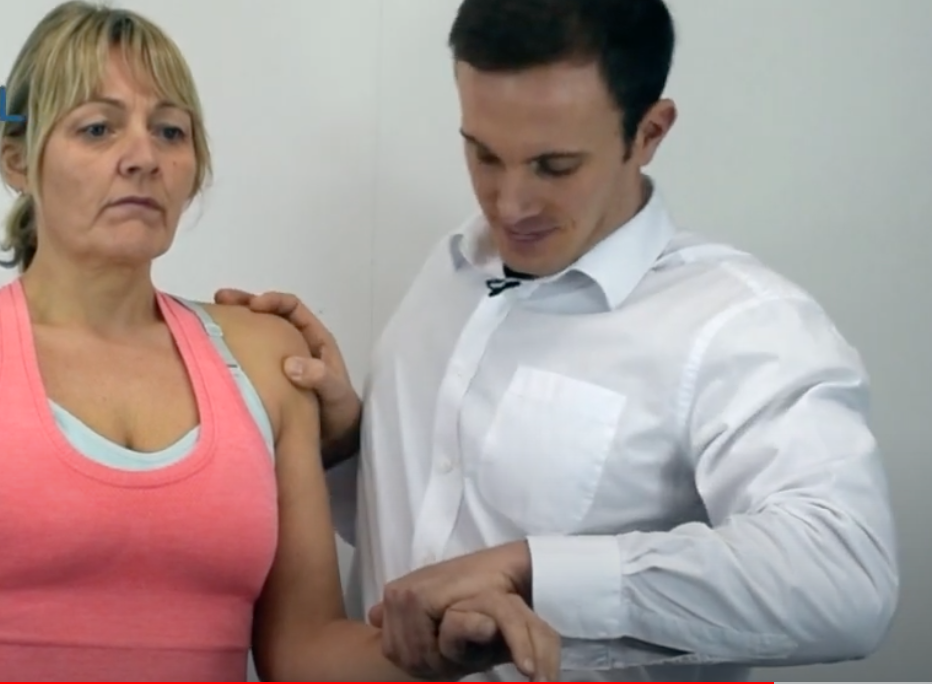
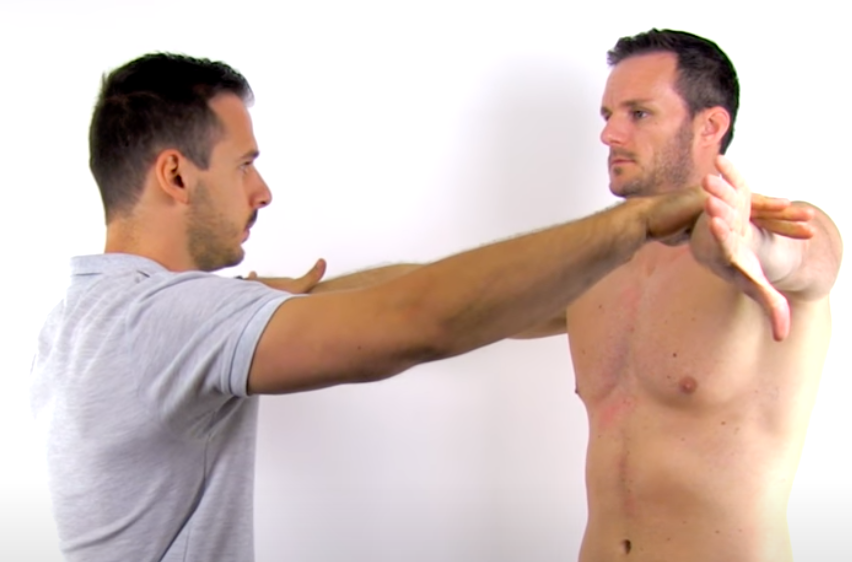
Supraspinatus Test
Empty Can
(+) weakness or pain
A positive test result indicates a supraspinatus tendon tear or muscle, or neuropathy of the suprascapular nerve.
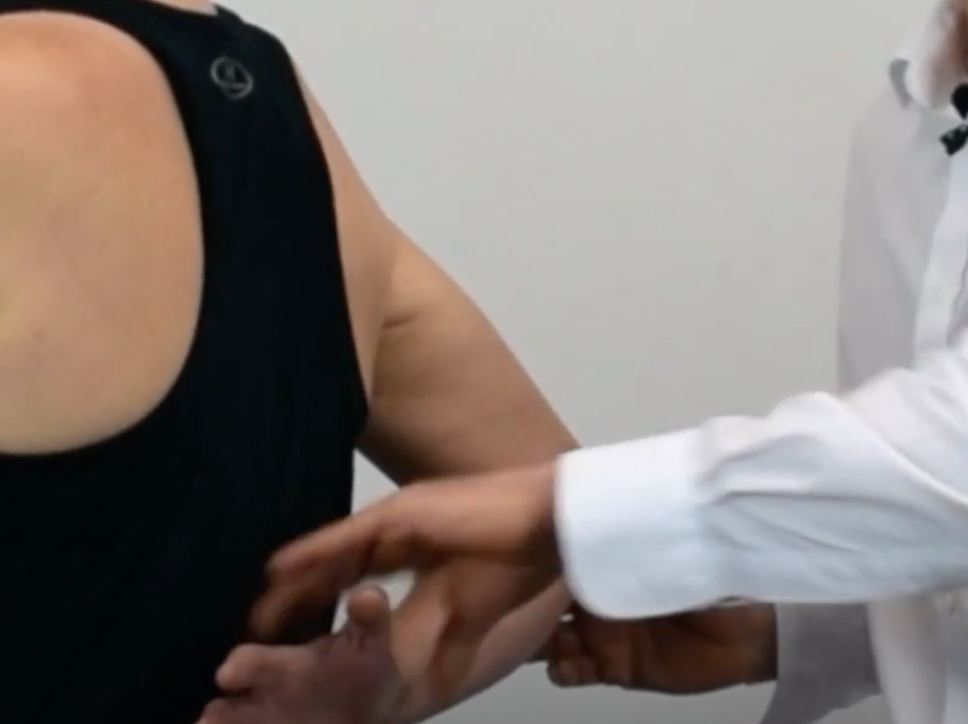
Subscapularis Test
External Rotation Lag Sign
(+) supraspinatus and infraspinatus are torn, the arm will medially rotate and spring back anteriorly indicating a positive test
(+) arm falls or drops into medial rotation, the test is considered positive for tears to infraspinatus, supraspinatus and subscapularis
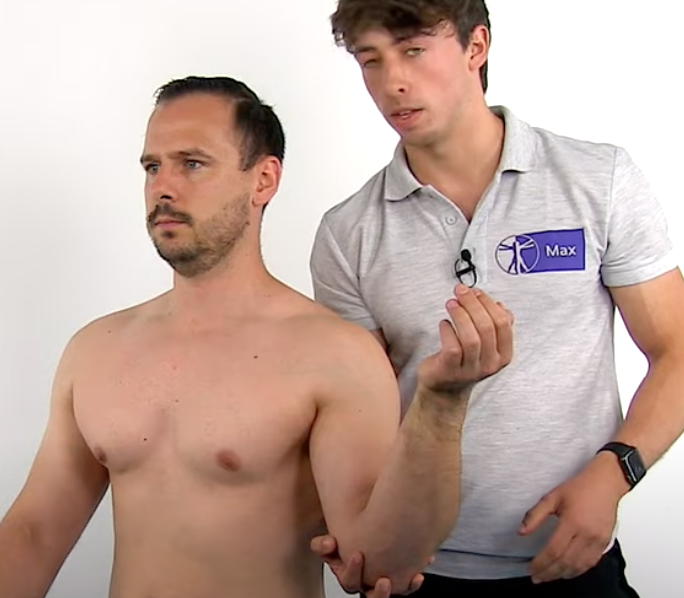

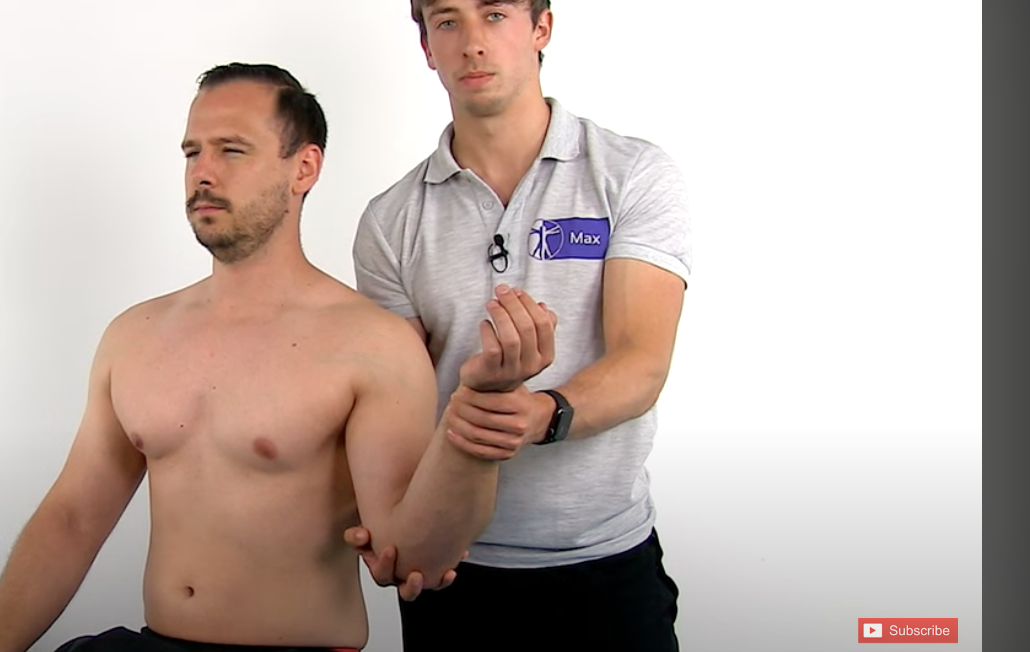
Subscapularis Test
Lift Off Sign
(1)Abnormal motion in the scapula during the test may indicate scapular instability.
(2) With a torn subscapularis tendon, passive and active lateral rotation increases
Subscapularis Test
Spring Back Test
(+) hand moves toward the back, subscapularis cannot hold the position due to weakness or pain
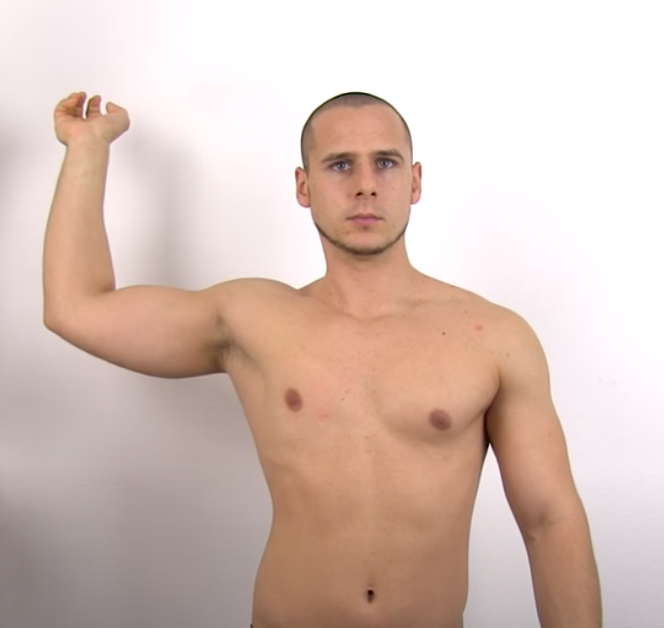

Infraspinatus Test
Lateral Rotation Lag Sign
(+) cannot hold the position and the hand springs back anteriorly toward midline = infraspinatus and teres minor weakness or pain (Drop Sign)
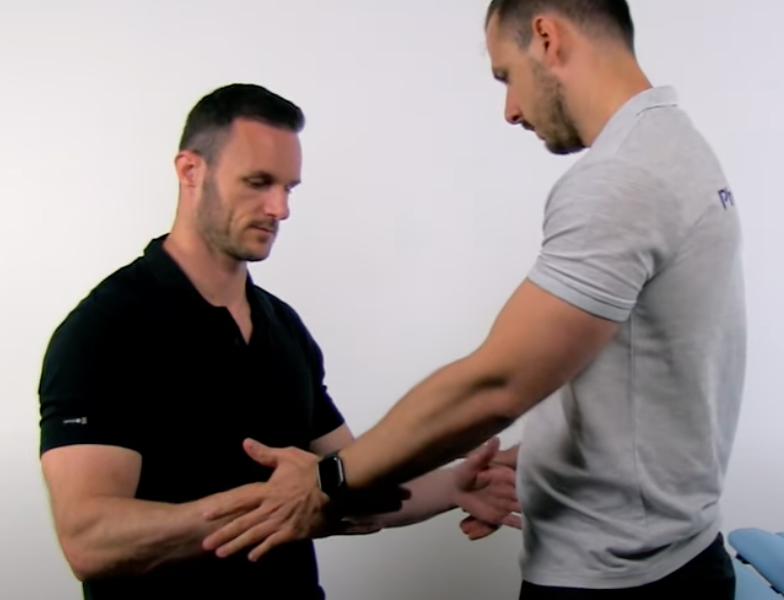

Infraspinatus Test
Infraspinatus Test
(+) Pain or the inability to resist medial rotation indicates infraspinatus strain.

Teres Minor Test
Horn Blower Sign
(+) unable to laterally rotate the arm = tear of teres minor
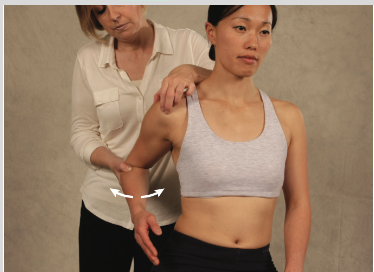
General Rotator Cuff Test
palpate rotator cuff tendons while moving elbow in IR/ER
Rent Test
(+) presence of a depression of one finger width or a more prominent greater tuberosity (relative to the other side) = a rotator cuff tear.
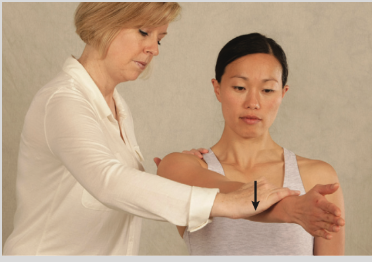
General Rotator Cuff Test
Whipple Test
(+) partial rotator cuff tears and/or superior labrum tears if the patient cannot resist.
Trapezius Test
Read Book
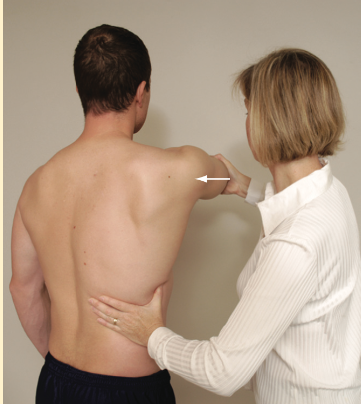
SA Test
Punch Out test
(+) if scapular winging is eliminated = posterior instability due to serratus anterior weakness.
(+) medial border scapula winging or difficulty in abducting or forward flexion >90 = SA weakness or paralyzed
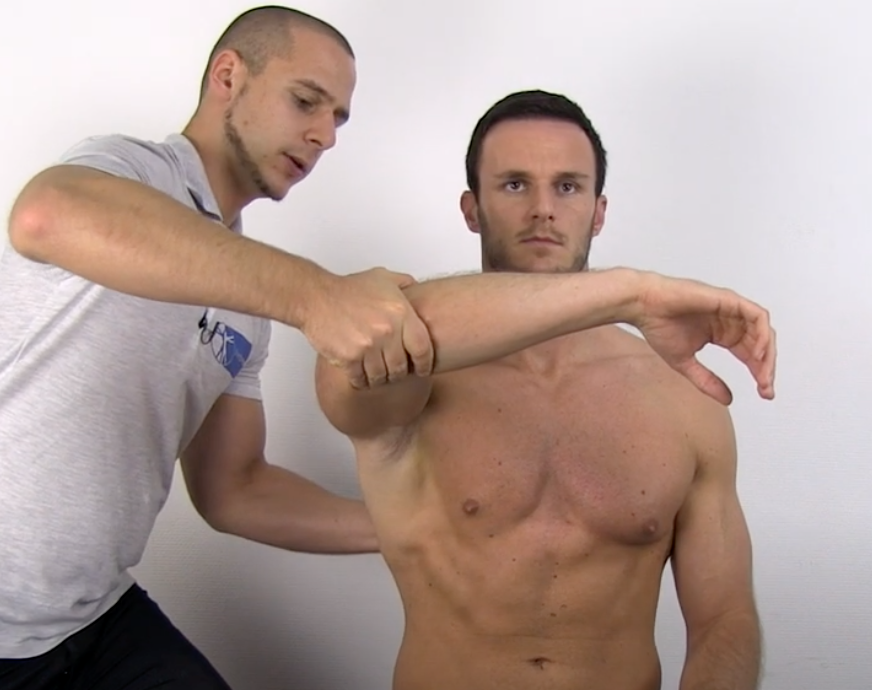

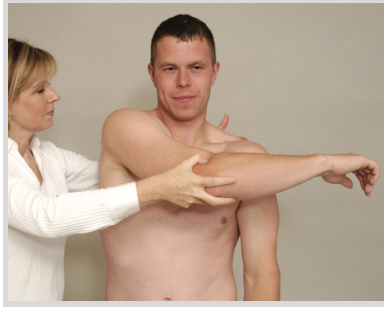
AC JOINT TEST
flex 90° and horizontally adducts to opposite shoulder
Horizontal Adduction
(+) pain in AC or SC
(specific joint pain = + for that joint)
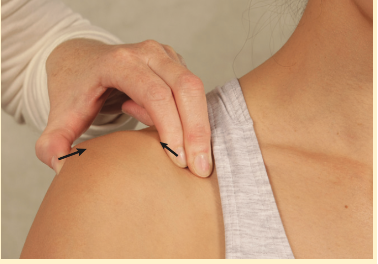
AC JOINT TEST
Squeeze AC joint
Paxinos Sign
(+) pain in AC joint
Ligament Pathology
TESTS FOR NEUROLOGICAL FUNCTION
(+) Pain in the form of tingling or a stretch or ache in the cubital fossa indicates stretching of the dura mater in the cervical spine.
for cervical radiculopathy
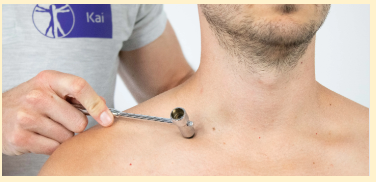
TESTS FOR NEUROLOGICAL FUNCTION
It is performed by lightly tapping (percussing) over the nerve to elicit a sensation of tingling in the distribution of the nerve
Tinel Sign
(+) Tingling sensation in one or more of the nerve roots.
Area of the brachial plexus above the clavicle in the area of the scalene triangle is tapped

Tests for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
The patient stands and abducts the arms to 90°, laterally rotates the shoulder, and flexes the elbows to 90° so that the elbows are slightly behind the frontal plane. The patient then opens and closes the hands slowly for 3 minutes
Roos Test
(+) unable to keep the arms in the starting position for 3 minutes or suffers ischemic pain, heaviness or profound weakness of the arm, or numbness and tingling of the hand during the 3 minutes
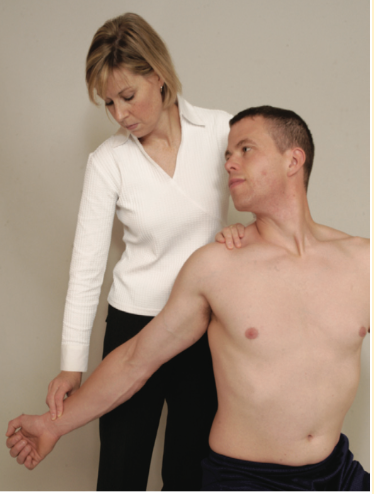
Tests for Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
The examiner locates the radial pulse. The patient’s head is rotated to face the test shoulder. The patient then extends the head while the examiner laterally rotates and extends the patient’s shoulder. Instruct the patient to take a deep breath and hold it.
Adson Maneuver
Positive Sign: Disappearance of the pulse
FIGHTINGGGGGG
😄