Tissues- Chapter 2.3
major types of tissue- epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
functions of epithelial tissue- protection, secretion, absorption, filtration, excretion, senses
Structure:
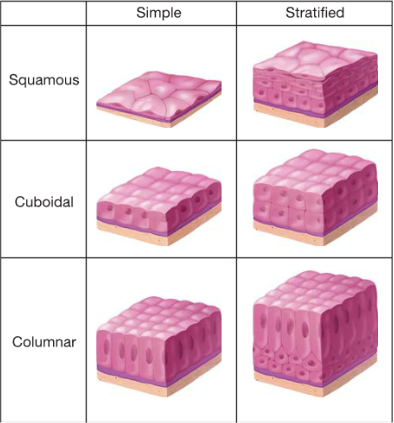
simple- one layer
squamous- flat cells
stratified- multiple layers
cuboidal- cube shaped
columnar- column shaped
simple squamous shape- single layer of flat cells
simple squamous function- diffusion and filtration
simple squamous location- found in air sac of the lungs
simple cuboidal shape- single layer of cube shaped cells
simple cuboidal function- secretion and absorption
simple cubiodal location- kidney tubules, surface of ovaries
simple columnar shape- single layer of long cells, have goblet cells and microvilli
simple columnar function- secretion and absorption
simple columnar location- digestive tract and uterus goblet cells
stratified squamous shape- several layers, flat
stratified squamous function- protection
stratified squamous location- lines body cavities; skin and mouth
goblet cells- secrete %%mucus%%
microvilli- projections that %%increase the cell's surface area%%
Pseudostratified Columnar:
pseudostratified columnar shape- single layer with nuclei at various levels, can have g%%oblet cells and cilia%%
pseudostratified columnar function- %%secretion and cilia-aided movement%%
pseudostratified columnar location- linings of respiratory passages, tubes of reproductive system
Transitional Epithelium:
transitional epithelium shape- thick, layered cuboidal cells
transitional epithelium function- stretchable tissue, forms barrier to block diffusion transitional epithelium location- urinary bladder
%%gland%%ular epithelium- cells that are specialized to produce and secrete substances, makes up the %%body's glands%%
Connective Tissue:
connective tissue - most abundant tissue in your body, binds structures together
connective tissue function- provides support, protection, framework, fills space, stores fat, produces blood cells, fights infection
connective tissue composed of- scattered cells within a matrix, a ground substance and fibers
collagen and elastin- connective tissue
common types of connective tissue cells- %%mast cells, macrophages, fibroblasts%%
Types of Connective Tissue:
collagenous fibers- strong, flexible, %%not very elastic%%, found in bones, ligaments
elastic fibers- %%not as strong,%% very elastic, found in ears, vocal
areolar tissue (%%loose%% connective tissue)- binds skin to underlying organs, forms thin membranes throughout body
adipose tissue (%%fat%%)- protective cushion, insulation to preserve body heat, stores energy
fibrous connective tissue- thick collagenous fibers and fine network of elastic fibers- %%few cells, poor blood supply%%, thus slow healing
Important Tissue:
bone tissue- %%osseus tissue%%, rigid due to mineral salts
%%blood%% tissue- %%circulates%% throughout the body
muscle tissue- skeletal, cardiac, smooth
skeletal tissue- striated and %%voluntary%%
smooth tissue- hollow organs, %%involuntary%%
%%cardiac%% tissue- wall of the %%heart%%
Cartilage:
cartilage- all cartilage cells are called %%chondrocytes%%
hyaline cartilage- covers %%ends of joints%%, padding
elastic cartilage- external ear, larynx
fibrocartilage- %%tough, shock absorbing%%, located between vertebrae
Nerve:
nerve tissue- found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
neurons- %%transmit impulses%%
neuroglia- protection and support