COBCSRG QUIZ 2
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
natural step funnel
backcasting, examining the future as we emerge in the funnel
Business Environmental Responsibility:
The Market Approach
Society is willing to pay for pollution reduction as the perceived benefits outweigh the costs
Alternative policies that could address pollution and pollution-related disease would never be considered through market solutions
Markets are incomplete (at best) in their approach to the overall social good
What is good and rational for a collection of individuals is not necessarily what is good and rational for a society.
Business Environmental Responsibility: The Regulatory Approach
unregulated
tort law (civil lawsuits).
A broad consensus emerged in the Philippines in the late 1990's and early 2000's that _ markets are an inadequate approach to environmental challenges.
Before this legislation was enacted, the primary legal avenue open for addressing environmental concerns was _ law
The Clean Air Act of 1999 (RA 8749)
The Clean Water Act of (RA 9275)
The Solid Waste Management Act of 2000 (RA 2000)
The Toxic Substances and Hazardous and Nuclear Wastes Control Act of 1990 (RA 6969)
Much of the most significant environmental legislation in
the Philippines
The Clean Air Act of 1999 (RA _)
The Clean Water of (RA _)
The Solid Waste Management Act (RA _)
The _ (RA 6969)
Business Environmental Responsibility: The Sustainability Approach
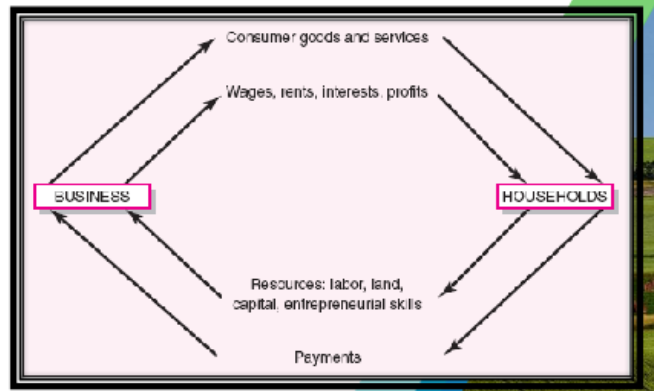
Circular flow model
does not
"_" explains the nature of economic transactions in terms of a flow of resources from businesses to households and back again
Two aspects of the circular flow model are worth noting.
It (does not or does?) differentiate natural resources from the other factors of production
The model treats economic growth as both the solution to all social ills and also as boundless
eco-efficiency
model entire production in the biological process
closed-loop
biomimicry
principles for a sustainable business:
efficient use of natural resources
doing more with less
: waste put back to the process
- waste of one activity, is resource of one another
take-make-waste → cradle to grave → shift from products to service
cradle to grave
shift from products to service
service-based economy
continuum of biomimicry
Business takes resources, makes products out of them, and discards whatever is left over.
Business taking responsibility for its products
"Life-cycle" responsibility
Business should be responsible for incorporating the end results of its products back into the productive cycle
Cradle to grave
Create incentives to redesign products so that they could be recycled efficiently and easily
Traditional economic and managerial models - consumer demand as the demand for products
A _ interprets consumer demand as a demand for services
+ Decisions do not reflect the will of the people but the private will of individuals or corporations who bribe elected or unelected government officials.
+ Government policies serve individual interests rather than the public interest or the interest of the public.
is corruption anti-democratic?
+ Lack of transparency and free flows of information
+ Lack of a free press
+ Lack of government accountability through a system of democratic elections
+ Inability of civil society or NGO's to monitor the government
what r some causes of corruption
XII: NATIONAL ECONOMY AND PATRIMONY
6
The Philippine Constitution on the Social Purpose of Private Property
+ ARTICLE _: NATIONAL ECONOMY AND PATRIMONY
+ Section _. The use of property bears a social function, and all economic agents shall contribute to the common good. Individuals and private groups, including corporations, cooperatives, and similar collective organizations, shall have the right to own, establish, and operate economic enterprises, subject to the duty of the State to promote distributive justice and to intervene when the common good so demands.
II
9
Social Purpose of Private Property
ARTICLE : STATE POLICIES
Section . The State shall promote a just and dynamic social order that will ensure the prosperity and independence of the nation and free the people from poverty through policies that provide adequate social services, promote full employment, a rising standard of living, and an improved quality of life for all.
XIII
1
ARTICLE _, SOCIAL JUSTICE AND HUMAN RIGHTS
Section _. The Congress shall give highest priority to
the enactment of measures that protect and enhance the right of all the people to human dignity, reduce social, economic, and political inequalities, and remove cultural inequities by equitably diffusing wealth and political power for the common good.
To this end, the State shall regulate the acquisition, ownership, use, and disposition of property and its increments.
XIII
3
ARTICLE _ SOCIAL JUSTICE AND HUMAN RIGHTS
Section _. LABOR
+ The State shall afford full protection to labor, local and overseas, organized and unorganized, and promote full employment and equality of employment opportunities for all.
+ It shall guarantee the rights of all workers to self-organization, collective bargaining and negotiations, and peaceful concerted activities, including the right to strike in accordance with law. They shall be entitled to security of tenure, humane conditions of work, and a living wage. They shall also participate in policy and decision-making processes affecting their rights and benefits as may be provided by law.
+ The State shall promote the principle of shared responsibility between workers and employers and the preferential use of voluntary modes in settling disputes, including conciliation, and shall enforce their mutual compliance therewith to foster industrial peace.
+ The State shall regulate the relations between workers and employers, recognizing the right of labor to its just share in the fruits of production and the right of enterprises to reasonable returns to investments, and to expansion and growth.
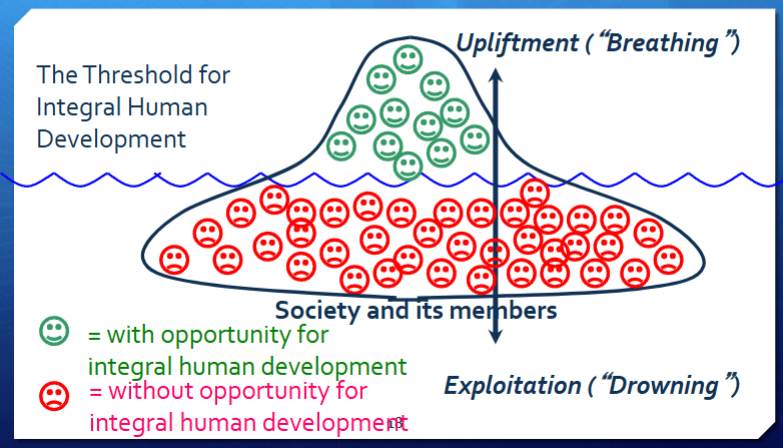
Graphics for the boat of life
yes, they lead to trouble. politics shld be left to politicians
should businesses avoid political action?
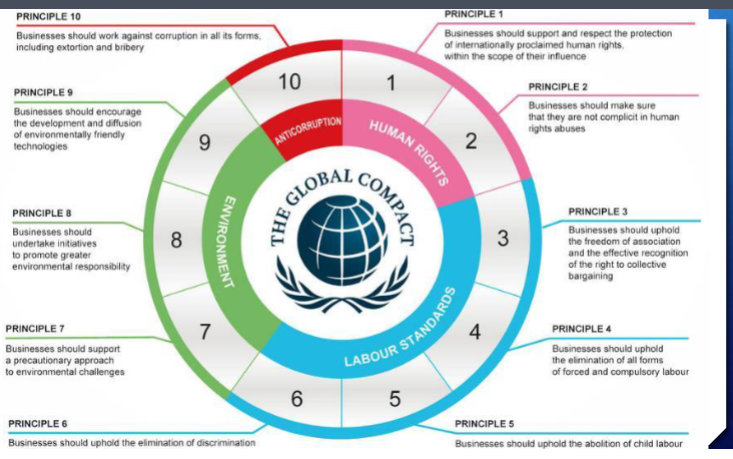
human rights, labor, environment, and anti-corruption + find opportunities
10 global compact principles
how do businesses contribute to the sdgs
employment security
most significant aspect of work from employee’s ethical perspective
due process
the right to be protected against the arbitrary use of authority
Risks
Relative risks
Discussing risks
"_" can be defined as the probability of harm
"_" is determined by comparing the probabilities of harm involved in various activities
OSHSA R.A. 11058
Standards
Department of Labor and Employment
_
Inform employees on all types of hazards in the workplace and having the right to refuse unsafe work, as well as providing facilities and personal protective
Help curb the increasing cases of diseases and injuries in the work environment that confront the country (PSA 2015)
Back pain (32.8%)
Hypertension (11.5%)
Neck and shoulder pain (11.4%)
Corporate Governance
Broadly speaking, _ refers to the processes which enable the top management of a corporation - particularly the board of directors, most commonly elected by the stockholders - to direct, monitor, and control the activities of operating management in order to achieve the strategic vision of a corporation.
the benefit of the shareholders
allegiance to the company.
employees, customers, suppliers, and the communities
In the US, directors are more likely to define their role as running the company for _.
In Germany, directors are more likely to frame their duty in terms of their _
In Japan, directors may give precedence to stakeholders' interests representing _.
Agency Theory
Theoretical Perspectives on Corporate Governance
_ emphasizes the need for boards to control management against the latter's potential for excessive self-interest to the detriment of the stockholders.
Int
Shareholders
Board of Directors
Management
Invest in the company
Oversees management
Makes decisions in the interests of the shareholders
Management
Day to day operations
Identifies and manages corporate risks
Stewardship Theory
recognizes that individuals who are motivated by intrinsic and intangible rewards such as affiliation, achievement, and personal growth tend to align themselves as stewards with goals for an involvement- and trust-oriented organization.
Stakeholder Theory
The portrays the company’s duty to earn the trust of various stakeholders by behaving in a trustworthy manner towards its stakeholders.
Code of Corporate Governance
2 independent directors
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC):
_
Require corporations to submit a Manual on Corporate Governance
Require full disclosure on any aspects of company activities which could affect share price
Require the appointment of at least _ or 20% of Board membership (the lesser)
Recommend the separation of the role of the Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer (CEO)
appointment of compliance
"comply-or-explain"
SEC revisions on code of corporate governance
Require _ officers
Shift to _ approach to compliance with corporate code
Increase in stakeholder-oriented and social responsibility provisions
Code principles on sustainability and social responsibility merges Corporate Governance and Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate culture
_ is the combined belief of members about what is right and wrong in going about its business activities.
An ethical business organization motivates its members to act in the most balanced interest of its various stakeholders.
Amoral Corporation
Legalistic Corporation
Responsive Corporation
Emergent Ethical Corporation
Ethical Corporation
Stage 1: _ - Pursues winning at any cost; views employees merely as economic units of production
Stage 2: _ - Concerned with the letter of the law, not the spirit; adopts legalistic code of conduct
Stage 3: _ - Interested in being a responsible corporate citizen, primarily because it is expedient, not because it is right; beginnings of codes of conduct
Stage 4: _ - Recognizes the existence of a social contract between business and society, and seeks to instill that attitude thought out the corporation
Stage 5: _ - Balances profits and ethics so completely that employees are rewarded for walking away from compromising actions; includes ethical issues in training; has mentors to give moral guidance to new employees
A. Rights of shareholders
B. Equitable treatment of shareholders
C. Role of stakeholders
D. Disclosure and transparency
E. Responsibilities of the board
ASEAN Corporate Governance looks at corporations' practices along the areas of: