useful tips for exam 2 - ch 5 periodic trends
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
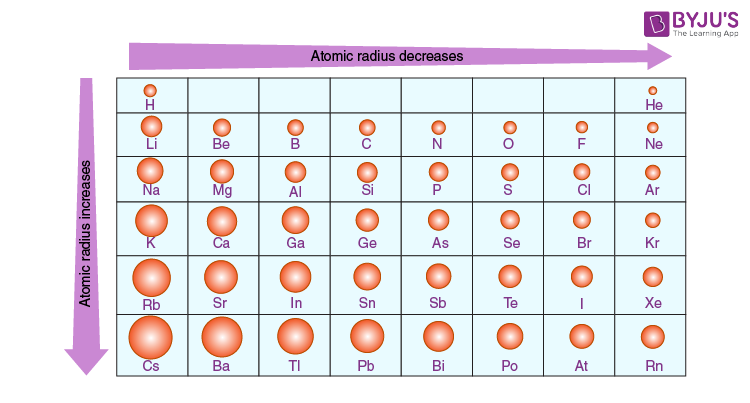
what does the atomic radius trend tell you?
atomic radius increases ↓
atomic radius decreases →
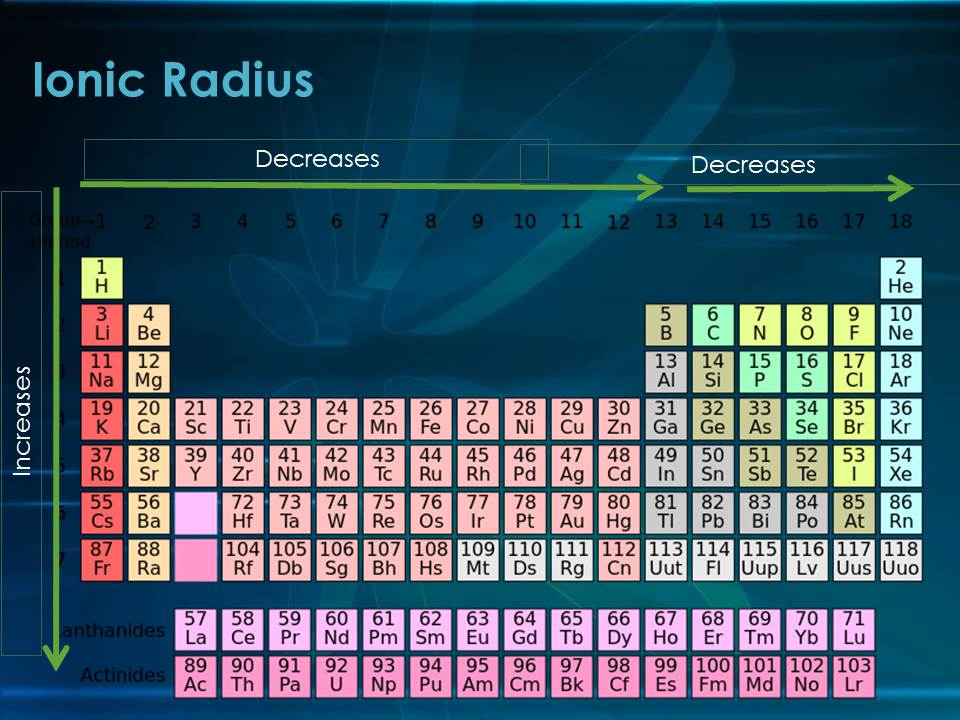
what does the ionic radius trend tell you?
ionic radius increases ↓
ionic radius decreases →
why does the atomic radius of elements → decrease in size?
the electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus by the increase in protons, this causes the atomic radius to decrease in size
why does the atomic radius of elements ↓ increase in size?
the electrons fill new outer shells, meaning they occupy higher energy levels that are farther away from the nucleus. this causes the atomic radius to increase in size
why does a cation have a smaller ionic radius?
the cation loses electrons, making it more positive. this makes the attraction between the protons and electrons greater and pulls the electrons toward the nucleus. so the ionic radius shrinks
why does an anion have a larger ionic radius?
the anion gains electrons, making it more negative. this makes the electrons repel each other, expanding the electron cloud. so the ionic radius increases
why does the ionic radius increase ↓ in size?
there are more electrons filling outer shells, making the electrons repel one another and increase the size of cloud around the atom. this causes the ionic radius to increase
why does the ionic radius decrease → in size?
the electrons are being pulled closer to the nucleus by protons, which shrinks the electron cloud around the atom. this causes the ionic radius to decrease
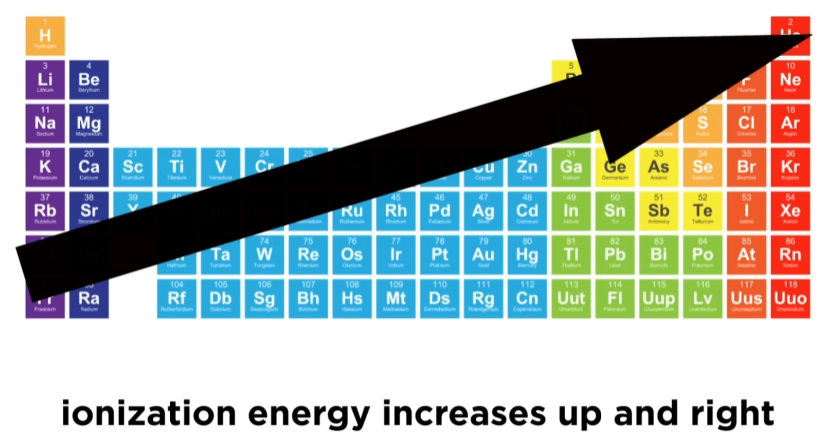
what does the ionization energy trend tell you?
ionization energy increases →
ionization energy decreases ↓
what is ionization energy?
the minimum amount of energy required to remove the most loosely bound electron from its shell
why does ionization energy increase →?
elements → the periodic table have a smaller atomic radius. this means that the electrons are closer to the nucleus, meaning that it is harder to remove the tightly bound electron. that is why ionization energy is high and increases from left to right on the periodic table
why does ionization energy decrease ↓?
elements ↓ the periodic table have larger atomic radius. this means that the electrons are farther away from the nucleus, meaning that it is easier to remove the loosely bound electron. that is why ionization energy is low and decreases down the periodic table
what is the way to order species of ions from smallest to largest ionic radius?
cation → neutral → anion
what is electronegativity
the ability of an atom to hold onto electrons tightly
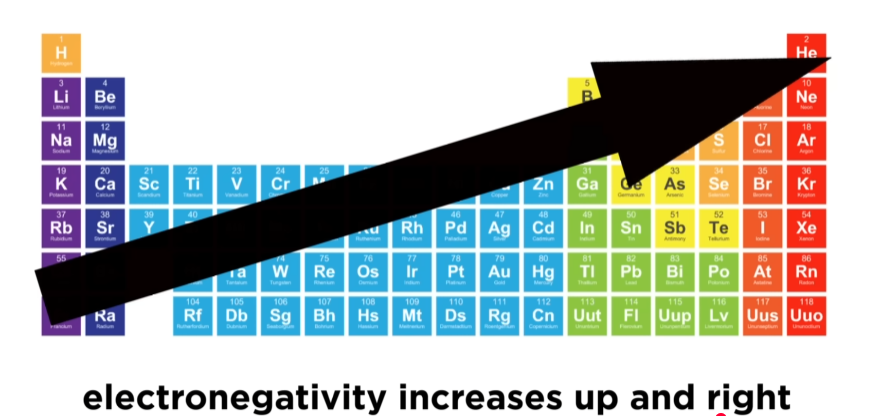
what does the electronegativity trend tell you?
electronegativity increases →
electronegativity decreases ↓
why does electronegativity increase ↑ →?
elements with a smaller atomic radius (little distance between the nucleus and electrons) have more protons per electron. so the nucleus will hold onto electrons more tightly
why does electronegativity decrease ↓ ←?
elements with a larger atomic radius (bigger distance between the nucleus and electrons) have more electrons per proton. so the nucleus will not hold onto electrons very well