Autonomic Nervous System 2
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What kind of innervation is in vascular smooth muscle?
sympathetic maintains blood pressure
there are un-innervated M receptors in endothelium (when stim cause vasodilation)
What receptor distribution is found in the skin and reservoir veins? What does it cause?
alpha 1
innervated by epi and norepi leading to vasoconstriction
What receptor distribution is found in the skeletal muscle? What does it cause?
alpha 1 - innervated by norepi causing vasoconstriction, high levels epi causes vasoconstriction
beta 2 - low level epi causes vasodilation
What receptor distribution is found in the visceral and renal vasculature? What does it cause?
alpha 1 - norepi and high levels epi of epi or dopamine cause vasoconstriction
beta 2 - low levels epi cause vasodilation
dopamine receptors - low levels dopamine cause vasodilation
What components contribute to stroke volume?
preload - how much blood goes into heart
afterload - pressure heart has to push against
contractility - how hard heart pumping
What contributes to cardiac output?
stroke volume and heart rate
What contributes to mean arterial pressure?
cardiac output and peripheral vascular resistance
How does parasympathetic innervation impact the cardiovascular system?
decreased heart rate due to node innervation
decreased cardiac output
How does sympathetic innervation impact the cardiovascular system?
B1 receptors increase contractility and heart rate increases SV and CO
alpha 1 receptors increase peripheral vascular resistance, B2 decreases resistance (generally increases MAP)
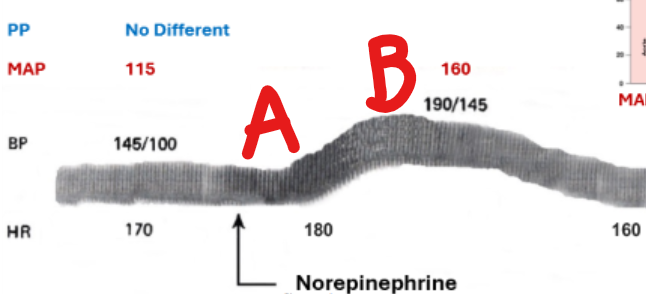
Explain what happens at points A and B
A - HR increases due to B1 receptors
B - vasoconstriction and overall increases pressure
When feeling pulse can you feel an increase in MAP?
not necessarily
when feeling pulse only feeling pulse pressure (difference between systolic and diastolic pressure) MAP can increase while difference between two pressures remain the same
What affects does norepi have on the cardiovascular system?
a1 - increases peripheral vascular resistance
B1 - increases contractilty, HR thus increases SV, CO
increases MAP
Where are baroreceptors found? What do they do?
aortic arch in carotid artery
sense changes in pressure and send impulses to vasomotor complex in medulla
What is the baroreceptor reflex (increased pressure)?
sends impulses to vasomotor complex to decrease sympathetic impuls to arterioles
increases parasympathetic impulses to heart and decreases HR/CO
works in reverse for decreases pressure
How does parasympathetic innervation impact the respiratory system?
Vagus nerve innervates M receptors
bronchoconstriction and mucus secretion
How does sympathetic innervation impact the respiratory system?
B2 receptors stimulates bronchodilation
How does parasympathetic innervation impact the GI system?
facial nerve - stimulates salivary glands
vagus - innervates esophagus, stomach, pancreas, livier, small intestine to relax sphincters, stim GI motility and gastric acid secretion
lumbosacral intumescence - innervates large intestine stimulates GI motility
How does sympathetic innervation impact the GI system?
reduced salivary gland secretion
reduced motility/gastric acid secretion and increased sphincter contraction
increased glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
decreased digestive enzyme from acinar cells and increased insulin from islet cells
increased lipolysis
How does pyridostigmine bromide cause intussusception?
blocks AChesterase so ACh concentration goes up and stimulates NM and NN receptors to increase intestinal motility
goes to intestine first so has highest concentrations in gut and interacts with ACH junction locally to cause intussusception
How does parasympathetic innervation impact the genitourinary system?
erection
relaxes trigone and induces urinary bladder fundus (stimulates urination)
How does sympathetic innervation impact the genitourinary system?
ejaculation
uterine contraction
increases renin secretion (increases blood pressure)
contracts trigone and relaxes fundus to prevent urination
How does parasympathetic innervation impact the eyes?
increased tear formation by lacrimal/meibomian glands/goblet cells/and 3rd eyelid glands
CN3 - contracts ciliary muscles so lens rounder and accommodate near sight, circular muscles contract causing miosis
open anterior chamber angle to increase aqueous humor outflow and decrease intraocular pressure
How does sympathetic innervation impact the eyes?
alpha receptors - contract radial muscles leading to mydriasis (dilation)
beta - increases aqueous humor production and increases intraocular pressure (closes outflow channel), relaxes ciliary muscle so lens flattens and accommodates distant sight
How does sympathetic innervation impact the spleen?
alpha mediated contraction (PCV increases)
beta2 mediated relaxation
How does sympathetic innervation impact the sweat gland secretion?
cholinergic most species
B2 mediated in horses
How does sympathetic innervation impact the piloerector muscles?
alpha mediated contraction (raises hair)