Kin 1132 / LL4 / Respiratory System
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
What structures are within the Upper-Airways?
Nose
Nasal Cavity
Pharynx
What structures are within the Lower-Airways?
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Lungs
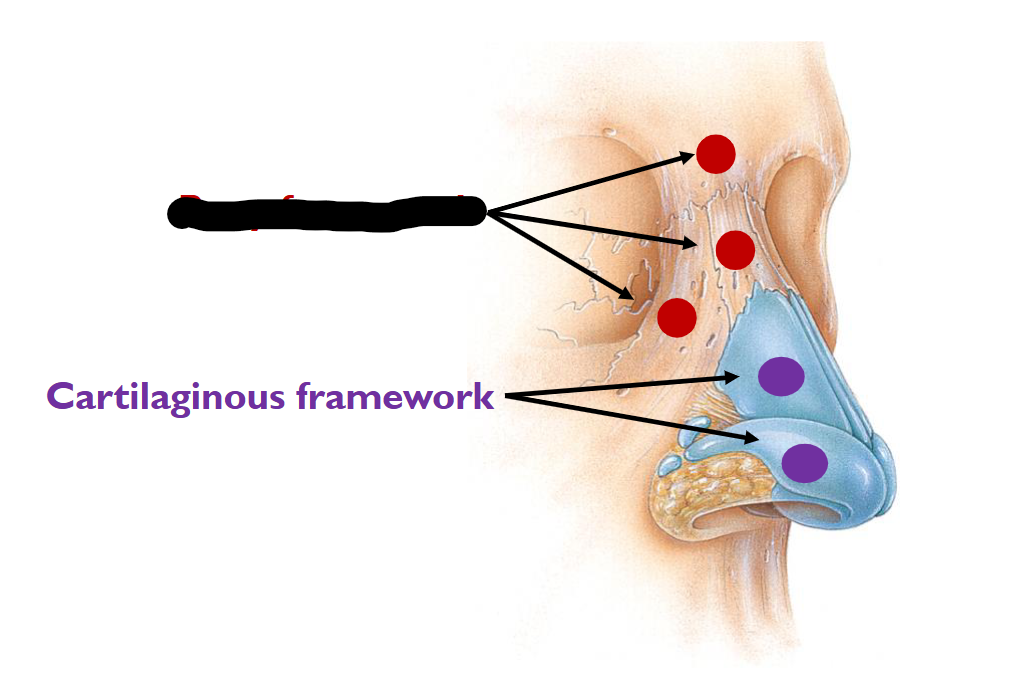
(UPPER-AIRWAY); What is this?
Bony Framework
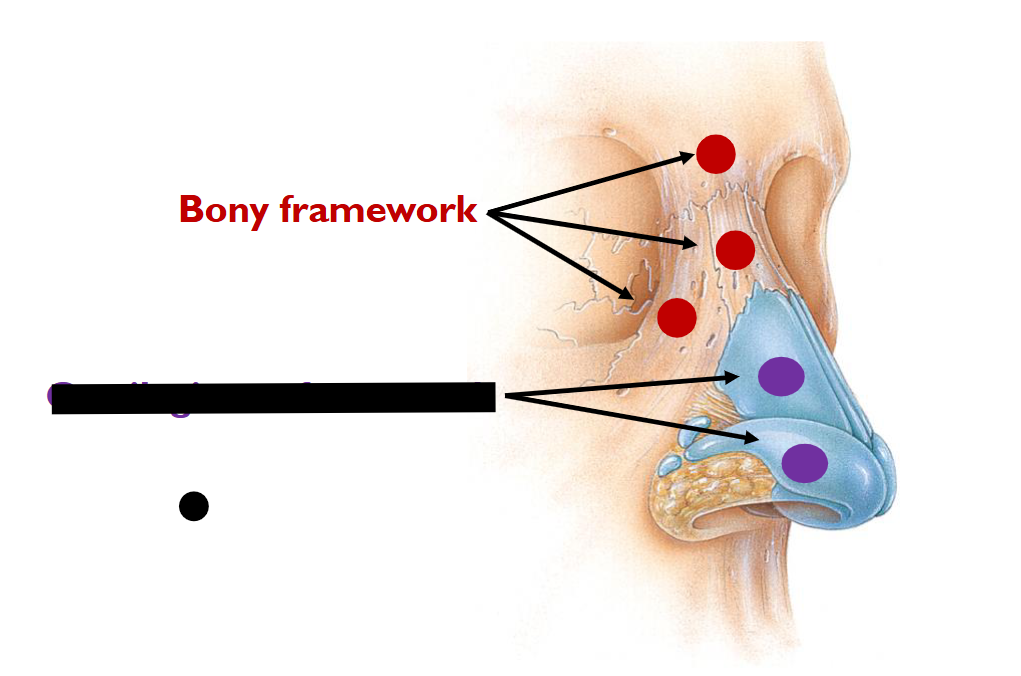
(UPPER-AIRWAY); What is this?
Cartilaginous Framework
How many pairs of the Nasal Conchae is visible from Anterior View?
2-Pairs
What are the functions of the Nasal Conchae / Mucous Membrane
Increases surface area in internal nose
prevents dehydration by trapping water droplets during exhalation
warms the air, blood in the capillaries
MOISTENS THE AIR
Traps dust particles
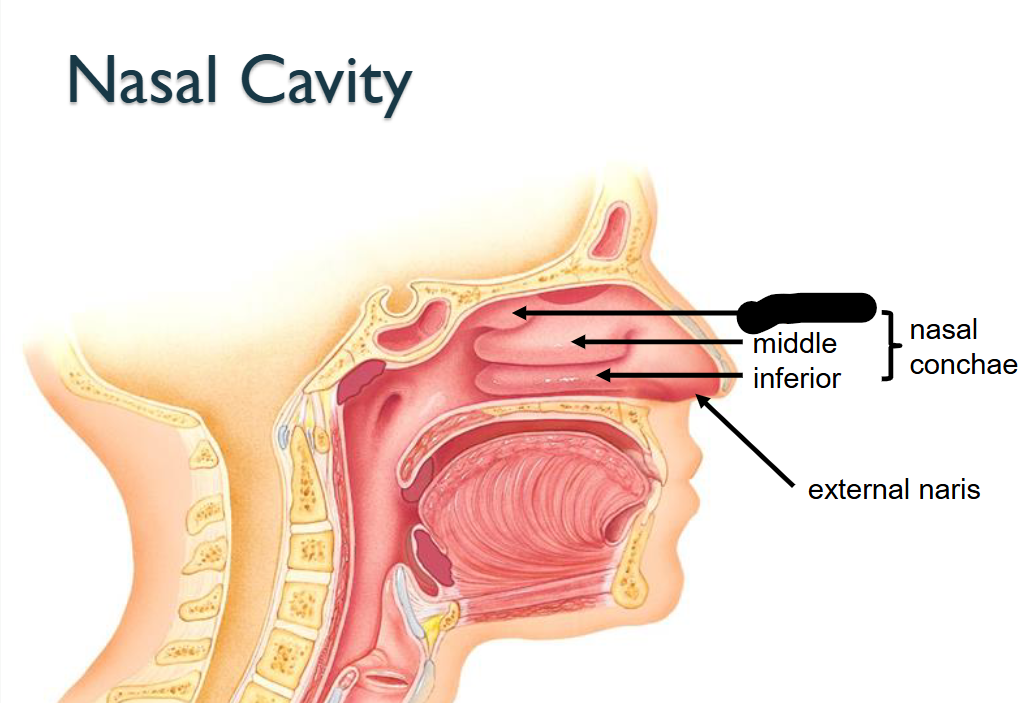
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Inferior Nasal Conchae
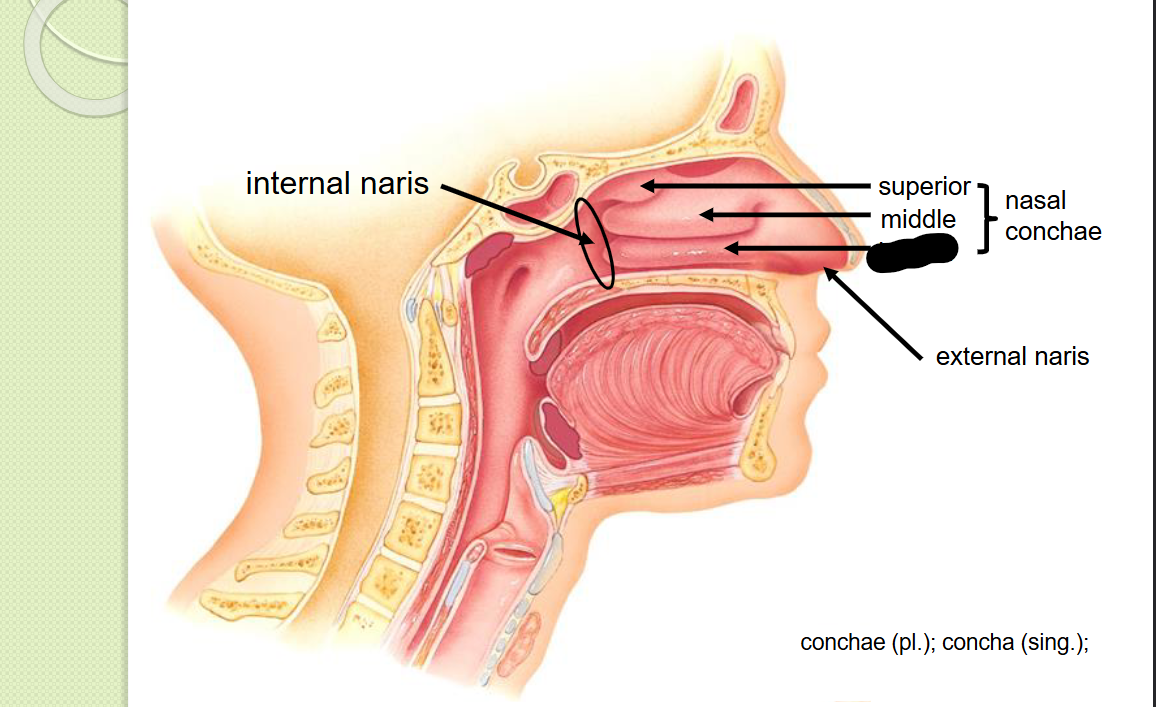
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Superior Nasal Conchae
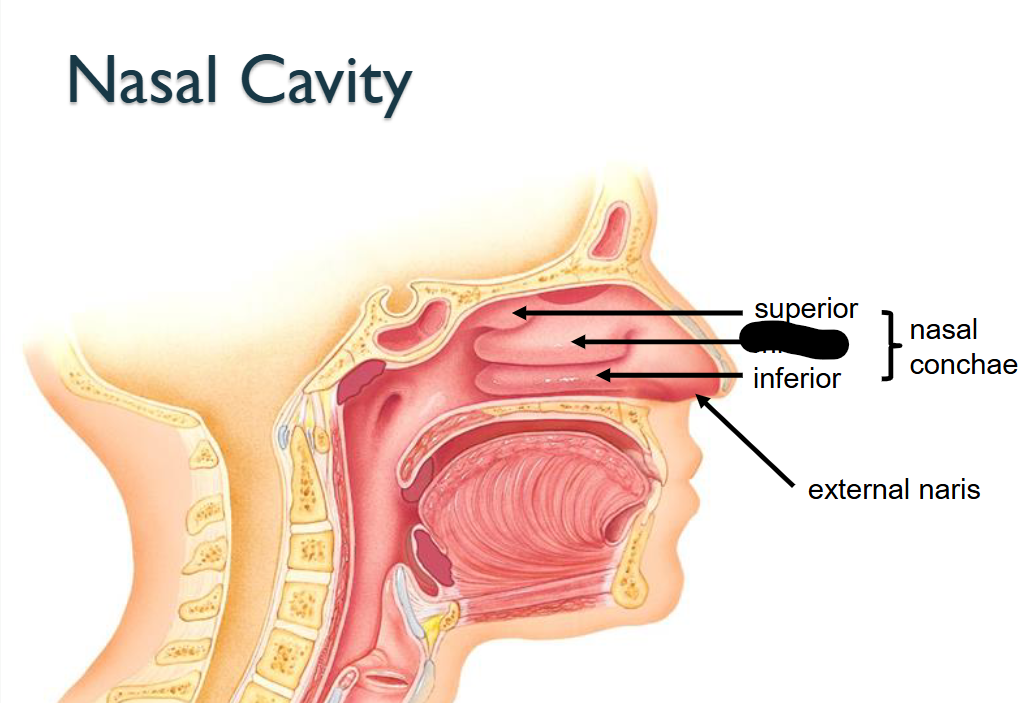
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Middle Nasal Conchae
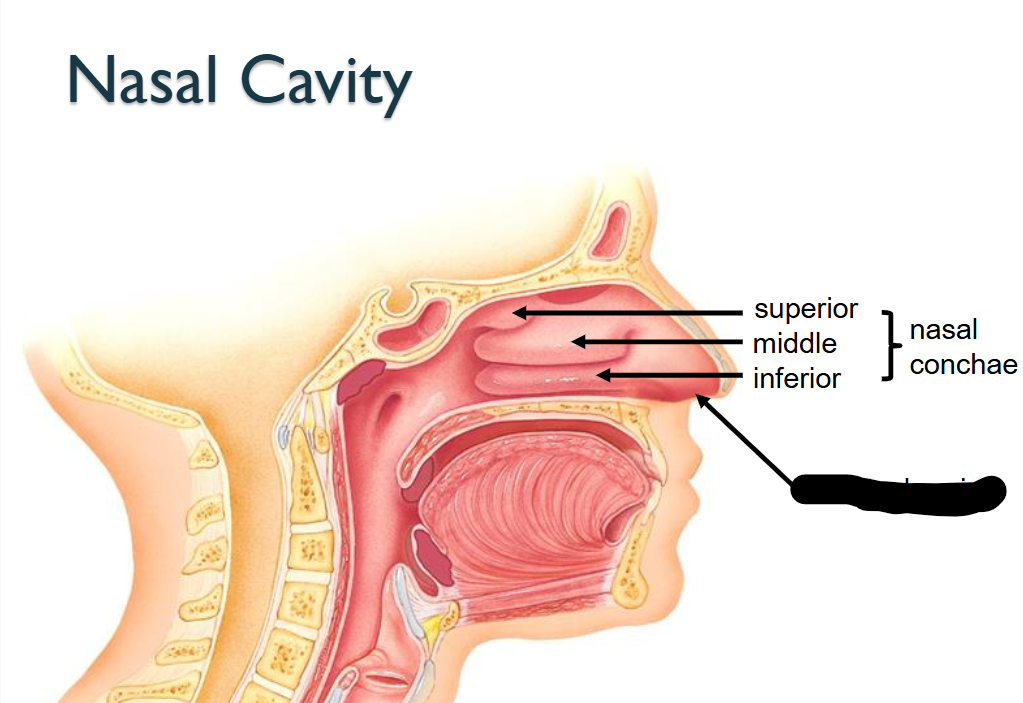
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
External Naris
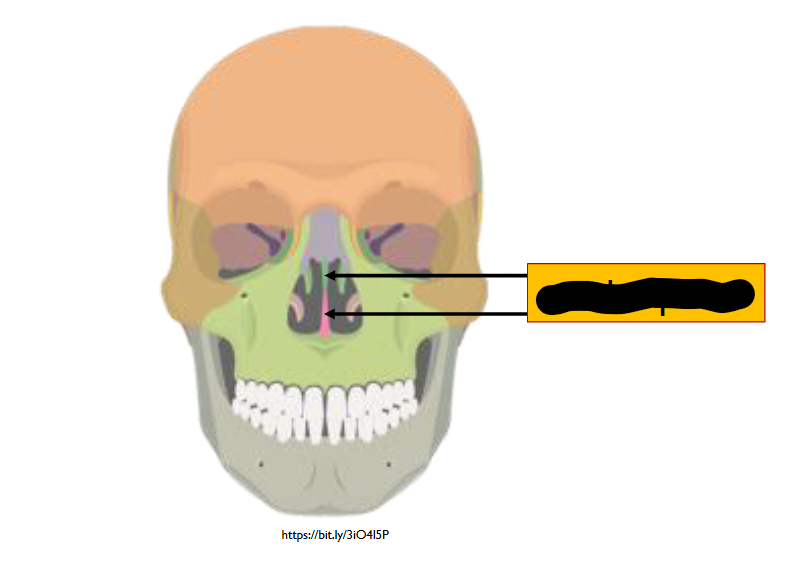
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Nasal Septum
What does the Nasal Septum do?
Vertical structure > divides the nasal cavity into right/left sides
Anterior part includes; primarily hyaline cartilage > REMAINDER formed by Vomer/Perpendicular plate of Ethmoid, Maxillae and Platine Bones
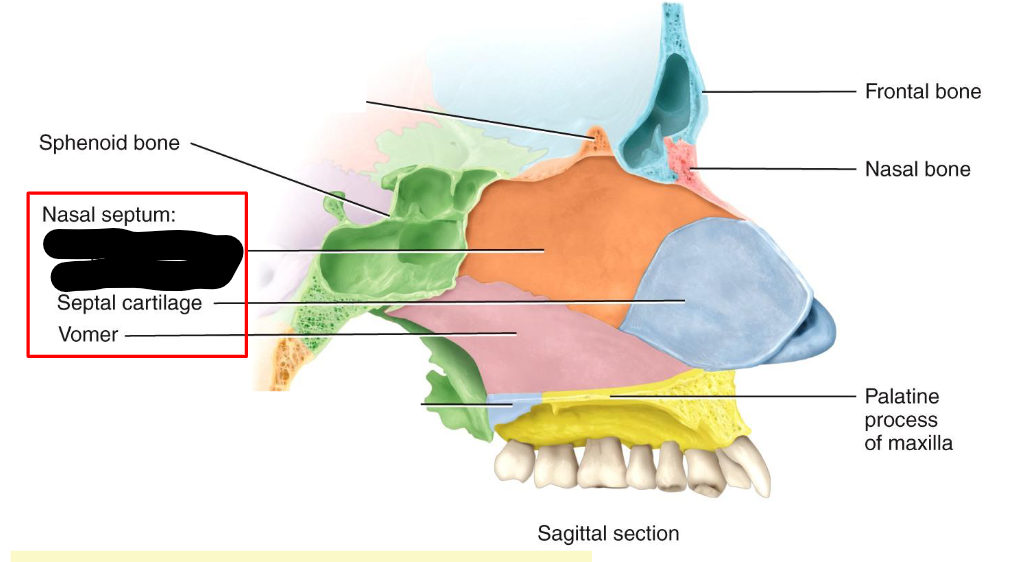
What structure is this within the Nasal Septum?
Perpendicular Plate of ethmoid bone
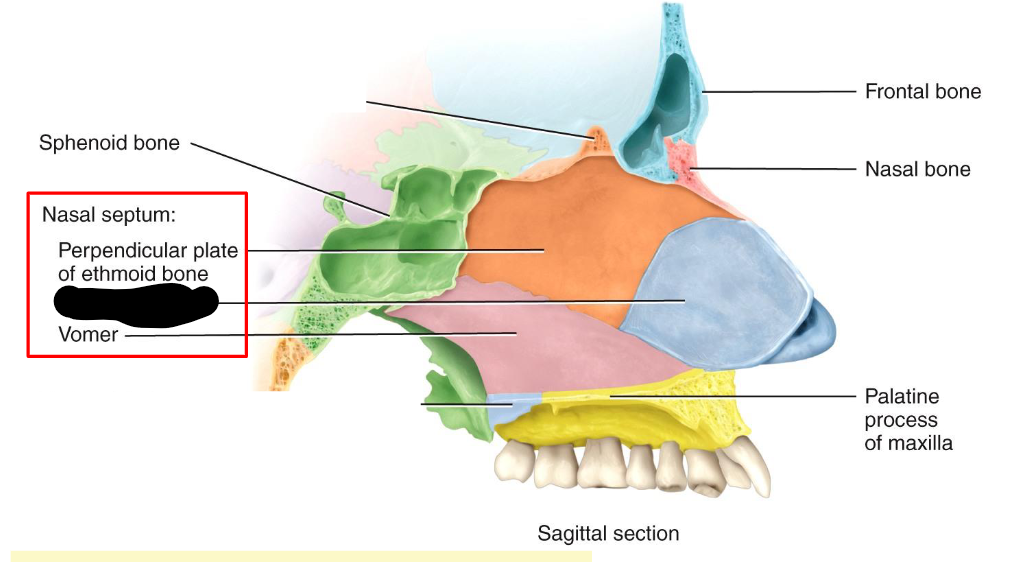
What structure is this within the Nasal Septum
Septal Cartilage
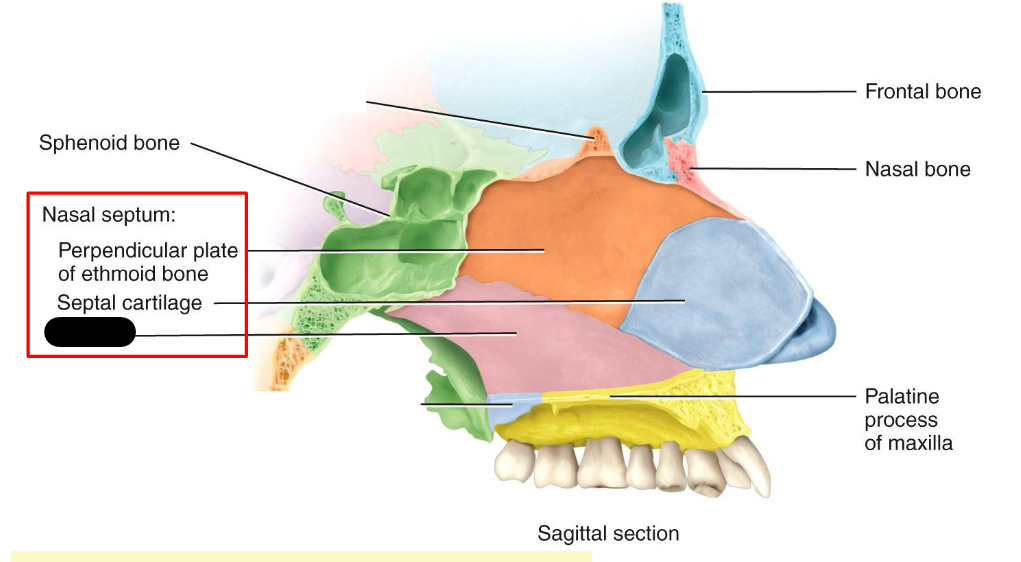
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Vomer
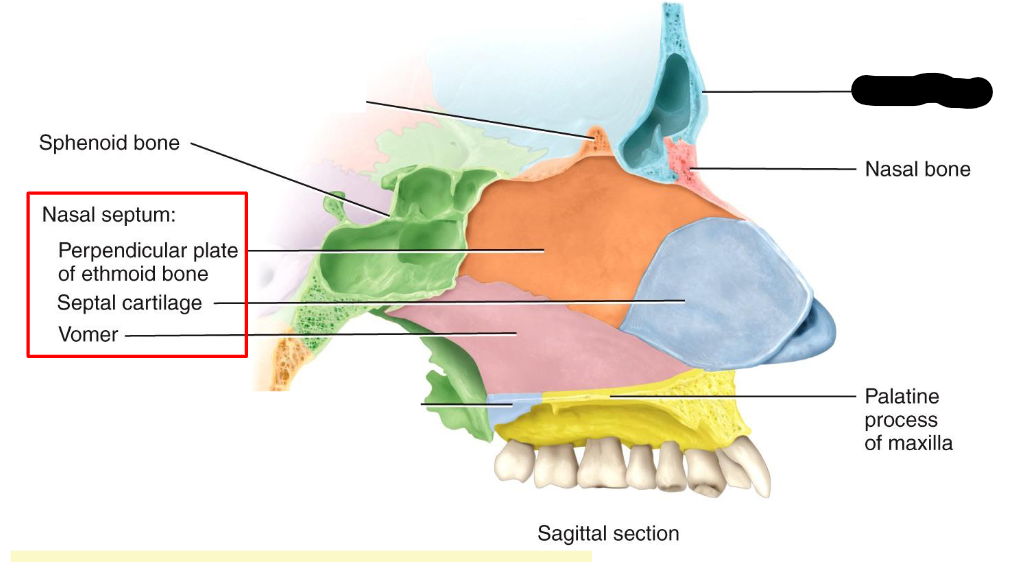
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Frontal Bone
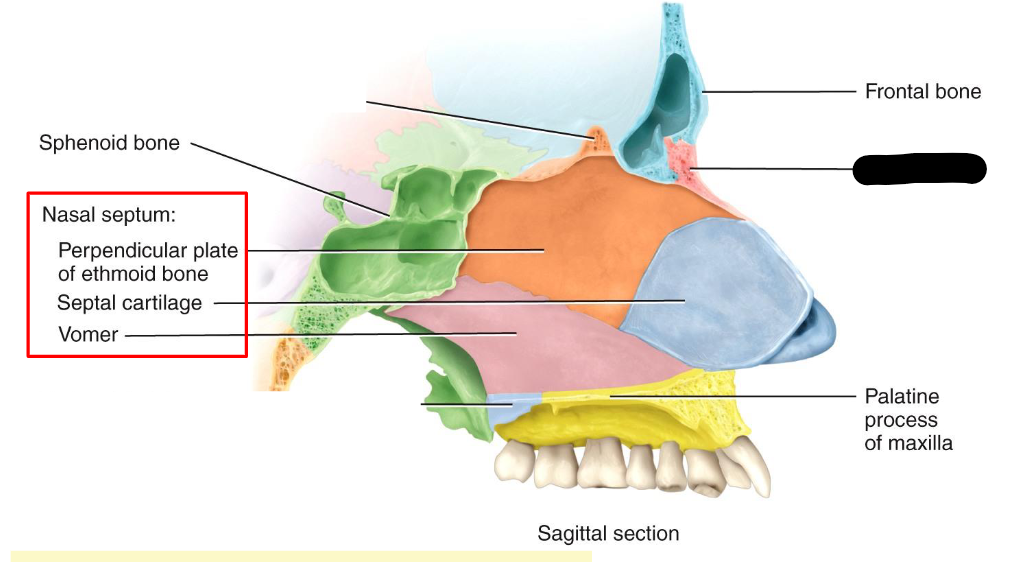
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Nasal Bone
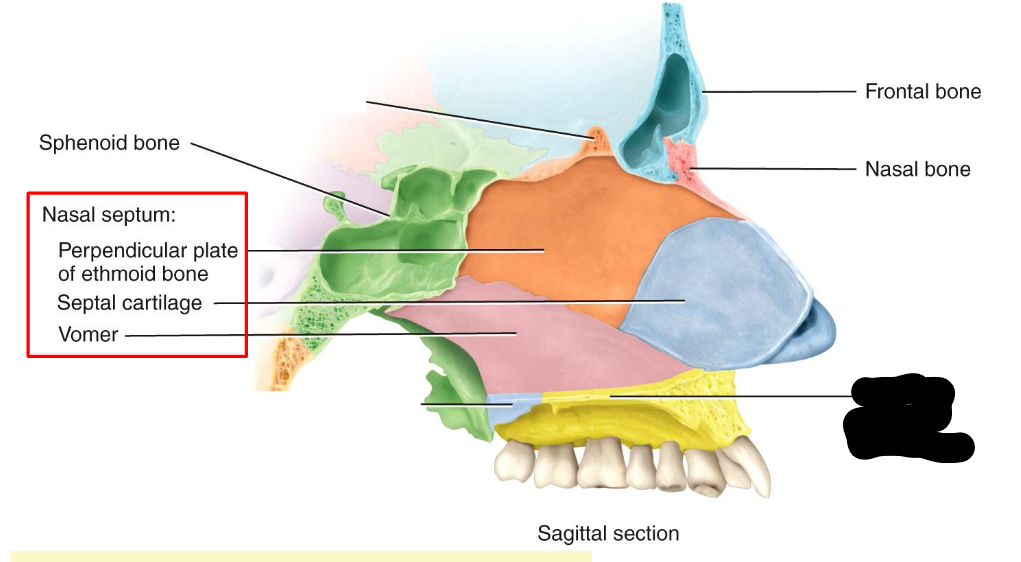
What structure is this within the Nasal Cavity?
Palatine Process of Maxilla
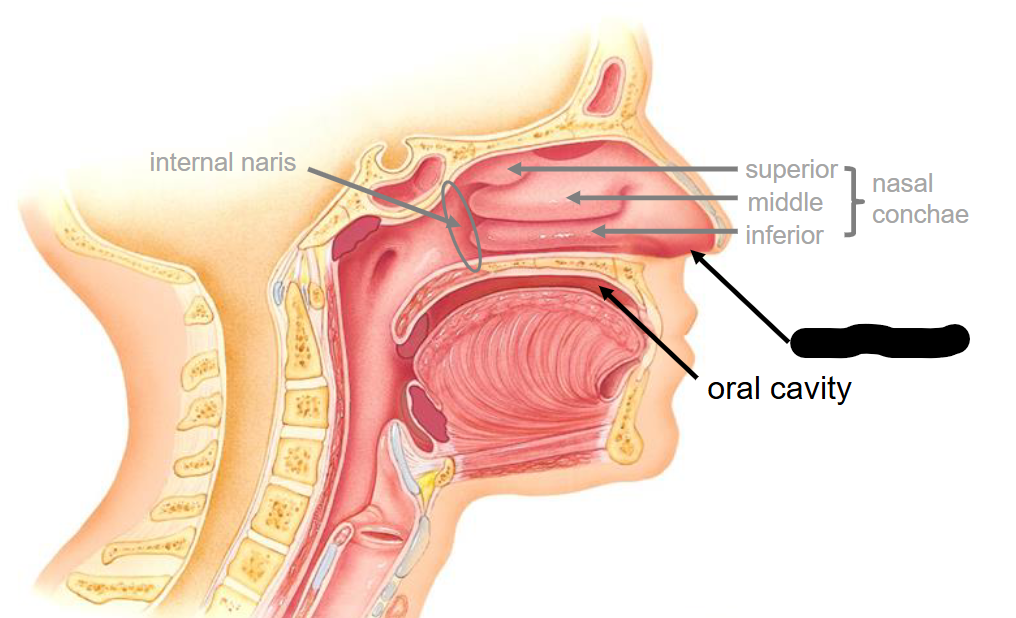
What structure is this
Oral Cavity
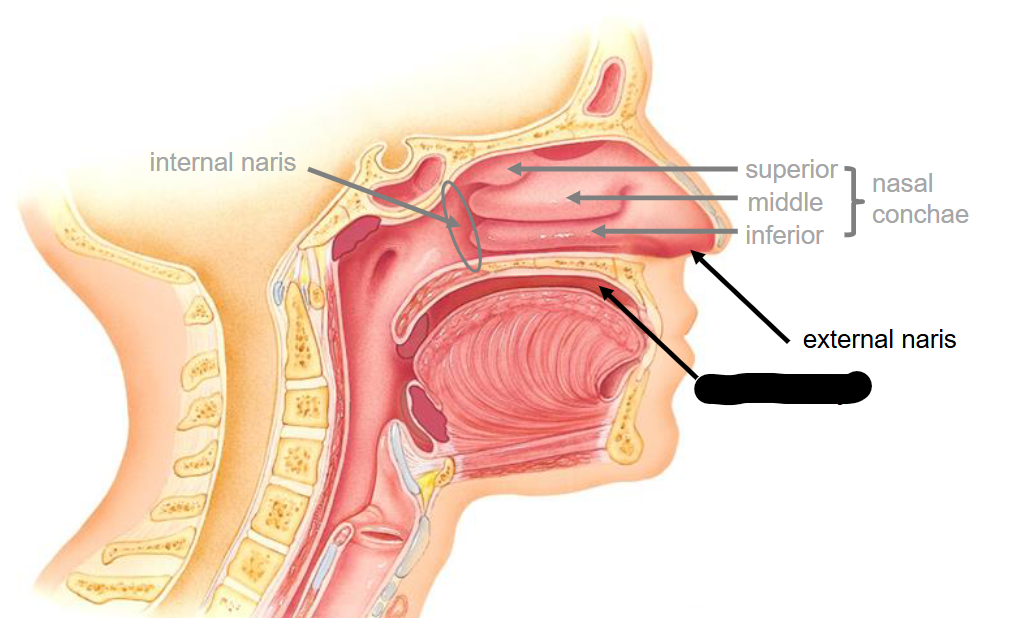
What structure is this
External Naris
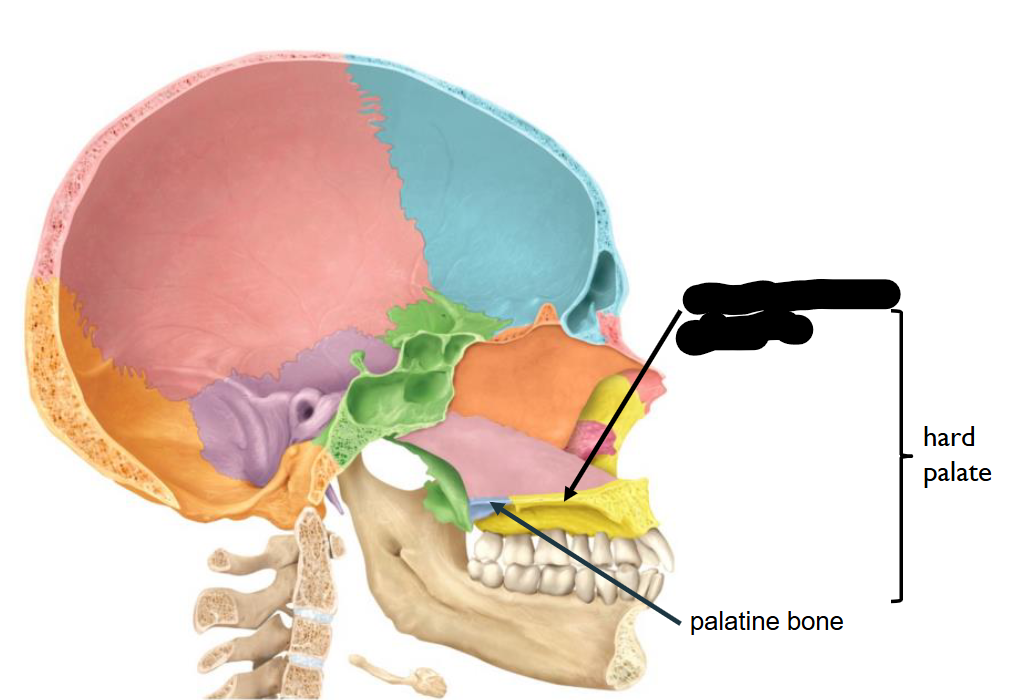
What structure is this?
Palatine Process of Maxilla
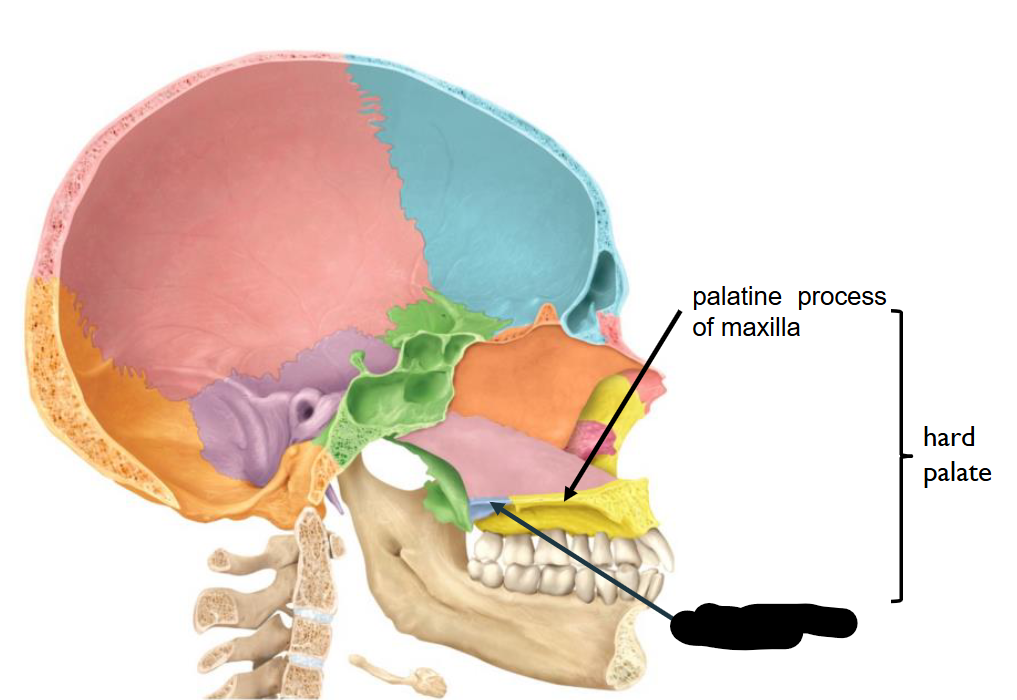
What structure is this?
Palatine bone
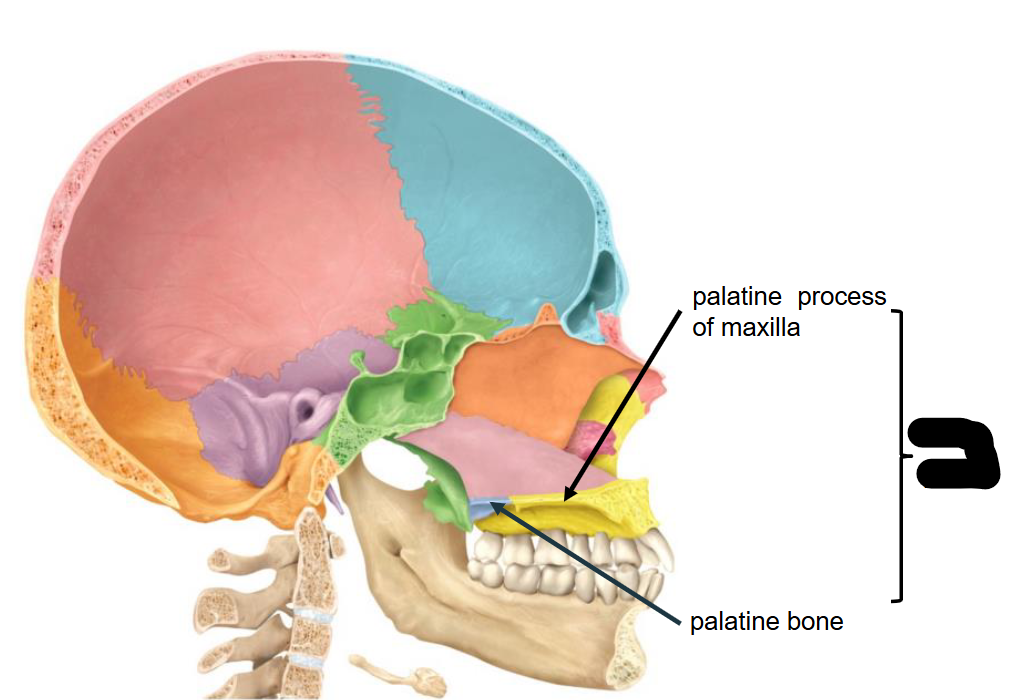
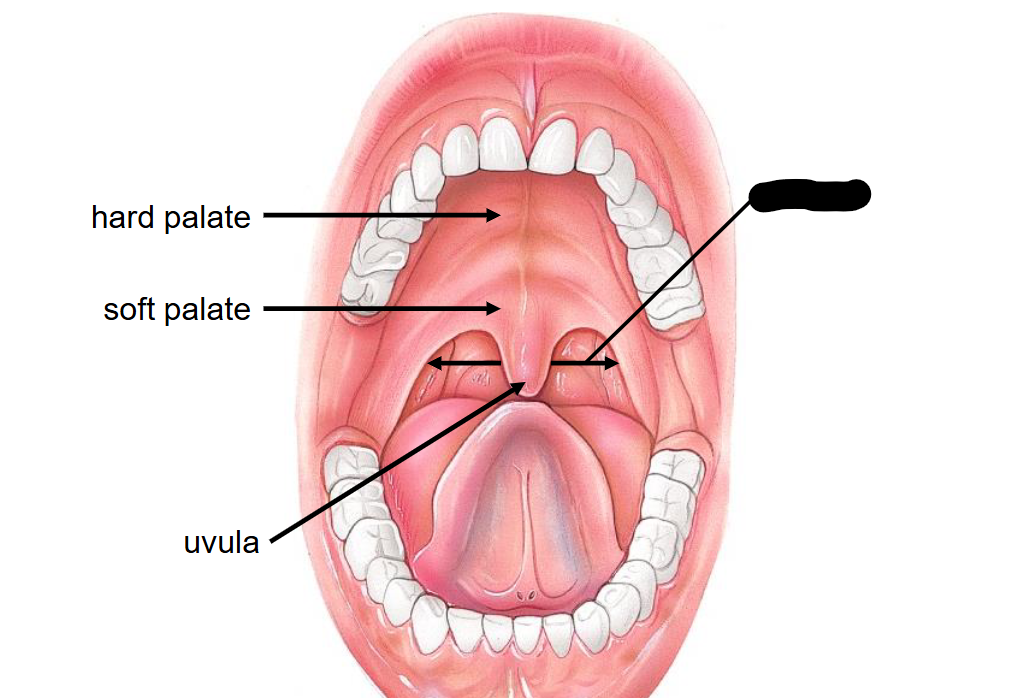
In combination of two Structure, what is this landmark called?
Hard Palate
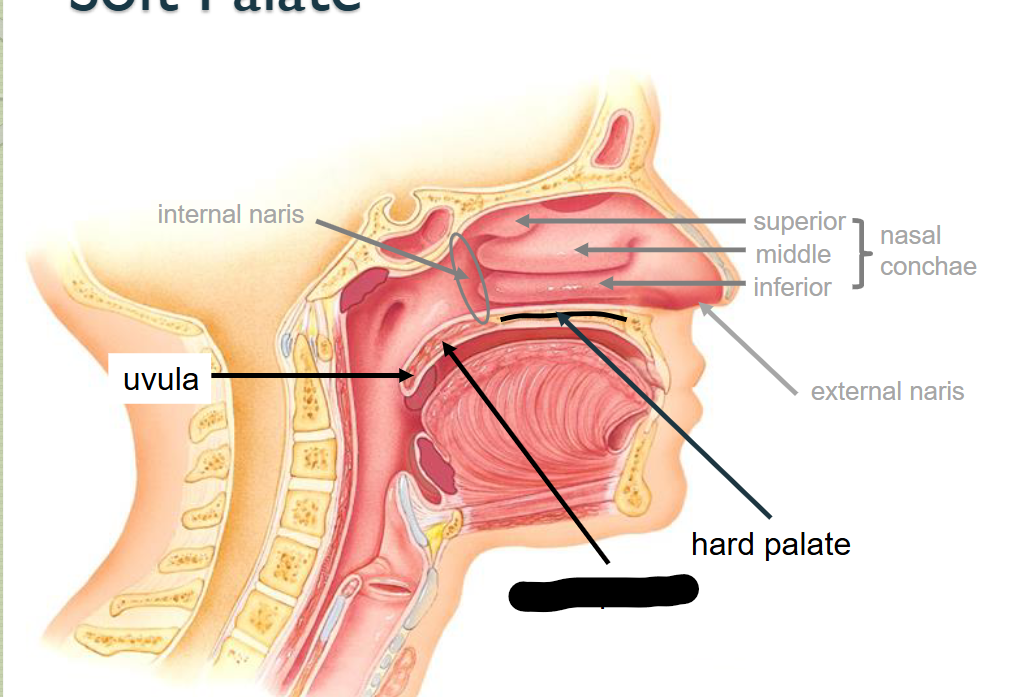
What structure is this?
Soft palate
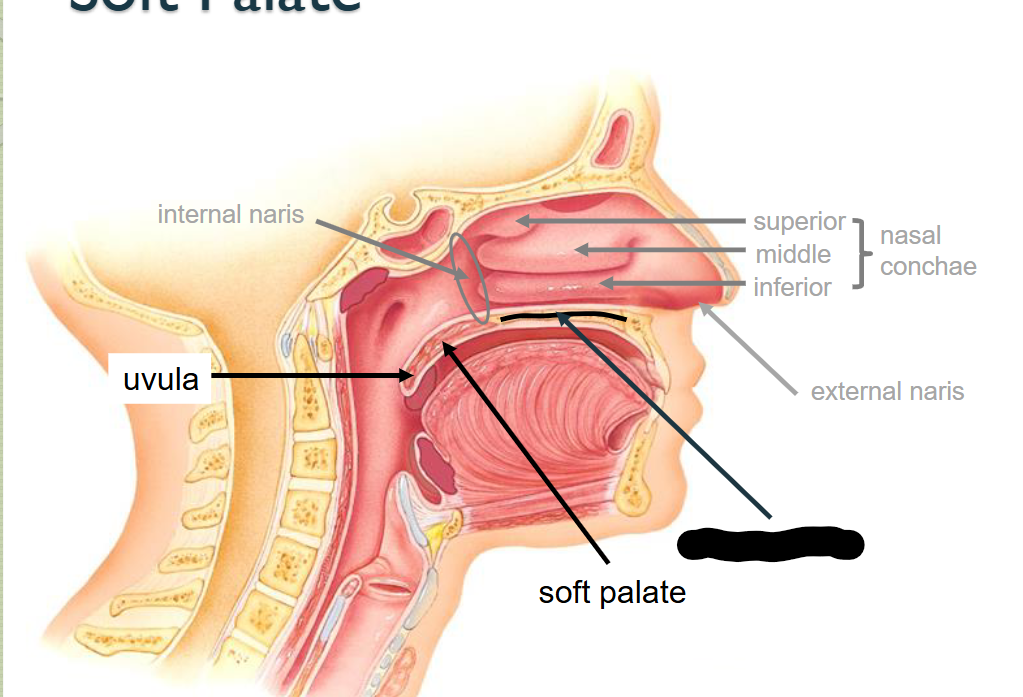
What structure is this?
Hard Palate
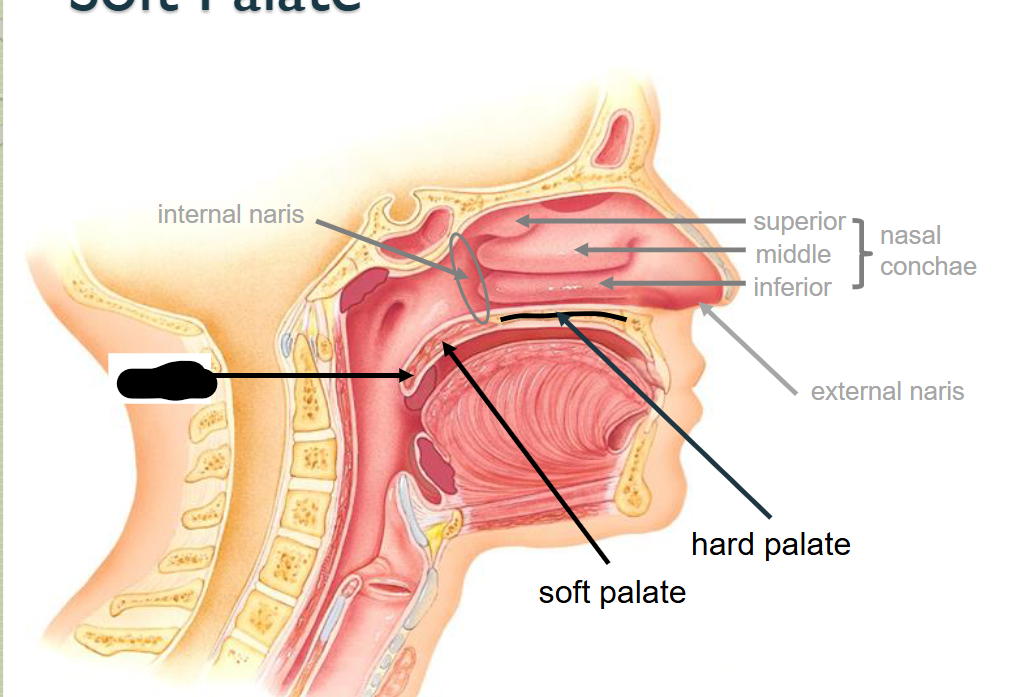
What structure is this?
Uvula
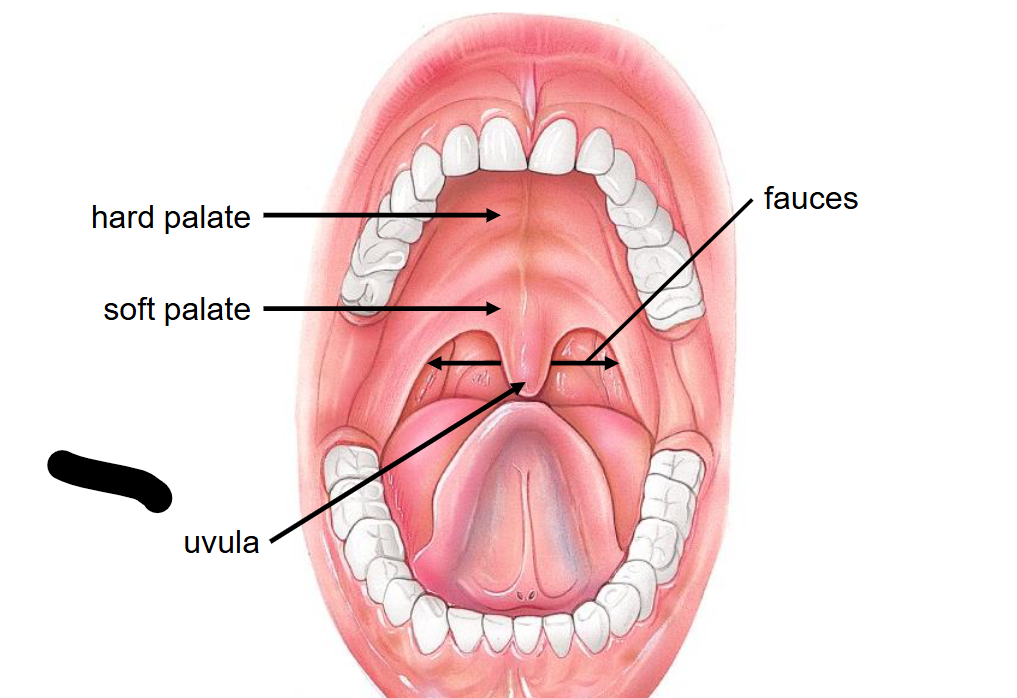
What structure is this?
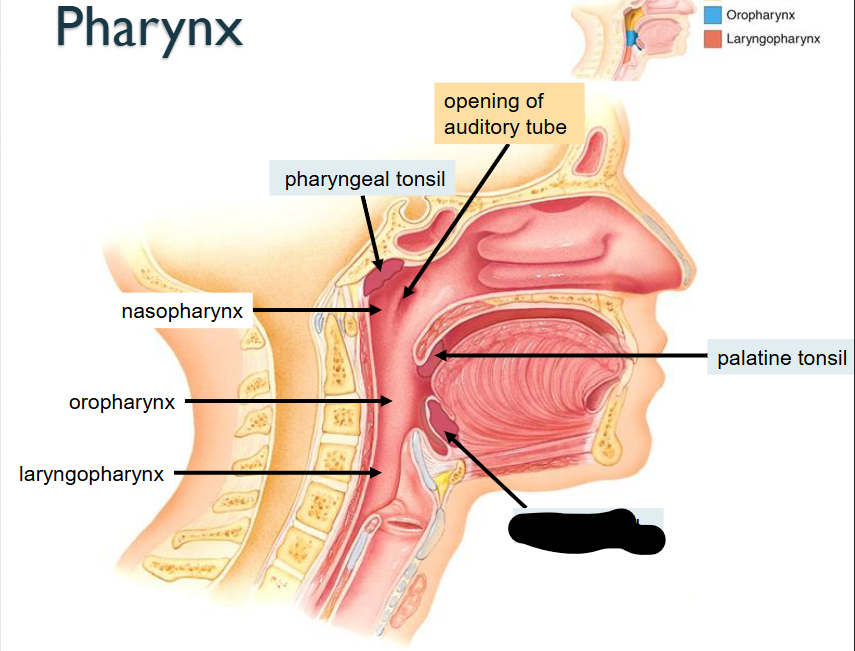
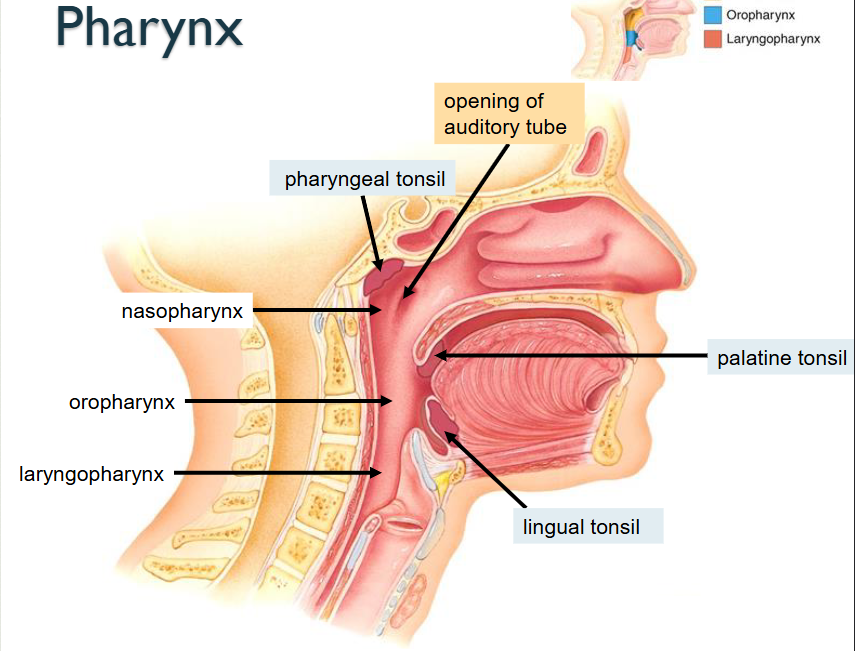
Opening of auditory tube
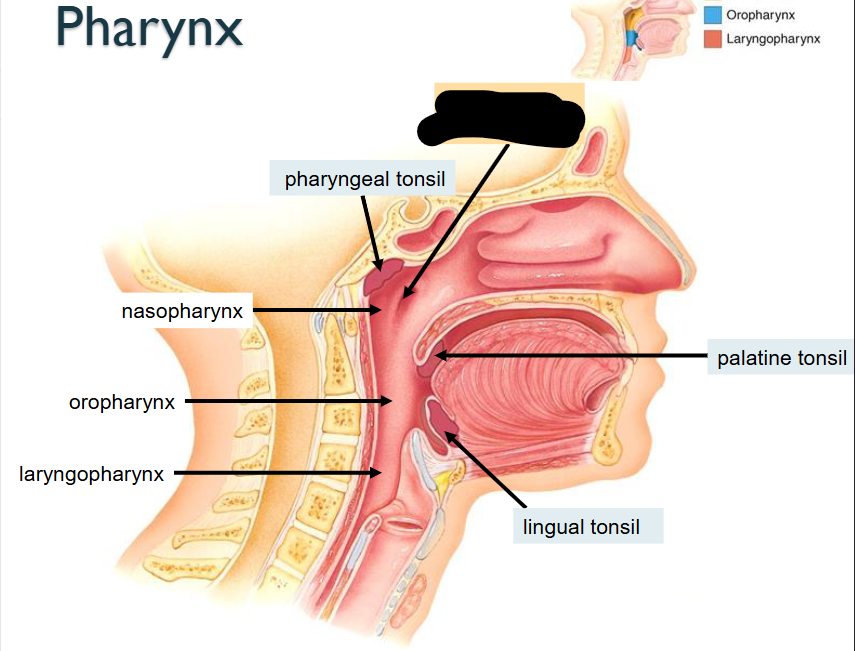
What structure is this within the Mouth?
Fauces
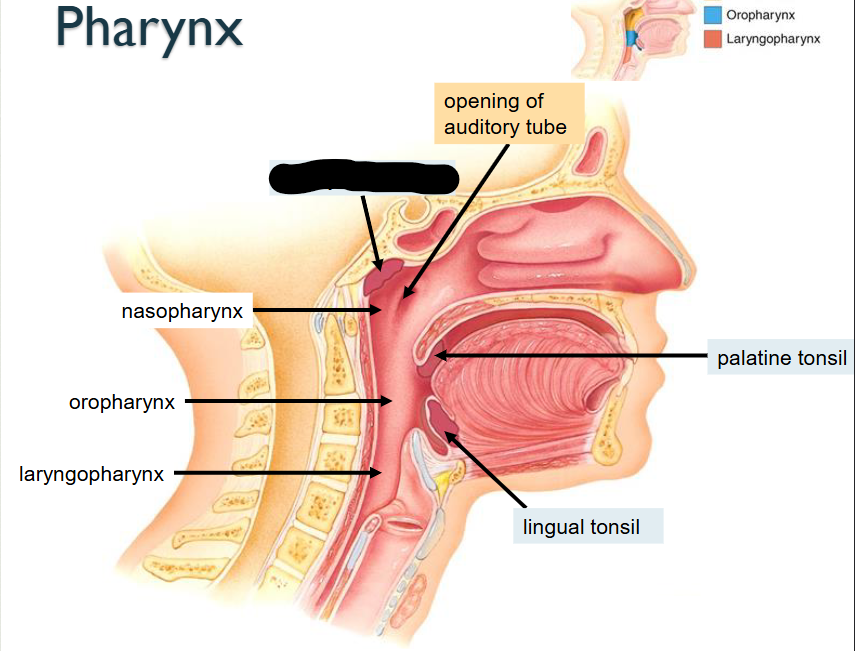
What structure is this?
Pharyngeal Tonsil
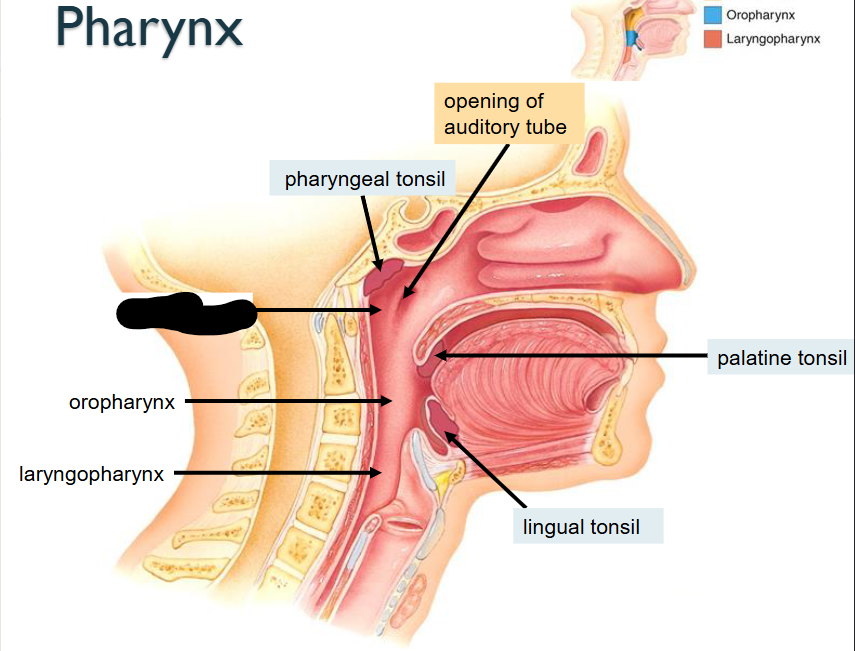
What structure is this?
Nasopharynx
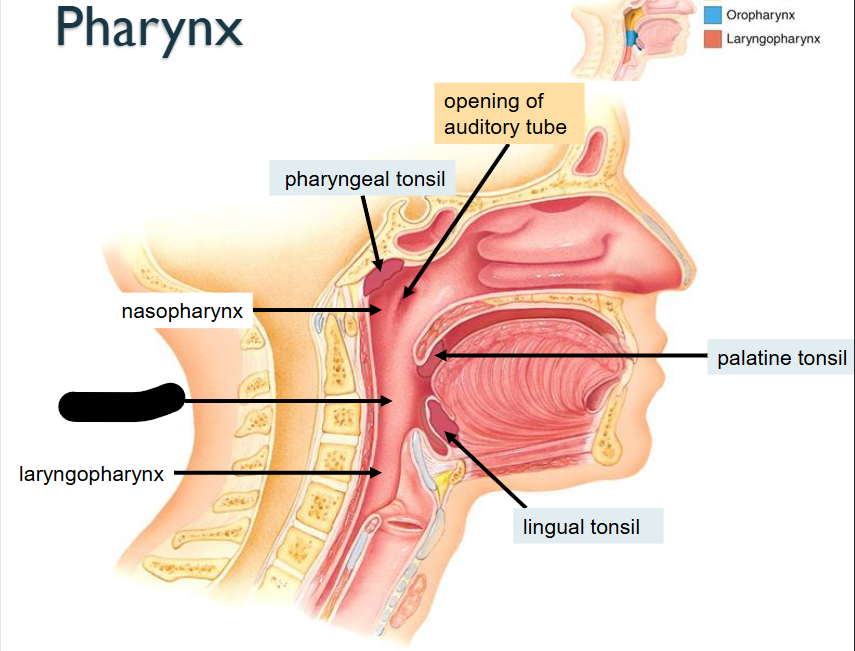
What structure is this?
Oropharynx
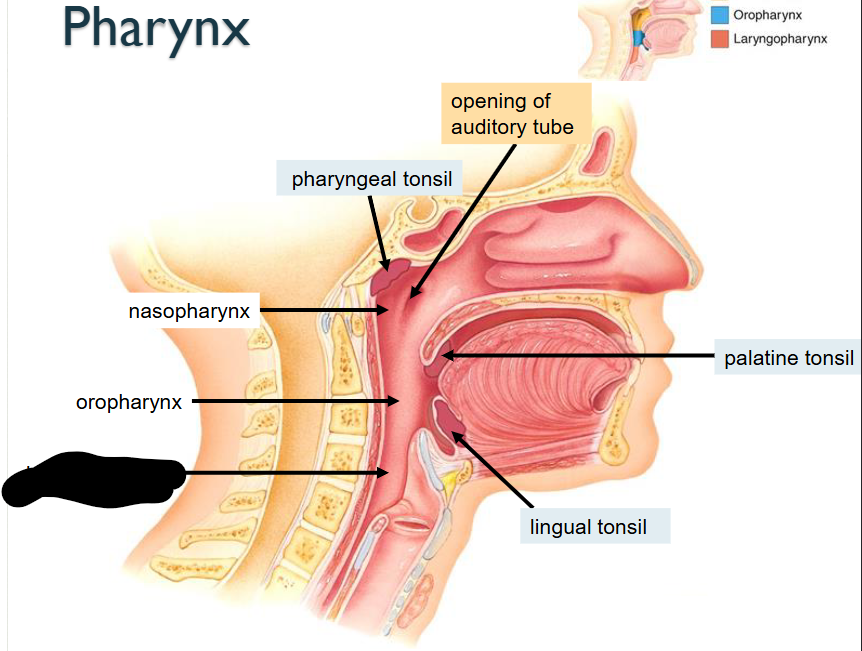
What structure is this?
Laryngopharynx
What structure is this?
Lingual Tonsil
What structure is this?
Palatine Tonsil
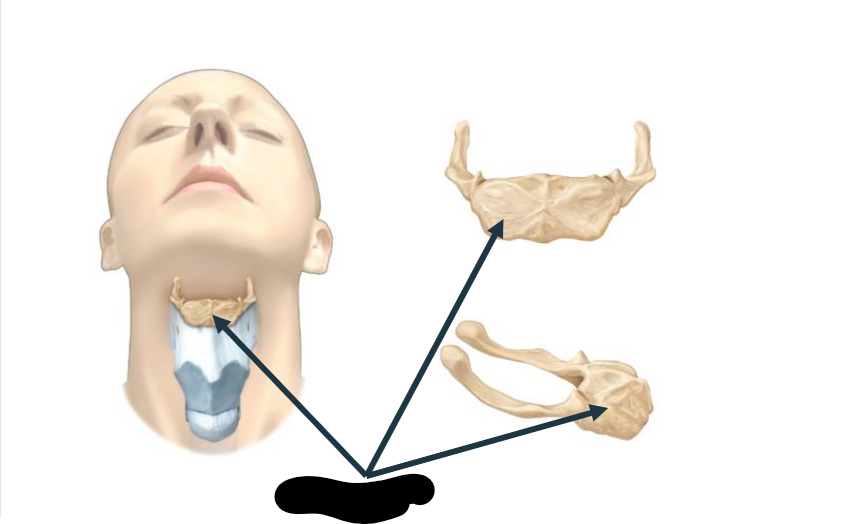
What structure is this?
Hyoid bone
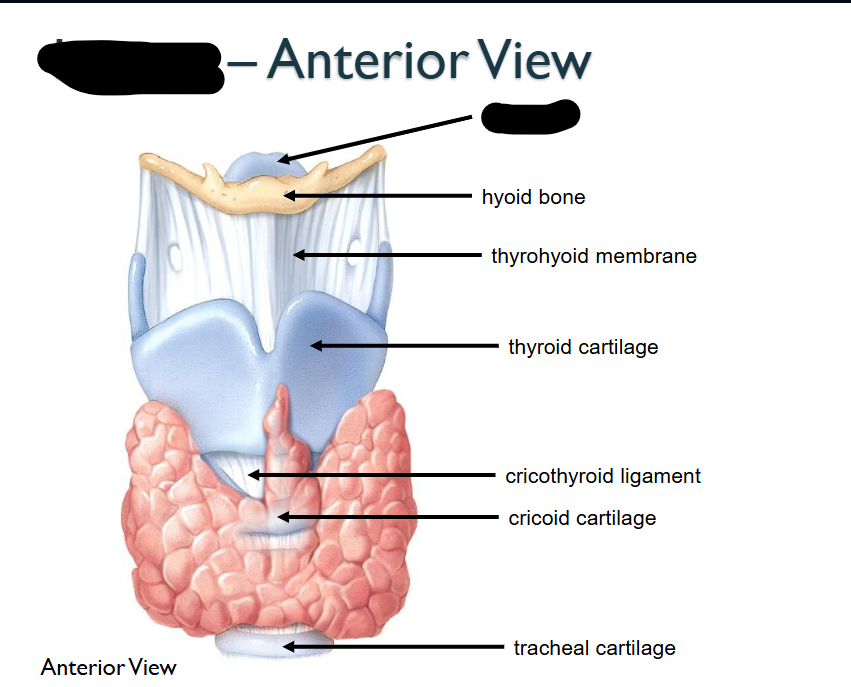
What structure is this within the Larynx?
Epiglottis
What structure is this within the Larynx?
Hyoid Bone
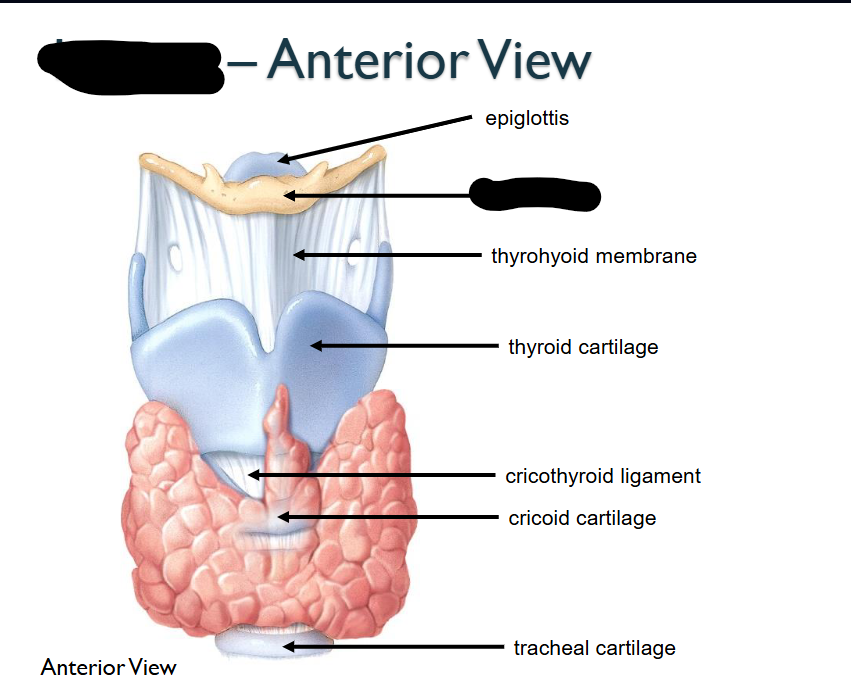
What structure is this within the Larynx?
Thyrhyoid membrane
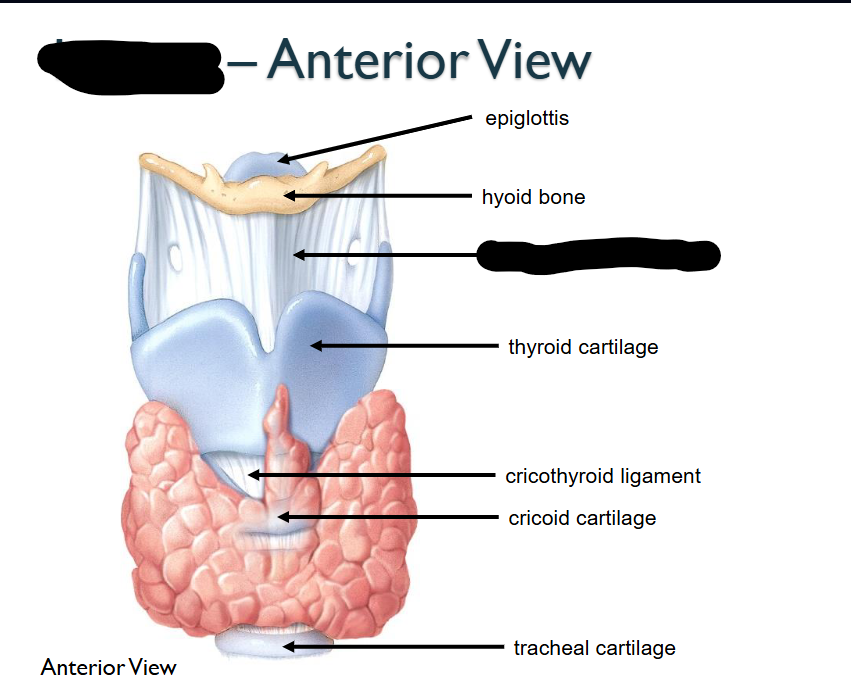
What structure is this within the Larynx?
Thyroid Cartilage
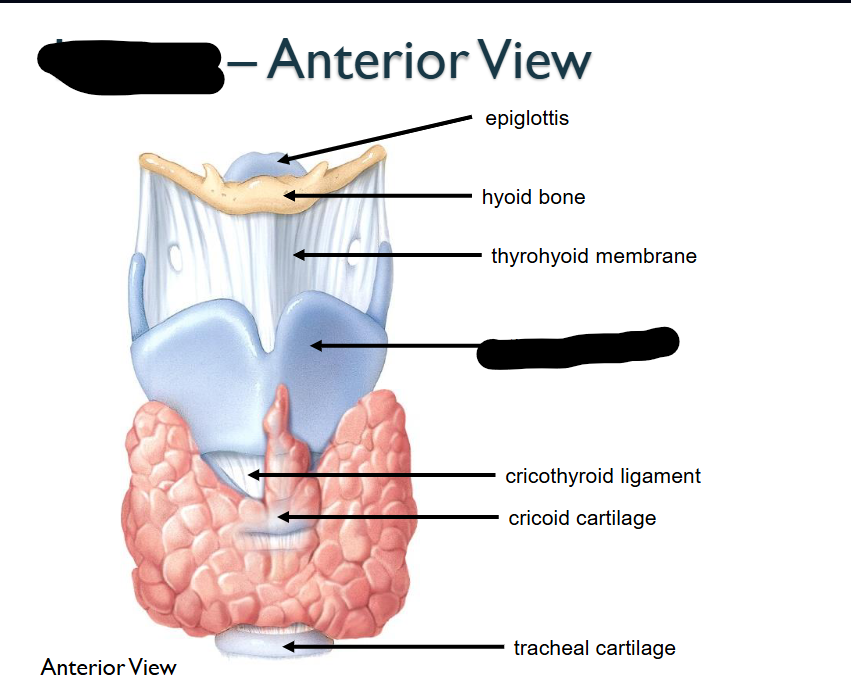
What structure is this within the Larynx?
Circothyroid ligament
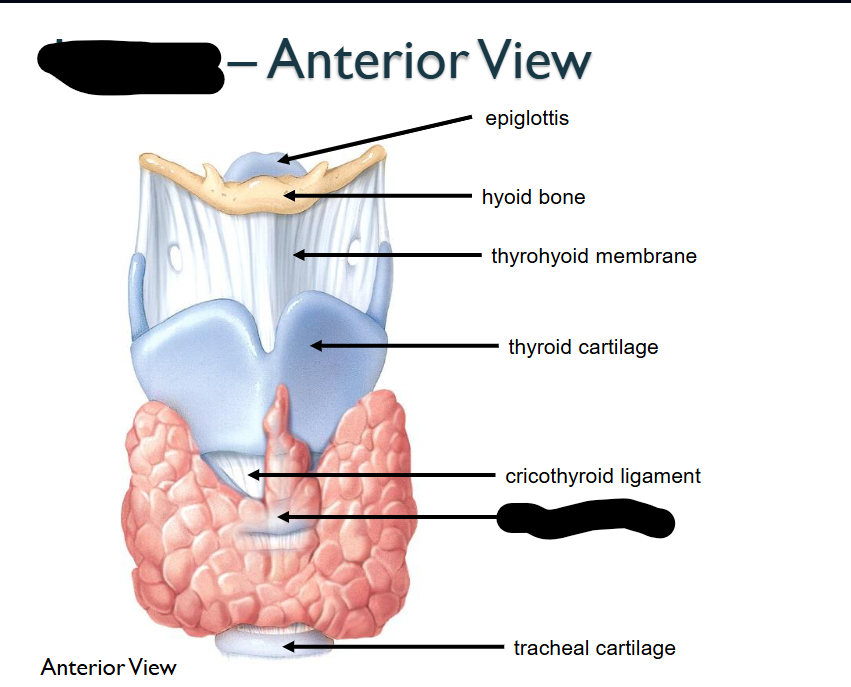
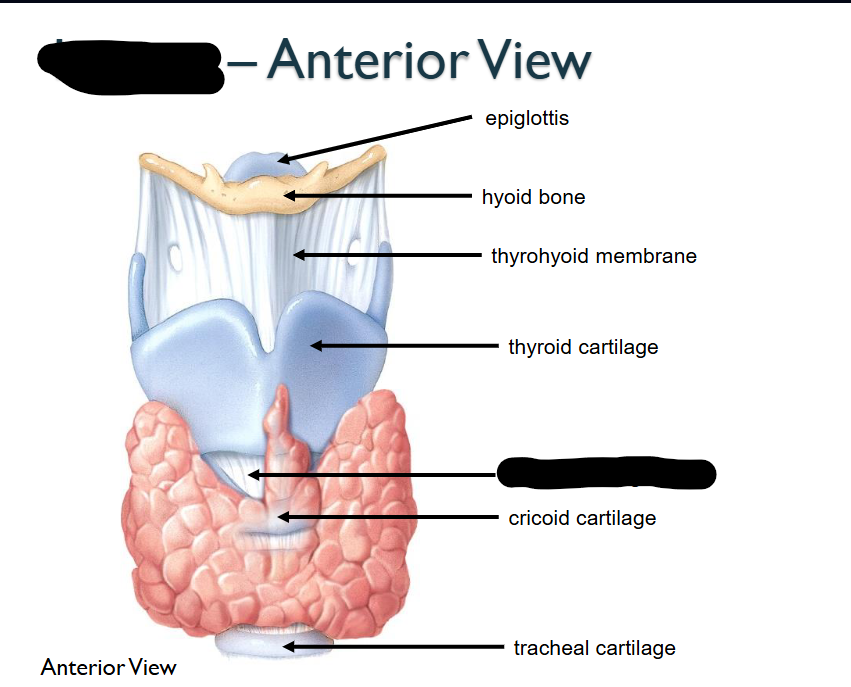
What structure is this within the Larynx?
Circoid Cartilage
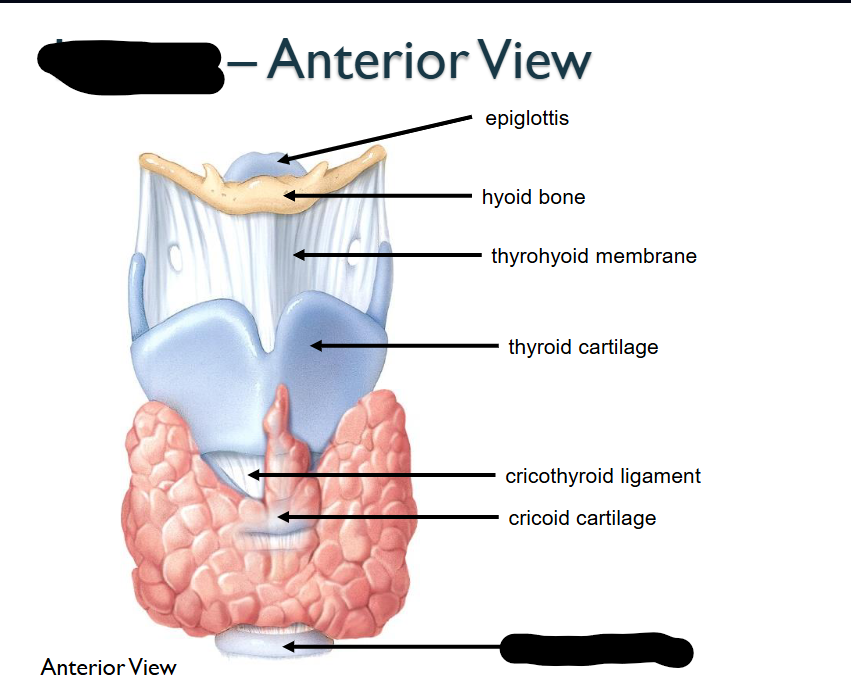
What structure is this within the Larynx?
Tracheal Cartilage
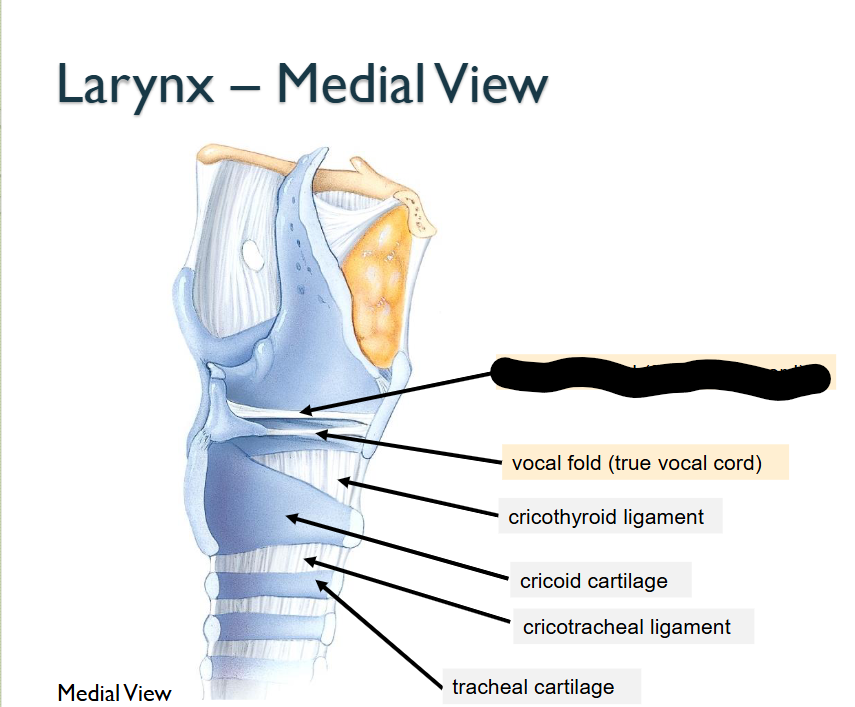
What structure is this, within the Larynx - MEDIAL
Vestibular Fold (False Vocal Cord)
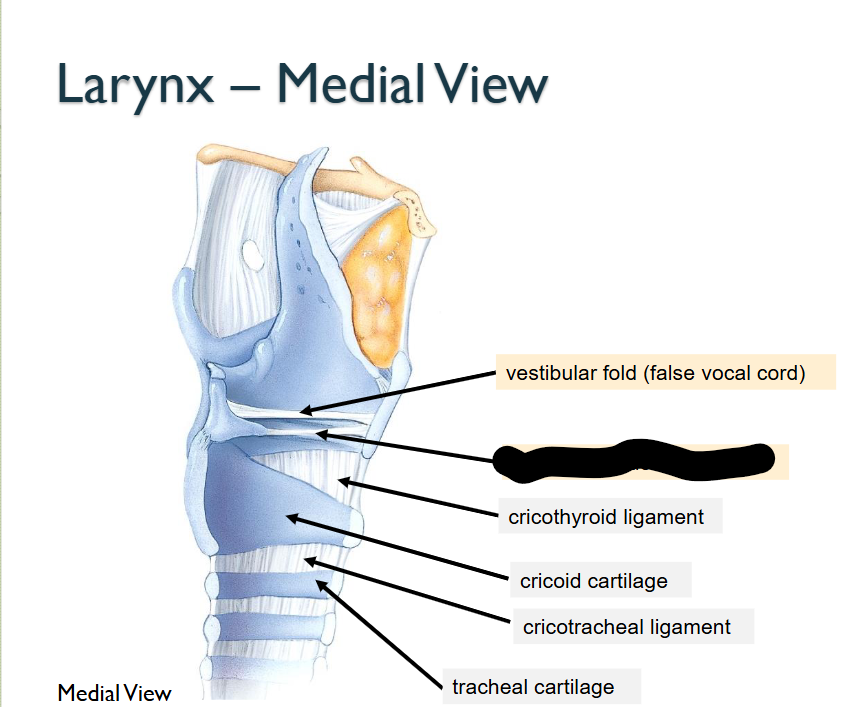
What structure is this, within the Larynx - MEDIAL
Vocal Fold (True Vocal Cord)
What is the main function of the Larynx?
Small particles (eg; dust, smoke food, liquids) pas into larynx > cough reflex occurs > expelling material
What is the main function of the Epiglottitis / Epiglottis Cartilage?
Acts as a protective flap / closing over larynx (voice box) / trachea (windpipe) when swallowing, preventing food/liquid from entering respiratory system > DIRECTS TO (ESOPHAGUS)
Attached to internal surface of thyroid cartilage
Is the Thyroid Cartilage larger in males?
YES / far more prominent with Laryngeal Promience / Adam’s Apple
What is the Cricoid Cartilage?
Ring-like hyaline cartilage forming the INFERIOR WALL of Larynx
Key landmark for emergency airway > usually in case of AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION
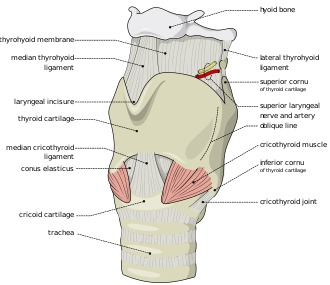
What does the Thyrohyoid membrane do?
Connects thyroid cartilage > hyoid bone
What does the Cricothyroid Ligament do?
Connects the Thyroid Cartilage > Circoid Cartilage
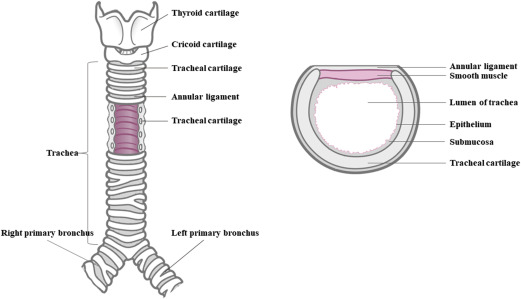
Main functions of Tracheal Cartilage?
C-SHAPED cartilage
OPEN-PART of C-SHAPE CARTILAGE RINGS > FACE POSTERIORLY > TOWARD ESOPHAGUS = FACILITATING COMFORTABLE / EFFIECNET SWALLOWING
C-Shaped Rings > provide semi-rigid support to maintain openesss’s > so tracheal walls don’t collapse inward > (esp during inhalation) / does not obstruct the air passageways
Main function / structural comp of the Glottis?
Consists of pairs-of-folds of Mucous Membrane > Vocal Cords (true vocal cords) in Larynx / space between them called > Rima Glottides
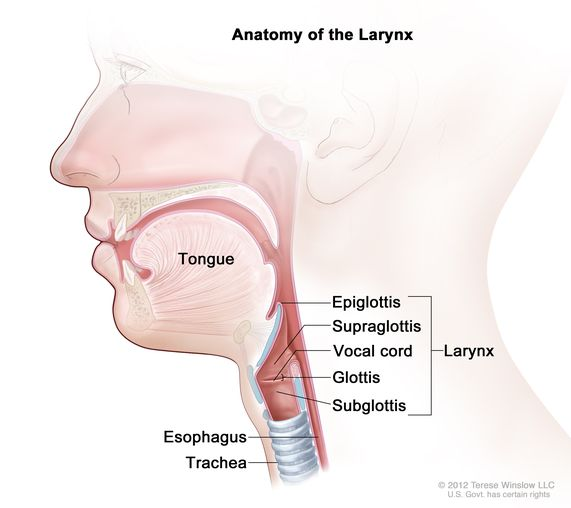
Main function / structural comp of the Vocal Cords?
Inferior pair, of two pairs of folds of > Mucous Membrane Of Larynx
PITCH IS PROD / CONTROLLED BY TENSION / VIBRATION of VOCAL CORDS > higher pittches indicate vibration are more rapid
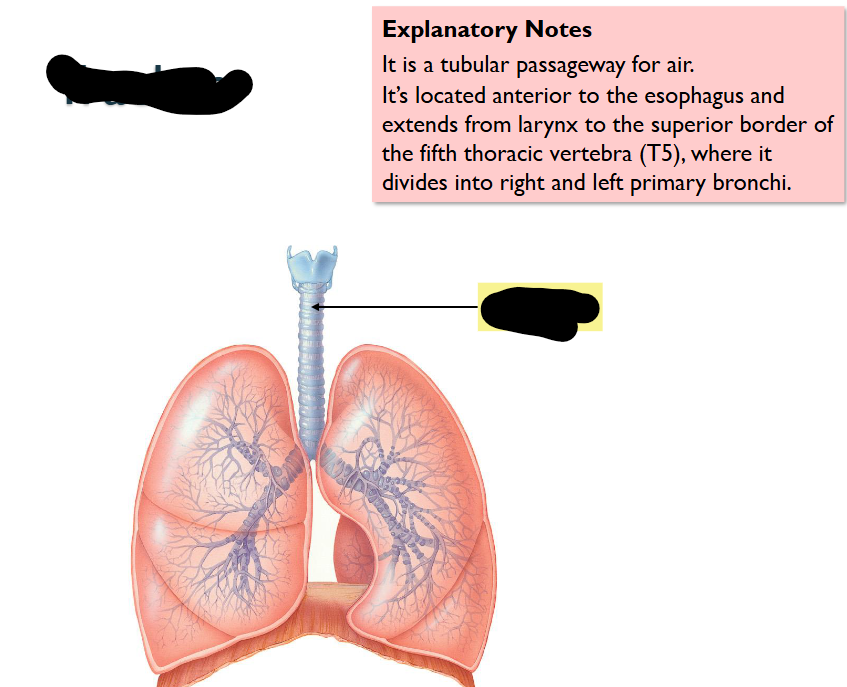
What Structure is this?
Trachea
Tubular passgaeway for AIR
Located: ANTERIORLY to ESOPHAGUS / EXTENDS from larynx - superior border of 5th thoracic vertebra (t5) = DIVIDES INTO RIGHT/LEFT PRIMARY BRONCHI
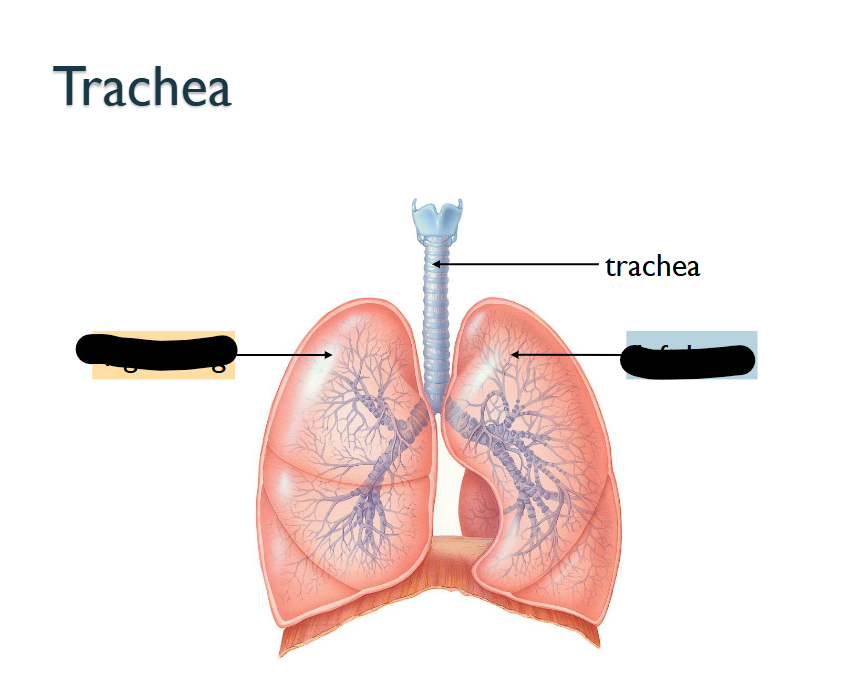
What direction?
(Left is > RIGHT LUNG) (right is LEFT LUNG)
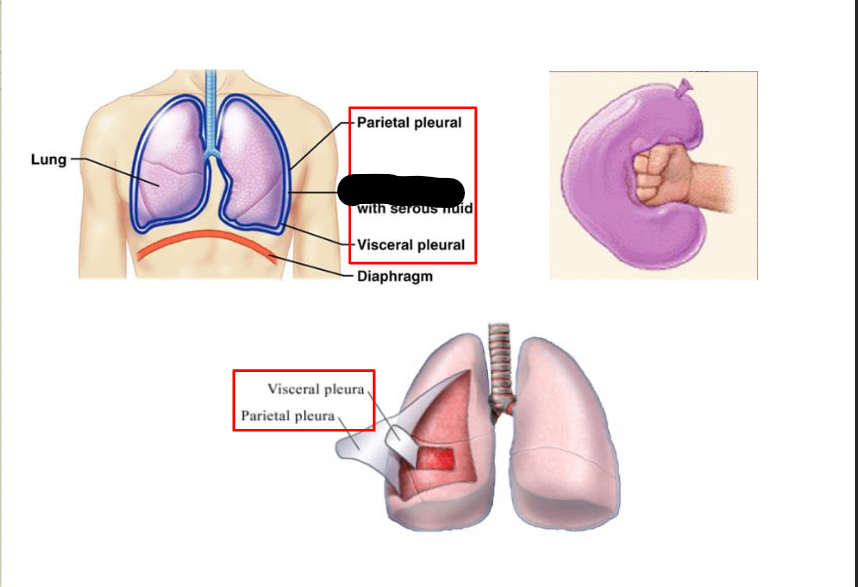
What Cavity is this?
Pleural Cavity
Space between visceral / parietal pleura > space contains tiny amount of serous fluid > has two KEY FUNCTIONS:
Serous Fluid > contiously lybericates plural surface = makes easy for them to slide over each other during inhalation/deflation
Serous Fluid > gen surface tension > pulls the visceral / parietal pleura ADJACENT to each other = allows the throacic cavity to EXPAND during Inspiration
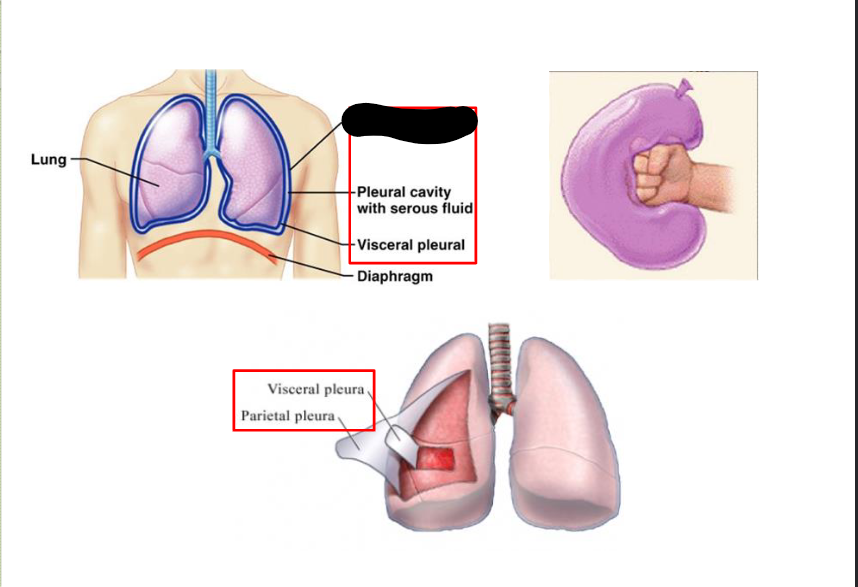
What structure is this within the Pleural Cavity?
Parietal Pleural
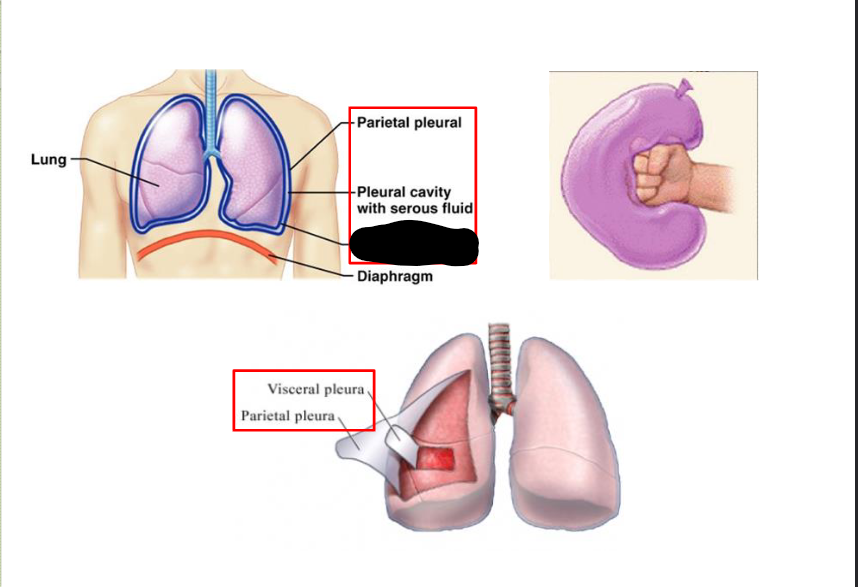
What structure is this within the Pleural Cavity?
Visceral Pleural
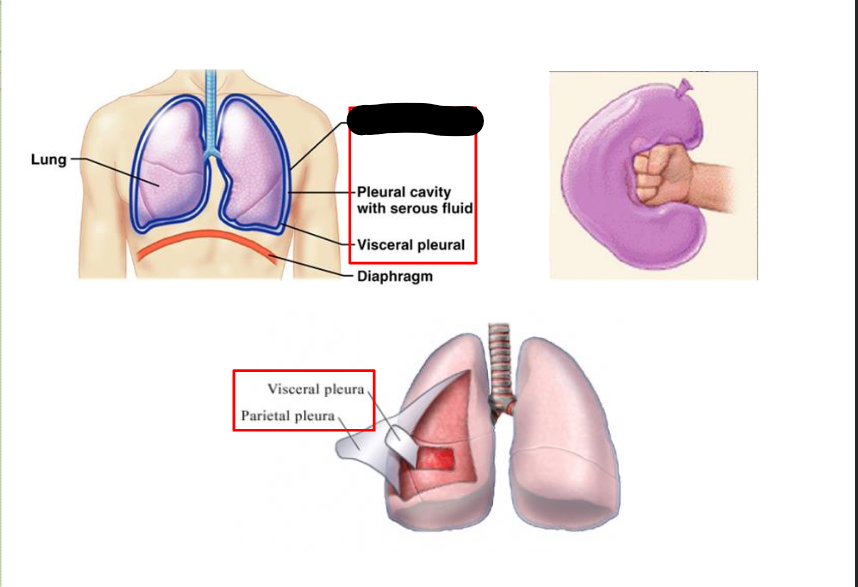
What structure is this within the Pleural Cavity?
Parietal Pleura
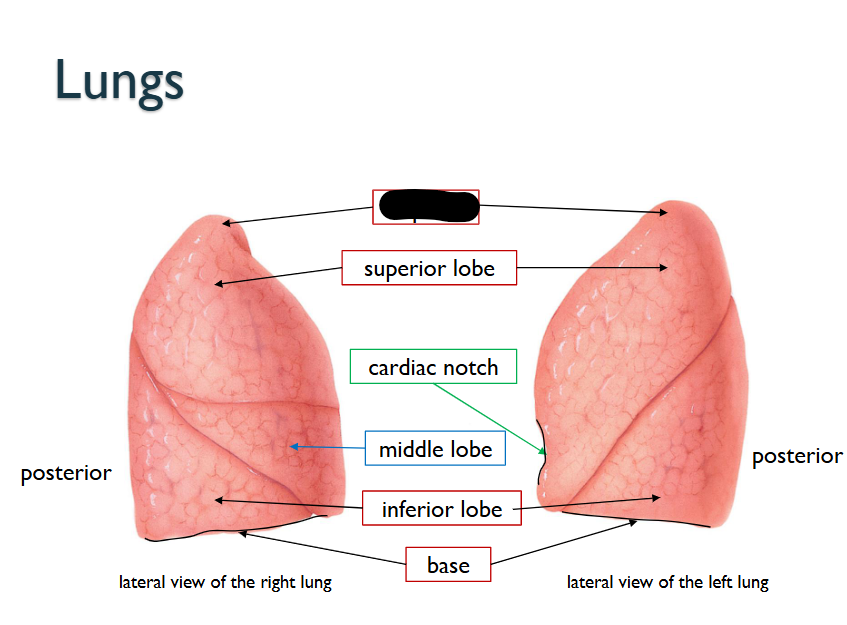
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Apex
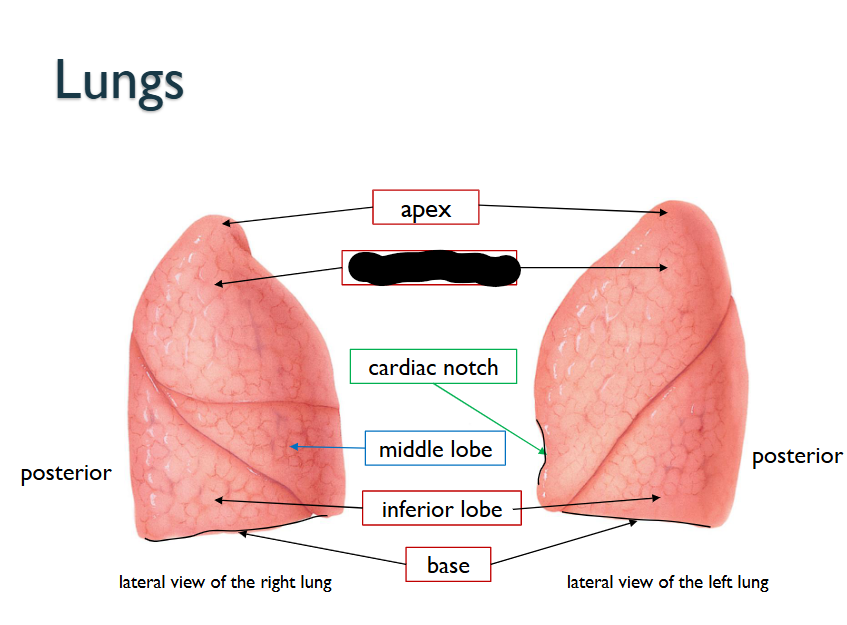
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Superior Lobe
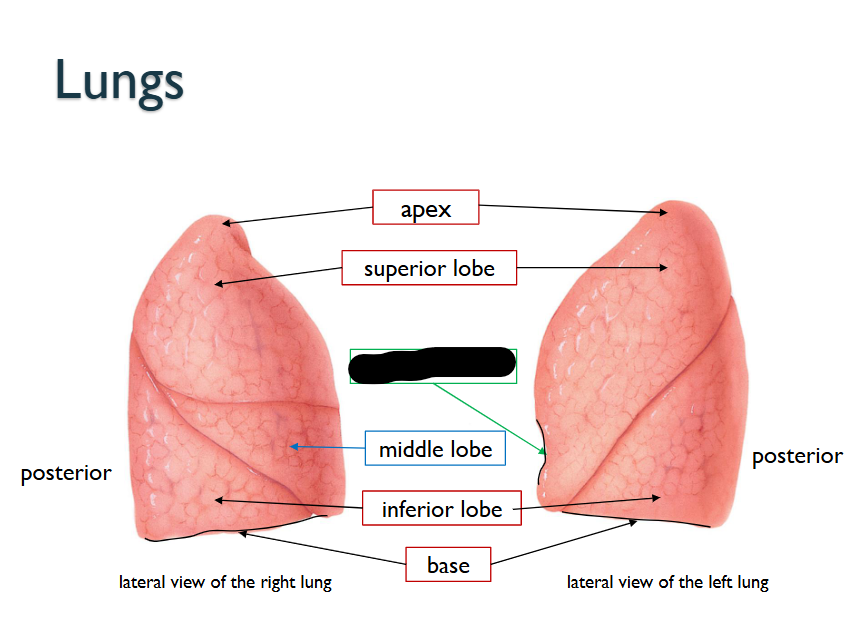
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Cardiac Notch
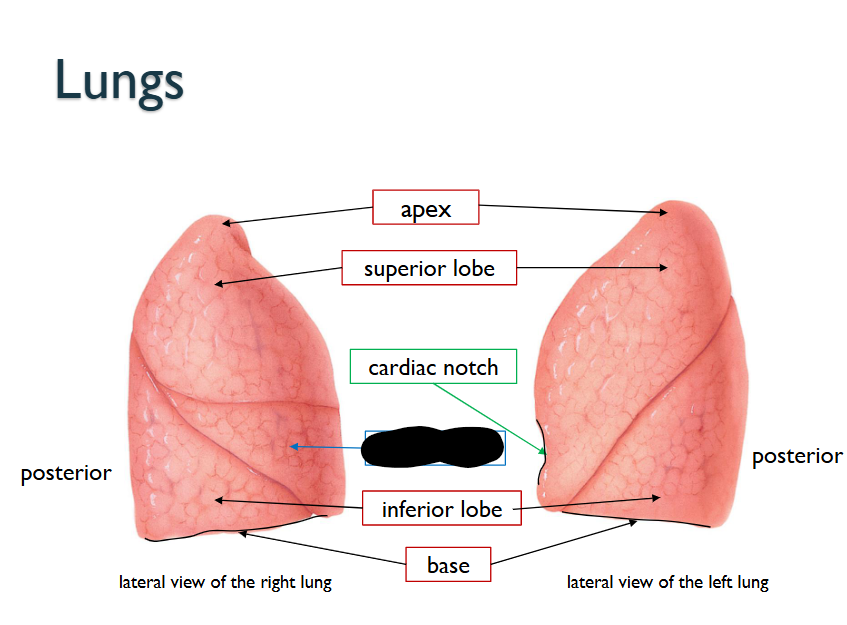
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Middle Lobe (ONLY WITHIN RIGHT LUNG)
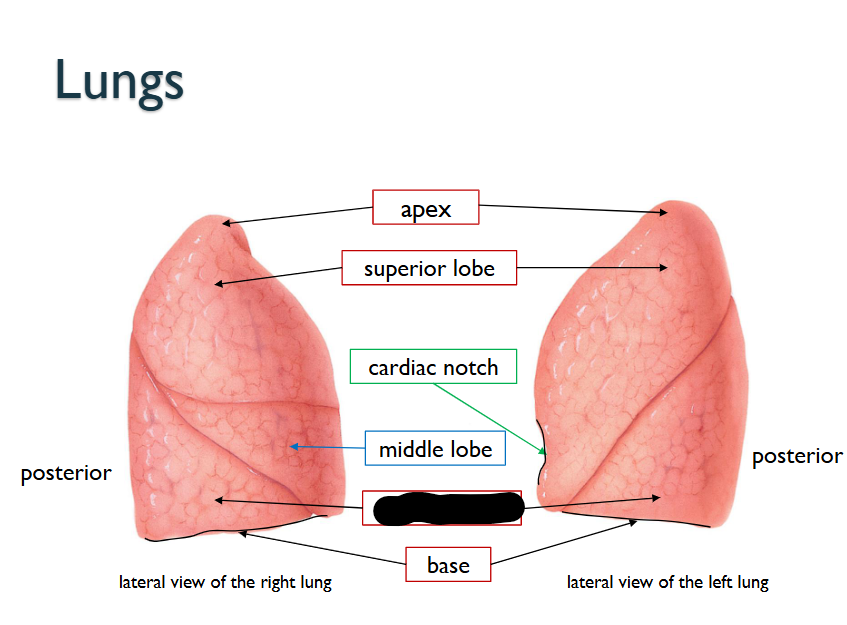
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Inferior Lobe
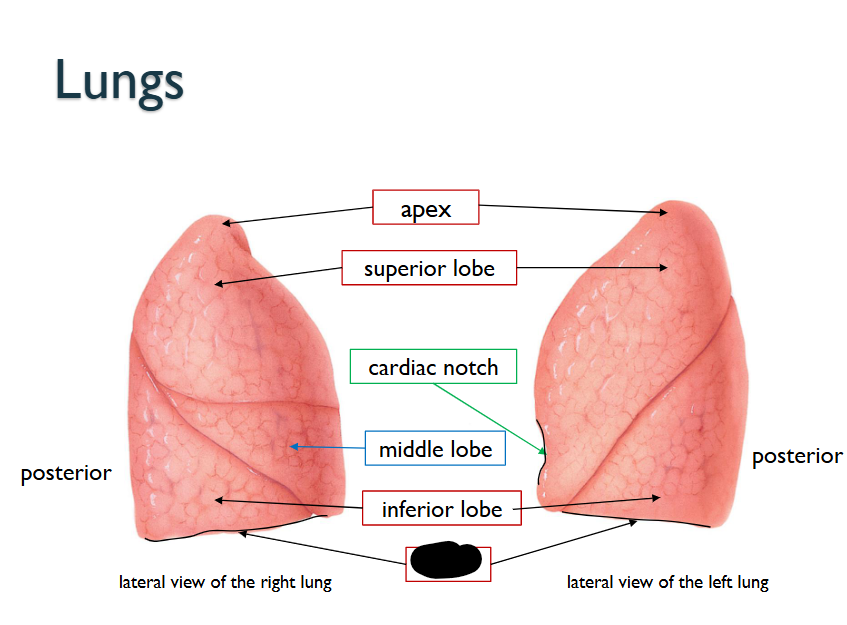
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Base
What does the Cardiac Notch do?
Concavity along Medial Border of LEFT LUNG = APEX OF HEART LIES
What does the Left Lung have that the Right Lung doesn’t
Consists of TWO-LOBES
10% smaller than RIGHT LUNG
What does the Right Lung have that the Left Lung doesn’t
Consists of THREE-LOBES
THICKER/BROADER
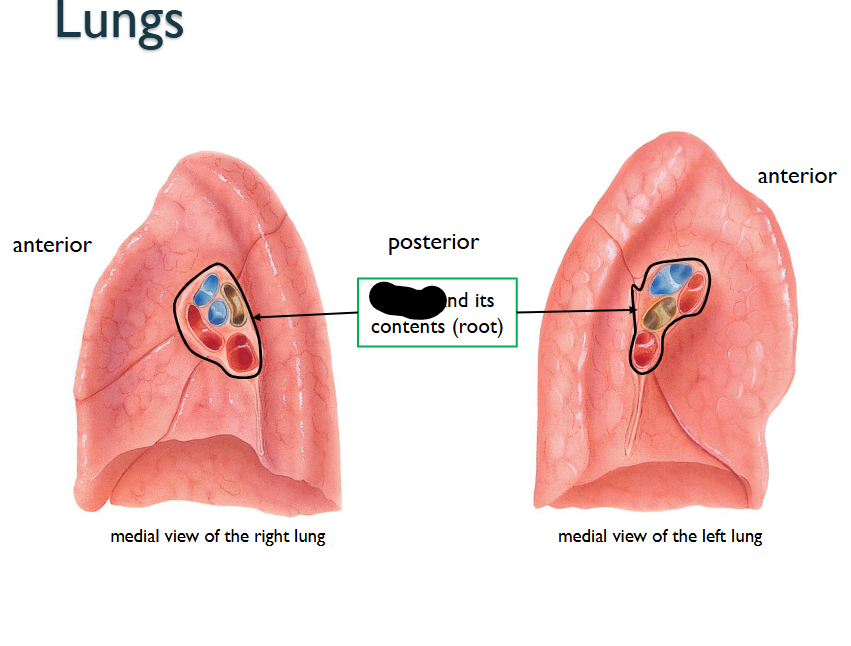
What structure is this within the Medial View of the Lung?
Hilum / its contents (ROOTS)
What is the Hilum?
Its a region, through which bronchi pulmonary blood vessles, lymphatic vessles / nerves ENTER/EXIT FROM
What is the Root?
GROUP OF STRUCTURES > (Bronchi, Pulmonary Blood Vessels, Lymphatic vessels, nerves) > EMERGE @ the Helium of EACH-LUNG
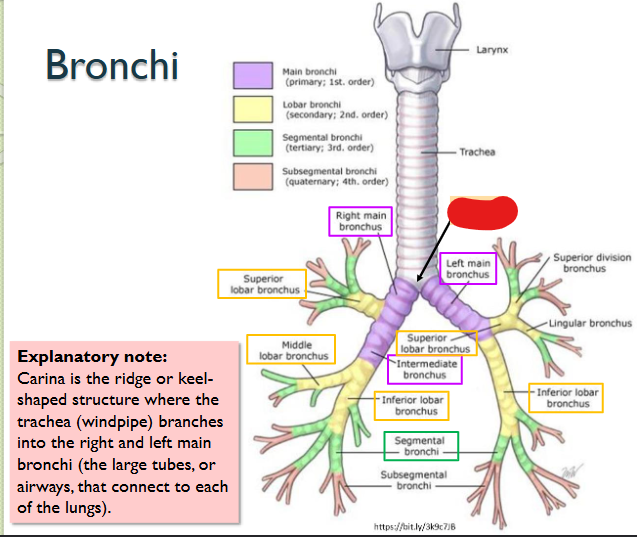
What structure is this within the Bronchi?
Carina
This is where the Trachea branches into right/left main bronchi > LARGE TUBES / AIRWAYS > CONNECT OF EACH LUNG
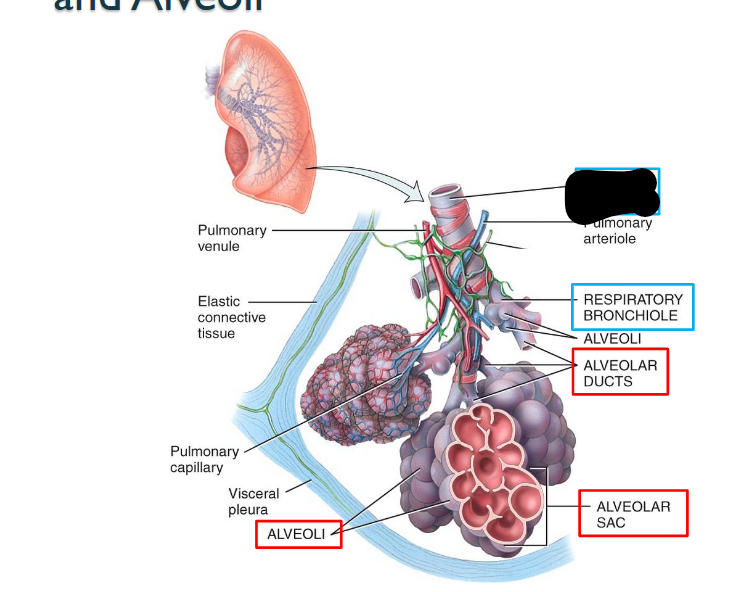
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Terminal Bronchiole
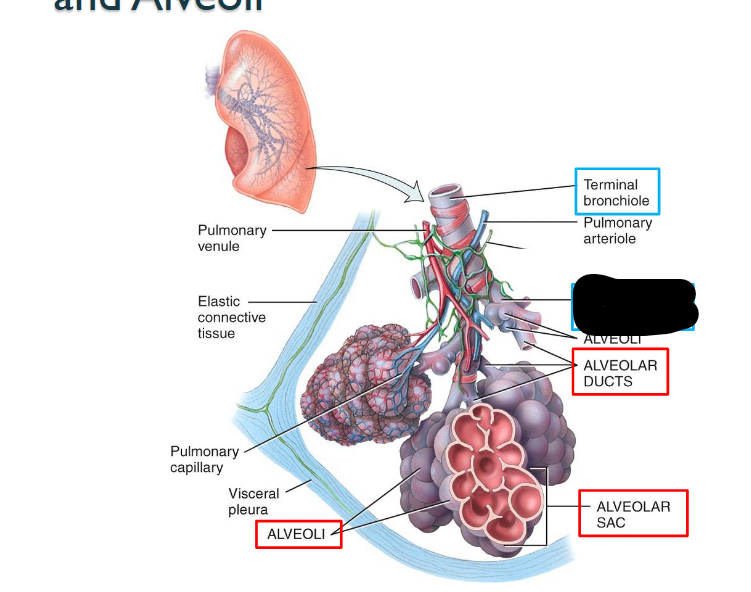
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Respiratory Bronchiole
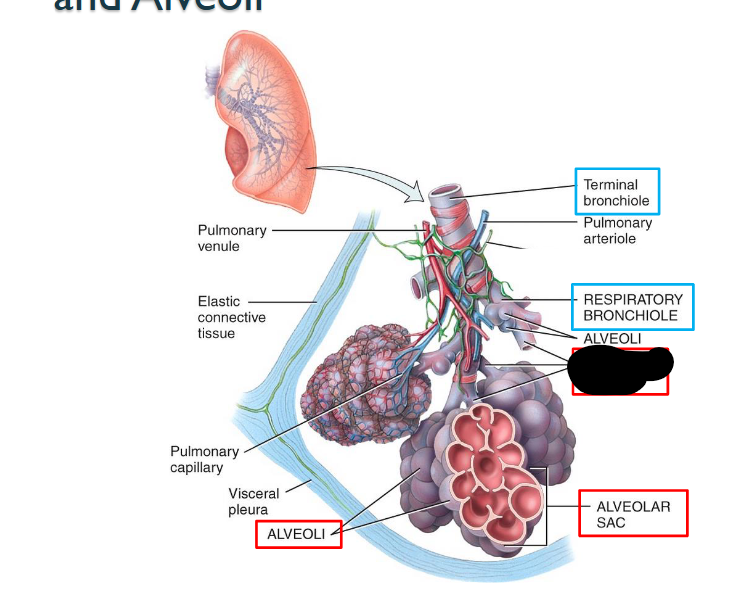
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Alveolar Ducts
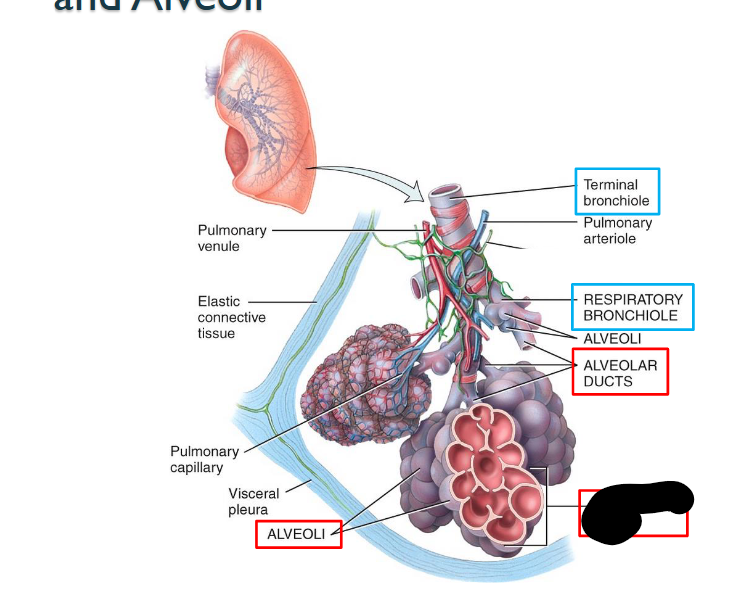
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Alveolar Sac
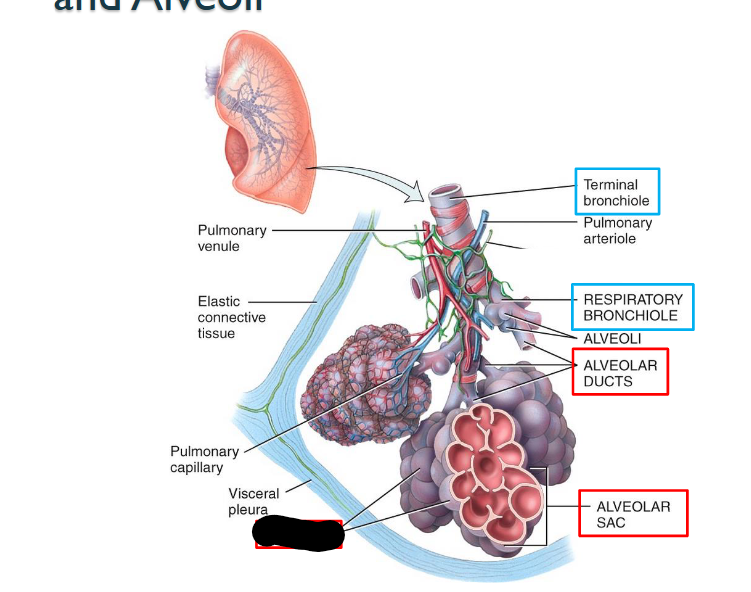
What structure is this within the Lungs?
Aleveoli
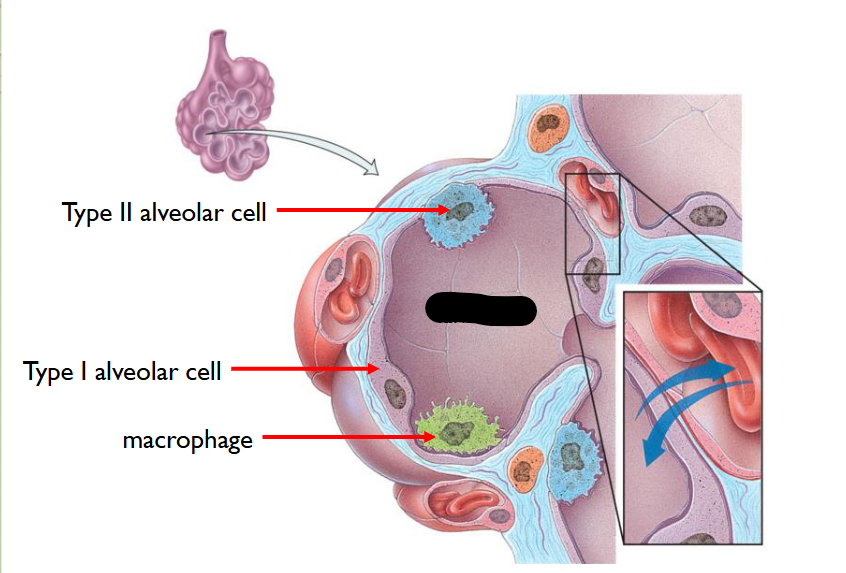
What structure is this?
Alveolus
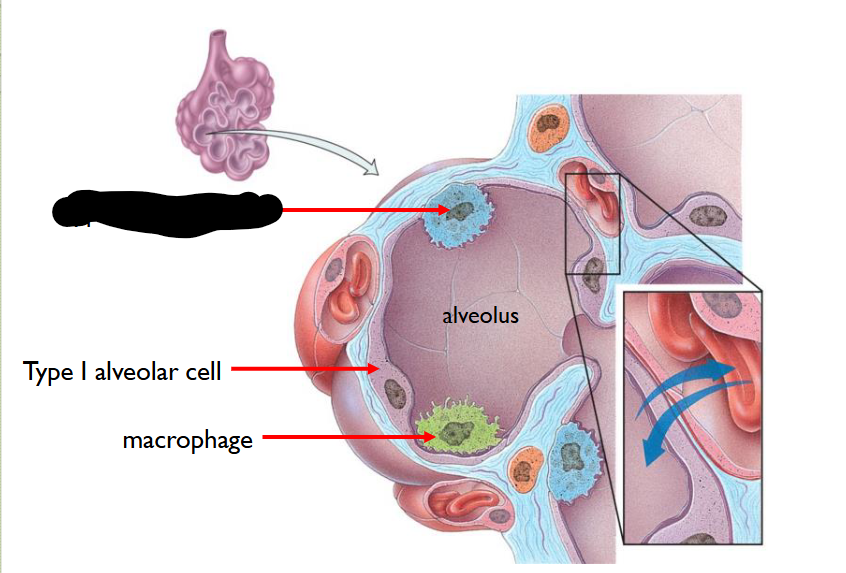
What structure is this within the Alveolus?
Type II Alveolar Cell
Fewer in number
Secrete Pulmonary Alveolar Fluid > moistens surface between air / cells and contains Surfactant > reduces tendency of Pulmoary Alevoli to collapse > MAINTAINS THEIR PATENCY (OPENNESS)
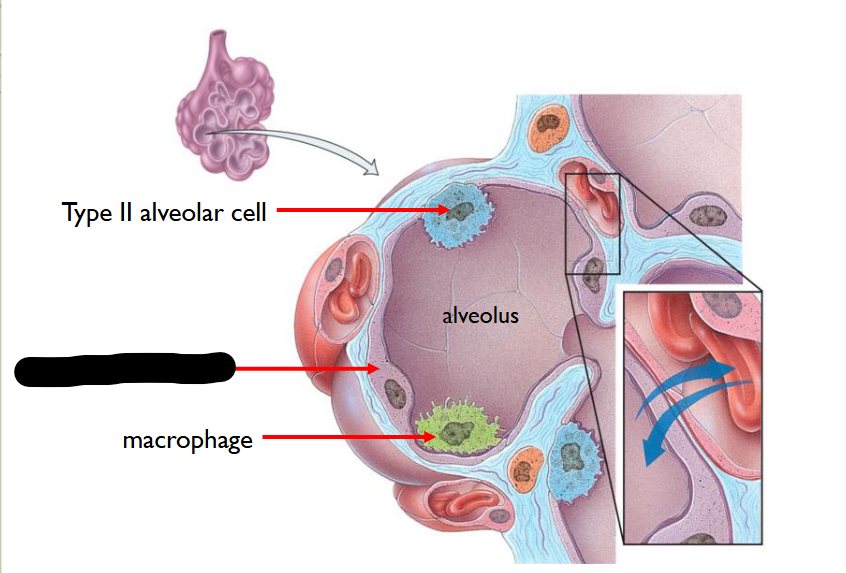
What structure is this within the Alveolus
Type I Alveolar Cell
95% of alveolar cells are this
FORM a nearly cont-lining of PULMONARY ALVEOLAR WALL
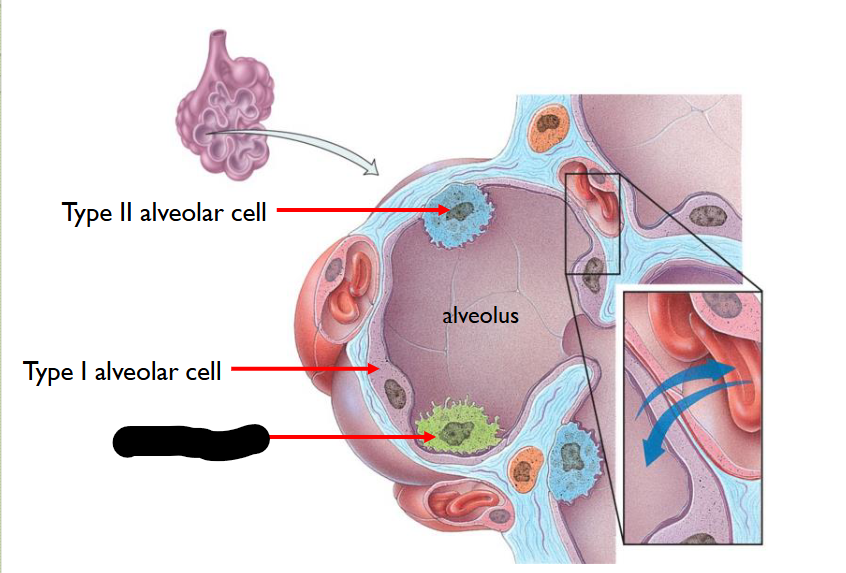
What structure is this within the Alveolus
Macrophage
Removes fine Dust Particles / other Debris > within Pulmonary Alevolar Spaces
How does the Bronchial Tree go in-order?
Trachea - Main Bronchi - Lobar Bronchi - Segmental Bronchi Bronchioles - Terminal Bronchioles (CONDUCTING ZONE)
Respiratory Bronchioles - Alveolar Ducts - Alveoli (RESPIRATORT ZONE)
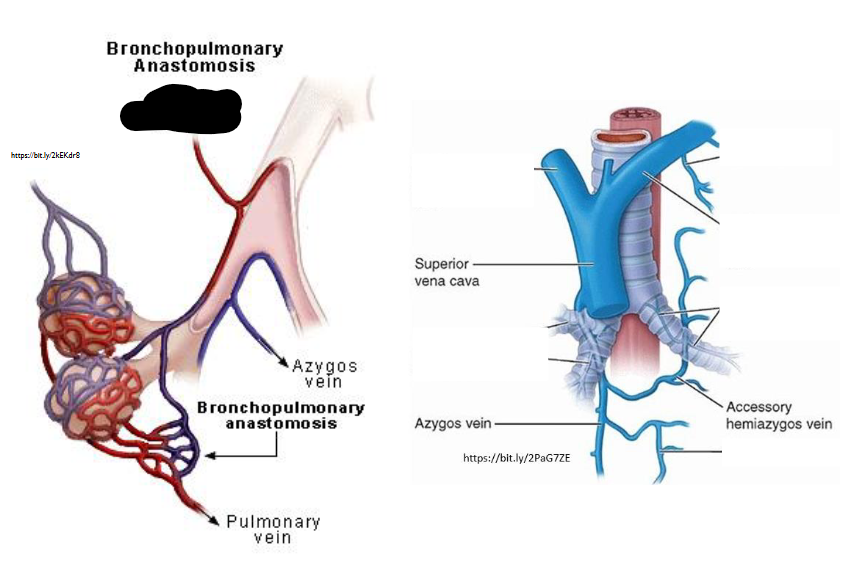
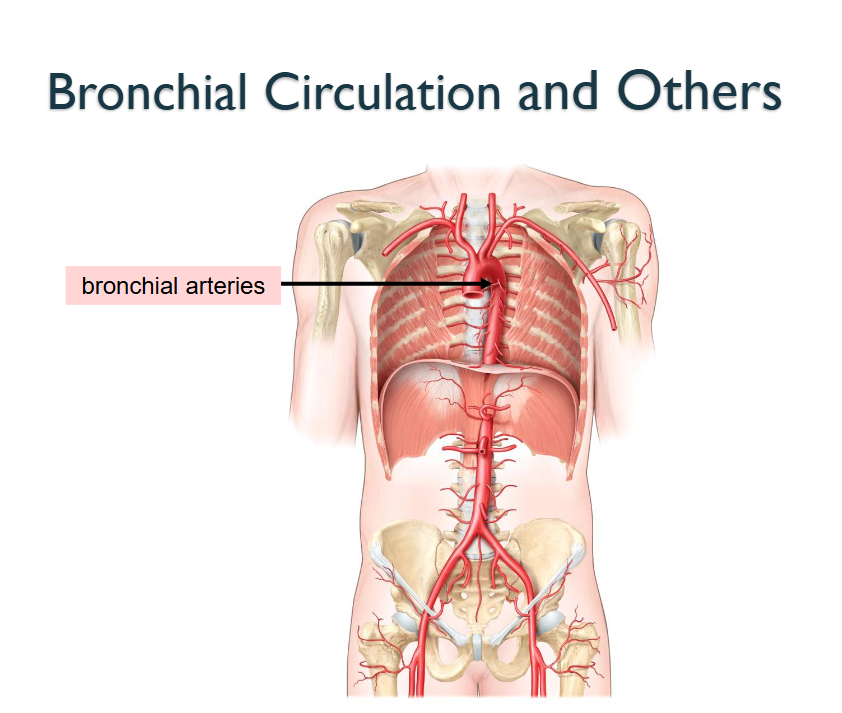
What Artery is this?
Bronchial Arteries
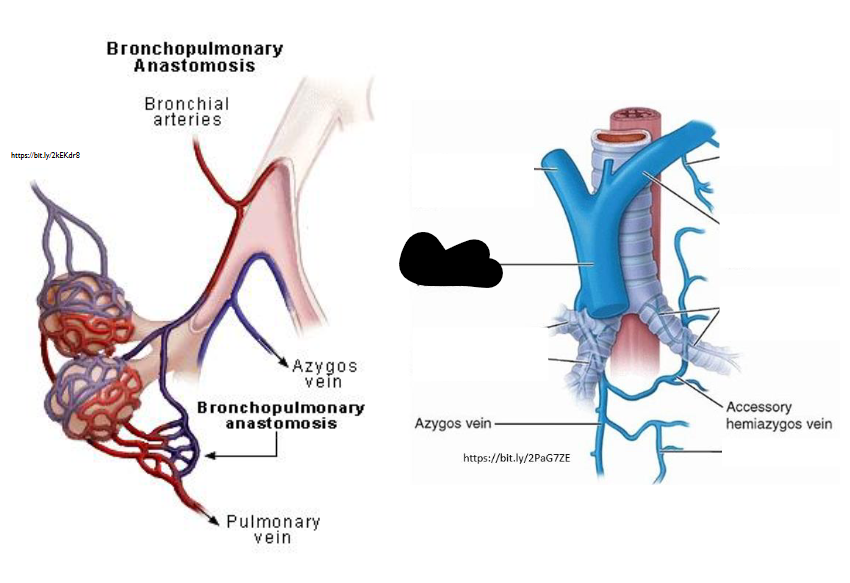
What Artery is this?
Superior Vena Cava
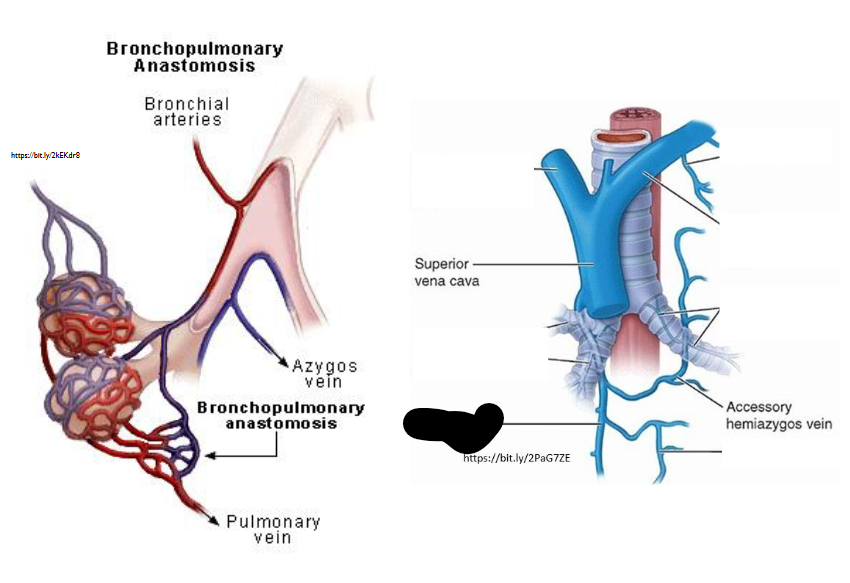
What Artery is this?
Azygos
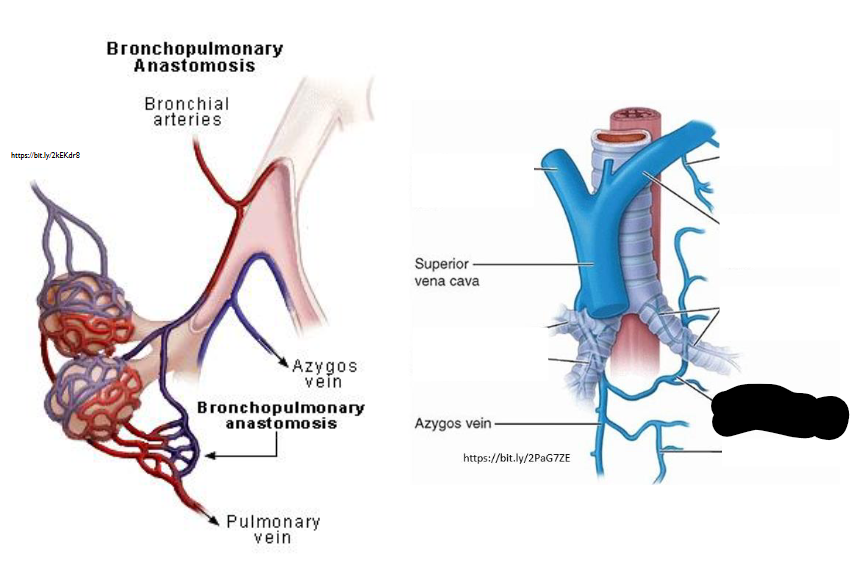
What Artery is this?
Accessory Hemiazygos
What Respiratory Muscle?
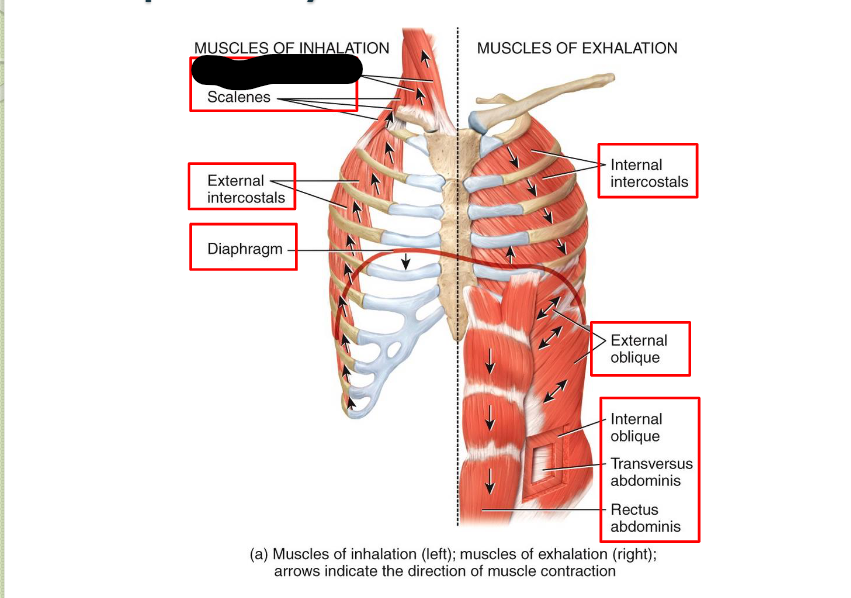
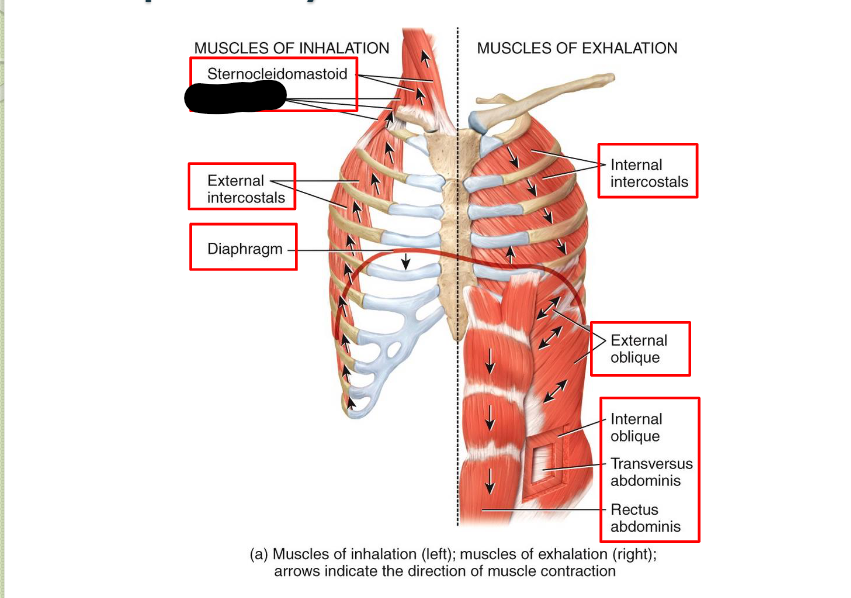
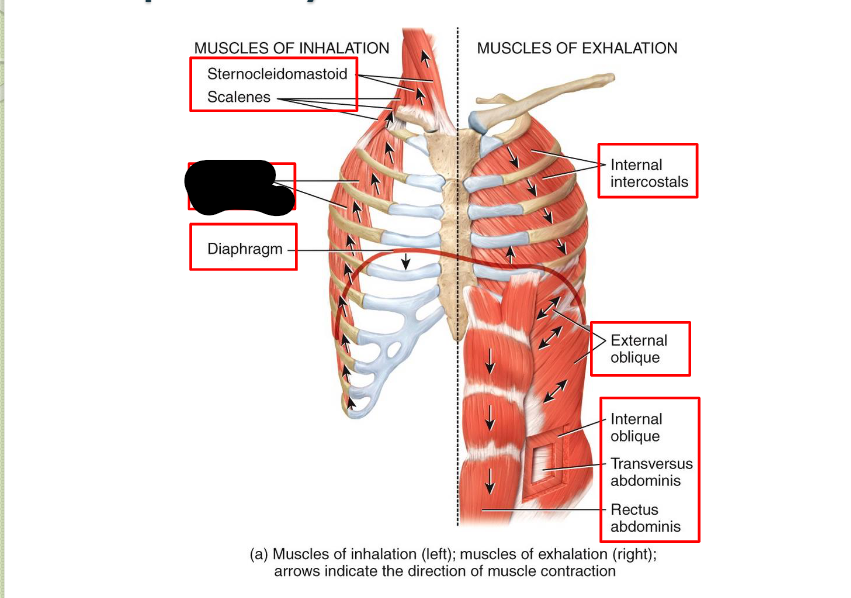
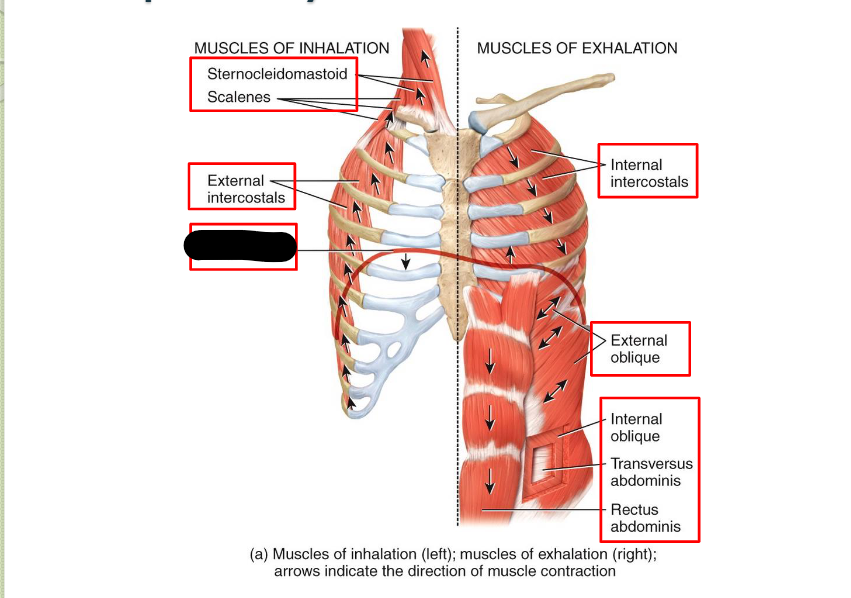
Sternocleidomastoid (Inhalation)
What Respiratory Muscle?
Scaleness (Inhalation)
What Respiratory Muscle?
External Intercostals (Inhalation)
What Respiratory Muscle?
Diaphragm (Inhalation)
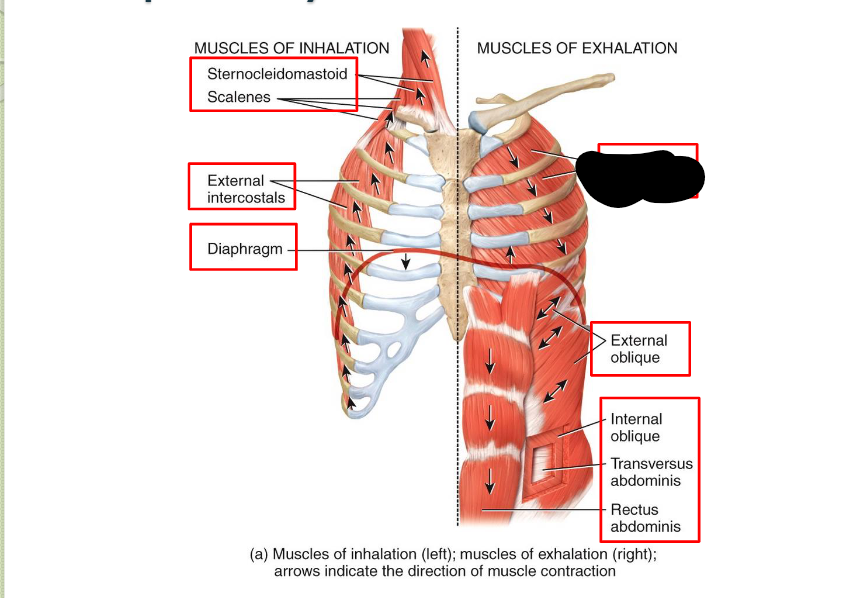
What Respiratory Muscle?
Internal Intercostals (Exhalation)
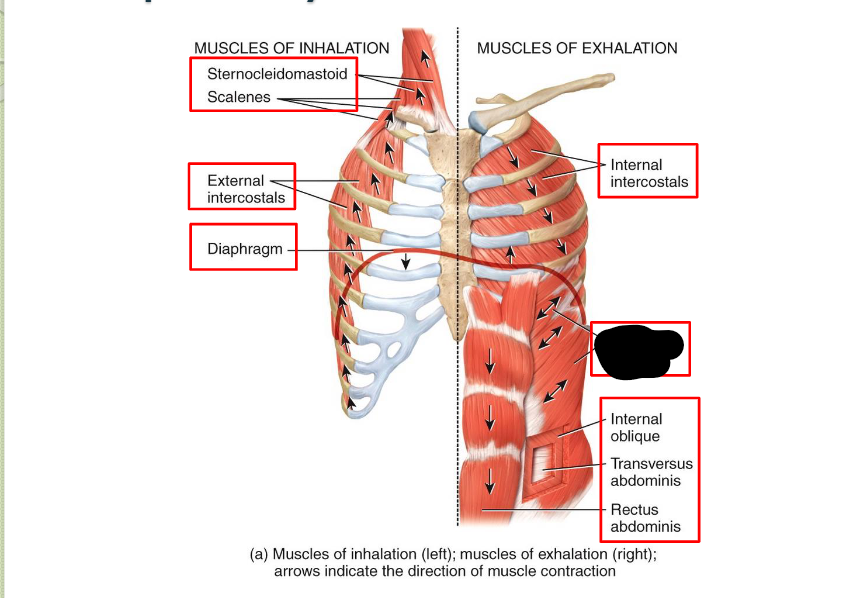
What Respiratory Muscle?
External Oblique (Exhalation)
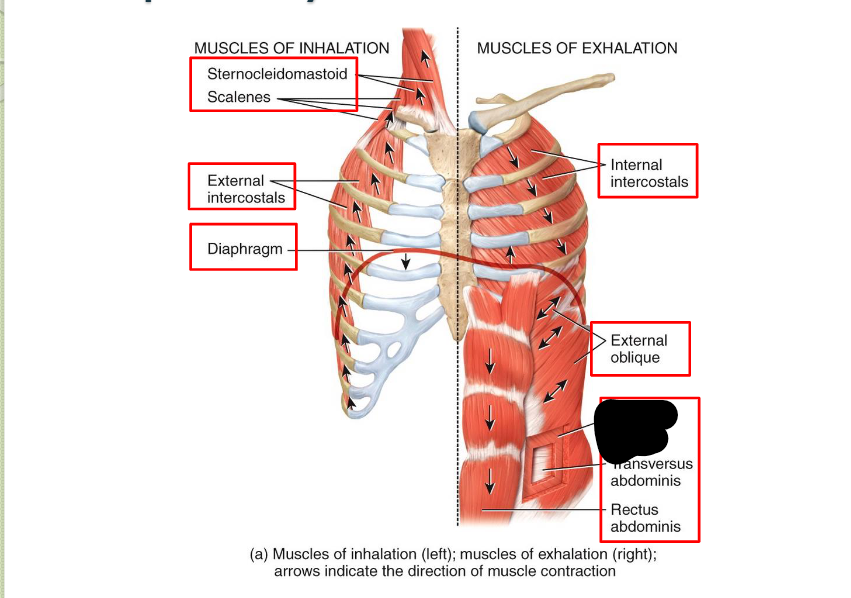
What Respiratory Muscle?
Internal Oblique (Exhalation)
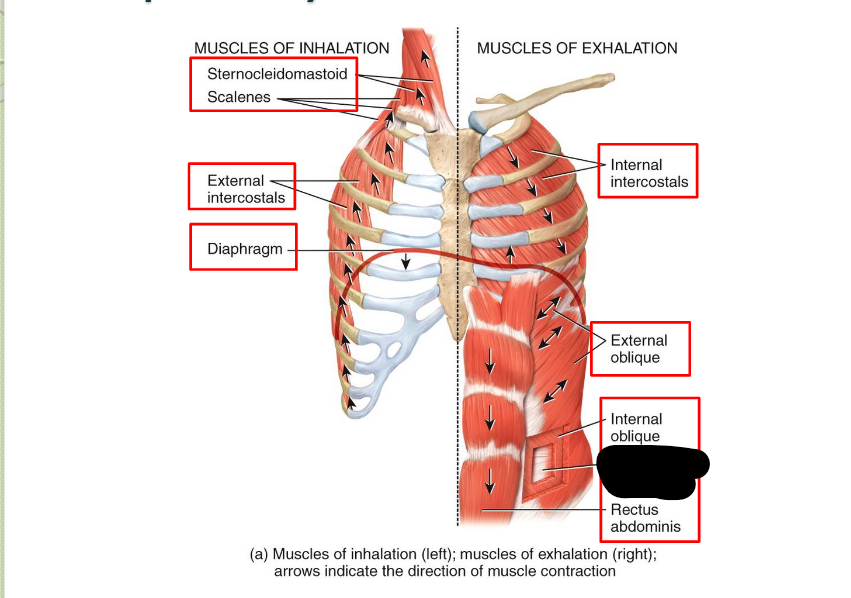
What Respiratory Muscle?
Transverse Abdominis (Exhalation)
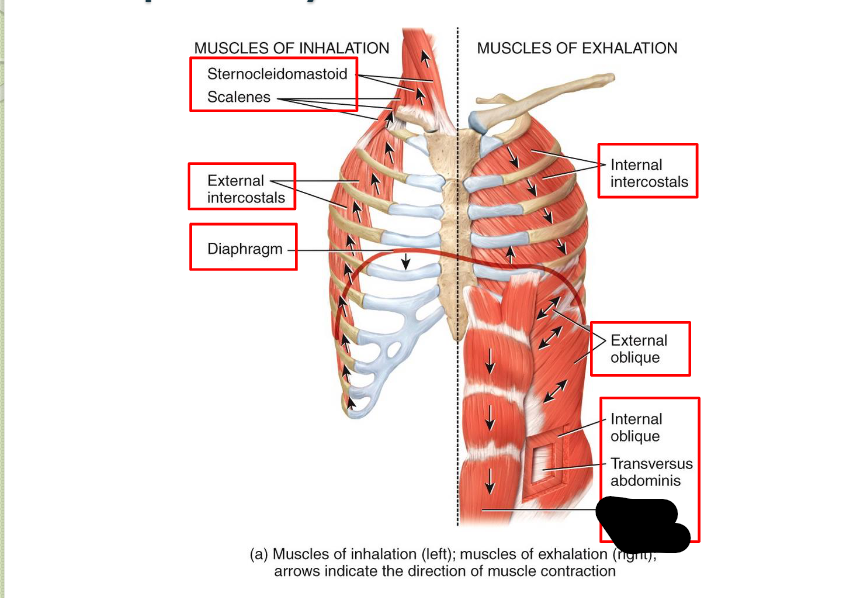
What Respiratory Muscle?
Rectus Abdominis (Exhalation)
The process of Gas Exchange?
R.Ventricle - P.Trunk - P.Arteries - p.Arterioles - P.Capillaries - P.Venules - P.Veins - L.Atrium
Conducts blood ciruclation > for EXTERNAL GAS EXCHANGE > allowing body to take in O2 / EXPE: C02
NOT RESPONSIBLE for nourishing lung tissue
What is the Process of Gas Exchange for Lung Tissue?
Left Ventricle - Aorta - (main portion) Bronchial Arteries - (sub-division; - lung tissue - right atrium) - (little portion) Lung Respirtory zone - (sub-division- pulmonary capillaries - left atrium)
Provides blood supply to / responsible for NOURISHING LUNG TISSUE
PART OF SYSTEMIC CIRUCLATION
What is Bronchopulmonary Arterial Anastomosis?
Unusual connection between pulmonary (heart - lung) / bronchial (lung - heart)
What is being worked upon during Inhalation / Eupnea? - (healthy breathing)
Diaphragm (75%)
External Intercostals (25%)
What is being worked upon during Strenuous Breathing?
Accessory Muscles:
Sternocleidomastoid (RAISES STERNUM)
Scalenes (PULLS up RIBS 1/2)
Pectoralis MINOR (PULLS up RIBS 3/5)
Internal intercostals
As well
with;
Abdominal Muscles
Rectus Abdominis
Extermal/Internal abdominal obliques
Transverse Abdominis