3.5 - economic growth,, short and long term, PPC
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
economic growth
increase in real GDP/ real quantity of goods and services produced over a period of time
measures of economic growth
% change in rGDP over time
% change in rGDP per capita over time (*better indicator of standard of living)
formula for %change in rGDP per capita
%change in rGDP per capita = (%change in rGDP) - (%change in population)
causes of growth
increase in AD *short-term
increase in SRAS *short-term
increase in LRAS *long-term
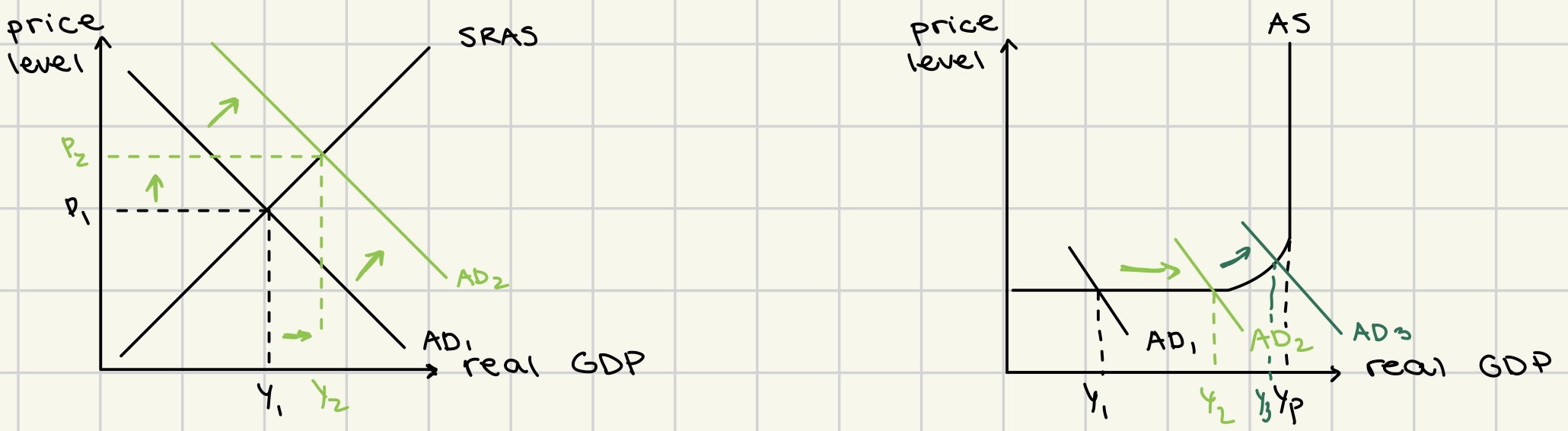
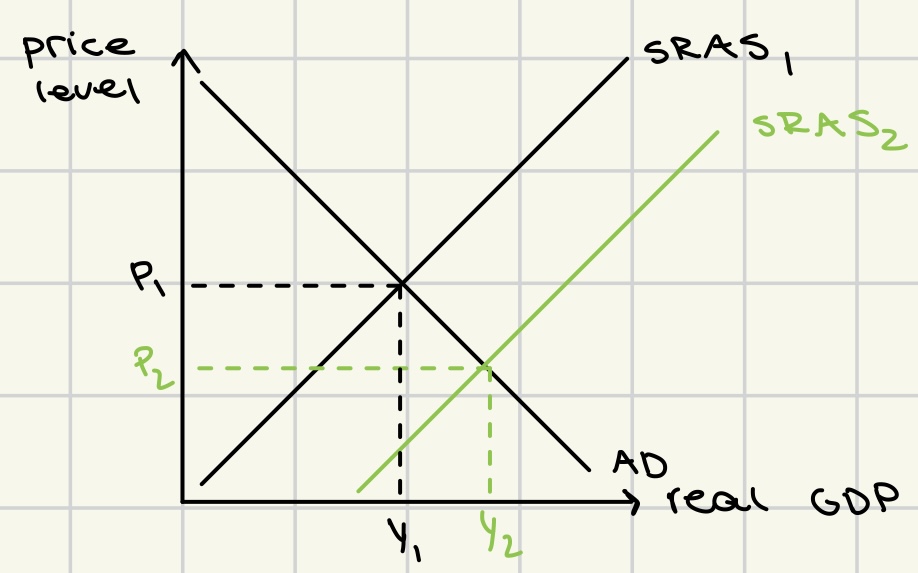
short term growth through increase in AD
monetarist:
increase in rGDP
no increase in potential output
no LRAS curve shift
Keynesian:
increase in rGDP
no increase in potential output
no AS curve shift

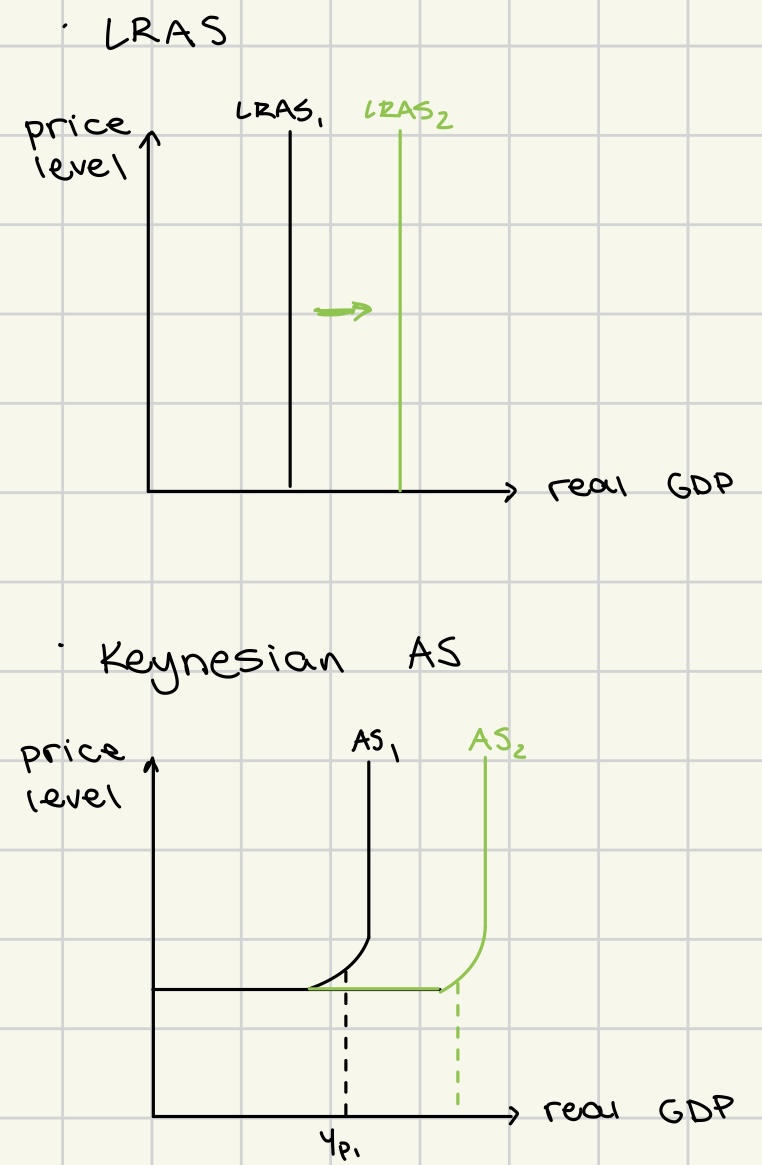
short run growth through increase in SRAS
less often way of growth
increase in rGDP
no increase in potential output
no LRAS curve shift
moved by
fall in prices of factors of production
increase in subsidies
positive supply shocks
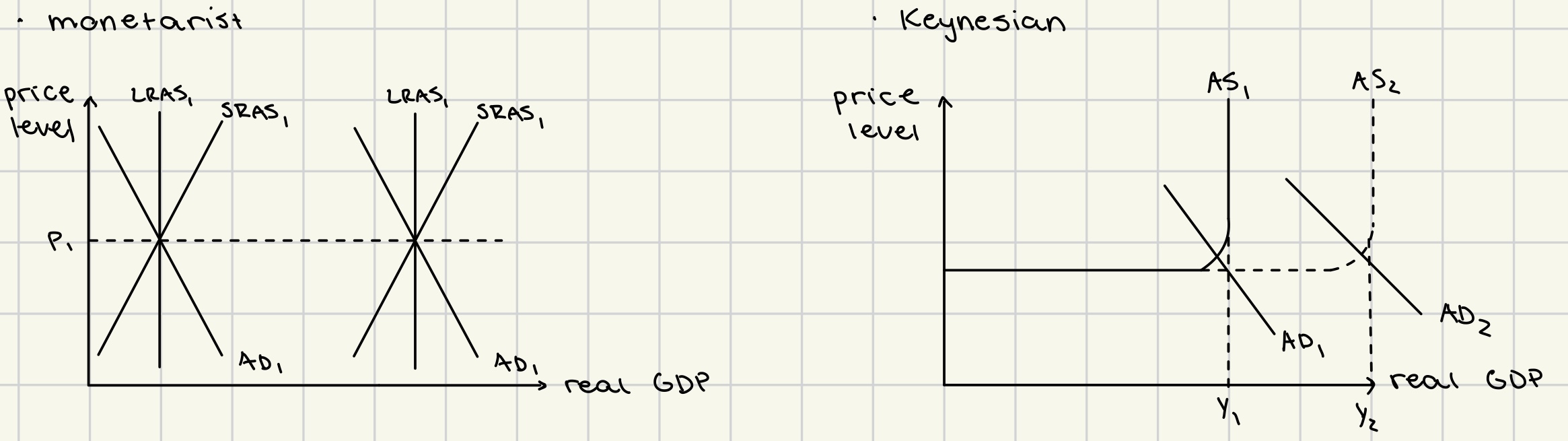
long term growth monetarist + Keynesian
due to
increase in quantity
increase in quality of factors of production
technological improvements
efficiency improvements
institutional changes
changes in macroeconomic equilibrium over long-term
due to
shifts in aggregate supply and demand
changes in productivity
adjustments in policy measures that enhance economic capacity
production possibilities curve (PPC) model
maximum output that can be produced by an economy with fixed resources and technology
given maximum employment of resources and efficiency in production
ways of moving closer to the PPC
reduced unemployment
improving the efficiency of resource use
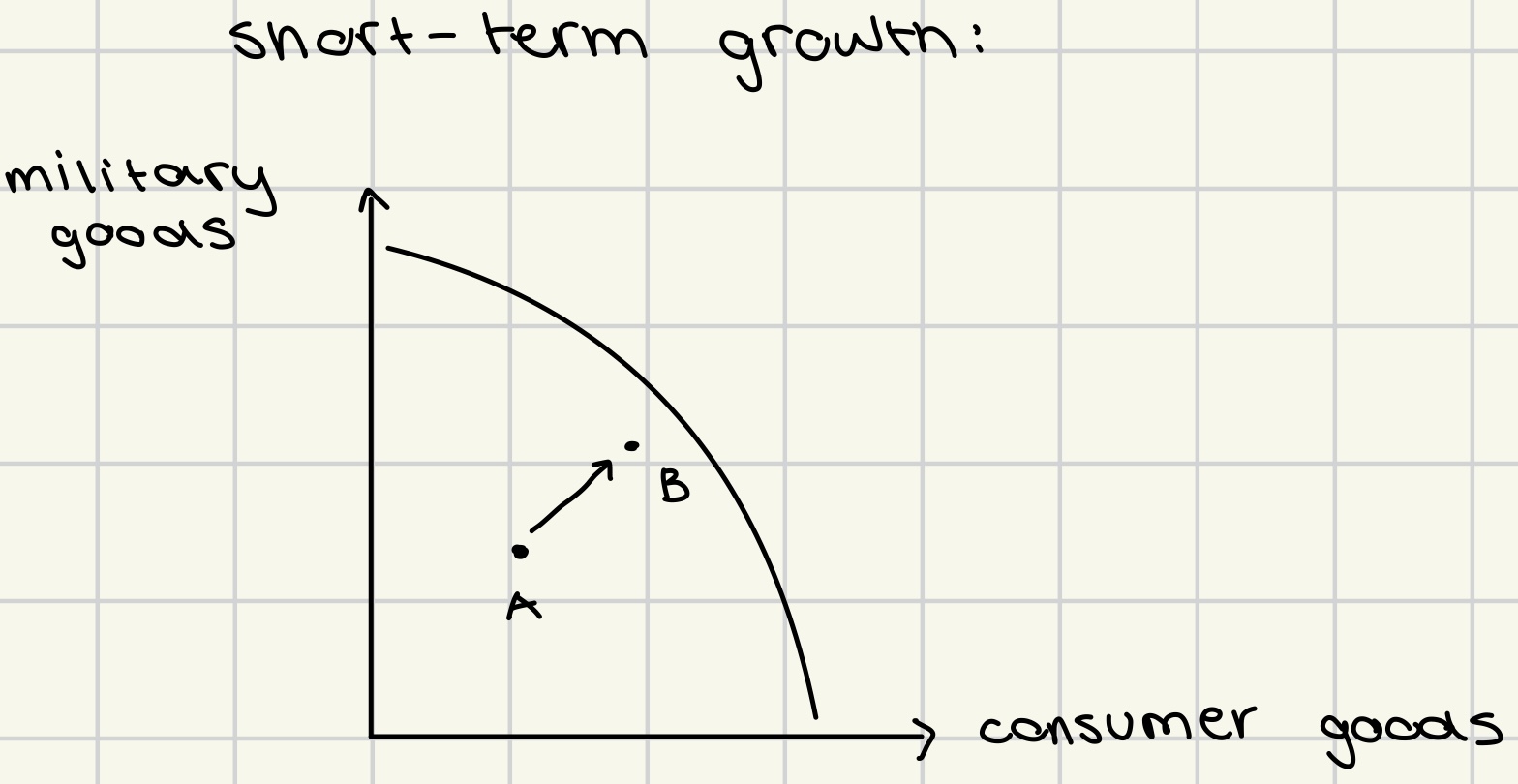
short-term growth on the PPC
reduction in unemployment
improvement in efficiency
*limited amount of economic growth (only A → B)
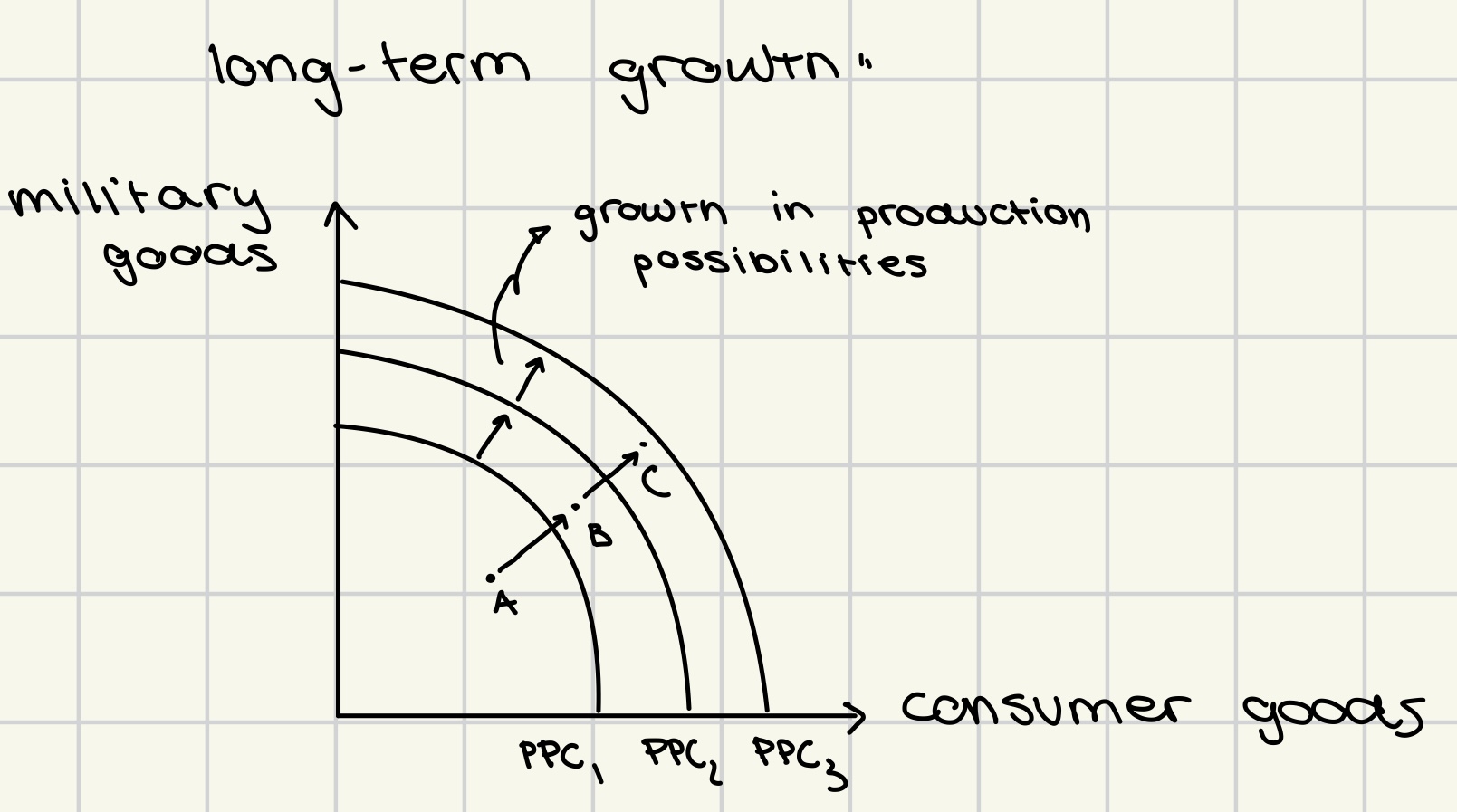
long- term growth on PPC
growth in production possibilities (PPC1 → PPC2 → PPC3)
actual growth (A → B → C)
increase in resource quantities (physical capital, ecological resources)
improvements in resources quality (physical capital, labor, ecological resources)
technological change
problem with long-term growth in PPC
as quantity and quality of resources grow, efforts must be made to
ensure sustainable development
avoid resource depletion
in order for the actual output to grow along with production possibilities
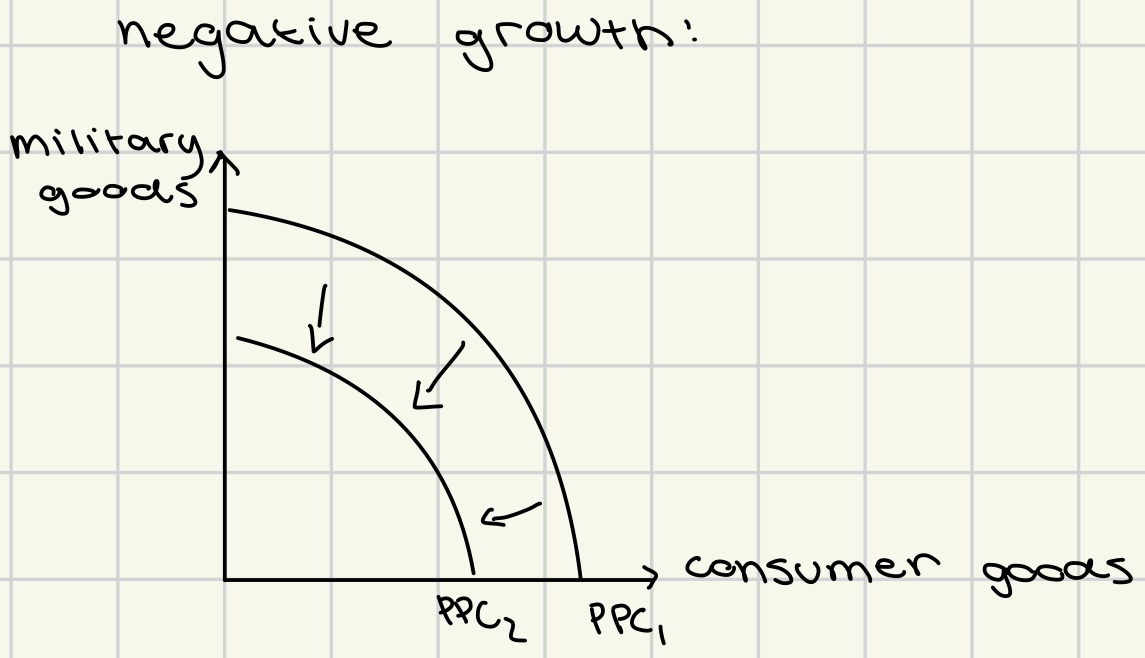
negative growth on PPC
less of the two goods is being produced
lower quantity
lower quality
factors affecting economic growth
higher standards of living
potential environmental degradation
distribution of income
living standards
levels of income, wealth and consumption
living standards ↑ when rGDP > population growth
factors of living standards that are affected by economic growth
distribution of income
household spending
share of income controlled by women
government spending on merit goods
potential environmental degradation
rapid growth => unsustainable resource use:
urban air pollution
soil degradation
flooding
overgrazing
deforestation
economic growth & environmental sustainability can be pursued when:
governments implement market-based policies
internalize the externalities → correcting them and providing incentives for sustainable resource use
governmental environmental regulations
increased emphasis on human capital production over physical capital
increased emphasis on ‘green’ investments
problem with factors affecting economic growth (living standards, environment, distribution of income)
due to likelihood of two-way causality it is difficult in real world to determine what causes what
…. economic growth → factors affecting → economic growth → ……