2. history of European colonization: Chapter 2: The major metropoles
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
27.32
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
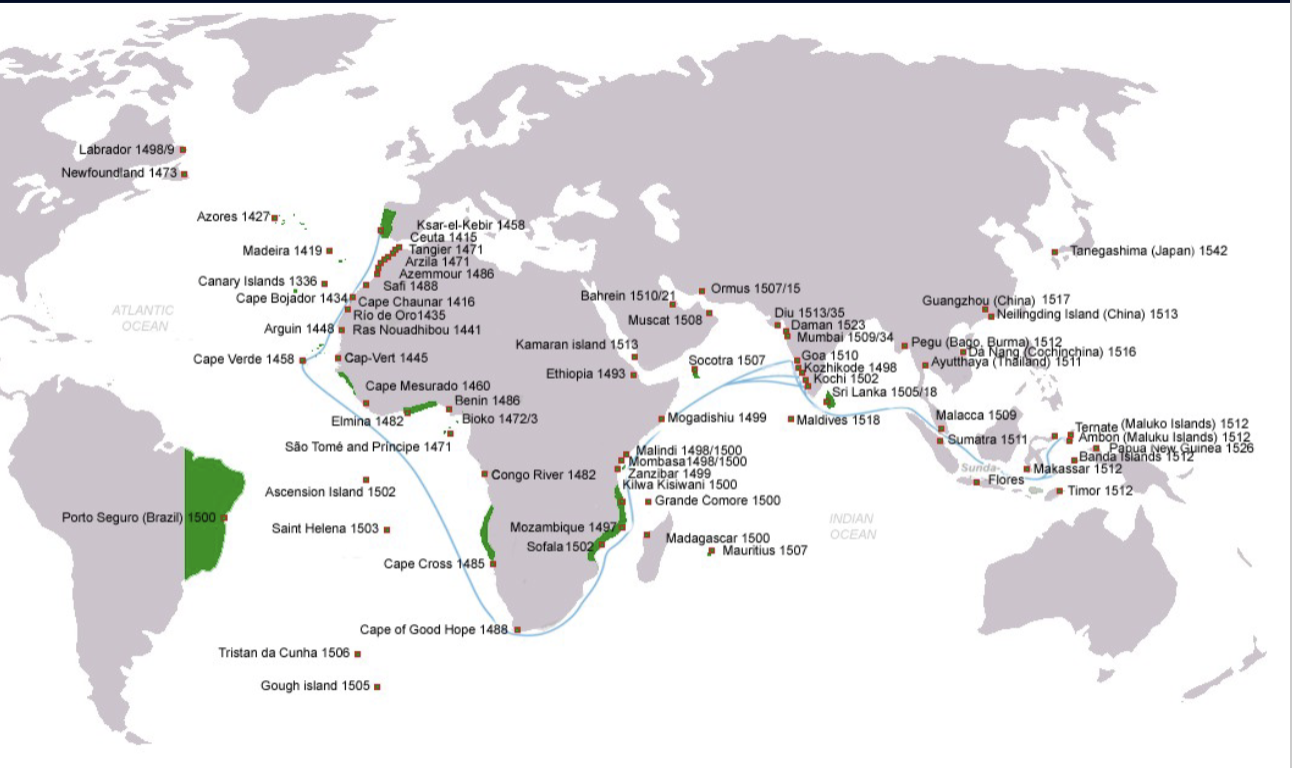
settlements Portugal dates
1415: ceuta (first settlement)
1419: madeira
1427-1431: azores
1434: cape bojador
1460: cape verde
1462: serra lyoa
1470: sao Tomé and Principe
1472: Bioko
1473: annobon
1483: congo river (diogo cao)
1487: cape of good hope (bartolomeu dias) = hope to circumvent africa and reach india
india:
1498: Calicut (vasco da gama)
1510: Goa (afonso de albuquerque)
Henry the navigator
late 14th till 15th century
prince of Portugal
obsessed with naval travel and supported trips
reasons portugese exploration
location
fighting muslims
ottomans (emerging in 15th century) blocked old trade routes with east
portuguese nation < Reconquista (recapture territory) on muslims
aspirations
hope to find gold
prester john (legend) and a grand alliance christians (hoped to create this)
estado da india
indian state
established by afonso de albuquerque in goa (capital portugese empire)
dominance of the oceans
armed ships
enclaves
no conquest of land due to demographic incapacity
trade with Europe
40% pepper trade
taxation of trade on the indian ocean
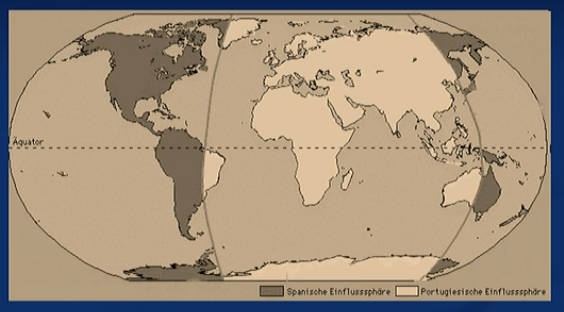
Spanish reach america
1492 => Portugal had rejected columbus in 1484 (very upset)
treaty of tordesillas
1494
—> solving spanish-portugese rivalry by dividing the world into 2 spheres of influence
(very similar to situation in berlin after war
Portugal reaches Brazil
1500
Pedro Alvares Cabral
not only trade but also plantations
gradually more to the inland for slaves and gems (<=> Africa)
immigration of europeans and African slaves
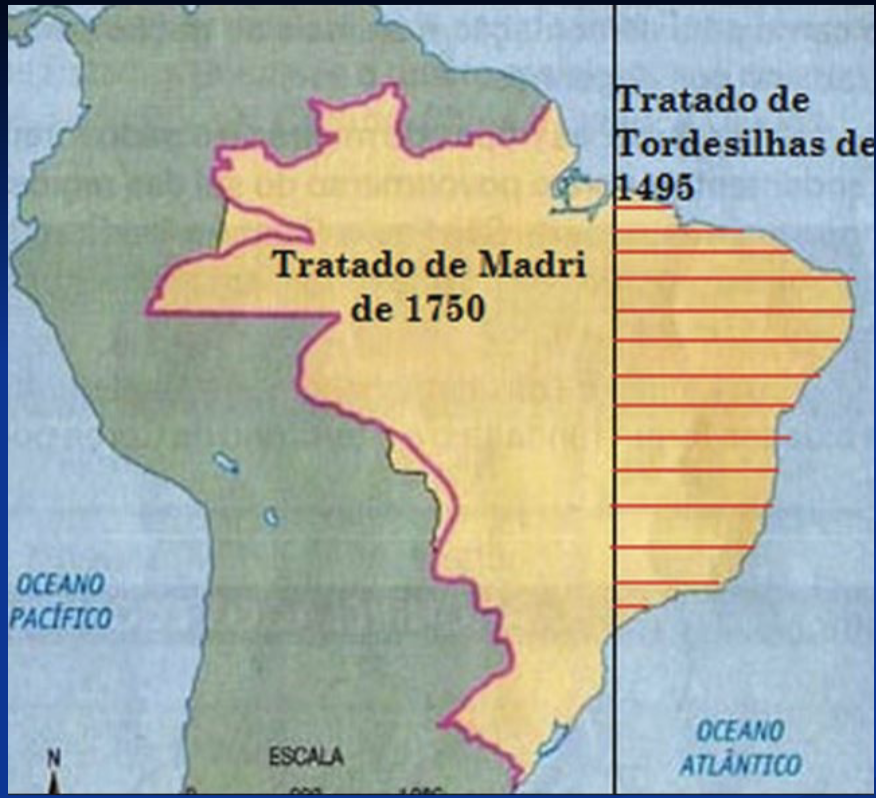
treaty of Madrid (1750): correction on Tordesillas
collapse of portugese empire (disintegration)
1578: defeated by Morocco at El Ksar-el-Kebir
death of king sebastian
1580-1640: Portugal occupied by spain (same monarch)
1588-1654: weakened by spain’s wars (against the dutch,…)
dutch and english victories in Asia
Portugal loses inter alia malacca (Malaysia) and Ceylon (Sri lanka)
portugal keeps Macau, portuguese India and East Timor
portuguese victories in Brazil and Africa
19th c: loss of brazil & expansion in Africa (Angola and Mozambique)
1974: decolonization after carnation revolution
Spain as unique and pioneer
used mostly Italian travellers: Columbus, Amerigo Vespucci,
pioneer
conquest of vast territories (<=> portugal = trade settlements)
economic exploitation
demographic impact
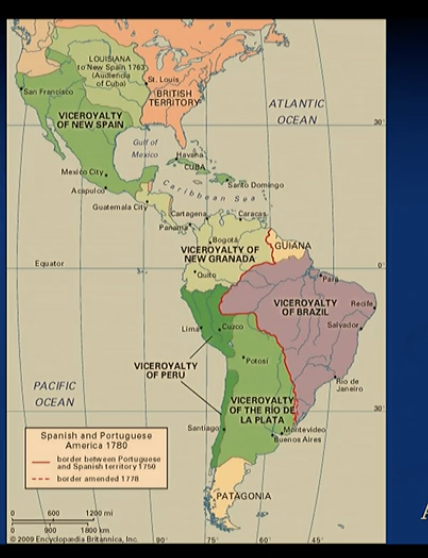
conquest of vast territories by spain
1492: Hispaniola (Haiti + Domenican Republic) => first capital of spanish colonial empire in santo domingo (first one in America)
1512: Panama (american continent)
1519-21: Mayas & aztecs (cortés) —> New Spain
1524-32: Incas (Pizarro) —> New Grenada & Peru
1536: Buenos Aires; 1541: Santiago
Philippines (1521: Magellan=first to circumvent the globe; 1565: Manila)
North America:
1565: florida
1595-: New Mexico (and Arizona)
1602 (actually 18th c.): California
1763: Louisiana (took over french colony)
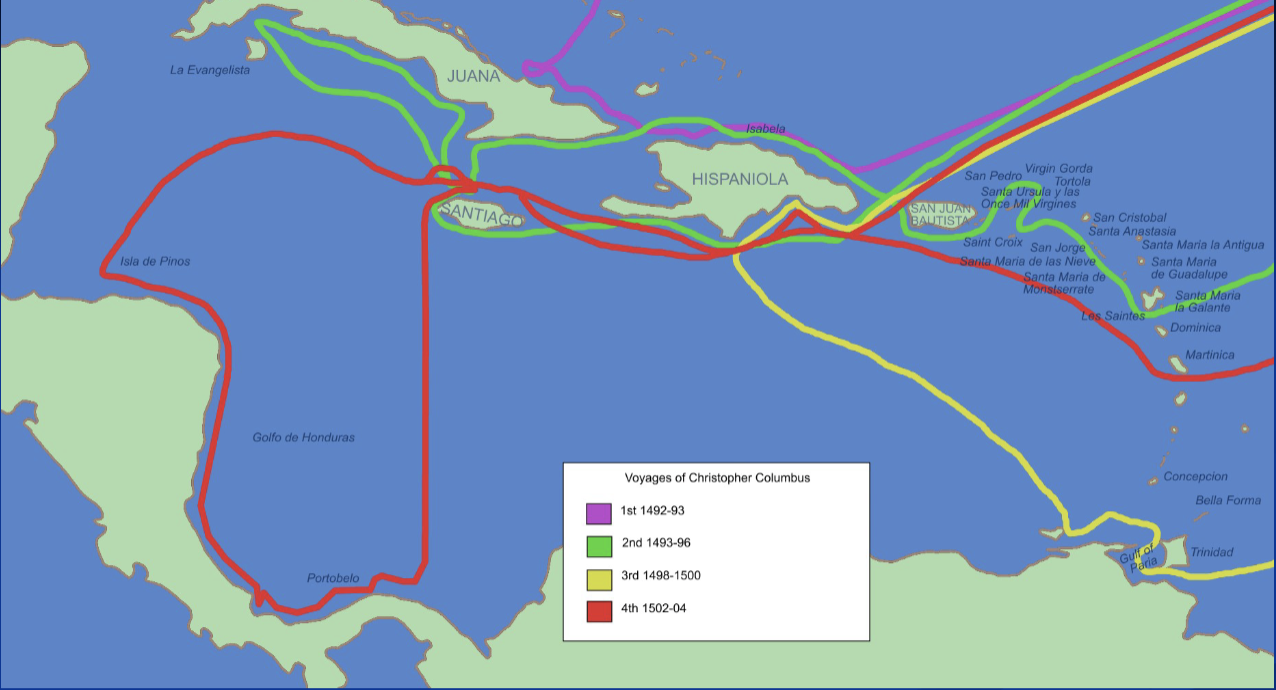
voyages of Christopher columbus
1492-1504
economic exploitation by spain
new forms of enrichment (making money out of colonies) => became richest country in Europe
silver mines in Mexico and Peru
plantations & Haciendas (coffee, cotton, sugar)
but
inflation and bankruptcy
many wars
victories: charles V, lepanto (1571)
defeats: Armada (1588) & thirty years’ war (1618-1648)
1713: loss of possessions in Italy and Low Countries
demographic impact of Spain
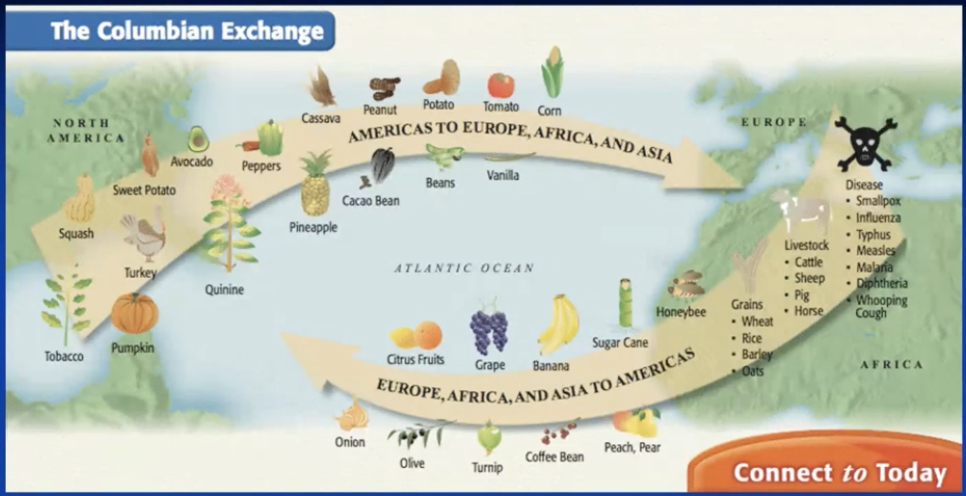
the columbian exchange
Fauna and Flora
diseases (smallpox and influenza)
Hispaniola: 3-4 M = 1500: 15000 ppl, 1570: 0 ppl
America: 1600: 1/10 of ppl in 1500
almost empty continent => new immigration waves
white settlers
240.000 Spaniards in 16th and 500.000 in 17th c
the transatlantic slave trade (mostly by Portugal) = deportation of 11M African slaves
ethnic mixes: mestizos (EU + local populations), mulattos (EU + Africans) and zambos (Americans + Africans)
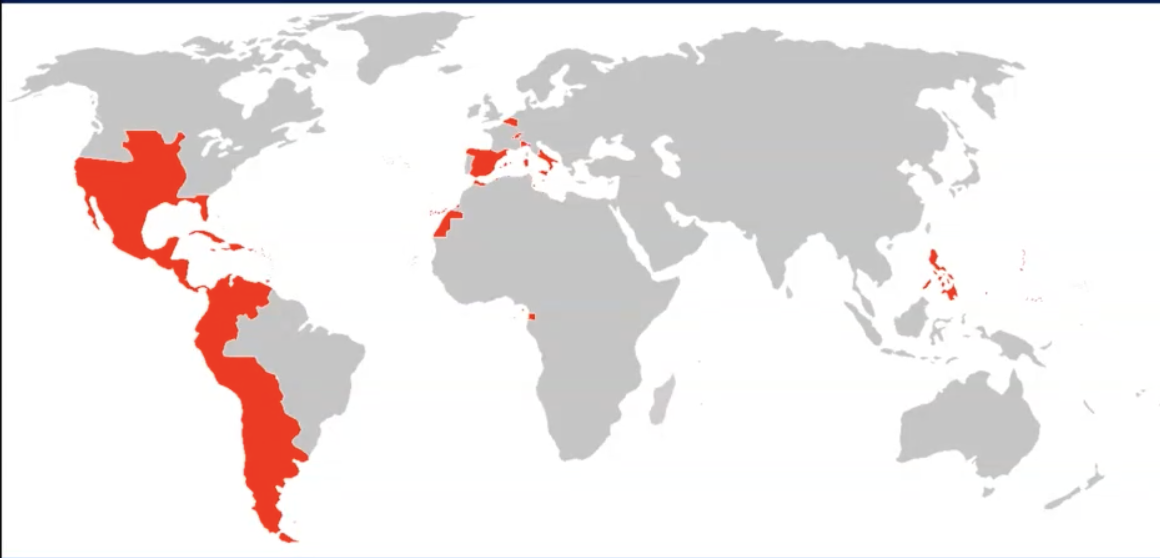
disintegration of spanish empire
17th century: loss of many carribean islands
jamaica, st domingue (haiti), guyana,…
18th c: still victorious
The Jenkins’ Ear War (1739-1742) = spain defeated britain, spanish empire kept existing for another century
1810-1825: decolonization
loss of latin american continent
1898: Spanish-american War
loss of puerto rico, cuba and philippines
20th c: minor colonies
equatorial guinea, spanish sahara, parts of morocco
dutch particularities
background
naval expertise (just like portugal and Spain)
eighty years’ war with spain (and portugal)
—> low countries split in north and south
—> stretched to colonies
the officially chartered company (17th century)
first modern joint stock company (shares)
—> accumulate a lot of money for rather risky project, since there were many share holders individual risk was reduced
trading firm with military and political power (state was involved)
two companies (smaller comagnies joined)
1602: Vereenigde Oost-indische compagnie
1621: westindische (caribean) compagnie
trade monopoly
initially spices, later also coffee, tea and textile
the northeastern passage
dutch republic: willem Barentsz (1594-97)
reached spitsbergen, wintering on nova zembla
looking for india
decided it was not the best idea
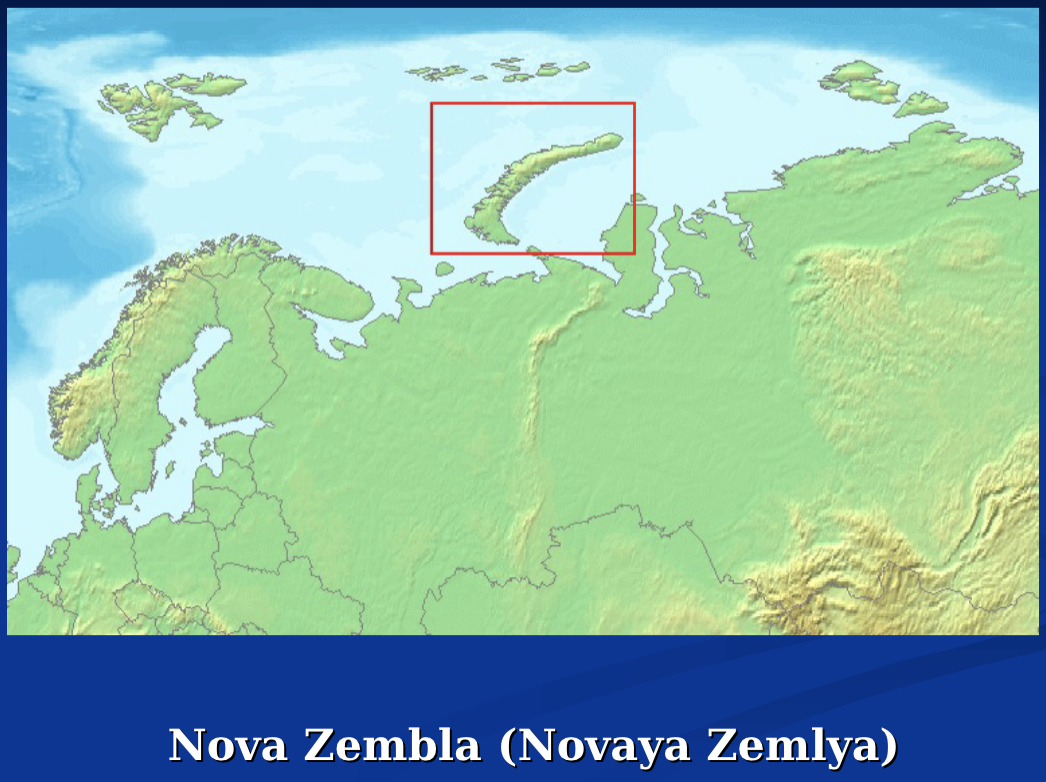
muscovy company
England
1555
reached novaya zemlya, via white sea to russia
the northwestern passage
Henry Hudson (1565-1611)
2 trips looking for passage to india:
1609: for the dutch VOC => New York (Hudson river)
1610: for england => Canada (hudson bay)
—> killed by crew
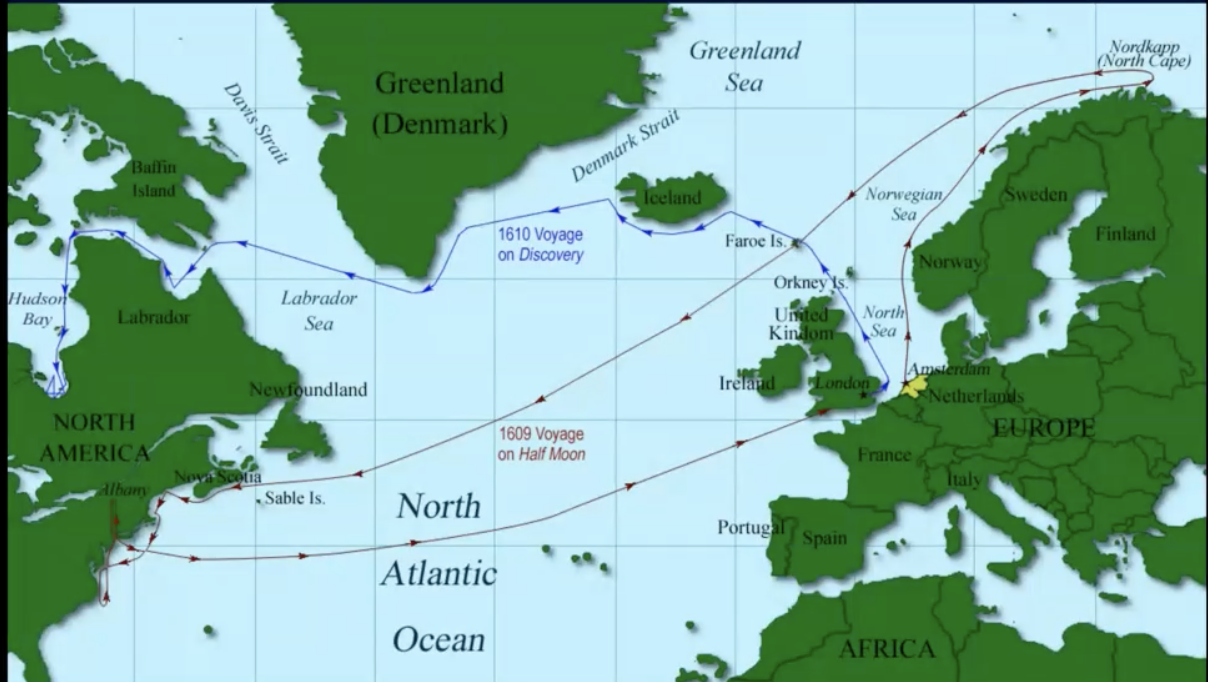
timeline the New Netherlands
1609: explored (Hudson)
1615: first fortification
1623: province
1626: purchase of manhattan (island, very cheap)
Peter Minuit (“Belgian”) & new amsterdam (Island Man)
1664: conquered by England
New York
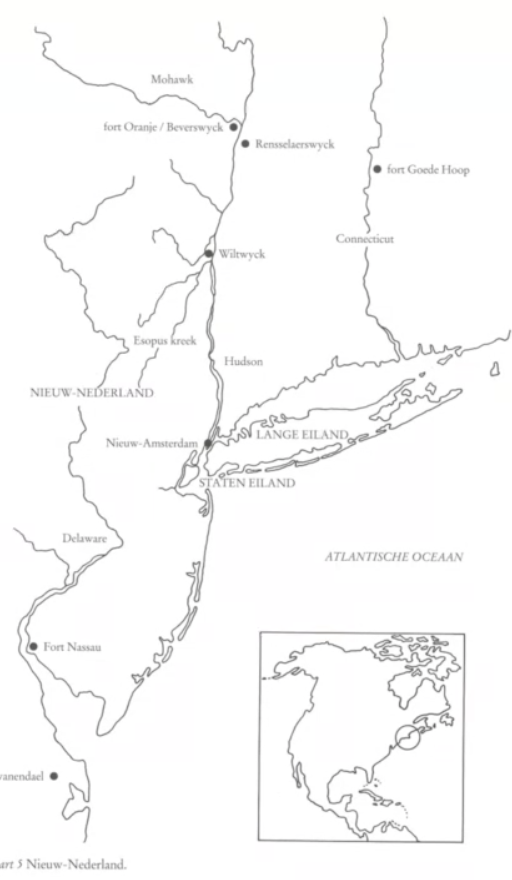
the southeastern passage
Jan Huygen van Linschoten (1563-1611): Itinerario (1596)
after failures of northwestern and northeastern => went to portuguese for information (experience, information from arabs,…)
kickstart golden age VOC
conquests VOC
1605: spice islands (moluccas, present day indonesia) = treasury of spices
—> cloves, cinnamon, nutmeg, pepper,…
1619: batavia (java, present-day jakarta)
1641: Malacca (present day Malaysia) = very strategic
1658: Ceylon
India
European settlements in India
coastline was patchwork of different european empires
inland was not European
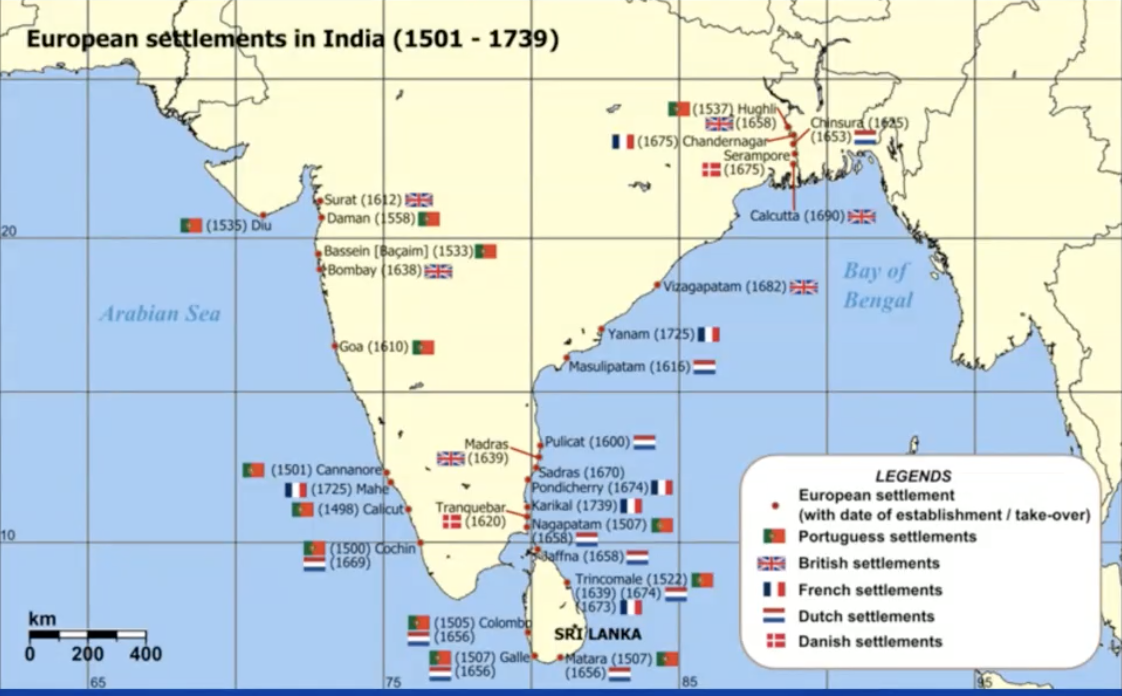
trade posts VOC
Taiwan (1624, 1662 driven away by coxinga)
Japan (1641-1853 the Dutch only Europeans who were allowed to trade once a year on artificial island Deshima near Nagasaki = superior position)
resupply points VOC
cape colony (Jan van Riebeeck, 1652) = dutch settlers called boeren
further exploration by VOC
New Holland (Australia)
—> dutch captains: Willem Jansz (beginning 17th c), Abel Tasman (middle 17th c —> tasmania) = did not completely circumvent the island, Johan Blaeu (1659)
New Zealand
piracy WIC
compete with spanish in america (caribean) => attacked spanish ships full of silver
Piet Hein (1577-1629) and the Silver Fleet (1628) = successful raid
state terrorism
wars WIC
with spain
dutch antilles (Aruba, Curacao, Bonaire): 1620-1648
with portugal
ex temporary conquest Recife/Mauritszstad Brazil: 1630-1654)
with england
1664: loss of New Netherlands => not too bad cuz much more interested in more lucrative Guyana’s
1667: conquest of Suriname on England (British Guyana)
English particularities
similar to other European metropoles:
maritime tradition (it’s an island!)
competition (17th c: Dutch, 18th c: French, 19th c: Russia)
different from other European metropoles
The Irish experience (1536)
the colonization of Ireland
establishment of plantations
settlers gained demographic majority in some regions
families were moving not just men
technological innovations (religious reasons)
mass-produced articles (textiles,…) rather than luxury goods (<=> Dutch empire)
profusion rather than scarcity and monopoly
first decades English colonization
John Cabot (1451-1498): 1497 Newfoundland (Italian sailor under English flag)
Francis Drake: 1577-1580 world travel (reached California) = circumvented the globe
= attempts to make own discoveries
the first voyages around the world
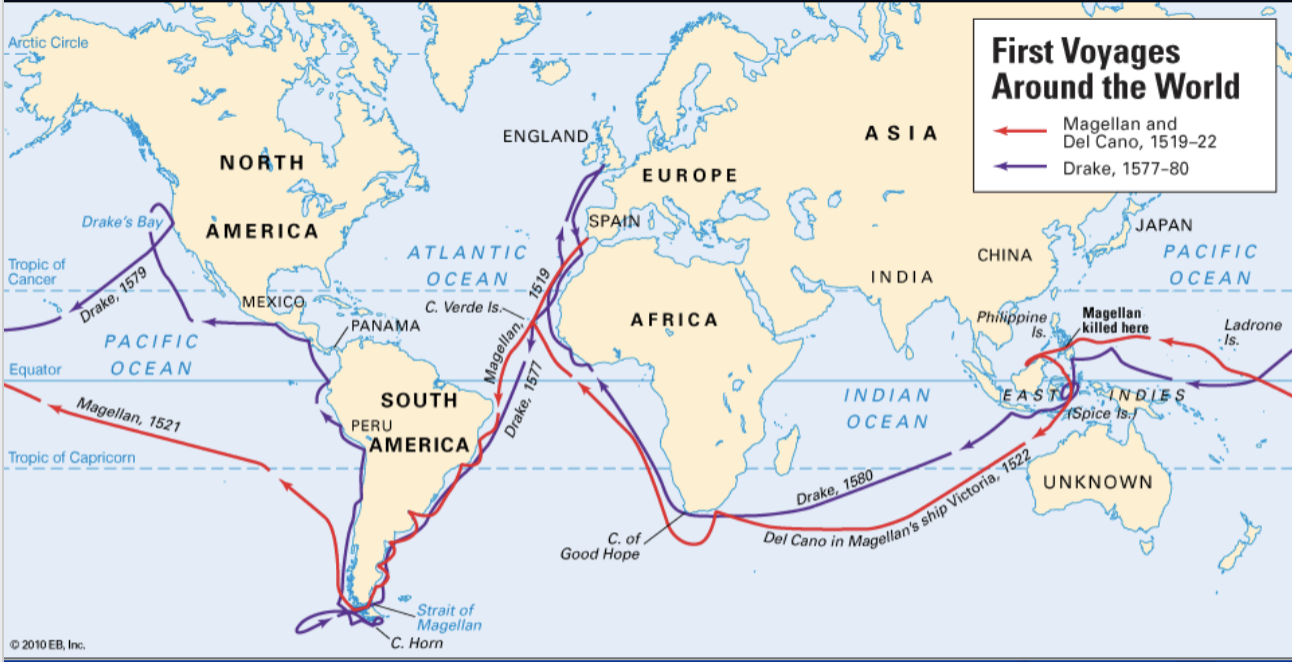
piracy and raids England
Francis Drake (in peacetime) = attacked spanish silver fleets (state terrorism)
Henry Morgan in the 1660s (first governor of Jamaica)
Wars england
with spain
Francis Drake: 1588 defeat Armada (Spanish fleet)
conquest of spanish or foundation of new colonies
England in the caribbean
gradual conquest of spanish colonies
many attempts ia Barbados and Guyana = permanent
1655: Jamaica (Morgan becomes governor)
1666: Bahamas
profit from sugar plantations
1773: Jamaica 5X more profitable than British North America (=> much more keen on keeping this colony)
carribean planters were willing to pay roughly 8 or 9 times what a slave costs on the West African coast
England in North America
1607-1624: Jamestown (Virginia company, first english company —> pocahontas) = economy
tobacco, but exhausted soil and prices collapsed
terra nullius and native americans
1620: Plymouth (Pilgrim Fathers, first permanent english colony in present-day US) = religion
families & procreation (one of many reasons why america now majority white populations) vs mixed races in spain
1644: New York = conquest
1681: Pennsylvania (william Penn & Quakers) = philosophy (±religious)
Tolerance: Philadelphia (“brotherly love”)
mass migration (British Isles, Germany,…)
==> different colonies established in different times for different reasons
The thirteen Colonies
British North America
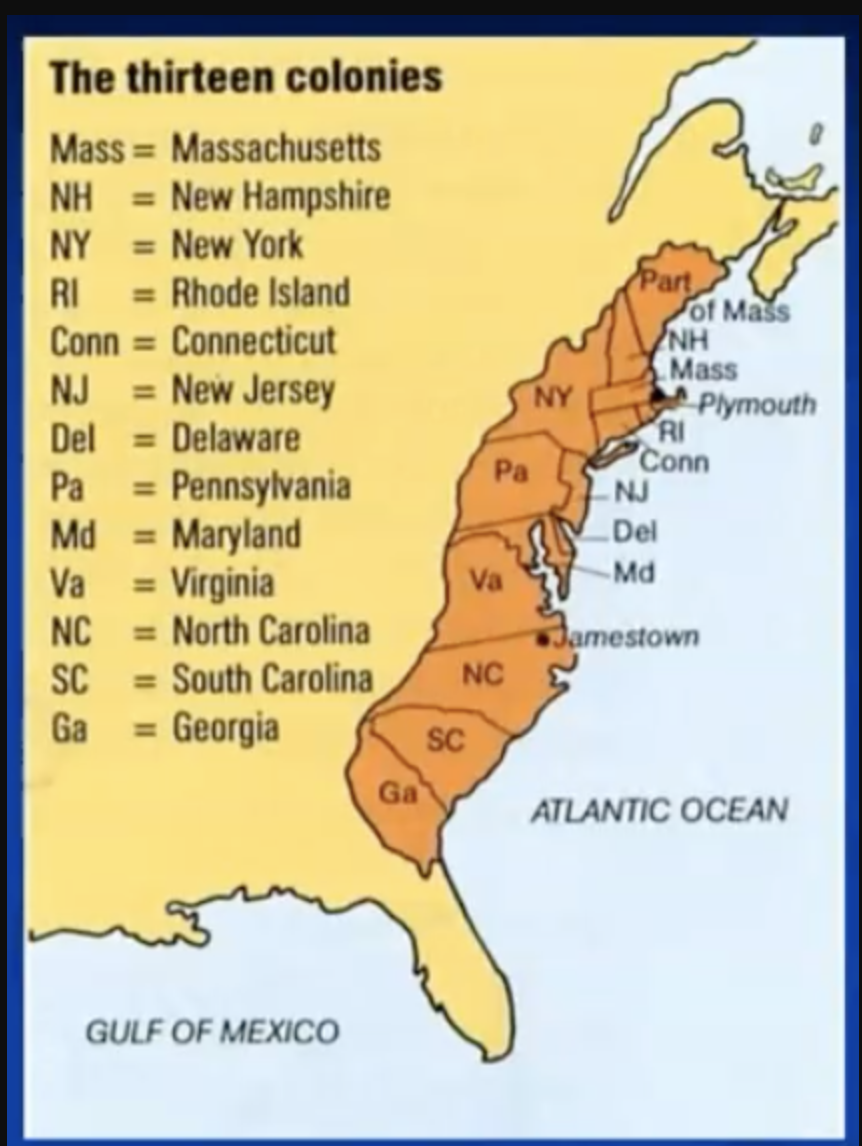
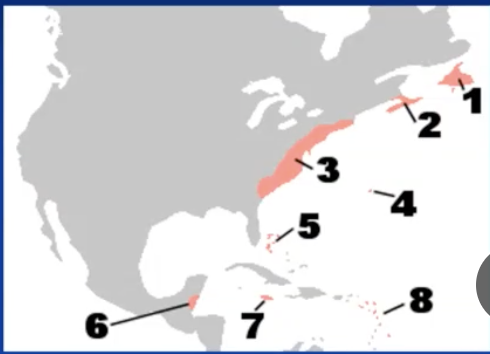
British colonies in north america cs 1750
Newfoundland
Nova Scotia (acadia)
the thirteen colonies
bermuda
bahamas
belize
jamaica
lesser antilles
England in Asia
1600: English East India Company
only 1/10 of means of VOC
first attempts
succes in India (1612: Surat on Portuguese)
Failure in East Indies (1622: ‘massacre of Amboyna’)
gradual growth
1639: fort St George (Madras/Chennai)
1661: Bom Bahia (bombay/mumbai)
1690: Fort william (calcutta/kolkata)
Anglo-Dutch Wars
Oliver Cromwell (17th c, interregnum, lord protector of the commonwealth of england, scotland and ireland)
expansion of naval fleet
doubled between 1649 and 1660
navigation acts (1651, 1660)
restricted foreign shipping for trade England and its colonies = obstruct the Dutch => war
1652-54, 1664-67, 1672-74
dutch proved stronger than england (victories Maarten Tromp and Michiel De Ruyter)
Glorious revolution
1688
william III of Orange marries Mary of England
collaboration
bank of england & stock exchange (financial expertise of dutch)
dutch keep supremacy until 1720
most important centuries for major metropoles
15th c: portuguese
16th c: Spanish
17th c: Dutch
18th c: English
french particularities
world leader eg in 1700
territory: france 2x larger than britain
population: france 3x larger than britain
little colonial interest (focussed on European continent)
colonies: often (some exceptions) big and thinly populated areas (didn’t want to lag behind <=> failed to invest)
little development
little immigration (exception algeria)
more about politics than about trade
compagnie des indes: nobles rather than merchants
1740: french export from india only half of british one
the New World France
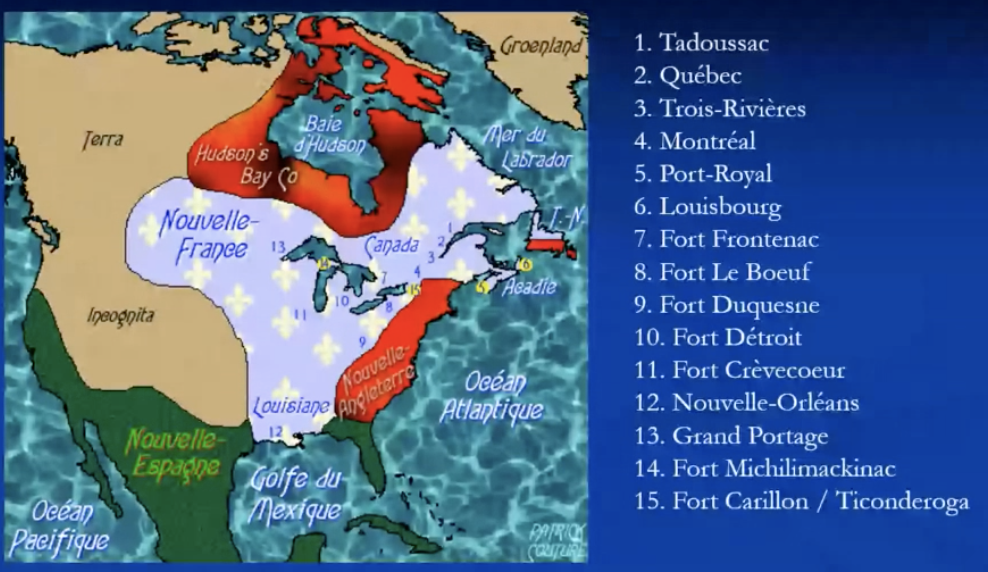
Canada
1534-42: Jacques Cartier explores St Lawrence
1604: Acadia
1608: Samuel de Champelain founds Québec
French Guyana (1624 ff)
many traces of French: place names, baguettes, buildings,…
Caribbean (1635ff)
Guadeloupe & Martinique (conquered on the spanish)
St Domingue (Haiti, officially in 1697) (half of hispaniola, first place columbus reached)
Louisiana
named after Louis XIV
1682: Cavalier de La Salle (1643-1687) sails the Mississippi river => french able to claim large territory
La nouvelle france
very big => surrounded british north america
France in the old world
1624ff: Senegal
1664: compagnie française des Indes orientales
islands in indian ocean
réunion, mauritius, seychelles
1673ff: colonies in India
pondicherry, chandernagar,…
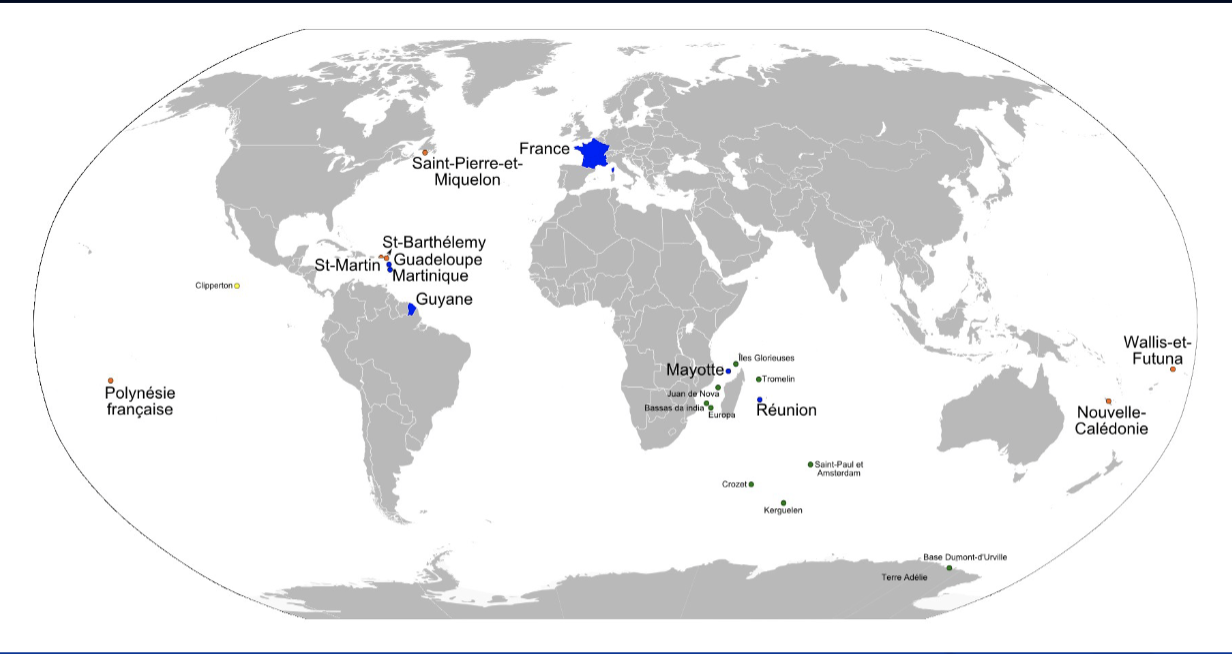
la france d’outre-mer
overseas departments and territories of France
Ostend company
1717-1731
Austria got southern netherlands => access to north sea
55 ships to China and India
Banquibazar (1726-29/44) = settlement in India => “first belgian colony”
other metropoles
Ostend company
Danish East India Company (1616)
Swedish East India Company (1731-1813)
Prussia
Courland