Descriptive Study Designs in Research
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Hypotheses Development
Data from descriptive research aids future hypothesis testing.
Explanatory Techniques
Methods like longitudinal or cross-sectional for deeper insights.
Surveys
Common tool for collecting descriptive research data.
Secondary Analysis
Utilizes existing databases for descriptive research insights.
Qualitative Study Designs
Classified under descriptive research for in-depth understanding.
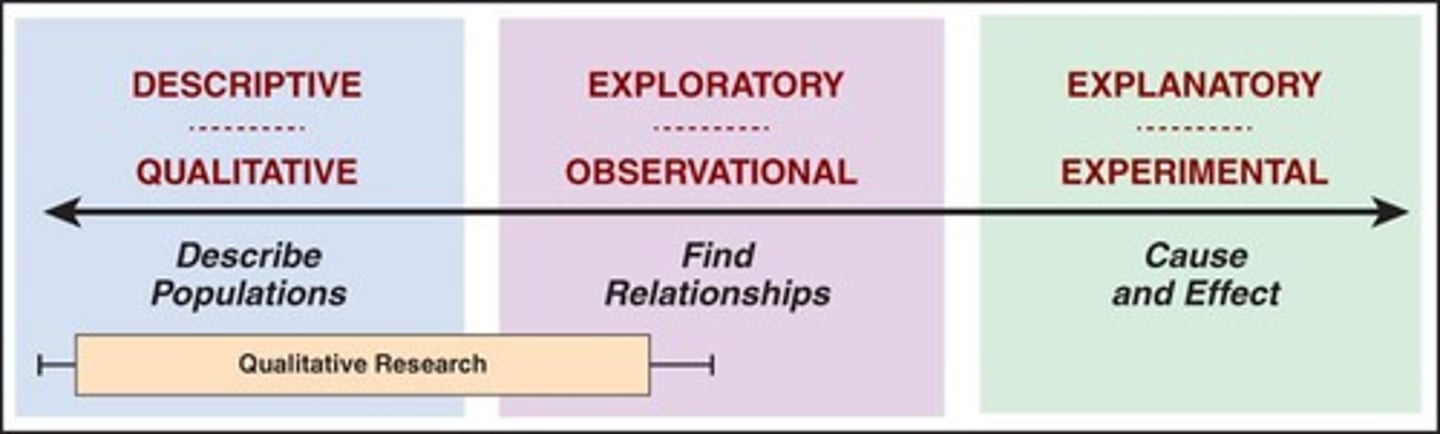
Exploratory Study Designs
Focus on understanding phenomena without predefined hypotheses.
Quantitative Methods
Involves numerical data and statistical analysis.
Human Experience Assumption
Assumes logical relationships in human behavior and interactions.
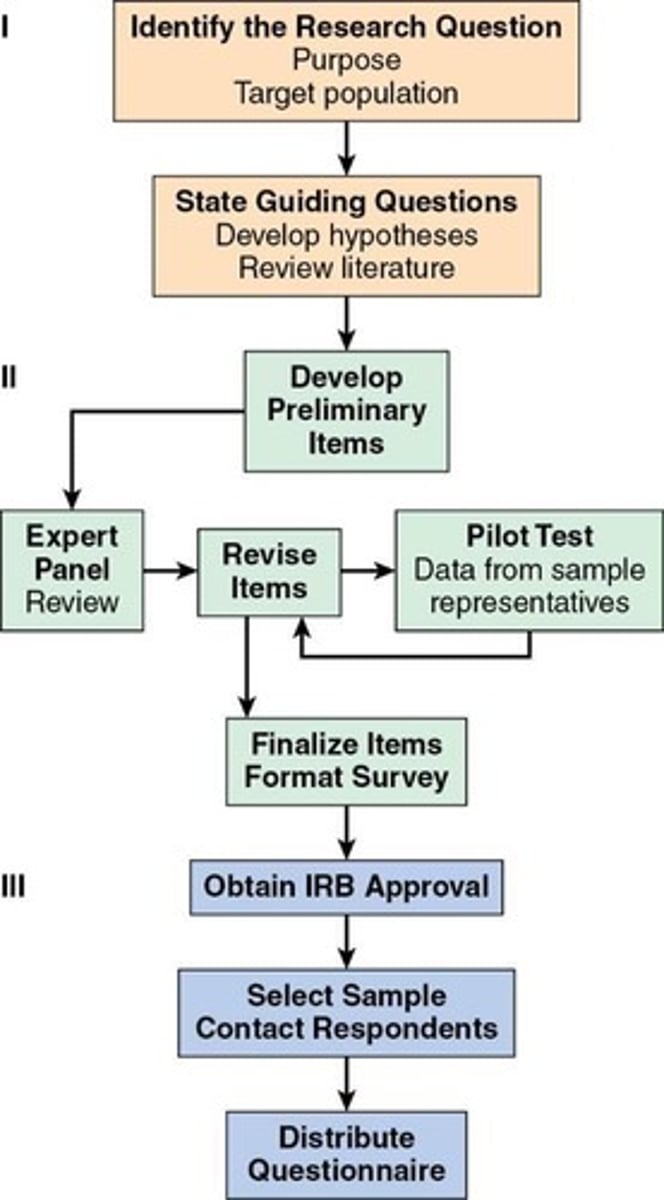
Descriptive Surveys
Characterize knowledge, behaviors, and demographics.
Questionnaires
Structured surveys captured via self-report.
Informed Consent
Required before conducting research with participants.
Double-barreled Questions
Ask about two issues in one question.
Inductive Inquiry
Observation leads to explanation in research.
Descriptive Statistics
Used to provide context in qualitative studies.
Mixed Methods Study
Combines qualitative and quantitative data collection.
Purposeful Language
Deliberate wording to avoid bias in questions.
Research Complexity
Developing questionnaires requires careful planning.
Naturalistic Inquiry
Suggests that a phenomenon is only understood in context and from multiple perspectives
Inductive Reasoning
Data are collected and conclusions are reached based on this information
Constructivism
Knowledge is constructed through experiences.
Our understanding of the world is "constructed"
Purposive Sampling
Participants selected for specific research purposes.
Snowball Sampling
Participants recruit others from their networks.
Naturalistic Observation
Observing phenomena in their real-world settings.
Qualitative Data Collection
Methods include interviews and focus groups.
Interviews
One-on-one discussions led by trained interviewers.
Semi-structured interview guide with open-ended questions
Focus Groups
Group discussions facilitated by trained moderators.
Semi-structured focus group guide to facilitate discussion
Artifacts Analysis
Analysis of objects that provide information about the subject of interest
•May also review documents or archives
Photovoice
Participants document themes through photos/videos.
Field Notes
Researcher's observations and impressions recorded unobtrusively. Describe what is seen and researcher's impressions
Participant Observation (data collection)
Researcher engages in participants' natural activities.
Qualitative Data Coding
Structuring narrative data. Foundation for determining how themes or concepts emerge from data by giving structure to data
Codes
Smallest text units representing themes in data. words or phrases
Content Analysis
Systematic technique to draw inferences & coding textual material
Analyzing text by counting word frequency.
Qualitative Data Analysis
Tools like NVIVO and Atlas.ti for analysis. or analysis by hand. Time consuming
Qualitative Study
Research focusing on non-numerical data collection.
Quantitative Data
Data expressed in numerical form for analysis.
Research Questions
Broad inquiries avoiding specific hypotheses.
Interview
One-on-one conversation for data collection.
Artifacts
Analysis of objects providing subject-related information.
Qualitative Data
Large volumes of non-numerical data generated.
Coding
Structuring narrative data to identify themes.
Data Analysis Software
Tools like NVIVO for qualitative data analysis.
Hypothetical Example
Illustrative case study for qualitative research.
Grounded Theory
Theory developed from data analysis and collection. explains data
Phenomenology
Explores and describes lived experiences of individuals. describes phenomenon
Participatory Action Research
Knowledge generation to address social issues. and inform action
Ethnography
Study of cultures and social practices. groups of people
Constant Comparison
Ongoing analysis of data during research process.
Theory Development
Creating explanations based on collected data.
Theoretical Model
Framework explaining observed behaviors or phenomena.
Thick Description
In-depth portrayal of social practices and meanings.
Critical Appraisal
Systematic evaluation of research article strengths and weaknesses. AMSTAR
Bias
Prejudiced consideration affecting research outcomes. (overreliance on accessible participants, hawthorne effect, influence of participants and sit on researcher)
Hawthorne Effect
Participants alter behavior due to researcher presence.
Trustworthiness
Criteria ensuring qualitative research reliability and validity. (credible, transfer, depend, confirm)
Credibility
Authenticity of capturing participants' true experiences.
Credibility is marked by
-Thick description
•Triangulation
•Member reflections/member checking
•Negative case analysis
Transferability
Ability to apply findings to different contexts. marked by purposive sampling and thick description
Dependability
Consistency of research findings over time. audit trail and triangulation
Confirmability
Objectivity of the research findings. neutrality of data.
Confirmability is marked by
reflexive researchers, review by peers or population of study, audit trail, triangulation
Triangulation
Using multiple methods to validate research findings.
Member Checking
Participants verify accuracy of research interpretations.
Negative Case Analysis
Identifying exceptions to refine research conclusions. conflicts
Audit trail
Documenting research decisions for transparency.
Reflexivity
Researcher's self-examination of biases.
other strategies for trustworthiness
Interviewer/data collector training
Prolonged engagement
Saturation
Code-recode
Peer debriefing
Prolonged engagement
Extended interaction to build trust and understanding.
Saturation
Point at which no new data emerges.
Code-recode
Reanalyzing data to ensure consistency in coding.
Peer debriefing
Discussing findings with colleagues for feedback.
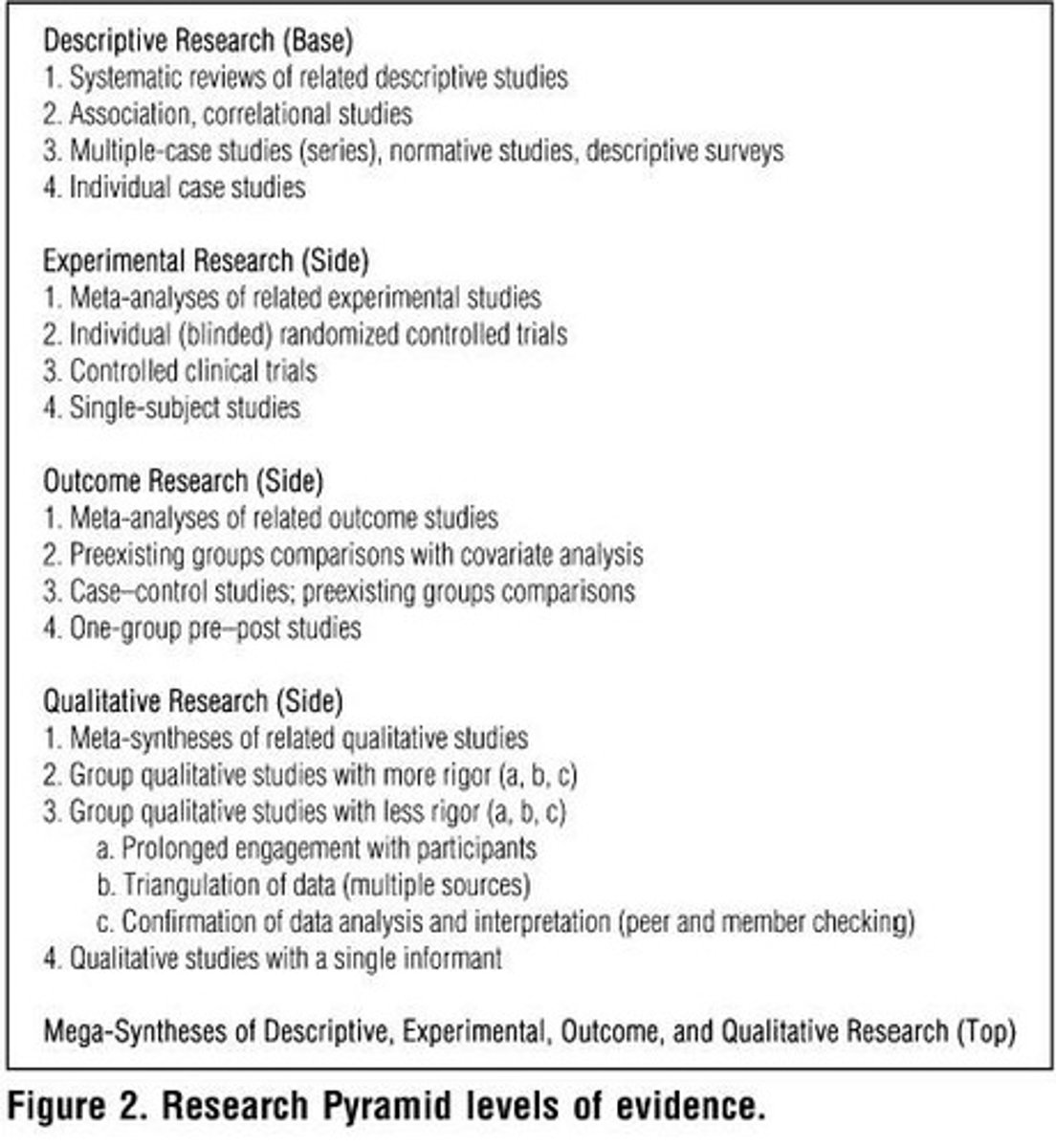
Research Pyramid
Model illustrating levels of evidence in research.
Mixed Methods Research
Combining qualitative and quantitative approaches to increase validity