muscle receptor physiology
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
muscle spindle / DTR
responds to muscle spindle stretch
reflex contraction due to stretch of gamma motor neuron activation
conscious proprioception
awareness of the sense of force created by muscle contraction
where are alpha motor neurons founc
muscle fiber
where is muscle fibers found
intrafusal
muscles that are responsible for fine, skilled movements have higher density of what
muscle spindles
nuclear bag fibers
type of intrafusal fiber
nuclei is scattered
bigger than nuclear chain
nuclear chain fibers
type of intramural fiber
nuclei are in a line
smaller / thinner than bag fibers
primary sensory ending (Ia fibers)
detect velocity of stretch of muscle and absolute length of muscle
wrapped around nuclear chain and bag
secondary sensory ending (II fibers)
only detect absolute length of the muscle
smaller than Ia
efferent motor intervention
muscle spindle is the only sensory receptor to have this
motor component
gamma motor neurons
attached to the intrafusal fibers at the contractile ends of the fiber
is always turned on
enables intrafusal fibers to contract
activated by CNS
alpha-gamma coactivation
activated by CNS
keeps the spindle shortened to correspond with he length of extrafusal fibers and allow for immediate response by spindle
alpha motor neuron is damaged =
muscle contraction will not work and reflex will be absent
some alpha motor neurons damaged =
reflex will be hypo reflexive
GTO
found in musculotendinosus junction
sensory component
reflex control of muscle tension - opposite of muscle spindle
Ib fibers
what is the stimulus for GTO
muscle contraction or extreme passive stretch

somatosensory cortex (postcentral gyrus)

somatomotor cortex (pre central gyrus)
meninges layers from superficial to deep
dura
arachnoid
pia
where is CSF located
subarachnoid space
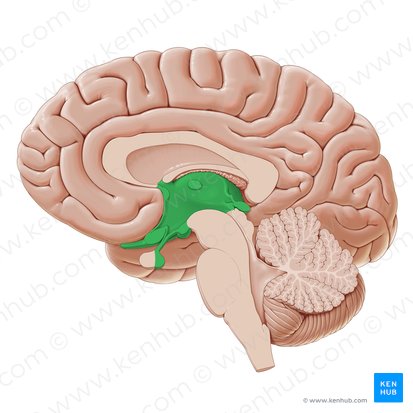
what is it and what does it include
diencephalon
includes: thalamus and hypothalamus
what level does the spinal cord end
L1 / L2