DBMS L6
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Using DDL Statements to Create and Manage Tables
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Database Objects
table
view
sequence
index
synonym
Table
Basic unit of storage; composed of rows
View
Logically represents subsets of data from one or more tables
Sequence
Generates numeric values
Index
Improves the performance of some queries
Synonym
Gives alternative name to an object
Naming Rules
Table names and column names:
Must begin with a letter
Must be 1-30 characters long
Must contain only A-Z, a-z, 0-9, _, $, and #
Must not duplicate the name of another object owned by the same user
Must not be an Oracle server-reserved word
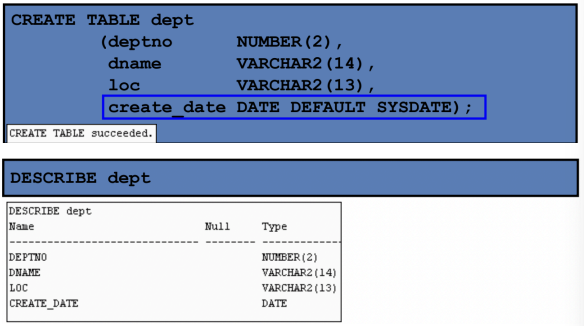
CREATE TABLE Statement
You specify:
Table name
Column name, column data type, and column size

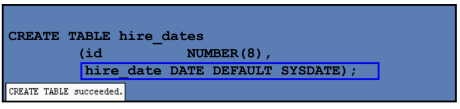
DEFAULT Option
Specify a default value for a column during an insert
Literal values, expressions, or SQL functions are legal values
Another column’s name or a pseudocolumn are illegal values
The default data type must match the column data type
Creating Tables
VARCHAR2(size)
variable-length character data
CHAR(size)
fixed length character data
NUMBER(p, s)
variable length numeric data
DATE
date and time values
LONG
variable length character data (up to 2 gb)
CLOB
character data (up to 4 gb)
RAW and LONG RAW
raw binary data
BLOB
binary data (up to 4 gb)
BFILE
binary data stored in an external file (up to 4 gb)
ROWID
a base-64 number system representing the unique address of a row in its table
TIMESTAMP
date with functional seconds
INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH
stored as an interval of years and months
INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND
stored as an interval of days, hours, minutes, and seconds
Constraints
enforce rules at the table level
prevent the deletion of a table if there are dependencies
Constraint Types
NOT NULL
UNIQUE
PRIMARY KEY
FOREIGN KEY
CHECK
Constraint Guidelines
You can name a constraint, or the Oracle server generates a name by using the SYS_Cn format
Create a constraint at either of the following times:
At the same time as the creation of the table
After the creation of the table
Define a constraint at the column or table level.
View a constraint in the data dictionary.
constraint syntax

Column-level constraint syntax

Table-level constraint syntax

Example of a column-level constraint

Example of a table-level constraint

NOT NULL Constraint
Ensures that null values are not permitted for the column
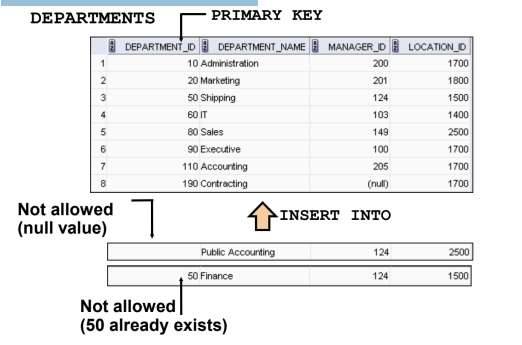
UNIQUE Constraint
Defined at either the table level or the column level
PRIMARY KEY Constraint
FOREIGN KEY Constraint
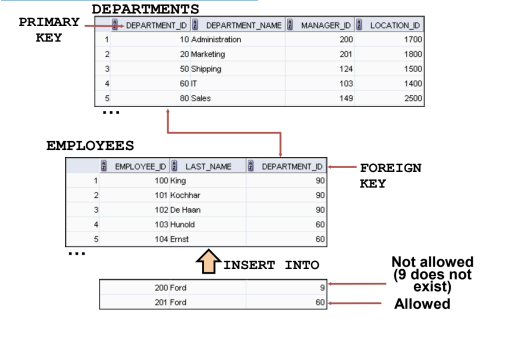
FOREIGN KEY
Defines the column in the child table at the table-constraint level
REFERENCES
Identifies the table and column in the parent table
ON DELETE CASCADE
Deletes the dependent rows in the child table when a row in the parent table is deleted
ON DELETE SET NULL
Converts dependent foreign key values to null
CHECK Constraint
Defines a condition that each row must satisfy