Ortho Exam 2 - Lecture 8
1/22
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
Rheumatoid Arthritis - define
systemic inflammatory disease, affects the lining of multiple joints (synovial membrane) and can affect other organs
RA Etiology and Pathology
environmental and genetic factors
Synovitis - inflam. of synovial tissues
Destruction - proteolytic enzymes help regulate inflam. response
Deformity - articular destruction, capsular stretching, tendon rupture
RA sympotoms
pain, swelling, and redness in joints with fatigue and prolonged stiffness after rest
pain, joint destruction, deformity, instability
RA X-ray changes
joint space narrowing, pero-articular osteopenia, cartilage erosions, x-rays DO NOT provide differential diagnosis of RA
Osteoarthritis
chronic joint disorder, progressive softening and disintegration of articular cartilage accompanied by new growth of cartilage and bone at the joint margins and capsular fibrosis. Most common
OA risk factors
age, females, abnormal joint alignment, hereditary, joint injury/overuse, obesity
OA symptoms
gradual onset, steady/intermittent pain in a joint.
pain, swelling, stiffness, deformity, instability, loss of function
3 mechanisms of OA
mechanical disparity: stress applied to articular cartilage and strength of articular cartilage
increased stress: increased load (BW or activity, and decreased area (varus knee or dysplastic hip)
weak cartilage: age, stiff, soft, abnormal bony support
OA Degeneration Mechanism
loss of compressibility, vertical fractures from surface to cartilage substance, pitted surface, large ulcers, exposed bone
deeper chondrocytes proliferate, forming clusters - Weichselbaum’s lacunae
OA Etiology
genetic, metabolic, hormonal, mechanical, and aging etiology
OA X-ray changes
narrowing of articular cartilage, radiodensity of subchondral bone, radiolucencies, peripheral osteophytes (bone spurs)
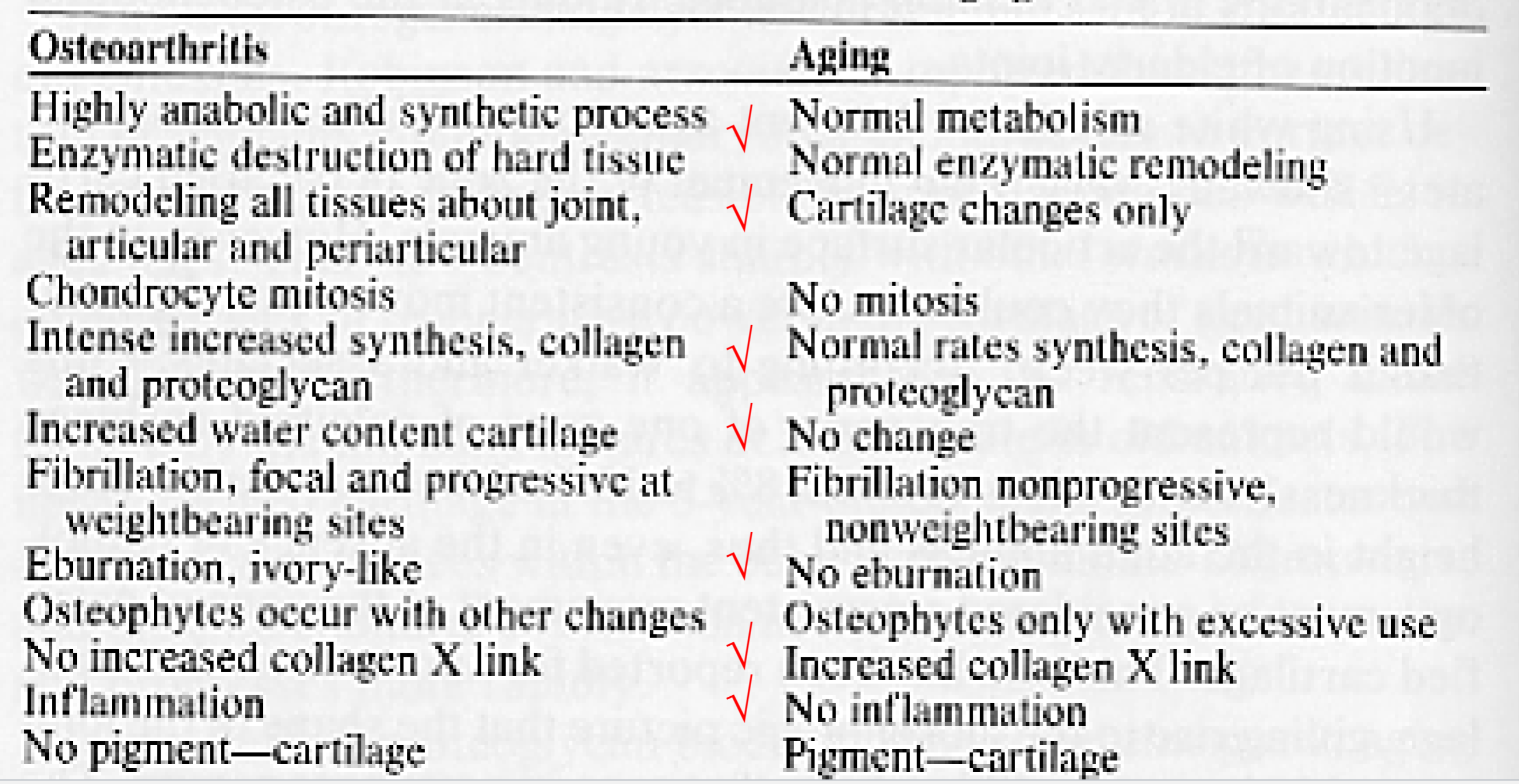
key differences between OA and aging
Osteoporosis Definition
progressive systemic skeletal disorder - low bone mass and mineral density, deterioration of micro-architecture, compromised bone strength
bone resorption > bone formation
How to detect deviations for diagnosing osteoporosis
BMD measurement relative to the typical peak bone mass of healthy 30-year-old of the same gender and race
standard deviation from peak mass is called the T score (used for people >50 years)
Why use T score in post - menopausal women and men over 50?
predicts risk of future fracture. A higher, positive t-score means normal bone density. negative t scores means low bone mass or disease
osteopenia (T-score)
reduced rate of bone formation and bone mass, defined as less than -1.0 and greater than -2.5
osteoporosis (T-score)
-2.5 or lower, aka a bone density 2.5 standard deviations below the mean of a 30 year old
When can you see changes in radiographic structural effects
after about 30% of bone is lost
Osteomalacia/Rickets Definition
uncalcified “soft bones” due to insufficient mineral or osteoblast dysfunction, osteoid accumulates and doesn’t mineralize properly, and vitamin D deficiency. this can cause curvature
Rickets - osteomalacia in children
Paget’s Disease (Osteitis Deformans) Definition
bone enlargement and thickening
increase osteoclast/blast activity = increased bone turnover
Osteonecrosis (Avascular Necrosis) Definition
results from bone ischemia, due to trauma, corticosteroid use, idiopathic cases
pain with activity, pain at rest, focal articular changes on radiographs
Perthes’ Disease
necrosis of the secondary ossification center of the proximal femoral epiphyses, with subsequent remodeling of regenerated bone
impacts growth plate, pediatric patients