mbio 1220 the adaptive immune response, lecture 13
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
the adaptive immune response
a specific defensive response to invasion by a foreign object
this can be acquired naturally or artificially
natural adaptive immunity: an organism or toxin enters the body and promotes an immune response (getting dirty)
way you exposed determines which you have
artificial adaptive immunity: results form an immunization wit a vaccine (0 natural)
both types are specific and have a memory component
natural adaptive immunity:
an organism or toxin enters the body and promotes an immune response (getting dirty)
artificial adaptive immunity:
results form an immunization wit a vaccine (0 natural)
specifc
the immune response protects against one disease
does not protect against other diseases
the only exception is when two diseases are very closely related
ex. small pox and cow pox
memory component
results in a much stronger response upon re0exposure
long term immunity: possibly for life
the immune system
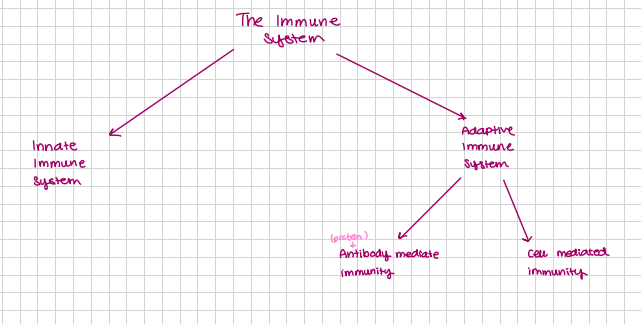
adaptive immunity involves two general repsonses
antibody mediated response
cell mediated response
antibody mediated response
also referred to as the humoral response
mediated by small molecules called antibodies or immunoglobulin (Ig)
antibodies specifically bind to an inactive foreign particles (make anti-bodies)
foreign particles can be cells, toxins, pollen, etc.
neutralize them → “bear hug”
cell mediated response
not mediated by small molecules
triggers the activation of specific cells called lymphocytes
these lymphocytes recognize and destroy abnormal or infected host cells
they attack bigger targets such as tumor
regulated carefully! otherwise kill yourself
lose something valuable but saving the institution
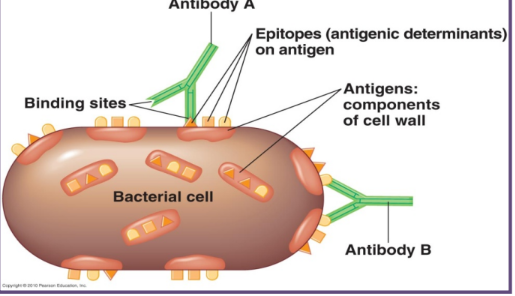
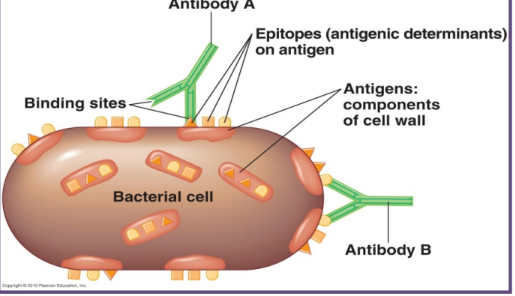
antigen
a foreign particle that enters the body
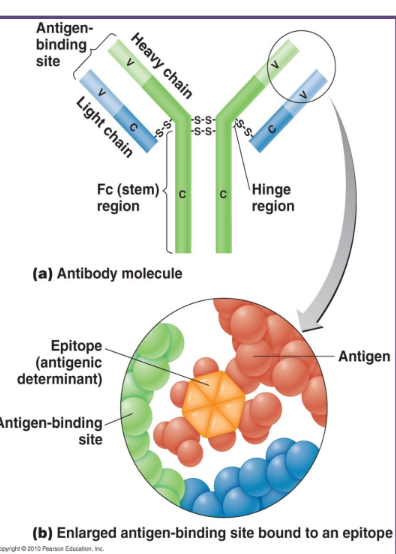
the antigen can be broken into smaller parts call epitopes → small part that you target (foreign part)
the epitope is the particular portion of the antigen that is recognized by the antibody
bacterium, virus, peanut, etc.
many ways to learn a bad guy via an antigen
the ones that are most immunogenetic
antibodies
proteins produced in response to the antigen
antibodies bind to the antigen in a very specific manner
like lock and key
monoclonal, polyclonal
made by us (protein)
epitope on one bad guy
antibodies (Ab) =
Immunoglobulins (Ig)
antibodies are made of 4 parts
2 identical heavy chains and 2 identical light chains which are held together by covalent bonds
each antibody has 2 identical antigen binding sites (Fab)
Fab is specific for one epitope
each antibody also has a constant fragment (Fc)
Fc binds complement proteins, and phagocytes
five classes of antibodies
immunoglobulin G (IgG)
immunoglobulin M (IgM)
immunoglobulin A (IgA)
immunoglobulin D (IgD)
immunoglobulin E (IgE)
immunoglobulin G (IgG)
most common
found in blood: can also enter tissues in regions of inflammation
can cross the placenta and confer passive immunity to a fetus
use these until you can make your own
IgG binds to antigens very tightly
monomers → 2 binding sites (good and strongly)
2 antigens are identical to each other
look for against HIV virus

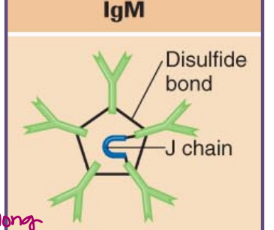
immunoglobulin M (IgM)
a pentamer:
consists of 5 antibody units
does not move into tissues as freely as IgG
it remains in blood
often found attached to the surface of B cells
this is the first type of antibody produced upon infection
first time, all the time, only lasts so long (then IgG)
IgM is very good at aggregating antigens
huge so it doesn’t leave the blood
FAB stays consistent, only bottom changes
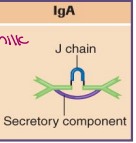
immunoglobulin A (IgA)
this is found as a dimer (two antibodies stuck together) → bind to 4 antigens that are all identical
IgA is found in bodily secretions
saliva, mucous, tears, and milk
functions to protect mucosal surfaces
IgA protects the gastrointestinal tract of newborns
passed via breast milk → exposed to infants
“this is what goes on in there”
immunoglobulin D (IgD)
unknown function
located on the surface of B cells
poor efficacy but good idea
it acts as a receptor on itself
in the plasma membrane
monomer
B cell produces antibodies
B cell will only ever produce one type of FAB
“advertisement”

immunoglobulin E (IgE)
found on the surface of certain immune cells
(tissue) mast cells and basophils (his inside)
when it binds to antigens the cell released histamine
this attracts complement and phagocytes to the area
histamine is responsible for allergy symptoms
peanut → bind to particle of peanuts → cell de-granulates → his is released and causes vasodilation
against allergies
FC IgG receptor for FC (foot) for IgE

what is the functions of an antibody?
agglutination
neutralization
complement activation
opsonization
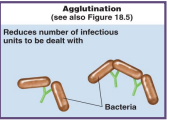
agglutination
antigens become stuck together
this reduces the number of infectious units to be dealt with
internalize with phagocyte and gets destroyed
“paper towel super absorbent”
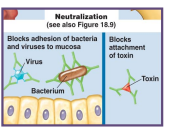
neutralization
the antibody binds to and inactivates toxin bacteria and viruses
neutralize behaviour
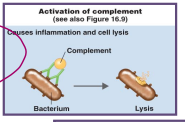
complement activation
the antibody binds to the bacteria: this acts as a starting point for the complement pathway (MAC attack)
one way to hit the first domino
set of protein, 30 of them off
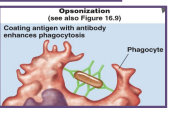
opsonization
this flags down phagocytic cells to destroy the antigen
captures
exact same way as complement protein
cells of the adaptive immune system
lymphocytes
b lymphocytes
t lymphocytes
antigen presenting cells
b lymphocytes
also referred to as B cells
antibody producing cells
involved in the humoral or antibody mediated response
produced in the bone marrow by stem cells (trained in bone marrow)
they need to have a trust source
only do it when we need it
when an antibody sticks to something, you made, trust it and take it seriously and respond
don’t turn immune system unless we are sure (otherwise might cause auto-immunity)
t lymphocytes
also referred to as T cells
these are produced in the bone marrow but mature in the thymus gland
help anti-body immunity
there are two types of T cells
Helper T cells (TH cells)
these help B and Tc cells prepare for an immune response
they are a part of humoral and cell mediated immunity
important for immune system
cytotoxic T cells (Tc cells)
these cells lyse foreign and abnormal host cells (infected or cancerous)
they are a part of the cell mediated immune response → why we can’t take drugs against viral infections
receive training → this healthy don’t kill, this not healthy, kill it
antigen presenting cells (APC)
macrophages, B cells, and dendritic cells
the stages of an antigen presenting cell:
the foreign material such as a bacterial cell is engulfed by the APC
the antigen is processed and presented to the T helper cells of the immune system along with self antigens
self antigens: these are part of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
this is a check to prevent the destruction of our own cells by mistake
T helper cells become activated against the foreign material
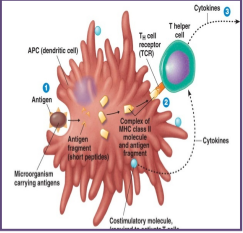
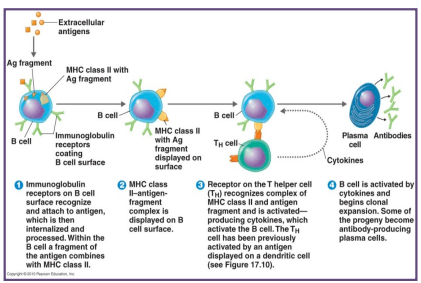
the stages in antibody production
the antigen enters the body
the antigen will be phagocytized and digested by a B cell
small fragments of the antigen will be presented on the surface of the B cell along with MHC
a T helper cell will bind to the antigen presenting B cell after recognizing the antigen bound to the MHC protein
the T helper cell will then deliver cytokines that stimulate B cell to undergo clonal expansion
the B cell multiplies to produce more identical B cells that will then fight off the specific antigen
clonal expansion
B cells divide and differentiate becoming either
a. plasma cells:
antibody producing cells
these cells have a short lifespan and produce many antibodies
b. memory cells :
these cells live for a very long time (20-30 years)
these cells circulate in the blood and propagate at very low level
when the memory cell encounters an antigen it will quickly change, multiplying and becoming an antibody producing plasma cell
booster constantly refreshes memory pool
primary response
this is the response the first time the body encounters the antigen
the antigen stimulates the production of low levels of antibody
this is a slow process taking 5-7 days (because you are learning)
IgM is made first followed by IgG (blood) and IgA (mucous membrane)
the major income: memory is built for the antigen (very very high level of antibodies)
through a vaccine or due to exposure
secondary response
this is the response that occurs during every subsequent encounter with the antigen
high levels of antibody are produced
this is a quick response taking only 1-2 days
as a result of this response the infection is quickly overcome
memory cells are replenished
cell mediated immune response
this is response is activated by invading cells or abnormal host cells
involves antigen presenting cells (APCs), T helper cells and cytotoxic T cells
cytotoxic T cells are responsible for destroying abnormal cells in the body
the stages of the cell mediated immune response include
Recognition of abnormal host cells:
cells infected with virus or bacteria
ex. cells infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis
cancer cells
foreign cells
ex. blood transfusions or bone marrow transplant
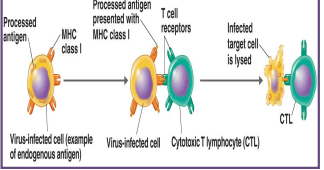
endogenous antigen is processed and displayed on cell surface:
presented on the surface of the antigen presenting cell together with the MHC I self antigen
different type of MCH then used during the Ab mediated responses
perforins:
these are released from the cytotoxic T cell
they poke holes in the membrane of the abnormal cell
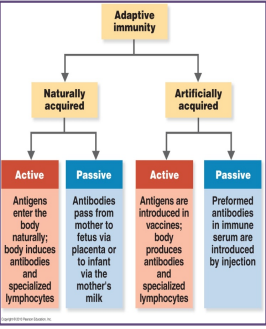
active immunization
active immunization
the body goes through the complete process to generate specific antibody or cytotoxic T cells
it can be natural or artificial
a. natural
when the antigen is encounter from the environment (primary response)
exposed naturally in your life
active
b. artificial
when the antigen is injected as a vaccine
take vaccine full of virus and poke it in you
we force exposure to get an outcome
active
“active: eating pizza”
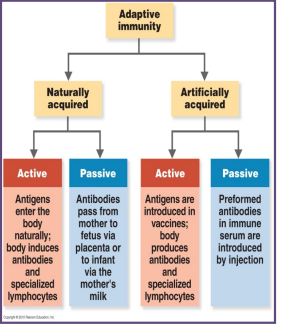
passive immunization
given ready made antibody: does not result in lasting immunity
can be neither natural or artificial
get just the product
a. natural
ex. from mother to infant
IgG is transferred from mother to fetus via placenta
IgA is transferred from mother to child via milk
b. artificial
pre-made antibody is injected
very fast acting for life-threatening situations
ex. snake venom
no anti-toxin antibody can be given (no memory)
ex. anti-rabbis shot → passive
then give vaccine → active has memory